Strategic Management Assignment Evaluating Strategic Decisions Taken By Toyota
Question
Task:
Strategic management assignment brief is to evaluate strategy in AMAZON or TOYOTA MOTOR organization under following headings:
- Eight different Mintzberge and Waters strategic behaviours: discuss with examples of your chosen organization.
- Emergent or Deliberate organization’s strategic behaviour: drawing on your previous answer of strategic behaviour, discuss whether your chosen organization exhibits more emergent or deliberate strategic behaviour.
- Emergent or Deliberate environment’s strategic behaviour: Discuss with supporting evidence, whether of your chosen organization’s operational environment (industry and local and/or international markets.
- Overall performance: Drawing on your answers to the previous answers, critically assess with supporting evidence of strategic behaviour of your chosen organisation.
Answer
Background Of Strategic Management Assignment
The current business environment is witnessing intense competition. Thus, corporate leaders of firms across the world are focused on developing strategies that can help firms overcome challenges in the volatile market. Moreover, effective strategic decisions also help firms to understand the opportunities in the global market and how these opportunities can be further utilized in order to grow within the sector. Effective strategic leaders focus on developing strategies on the basis of employees’, client and financial perspective (Terziev and Georgiev, 2017). There is no exception in case of Toyota. Toyota is one of the renowned firms operating in the automobile industry for a longer time period. The aim of this report is to evaluate strategic decisions undertaken by the strategic leaders of Toyota in order to strive in the competitive business environment.
Mintzberg and Waters strategic behaviours
In the year 1985, 8 different strategies were researched and presented by two researchers named Mintzberg and Waters. According to these researchers, strategies are mostly unplanned but it tends to emerge from practice (Neugebauer, Figge and Hahn, 2016). Strategic leaders of firms across the world tend to choose from these 8 strategies according to their business position and condition. There is no exception in case of Toyota.
Planned strategy
When organization can predict changes accurately it is known as planned strategy. The plan is imposed by authorities. The authorities of Toyota emphasized on advanced management. The managerial leaders of Toyota have focused on forming a mobile society by changing the business environment by 2030 (Toyota, 2017).
Ideological strategy
When members of organization focus on sharing common vision it is marked as ideological or deliberate strategy. It is found that both deliberate and emergent strategy is growing within the business environment and this strategy is also strong (Kopmann, Kock, Killen and Gemünden, 2017). Toyota’s strategic leaders have analysed the need for environment-friendly strategies. This gave rise to the EV strategies that aim at reducing carbon emission.
Entrepreneurial strategy
When owners impose their vision on the employees and the employees themselves cannot share their vision it is known as entrepreneurial strategy. Toyota has a top-down organizational structure and most of the decisions of the firm mainly price reductions or price rise, salaries and many more are taken by the top managers.
Umbrella strategy
It can also be marked as emergent strategy. The organization is also known for adopting new strategies that can establish a connection between technology and people (Toyota, 2022a). The product integration team decided to change the structure of the organization that further aims at coping with the change in the need of the environment.
Process strategy
When managers do not have any direct control on the decisions undertaken within the firm is known as process strategy. Integration of advanced technology within the core activities of the organization is a part of process strategy because in this case top level managers are not directly involved in decision making.
Unconnected strategy
When sub-group in a workplace takes control of various decisions within the workplace it is known as unconnected strategy. For example, the product integration team of Toyota decided to have separate. legal and HR teams for the sales and marketing divisions, manufacturing divisions. This decision has been completely undertaken by the product-integration team and not by the main managers.
Imposed strategy
When external group has an influence on the strategic decisions of a firm it is known as imposed strategy. Environmental decisions undertaken by Toyota are slightly imposed by customers and vendors.
