Understanding The Concepts And Purpose Of ISO Certification
Question
Task: The purpose of this individual assignment is to provide the student with an opportunity to demonstrate his/her mastery of one or more related topics discussed during this module and apply them in the context of the topic of this assignment.
You have studied concepts, models and topics set out in the module guide.
If you wish to improve your learning before embarking on this assignment, you may want to conduct a systematic search of relevant scholarly literature material. This is strongly advised.
The student is required to select TWO questions from the list below and submit a substantiated answer of between 1500 and 2000 words for each question. The student is also required to make a presentation of no longer than 5 minutes on ONE of his/her answers
Questions
1. In contrast to popular thinking at that time, in 1979 D. Philip Crosby argued that producing high quality goods did not cost more than producing goods of a lower standard. He argued that "quality is free" and could even be a source of profit to an organisation.
Discuss this issue and explain why this is true.
2. Explain the concept of process mapping using flow charts and why this is done. Draw a flow chart to show how you answered this question.
3. 1988 Zeithaml, Parasuraman and Berry developed the SERVQUAL-model as a quality management tool for use in service industries. Discuss the workings of this model. What criticisms do you have of the model? Identify at least 3 “gaps” that apply to Wittenborg.
4. Explain why the appraisal of product quality will depend on the viewpoint of the appraiser. Illustrate your answer by considering the "quality" of a suit-case as seen through the eyes of a) the manufacturer b) the retail sales point c) the end user and d) the environment. Name at least two other factors that influence our appraisal of product quality
5. What is the intended purpose of ISO 9000:2015? Does ISO 9000 serve its purpose? Will an organization with an ISO certificate produce goods of a higher standard than an organization without a certificate?
6. Explain the concept of benchmarking the quality of a manufactured product. What problems do organisations encounter when benchmarking? Illustrate your answer with actual examples.
7. Two of the most widely used tools of quality management are Pareto charts and Ishikawa diagrams. Explain the workings of these tools. Draw a Pareto chart of reasons that students fail exams at Wittenborg. You can make up the causes and the numbers yourself. Draw an Ishikawa diagram of one of the possible causes you have identified as being (one of) the reasons students are failing exams.
8. What is “Total Quality Management” or TQM? Show how an organization you are familiar with could use this concept to improve customer service.
9. The two concepts “Lean manufacturing” and “six sigma” are often combined by quality management consultants despite the fact that they are different concepts. Explain both concepts and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using each of them in a manufacturing environment.
Answer
Purpose of ISO 9000:2015:
International Standard provides the primary concepts of the vocabulary and the principles in the system of quality management assignment. This standard helps any organisation or foundation to understand the Quality management vocabulary in order to efficient and effective implementation of the standard (Pjr.com 2020). However, the effective application of the Quality Management assignment standard can give the realization of the value through the standard.
The ISO 9000:2015 considers seven principles over quality management assignment and theses seven principles helps to develop organisational promotion (Pjr.com 2020). The seven principles are mentioned below:
- Customer focus
- Leadership
- Engagement with the people
- Approach to process
- Improvement (Iso.org, 2020)
- Decision-making process through evidence
- Management of relationship (Shi et al. 2019)
The main purpose of the ISO 9000: 2015 consider the service area like customer focus, Leadership, people engagement policies, the approach of research, improvement, decision-making process and the relationship with the management of the organisation (Fonsec and Domingues, 2017). The details discussion over the purpose of that standard is given below:
The purpose of Customer focus:
The standard understands the requirements of the customer in prospect and also the existing customers demand. Therefore this standard helps the organisation to align the objectives of the organisation with the expectation and the demand of the customers. Satisfaction measurement can also be possible after adopting this standard in the quality management assignment process of any organisation (Asq.org, 2020). Customer relationship management guide is also provided by this standard. Therefore it can be said that in this sector fulfil the expectation of the customers are considered as the main aim. As per the standard, every organisation has to be understood about the satisfaction level of the customers and defiantly after buying or using the experience of the customers.
