Strategic Management Assignment Researching Business Case Of McDonald’s
Question
Task:
Write a research report on strategic management assignment critically examining the strategic solutions for the business case of your choice.
Answer
Executive Summary
This research on strategic management assignment is based on the fast food retail chain McDonald’s, which is also one of the brands that operate globally. With the help of the very effective business plan and strategic directions of operations, McDonald’s has enjoyed success over decades and has become a global giant from a regional force. However, with the rapid evolution of technology and a changing environment (both business and natural), all the global giants like McDonald’s have started facing sustainability issues that directly affect the companies and indirectly the customers. McDonald’s is responsible for developing new strategies and initiatives towards a sustainable and responsible future that will benefit both the company and the consumers.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background
The research is focused on the fast food retail giant McDonald’s that was first set up in USA in 1940. Over the years, the fast food retail company gained more and more and spread all over USA and then the neighbouring countries and then again globally. Global expansion of McDonald’s has really helped its business growth considerably, boosting its position to one of the top fast food retail chains in the world. McDonald’s generated $9.07 billion revenue from sales in the fiscal year 2019 itself and it boasts more than 210,000 employees working worldwide in all the stores and warehouses (McDonald’s, 2021). With the gradual progress in technology, the company has also considered using more sustainable approach towards business that will have less harmful impact on the environment as well as the customers globally.
1.2 Problem Statement
Although McDonald’s is one of the largest global fast food chains, the current operations including business approach is no longer suitable for long term sustainability. Hence, in order to maintain sustainability for long term, the company needs to develop new operational strategies that will help them reach their sustainability goals.
The main problem highlighted here is the lack of sufficient strategic approach of the company to remain sustainable for the long term. The company does have some specific plans and strategies in place for reaching sustainable goals but there should be more emphasis and research regarding the same for the company to remain sustainable and competitive. Additionally, the company also needs to consider global welfare issues in relation to their service categories and the industry they operate in. This research focuses this sustainability aspect for the company and the final desired outcome of the study is to recommend approach strategic plan for McDonald’s so that they are able to reach their sustainability goals.
1.3 Research Questions and Objectives
The main objectives that have been developed for the research are listed as follows.
- To analyse the current strategies of McDonald’s regarding supporting a circular economy
- To study the current operations of McDonald’s regarding sourcing of food and packaging materials
- To recommend a strategic plan for McDonald’s that will help them achieve their sustainability goals while also remaining competitive in the market along with standard growth globally
Based on the objectives developed above for the research, the following research questions have been developed for this research.
Q1. What are the current strategies of McDonald’s for supporting a circular economy?
Q2. How does McDonald’s involve in sustainable food and packaging sourcing?
Q3. How can McDonald’s improve their business strategies for achieving responsible production as well as consumption?
2. Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
Literature review is one of the most important aspects of any research as it creates the foundation of the research as well as develops various data points that can later be compared with the data analysis results in order to validate the research. However, using any article available online is not suitable for a serious research. It is necessary to identify peer-reviewed works of various reputed researchers who have used verified and valid data for their research instead of fake and made up data. In this research, literature review has been done in order understand and simplify various concepts related to business growth and sustainability that has helped significantly in formulating the rest of the research. Works of various reputed researchers have been collected from the university’s online library and have been used to identify and collect important concepts related to the research.
2.2 Responsible Production and Consumption as Sustainable Goal
According to authors Asad et al.(2019), for any business organisation operating in the food and hospitality sector, responsible production and consumption should be the top priority in the strategic direction in which the company operates. The authors have mentioned the concept of “Sustainable Development Goals” (SDG) that is a set of various global goals to be followed by business organisations in order to promote global sustainability, not only for the company but also for the consumers. Although there is a set of 17 goals overall, organisations operating in specific industry need to follow specific goals that are aligned with their area of operations and business (Jacob-John et al., 2021). The authors pointed out that for organisations like McDonald’s that operate in food and hospitality sector, Goal 12 of SDG is the most suitable to follow. The Goal 12, named Responsible Production and Consumption, has a subset of 8 different targets that are to be set by the organisations over a 10-Year Framework of Programs that will help them achieve sustainability and growth. These 8 targets are listed as follows.