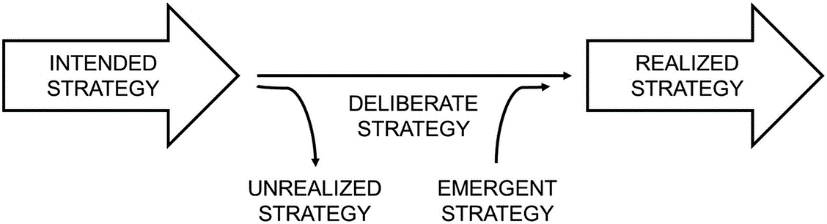
Source: Schühly, 2022
Pendulum metaphor
The strategic behaviour of firms that contain emergent and deliberate strategies are considered as pendulum behaviour. Toyota operates in the international or global markets. It can be said that Toyota is more intrigued towards deliberate strategies. The strategic leaders of Toyota have always focused on analysing the conditions of market. The organizational leaders of Toyota have found out how the interest and need of stakeholders are changing. After rigorous research, they have concluded that external stakeholders of firms across the world are intrigued towards strategies that aim at having a positive impact on the environment. In previous year, the president of Toyota organized a media meeting and declared the EV strategies that the company is going to adopt. The objective behind adopting this strategy is to reduce the emission of Carbon-di-oxide in order to control the rise in global warming (Toyoda, 2021). Thus, to satisfy stakeholders across the world the organization’s production team is focusing on manufacturing “carbon-reducing” vehicles.
In addition to this, the strategic leaders of Toyota also focus on undertaking strategies that can meet the needs of the employees within the workplace. The strategic team of the organization analysed the market and understood that Toyota should witness a structural shift that further can reduce the turnover rate of employees within the workplace. Previously, the management team of Toyota was facing employee redundancy. Corporate leaders were finding it difficult to leverage the skills and abilities of employees within the workplace so that the firm can gain competitive advantage. Therefore, officials of Toyota decided to open new campus that aims at distributing workers. Furthermore, the organization decided to form HR and legal team for the sales and marketing department, production department separately (Schweinsberg, 2017). This strategic adoption can also be marked as deliberate because the corporate leaders of Toyota have focused on analysing the market trends before adopting strategies.
On the contrary, if the strategic adoption activities of Toyota are looked at it can be said that Toyota has slightly adopted emergent strategies along with deliberate strategies. The organization is constantly focused on launching innovative or unique product in the market. It is found that Toyota have always taken unplanned and abrupt decisions of integrating new and emerging technology with the core product of the firm. Toyota also has a product integration team that aims at integrating new and emerging aspects in various products of Toyota (Yamamoto, 2021). The objective of this team is to cope up with the change in the need and demand of customers across the world.
Critical analysis
The primary mission of Toyota is to attract customers by offering them with high-quality and highly-valued products as well as services. The mission of Toyota makes the company more than just a “car production” firm. The mission of the organization has been structured in such a way that further has an influence on key strategic decisions of the firm. Toyota is marked as one of the “high-performing” company in the global market because the organization is known for combining technology along with the product design and the purpose of the firm. The strategies adopted by Toyota is also mobile that is further helping the company to expand in the global market (Mainwaring, 2018). On the contrary, Toyota has faced allegation regarding product design strategies. Customers accused that the organization is primarily focused on adopting environment-friendly strategies rather than concentrating on the actual design and aspects of the product. Despite, adopting cost-curbing strategies, Toyota experienced a huge decrease in sales because of faulty-air bags. This has further decreased the rate of satisfaction of large number of customers (Connell, 2018). The stock of Toyota also got affected due to this strategic decision of the firm.
In addition to this, the corporate team of Toyota believes that efficiency alone cannot bring major success within the workplace. Furthermore, the organization considers employee as one of the driving forces behind the excellent performance of the firm (Toyota, 2022b). Toyota believes that constant development of employee within the workplace is of utmost importance because it can further add value to the firm. Thus, Toyota invests a huge amount of money in training and developing workforce within the firm. On the contrary, Toyota still follows hierarchical organizational structure. The top-down flow of information within the workplace is known as hierarchical organizational structure (Krackhardt, 2014). This structure is generally followed by individuals who are autocratic in nature. It is also slowly becoming obsolete because organizational leaders are currently working towards decentralized organizational structure. Therefore, this aspect of Toyota’s strategic decisions must be changed by the strategic leaders in order to strive in the global market.