Leadership:
The leadership quality of any organisation must have their own visions and directions for improving the quality of the products or services (Hoyle, 2017). They must be adapting some challenging goals to achieve the target. Trust and values of any organisation can be developed through the quality of the products or services. Therefore as per the principals of the standard, there must be some ethics and moral values into the organisation. The contribution of the employees must be recognized by the higher authority of the organisation so that they can able to get the proper scope to improve his career.
Engagement of people:
The people or manpower of any organisation is the main value of the industry. Therefore any organisation must have the accountability of the people. They think about the enabling methods f the participating in some continues improvement methods’. The constraints and the problems within any organisation must be discussed with the employees (Javorcik and Sawada, 2018). Therefore in this section, the main purpose of the standard is to improve the involvement of the employees towards customers.
Approach Process
The approach process of the maximum organisation must be process controlled and able to measure the activities. The standard helps an organisation to link-up between the two activities of the organisation. Moreover, the standard has such power to analyse the process of work and the analysis tools which are required in the process.
Evidence-based decision making:
This section is one of the important parts of the quality management assignment of any organisation, because through appropriate decision the organisation can bale to, make the development. Therefore the ISO 9000: 2015 standard gives the scope of accessibility the reliable and accurate the data of the transaction (Javorcik and Sawada, 2018). The standard also said that canalization of the data must be fulfilled through appraise methods of data analysis. Data must be analysed as compare with the practical experiences of the employees. The decision-making tools also must be proper for any of the organisation.
Relationship management:
Management of relationship in any organisation must have an identity and considering both the long term and the short term establishment. At this area, the standard suggest about the management of the costing, optimization of the resources and the creation of the values. The parameters which mainly describes and developed through the international standard are sharing the expertise, information, resources and the partners every collaboration in business gives the developed activities and the improvement.
Therefore as per above discussion over the purpose, it is concluded that International standard press is a well-defined Quality management assignment Standard whose framework integrates the resources, concepts and the process of the principles.
Does ISO 9000 serve its purpose?
Yes, ISO 9000 serves its purpose. ISO 9000 is a collection of the guidelines to establish any organisation, maintained the organisation and maintain the quality of the movement. The implementing process of the standard does not have any kind of rigid set of requirements; therefore the organisations have the scope to flexible the norms and implement them as per the requirements of the organisation. The main approach f this standard is the process-oriented activity (Fonseca and Domingues, 2017). The working process is started after the Implementation of the process-oriented approach. After the implementation, several audits will be done in the organisation for checking the effectiveness of the quality management assignment system. There exist mainly three kinds of audit and they are 1st audit, 2nd audit and 3rd audit. 1st audit is considered as the internal audit of the organisation. As per the opinion of the standard, it is said that ISO 9000 motivate to do such kind of audit, so that organisation can able to know about the opinion of the outsiders and capable to know the parties who know best to the organisation. The 2nd party audit gives permission to the consumers to evaluate the organisation performance activity. Another alternative side of the 2nd audit is to get the certification of the ISO 9000 standard through any 3rd party audit. In such condition there exist the evolution of the terms ISO 9000 guidelines and the organisation is independent to implement as per the requirements.
ISO certificate produces goods of a higher standard than an organisation without a certificate:
ISO 9000 defiantly produces goods of a higher standard than an organisation without the certificate of the standard. The first thing which is mentioned here is the organisation who are not willing to take the certificate of the ISO 9000 standard then it can very clear that the organisation do not want to commit with the service of good quality. Every organisation has their own quality management assignment system but the ISO certificate give the scope to attainment the quality of the products by giving the specific steps towards the development of the quality management assignment system of the organisation (Iso.org, 2020). The main activity in the quality management assignment is to monitor the progress process and the services throughout the production. The development of the testing process is very much assembly for the feedback of the customers
As per the ISO 9000 standard, it is seen that there is the existence of such an organisation, who are satisfied through the progress of the organisation. They always want to know about the more effective and efficient methods of improvement. Therefore as per the demand of such organisations, the ISO 9000 standard must have to be updating the existing standard of the organisation (Iso.org, 2020). Therefore the continuous improvement can be possible as per the development of the technology and the information technology in the business platform.