- Developing a framework for sustainable consumption and production pattern
- Sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources
- Effective management of chemicals and wastes over an entire life cycle
- Reduction of food waste at retail stores, harvests, supply chains and production levels
- Reduction of waste generation by prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse of materials
- Promoting sustainable practices among suppliers, partners and other related companies
- Adopting sustainable public procurement practices
- Raising awareness among people regarding sustainable development
In addition to these 8 targets, the authors also mentioned that there are also 3 additional means that must be deployed to achieve the targets as listed as follows.
- Promoting removal of market distortions like fossil fuel subsidies
- Supporting scientific and technological growth of developing countries
- Developing specific tools for monitoring sustainable development impacts
2.3 Challenges to Achieve Responsible Production and Consumption
While a vast array of goals can be set for sustainable growth and long-term achievement of responsible production and consumption, the process to achieve them is full of challenges. Authors Derunova, Kireeva and Prushchak (2019) focused on this issue and mentioned that the term sustainable might be a ‘paradox’ to some organisations as achieving sustainability in all different aspects is extremely difficult. The authors specifically mentioned with example that the SDG goals that have provided subsets of specific targets and means to achieve those targets have failed to assume the fact that most of the targets may not economically and financially sustainable or feasible for many organisations. An organisation can announce and initiate various sustainability programs according to the SDG targets but that will also require significant financial investments (Schröder et al., 2019). Additionally, there might be several other challenges to achieve such targets due to various external factors that are not controlled by the organisations. The authors used the examples of KFC and Pizza Hut, two global giants in fast food retail industry, who have specific sustainable plans in place but also lack suitable management skills regarding food wastes and as a result, both of the companies contribute significantly towards global food wastage factor, as shown in the graph as follows.
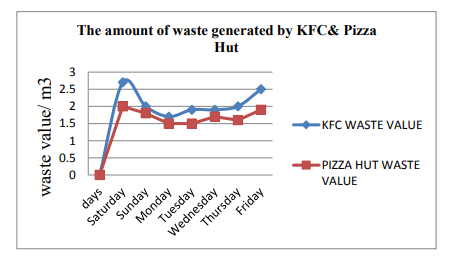
Figure 1: Waste Generated by KFC and Pizza Hut (Weekly)
(Source: Sjpub.org, 2021)
The authors mentioned that the purpose of showing this statistic is that setting specific goals for sustainable growth of organisations is not sufficient. The organisation must have a proper management structure in place whereas the management members have clear idea of the guidelines and means to achieve sustainability targets in order to ensure proper protocols and procedures are followed.
Authors Hernandez, Miranda and Goñi (2020) have spoken about another major challenge in this regard – animal farming and husbandry. The authors said that for the food industry, globally, millions of animals are raised, bred and butchered in order to supply animal-based products. The authors also showed a specific research data point that shows that animal husbandry is a major contributor towards greenhouse gas emissions globally (18%). In this regard, the authors Jindal?Snape (2020) commented that although animal farming and husbandry contributes to a major section of food and hospitality industry, it does not support the sustainability goals for an organisation working in this particular industry but this situation cannot be changed as well owing to the personal eating habits of the consumers around the world.
Another external factor that is a major challenge to responsible production and consumption, according to Su and Chen (2020), is the irregular consumer behaviour among different customer segments. Every individual customer has his own eating as well as waste generation habits that contribute to the overall food waste generation of the organisation. In spite of identifying different customer segments, it is virtual impossible for the organisation to identify consumption habits and behaviours of specific subsets and customers and hence, the food waste generation aspect remains very much unpredictable and out of scope of control of the organisation.
2.4 Conclusion
The literature review conducted above has provided important data points regarding sustainable goals with a global context including some of the global giants that are operating in the same industry as McDonald’s. The data and information collected from the literature can really provide a very important knowledge foundation on the basis of which, appropriate recommendations can be made to McDonald’s after the research study is completed.
3. Methodology
3.1 Research Design
As mentioned in the research proposal, exploratory research design has been followed in this particular research. The overall research focuses on the data available on McDonald’s regarding their sustainable growth strategies and approach towards responsible production and consumption. While the literature review has focused on the global perspective specific to the food and hospitality sector, the main research has been specific to McDonald’s company. Since the research has been specific to one organisation, special effort has been made to avoid bias and use cross-references in order to remove any kind of fake data or information that might have been provided by various sources.