Conclusion
The aim of this report was to critically analyse the strategic decisions undertaken by one of the renowned organizations operating in the automobile sector. The organization that has been chosen is Toyota. From the report, it can be concluded that deliberate strategies are generally adopted by the strategic leaders of the selected organization. The strategic leaders of Toyota emphasize on market research before undertaking any actions. Deliberate strategies helped the firm to develop skills and abilities of employees within the workplace and it has also resulted in increases in the rate of customer satisfaction. Apart from deliberate strategies, Toyota also focuses on adopting emergent strategies in order to cope up with the constant changes in the global industry. In the final part of the report, a critical analysis has been done that focused on describing the pros and cons of strategies that have been adopted by the strategic leaders of Toyota over several years of operation.
Reference List
Connell, 2018. Pros and Cons to Buying Toyota Motor Corp (TM) Stock. [online]. Available at https://finance.yahoo.com/news/pros-cons-buying-toyota-motor-140000039.html#:~:text=On%20the%20downside%2C%20Toyota%20was,4.1%20percent%20to%20521%2C000%20vehicles. (Accessed 22 February 2022).
Kopmann, J., Kock, A., Killen, C.P. and Gemünden, H.G., 2017. The role of project portfolio management in fostering both deliberate and emergent strategy. International Journal of Project Management, 35(4), pp.557-570.
Krackhardt, D., 2014. Graph theoretical dimensions of informal organizations. In Computational organization theory (pp. 107-130). Psychology Press.
Mainwaring, S. 2018. Purpose At Work: How Toyota Is Driving Growth, Innovation And Impact. [online]. Available at https://www.forbes.com/sites/simonmainwaring/2018/11/13/purpose-in-action-how-toyota-is-driving-growth-innovation-and-impact/?sh=d5176aa47fbc (Accessed 22 February 2022).
Neugebauer, F., Figge, F. and Hahn, T., 2016. Planned or emergent strategy making? Exploring the formation of corporate sustainability strategies. Business strategy and the environment, 25(5), pp.323-336.
Schühly, A.M., 2022. What Is Strategic Management and Why Do We Need It: Theoretical Foundations of Strategic Management. In Cultural Influences on the Process of Strategic Management (pp. 33-135). Springer, Cham.
Schweinsberg, C. 2017. Toyota Vows Better Speed to Market, Employee Retention. [online]. Available at https://www.wardsauto.com/industry/toyota-vows-better-speed-market-employee-retention (Accessed 22 February 2022).
Terziev, V. and Georgiev, M., 2017. Highlights of the evolution of the'Balanced Scorecard'idea as a model for managing strategy development and control. Strategic management assignment IJASOS-Internationale-Journal of Advances in Social Sciences, 3(8).
Toyoda, A., 2021. Video: Media Briefing on Battery EV Strategies. [online]. Available at https://global.toyota/en/newsroom/corporate/36428993.html (Accessed 22 February 2022).
Toyota, 2017. The Changing Business Environment and the Expansion of Mobility Value. [online]. Available at https://www.toyota-global.com/pages/contents/investors/ir_library/annual/pdf/2017/ar17_2_en.pdf (Accessed 22 February 2022).
Toyota, 2022a. Toyota Global Vision. [online]. Available at https://global.toyota/en/company/vision-and-philosophy/global-vision/ (Accessed 22 February 2022).
Toyota, 2022b. Employees. [online]. Available at https://global.toyota/en/sustainability/esg/employees/ (Accessed 22 February 2022).
Yamamoto, K. 2021. Toyota's Discerning Approach to Car-making and Challenges for the Future. [online]. Available at https://global.toyota/en/newsroom/corporate/35891478.html (Accessed 22 February 2022).