There exist several small business organisations that are also very much helpful to use the ISO 9000. A small organisation can able to take a good opportunity to expand its business internationally. However, by the implementation of the standard the quality management assignment must incise the quality of the process and lack of inefficiency of the organisation will also able to decrease. The business opportunity of the organisation will also increase through the implementation of the standard (Fonseca and Domingues, 2017). The objectives of the organisation will able to verify through the quality management assignment of the standard. However, ISO 9000 helps in selling the business of any small organisation in the international market. The customers are also satisfied with the presence of such certificate and assured about the quality of the products or services. The value of the organisation and the ingrate system of the organisation will develop for the presence of the ISO 9000 certificate. The process of the organisation will also be well document by maintaining the framework of the international standard. The quality proof is very much important about the assurance of the quality towards the products and the services. Therefore it is easily said that the International standard will help to develop the reputation of the organisation and analysis any critical situation by testing the faults of any business activity.
There also exists another standard over the quality of the products and the services. However, the ISO 9000 is almost same as the other quality management assignment of the products. The other systems considered the health-related issues, the safety of the environment and continuity of the business and integration process of the business (Iso.org, 2020). Therefore they are aligned with the parameters like interests of the organisation, cost-reducing factors and improved efficiency factors of the ISO standard. In this way, the ISO 9000 stand and keeps the communication with the other standard system of any organisation. Therefore it is easily stated that by using various kinds of standards an organisation can able to increase the efficiency and the operation integrity.
Answer 6
Concept of benchmarking the quality of a manufactured product:
Benchmarking is a practice in which the process of business comparison is done through the performance metrics. In this practice, the best practices of other companies are compared with any particular business. The main three dimensions of the measurements are the Quality, cost and time (Hileman and Rauchs, 2017). It can able to provide the required insights for understanding the comparison with one company to another. The other areas which are also developed through it are the work process, systematic approach and the areas of the identification. The improvement through benchmark is also dived into two processes pf the improvement and they are incremental improvements and another one is dramatic improvements.
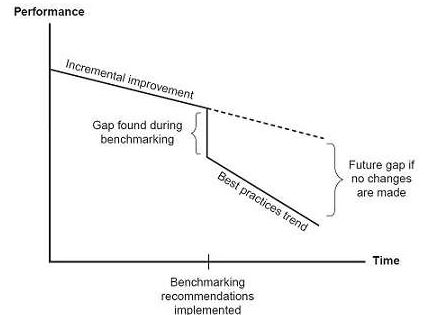
Figure 1: Incremental Quality Improvement vs. Benchmarking Breakthroughs
(Created by Duan et al. 2016)
As per the graph of the performance vs. Time, it is seen that the improvement f the incremental is not parallel to the time. The point, in which the best practice trends will strata, is the recommended place of the implementation of the benchmarking. The gap during the benchmark process must be identified as the future gap of the changes if there is no development as per the requirements.
There exist four types of Benchmarking methods and they are internal benchmarking, competitive benchmarking, functional benchmarking and the generic benchmarking.
Internal Benchmarking: This kind of practice considers the comparison into any organisation within the similar process of ay activity (Duan et al. 2016).
Competitive benchmarking: this kind of benchmarking is done between the direct competitors over the methods of the activity, process of the activity and the service of the activity.
Functional benchmarking: this kind of benchmarking is done between two similar practices in the same area of function, through the immediate industry (Xiao et al. 2017).
Generic benchmarking: This concept of benchmarking is broad. The comparison is done between two unrelated business processes but over the same practices. In this benchmarking method, there is no immediate industry or same industry for comparison (Houle and McCrory, 2017).
Quality will be improved through two types of benchmarking areas and they are the technical benchmarking and Competitive benchmarking. In technical benchmarking methods there is a performance by the design process of any organisation to another for determining the capabilities of services or the products. In this case, the comparison is basically done with the leading organisation in the current market. The organisation which is compared with another must be protect the designers as they are able to help the rank of the products
The competitive benchmarking methods mainly focused over the organisation activity and compare the activity to another one leading organisation in context with the values, function, attributes and so on. Before doing any kind of benchmarking it will be obtained some hard data for the effective design of the benchmarking and the marketing efforts (Hileman and Rauchs, 2017).