For the purpose of the research, there were choices of three different types of data that could be used – qualitative, quantitative and mixed. Qualitative data deals with theoretical information whereas quantitative data deals with statistical data; mixed data involves both qualitative and quantitative data (Mohajan, 2018). After conducting a brief study of data types, it has been decided that this research will be done with qualitative data only. Hence, the main research involves collection of qualitative data on the specific research topic.
3.2 Data Collection
There are mainly two different methods of data collection – primary and secondary. Primary data collection requires the researcher to collect all the data himself by conducting his own survey / interview procedures after selecting a specific sample population. In this case, the researcher uses data collected only by him through the procedures of questionnaire survey or personal interviews following specific protocols (Moser & Korstjens, 2018). On the other hand, secondary data collection does not require actual data collection procedure; the research needs to simply find various sources of data already available online and use them for the purpose of the research.
Considering the nature and scope of this research, it has been identified that secondary data collection is the most suitable process for this research. Due to the limited scope of the research within a academic environment, conducting primary research on a global retail giant is significantly complex and difficult. Hence, for the entirety of the research, secondary data collection method has been used.
3.3 Data Analysis
There are several methods for data analysis depending on the nature and type of data collected and the research requirements. Some analyses can be done simply by studying themes and information whereas others need specific software like SPSS or NVIVO in order to get specific insight into the data collected for the research (Flick, 2017). However, those software programs are generally used for high level and complex research studies and hence, they have not been considered for this research,
The selected data analysis method for this particular research is thematic analysis. Thematic analysis is exclusive to qualitative data research and can be very useful procedure to analyse the data and reach the outcomes without much complexity. The basic essence of this data analysis technique is to identify and study various patterns within the data collected for the purpose of the research. In this case, the thematic analysis procedure has been applied on the secondary data collected from various online resources. Moreover, the thematic analysis process has also been used to interpret various points of view regarding the subject of the research that have significantly helped to formulate the final research findings and prepare suitable recommendations for McDonald’s.
3.4 Ethical Considerations
While conducting any research, big or small, certain ethical considerations are to be made and this research is no different (Assarroudi et al., 2018). The ethical considerations that have been made in this particular research are listed as follows.
- For the purpose of data collection, only those online sources have been used that are free for public view and data collection. No pirated sites or unauthorised data sources have been used in the process.
- Specific protocols set by the university for the research have been followed with due diligence.
- The research was conducted with a very professional approach.
- No names or personal information of individuals, who may have been associated with or subject of research, have been disclosed.
4. Findings from Analysis
For the purpose of analysis, data has been collected from various sources including McDonald’s official site. In order to avoid the bias from McDonald’s own website, several other data sources have also been used for cross verification. From the collected data, it is mostly clear that McDonald’s is already quite aware of its responsibilities for sustainable growth and development as well as responsible production and consumption of food for the consumers (Corporate.mcdonalds.com, 2021). As a result, the company has several large projects and goals in place that they want to achieve within the next 10 years period. This data analysis study focused on these goals for determining if these are sufficient or the company needs further planning and strategy development in order to achieve sustainability and responsibility goals.
Now, summarising the findings from the analysis, the following projects / major targets have been set in motion by McDonald’s in order to achieve their goals.
Climate Action – McDonald’s has pledged towards contributing less pollution and harmful emissions to the environment and has made a significant investment to reach the goal. The company has set a 2030 target to reduce emissions of greenhouse gas by 150 million tons and in order to achieve the same; the company has invested in and started utilizing renewable sources of energy (McDonald’s, 2021). The company data analysts have also estimated that the amount of reduction of greenhouse gas emission will be equivalent to planting 11 million trees. The company now focuses on the upgradation of restaurants that will be capable of producing sufficient renewable energy independently in order to fulfill daily energy requirements.
Packaging and Waste Management – The company has also deployed new strategies for packaging and waste management operations. The R&D wing of the company is on the process of constantly upgrading the packaging materials that will have lesser negative impact on the environment (McDonald’s, 2021). The company also aims to reduce waste generation by developing recyclable cups and plates that can be reused and thus reducing generation of wastes.
Sustainable Agriculture and Animal Farming – McDonald’s has the vision to create a sustainable culture in which agriculture and animal farming, which belong to the supply chain of the company, will thrive (McDonald’s, 2021). However, the company has admitted that there has been no specific strategy in place and the company is still researching on how to reach this specific target.
Conservation of Forests – The company aims to help in conservation of forests by reducing deforestation as much as possible. The company also aims to invest in technologies to control the plant based raw materials supply chain that will help their suppliers to harvest the raw materials without mass destruction of forests (McDonald’s, 2021). This is one of the biggest agendas that the company has adopted on urgent basis.
Water Stewardship – The final target of the company is to reduce water and energy consumption by much more efficient use of both of the resources in various activities like irrigation, farming and public amenities services (McDonald’s, 2021). The company has pledged to invest in developing technologies that aim to create new devices that can be much more efficient than the current ones in saving water and energy.
5. Discussion of Findings
From the findings of the research, it can be seen that the company has already set in motion several big investment projects that aim to fulfil the sustainability targets of the company. The company should be praised for taking such big steps towards a sustainable and responsible future that will benefit not only the company itself but also the consumers and the environment. However, it has also been identified that there are still several areas where the company lacks knowledge and even though they have set targets, they do not have clear idea on how to achieve such targets (Terry et al., 2017). Additionally, the company has been seen to roll all the projects in motion all together with the same timeline to be followed but it would have been much more effective if the company followed a step by step approach. From the information and data posted online by the company, it is also unclear whether the company has conducted sufficient amount of research before setting the targets regarding sustainability and responsibility.
6. Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
From the overall research, it can finally be concluded that McDonald’s has a clear vision on sustainable and responsible future and as a result, the company has rolled out several high value projects. However, some of the main initiatives have been standstill as the company is trying to gather more information and knowledge regarding how to achieve the targets. Moreover, it is also clear that the company does not have sustainable spending plan that might hurt the company in the future if one or more initiatives do not work out as expected.
Based on the study and analysis, the following strategic recommendations can be suggested to McDonald’s.
- Prepare a financial spending plan for the major initiatives in order to maintain sustainable spending against the annual revenue generated.
- Develop a step by step implementation plan instead of initiating all the projects at the same time.
- Deploy focus groups to collect data and information regarding specific projects that the company lacks knowledge in.
- Create partnerships with different entities in order extend initiatives of sustainable future over different parts of the world.
References
Asad, M. M., Hassan, R. B., Sherwani, F., Abbas, Z., Shahbaz, M. S., & Soomro, Q. M. (2019). Identification of effective safety risk mitigating factors for well control drilling operation: An explanatory research approach. Journal of Engineering, Design and Technology. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Muhammad-Shahbaz-21/publication/329764905_Identification_of_effective_safety_risk_mitigating_factors_for_well_control_drilling
_operation_An_explanatory_research_approach/links/5c1f1feb92851c22a33fd77e/Identification-of-effective-safety-risk-mitigating-factors-for-well-control-drilling-operation-An-explanatory-research-approach.pdf
Assarroudi, A., Heshmati Nabavi, F., Armat, M. R., Ebadi, A., & Vaismoradi, M. (2018). Directed qualitative content analysis: the description and elaboration of its underpinning methods and data analysis process. Journal of Research in Nursing, 23(1), 42-55.
Chan, S., Weitz, N., Persson, Å. and Trimmer, C., 2018. SDG 12: Responsible consumption and production. A Review of Research Needs. Technical annex to the Formas report Forskning för Agenda, 2030.
Corporate.mcdonalds.com. 2021. Our Planet. [online] Available at:
Crumley, E. T., Grandy, K., Sundararajan, B., & Roy, J. (2021). Media interviews as strategic external communication to maintain legitimacy for sustainability activities. Corporate Communications: An International Journal. Retrieved from https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/CCIJ-05-2021-0053/full/html
Derunova, E., Kireeva, N. A., & Prushchak, O. V. (2019). Inclusive development of the agri-food system as a driver for sustainable growth in the region’s economy. Scientific Papers Series Management, Economic Engineering in Agriculture and Rural Development, 19(3), 165-174. Retrieved from http://managementjournal.usamv.ro/pdf/vol.19_3/Art22.pdf
Ertz, M., Durif, F., Lecompte, A., & Boivin, C. (2018). Does “sharing” mean “socially responsible consuming”? Exploration of the relationship between collaborative consumption and socially responsible consumption. Journal of Consumer Marketing. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Myriam-Ertz/publication/324782229_Does_sharing_mean_socially_responsible_consuming_Exploration_of_the_rel
ationship_between_collaborative_consumption_and_socially_responsible_consumption/links/5c3e17d9458515
a4c7281191/Does-sharing-mean-socially-responsible-consuming-Exploration-of-the-relationship-between-collaborative-consumption-and-socially-responsible-consumption.pdf
Flick, U. (Ed.). (2017). The Sage handbook of qualitative data collection. Sage.