Problems solved by organisations encounter when benchmarking:
Every organisation must do the benchmarking activity over their products for the development of the quality. Through benchmark the organisation able to know about the current market situation and the progress report of the competitors. Therefore, they can able to identify the lacking of their own and detect the points of improvement. However, the benchmarking procedures state the problem-solving methods of any organisation (Van et al. 2018). At first after the critical analysis and the comparison any organisation team consider the facts and identify the places of the improvement. After that, the team decides about the planning of the improvement and collects the data as per the planning. The analysis of the organisation able to implement the process and gradually they adopt the process.
Definition of benchmark problem: However, there exist a set of optimized problems which is typically occurred during benchmarking. Every negative effect has different kinds of functions considering the parameters like measurement of performance, evaluation and the characteristics. There exists an algorithm over this evaluation, characteristics and the measurement of the performance. This algorithm behaves differently in various environmental conditions.
Main Three problems during the encounter of the benchmarking
The idea of the benchmark implementation strategies is used by several leading organisations for the best operation of the industry. Among those organisations, some of them still struggle with the primary level and some can able to achieve success. However, the main three areas of challenges during benchmarking are discussed below:
- Data availability, quality and relevance of statistics: the main key challenges faced by any organisation are the operation of the data during the industrial benchmarking. The challenging situation has happened during the benchmarking process when there is attacking of these four parameters and they are
- Availability
- Single central location
- Several common definitions (Van et al. 2018)
- Statistical sample sizes.
Therefore it is easily said that in the timing of the planning of benchmarking the quality process consists of the way to collect the data. Therefore this situation became very much challenging against the external organisation.
The internal benchmarking also faced some challenges and they are:
- Fosters of mediocrity
- Satisfactory results not gamed
- Growth options are limited
- Low performance of the improvement
- Atmospheric competitiveness not able to stretch (Houle et al. 2017)
- internal bias condition
The Competitive benchmarking process faced some challenges’ and they are as follows:
- limited secrets of the trading
- different kinds of legal issues
- threatening
- capitalized the weakness of the competitors
- information misleading
- low improvement of the performance
The functional benchmarking process faced some challenges and they are :
- divers culture in the corporate world
- absence of specific needs
- difficult to find out the common functions
- Lack of visualization in the adoption of the best practices through other organisation.
The generic benchmark methods also face various challenges and they are mentioned below:
- the concept will be difficult
- The class identity will also be difficult
- It takes a long time for prices
- Organisation of the class is also not suitable in nature.
Detection of the values from the results: the final stages of the benchmarking have generally two parts and they focused on the utilization of the process. This stage is one of the important processes of the benchmarking system. Therefore it is easily said that if the results are detected in the process of the benchmarking then appropriate process is not implemented in the area. However, the main challenge faced y the organisation is the challenges to take appropriate actions as per the results activity. Therefore to overcome this problem the organisation must be able to change the culture of the organisation and detect the effective needs of the organisation.
In the second part, the most challenging phase is to detect the decision that what to do in the next. Therefore it is easily said that the benchmarking process is considered as the one time failed to exercise and this is the opinion of most of the organisations (Duan et al. 2016). The key success elements of the benchmark process are developing a culture and then continue the process of improvement. Benchmark process will be successful when the results give knowledge and recommendations. Therefore the track of success is the actions and the continuous improvement based on the actions.
Granularity: In that case, the research of the benchmarking must be very much general or specific in nature. The main areas of challenges have identified the area of the business process which is need to be benchmarked. As the research process of the benchmark is too high or too low there exist some difficulties in the steps of the development. Operational excellence is an appropriate example of such kinds of challenges. The successful benchmarking process must not be very much specific or must not be very brief. The critical understanding and the results of the process must be goals oriented and the overall organisation must be dividing the goal to get better results.
Examples:
A proper example of benchmarking is illustrated through the main goals of an organisation. The project is over the department of housing. There exist main three goals and they are
- Reduce the rate of the residence vacancy
- Improved the satisfaction levels of the students
- Marked as the best possible time and the effort of the employees
Therefore it is easily noticed that the benchmarking process is defiantly a practice through which any organisation can able to understand the position in the current market. Moreover, the organisation detects the area of improvement (Xiao et al. 2017). However, it is suggested that if the organisation do not have any kind of expert and professionals then they will not be permitted to take the activity of the benchmarking (Kumar et al. 2016). Therefore, proper framework and structure must be present in the organisation, after that they can able to compare themselves with the leading organisations of the industry.