Hernandez, R. J., Miranda, C., & Goñi, J. (2020). Empowering sustainable consumption by giving back to consumers the ‘right to repair’. Sustainability, 12(3), 850. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/3/850
Huaccho-Huatuco, L., & Ball, P. D. (2019). The quest for achieving United Nations sustainability development goals (SDGs) Infrastructure and innovation for responsible production and consumption. Strategic management assignment RAUSP Management Journal, 54, 357-362. Retrieved from https://www.scielo.br/j/rmj/a/GhYD63FZQLx6hCmRLgRpp9m/?lang=en
Jacob-John, J., D’Souza, C., Marjoribanks, T. & Singaraju, S. (2021). Synergistic Interactions of SDGs in Food Supply Chains: A Review of Responsible Consumption and Production. Sustainability, 13(16), p.8809.
Jindal?Snape, D., Hannah, E. F., Cantali, D., Barlow, W., & MacGillivray, S. (2020). Systematic literature review of primary?secondary transitions: International research. Review of Education, 8(2), 526-566. Retrieved fromhttps://bera-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/rev3.3197
McDonald’s, (2021), Sustainability and diversity inclusion, Retrieved on 24th August from https://www.wherewomenwork.com/Career/2090/McDonalds-sustainability-diversity-inclusion
Mohajan, H. K. (2018). Qualitative research methodology in social sciences and related subjects. Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People, 7(1), 23-48.
Moser, A., & Korstjens, I. (2018). Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 3: Sampling, data collection and analysis. European journal of general practice, 24(1), 9-18.
Padela, A. I., Malik, S., Vu, M., Quinn, M., & Peek, M. (2018). Developing religiously-tailored health messages for behavioral change: introducing the reframe, reprioritize, and reform (“3R”) model. Social Science & Medicine, 204, 92-99. Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/download/56175576/1-s2.0-S0277953618301278-main.pdf
Schröder, P., Antonarakis, A.S., Brauer, J., Conteh, A., Kohsaka, R., Uchiyama, Y. & Pacheco, P. (2019). SDG 12: responsible consumption and production–Potential Benefits and impacts on forests and livelihoods. Sustainable Development Goals: Their Impacts on Forests and People; Katila, P., Colfer, CJP, de Jong, W., Galloway, G., Pacheco, P., Winkel, G., Eds, pp.386-418.
Sjpub.org, (2021), Understanding Sustainability, Retrieved on 24th August from https://www.sjpub.org/sjeer/sjeer-285.pdf
Statista, (2021), McDonald’s, Retrieved on 24th August from https://www.statista.com/topics/1444/mcdonalds/
Su, C. H. J., & Chen, C. D. (2020). Does sustainability index matter to the hospitality industry?. Tourism Management, 81, 104158. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Myriam-Ertz/publication/324782229_Does_sharing_mean_socially_responsible_consuming_Exploration_of_the_relati
onship_between_collaborative_consumption_and_socially_responsible_consumption/links/5c3e17d9458515a4c
7281191/Does-sharing-mean-socially-responsible-consuming-Exploration-of-the-relationship-between-collaborative-consumption-and-socially-responsible-consumption.pdf
Tanner, G., Schümann, M., Baur, C., & Bamberg, E. (2021). Too fatigued to consume (ir) responsibly? The importance of work?related fatigue and personal values for responsible consumption. International Journal of Consumer Studies. Retrieved from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcs.12655
Terry, G., Hayfield, N., Clarke, V., & Braun, V. (2017). Thematic analysis. The SAGE handbook of qualitative research in psychology, 2, 17-37. Retrieved from https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=AAniDgAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA17&dq=thematic+analysis&ots=doiaqmCgOY&sig=smvQr1
TWSON93YdrcEttfHweoa4