Literature review
Asq.org , 2020, About ISO, Available at: https://asq.org/quality-resources/iso-9000 [Accessed on 13th Jan 2020]
Duan, Y., Chen, X., Houthooft, R., Schulman, J. and Abbeel, P., 2016, June. Benchmarking deep reinforcement learning for continuous control. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 1329-1338).
Fonseca, L. and Domingues, J.P., 2017. ISO 9001: 2015 edition-management, quality and value. International Journal of Quality Research, 1(11), pp.149-158.
Hileman, G. and Rauchs, M., 2017. Global blockchain benchmarking study. Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, University of Cambridge, 122.
Houle, F.A. and McCrory, C.C., 2017, April. Water Splitting Catalyst Performance Benchmarking in the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis. In Meeting Abstracts (No. 35, pp. 1677-1677). The Electrochemical Society.
Hoyle, D., 2017. ISO 9000 Quality Systems Handbook-updated for the ISO 9001: 2015 standard: Increasing the Quality of an Organisation’s Outputs. Routledge.
Iso.org, 2020, About ISO, Available at: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:9000:ed-4:v1:en [Accessed 13th Jan 2020]
Javorcik, B. and Sawada, N., 2018. The ISO 9000 certification: Little pain, big gain?. European Economic Review, 105, pp.103-114.
Kumar, R., Ojha, A.K., Malmasi, S. and Zampieri, M., 2018, August. Benchmarking aggression identification in social media. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2018) (pp. 1-11).
Pjr.com , 2020, About ISO, Available at: http://www.pjr.com/standards/iso-90012008/benefits-of-iso-9000 [Accessed on: 13.01.2020]
Shi, Y., Lin, W., Chen, P.K. and Su, C.H., 2019. How can the ISO 9000 QMS improve the organisational innovation of supply chains?. International Journal of Innovation Science, 11(2), pp.278-298.
Van Mechelen, I., Boulesteix, A.L., Dangl, R., Dean, N., Guyon, I., Hennig, C., Leisch, F. and Steinley, D., 2018. Benchmarking in cluster analysis: A white paper. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10496.
Xiao, H., Rasul, K. and Vollgraf, R., 2017. Fashion-mnist: a novel image dataset for benchmarking machine learning algorithms. Routledge.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Parameters of ISO 9000
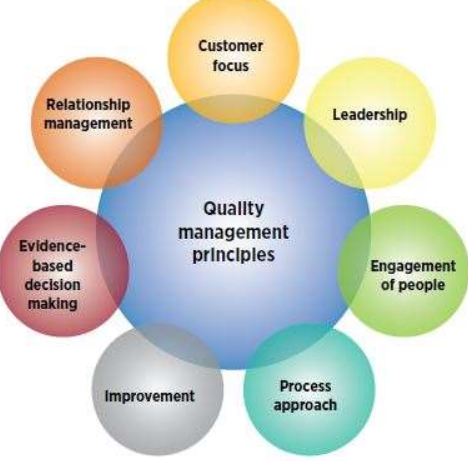
Figure 1: ISO 9000
Appendix 2: Benchmarking types
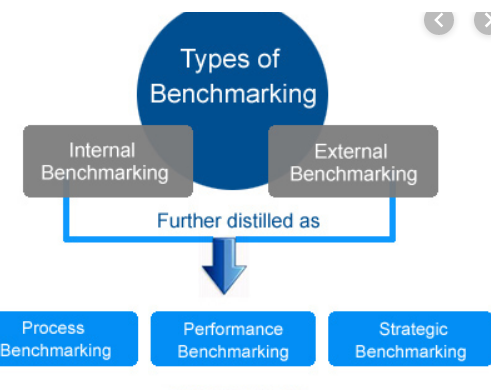
Figure 2: Types of benchmarking












