An Review Of Supply Chain Risk Management For A Project In The Automotive Industry
Question
Task: The exploration of this research is an analysis of supply chain risk management applies. This examination is founded on the vulnerability of supply chains in the automotive departments, drivers of supply chain in transportation is creating possible risk impact on the supply chains. Outcomes are predicted by the Probability Impact matrix is mainly differentiate between both risks of organisation which are internal and external. Additionally, tools of SCRM are calculated and influence on presentation is verified. To demonstrate alteration between organisations with a great level of SCRM and those are deprived of only inadequate in improvement in industries are arranged by cluster analysis depends on the issues affecting in the tools of SCRM. The collection of groups on behalf of the two actual methods of contract i.e. deterrent and sensitive SCRM. These groups are inspected to about prospective changes in the standings of performance procedures. This examination discloses that organisation requires better level of implication to reach good performance. Besides, outcomes reveal that companies are using sensitive SCRM for the measuring determined medium value regarding interferences
Answer
Abstract
In recent times the supply chain risk management process has become a foremost topic. In the corporate world, the supply chain experience to risks both from the organization’s end to the customer’s end. Due to this content, the readers will gain some bright ideas about the process. The role of the manager and customer will be discussed in this context. In this context, a review of recent literature will reveal some structure or dynamic approaches for the risks in the supply chain. However, in the field of supply chain risk management has no proper conceptual framework. In this context, several issues are investigated, and remedies are suggested that may be useful in a hard time. Risk can be raised due to faulty actions of employees or imposed by environmental issues. Both situations always leave a significant impact on the organization. Downtime is one of the significant issues that can create a fuss for any small or large organization. Every organization wants to expand its business and be present in the global market. In international business, the supply chain risk becomes more complicated; in this content, some idea is proposed to minimize the risk. The domestic supply chain is less risky than the global supply chain. Among the many reasons, one most important reason is that the interconnection of many networks or firms. There are so many reasons that make the supply chain more complex. Breakdown, political changes, disaster etcetera, can be a significant barrier to the change. In the last few decades, it has become the most crucial topic of discussion on supply chain risk management. The challenge to manage risk problems in the global scenario has become the most challenging factor even at sensitive products like the circuit board or raw materials. In many cases, it has been seen that the organization is unaware of the proper location from where the raw material coming.
Chapter 1
Introduction
The UK automotive industry is one of the most successful industries in the world that continues to attract considerable amount of global customers and revenue. The automotive supply chain of England exhibited £ 54 million boost up to the national economy for last four years due to efforts made by its government and automotive superpowers. The supply chain is prone to attract risk factors in the automotive industry, due to regulatory framework, demand and functionality. Modern global and national automotive industry and associated supply chain partners taking initiative to reduce risk associated with it which directly contributes to the production growth.
Due to the intricacy in the supply chain risk management process, it becomes quite challenging to identify the risks, and there are two different categories of risks. One is the internal risk that is in the functional process of the automotive companies, such as breakdowns of machines or problems related to information technology. Other external risks such as on site disasters and hazards are caused by men at work. There are more chances of having internally related risks than those of external ones, even though the external risks cause much more damage, and there could be risks related to strategy like environmental as well as the redistribution risks. Various issues like globalization, unavoidable disasters and unrest caused due to politics makes the supply chains prone to threats and uncertainly which makes the supply chain risk management methodology is highly vulnerable.
1.1 Context
Risks in the SCM leads to a significant loss of business in the various automotive industries. The supply chains are currently encountering rapid rise of a growing number of hazards. The reason why these risks should be identified at the first place and prevented before they cause issue in the revenue generation and national economic contribution.SCM which is always active becomes a high priority for the business. The various forms of risks might hold different value for different companies; some of the risks might be negligible for one while unavoidable for the others, the risks hold different values even if in the same industry due to the supply chains being configured and set up differently from one another. Some of the risks can be analyzed and solved from the help of external sources which needs more critical data while the others can be put down with smaller quantity of data internally (Alotaibi & Mehmood, 2017). A supply chain which is adapted to customers has more chances to become successful in the automobile industry, the design of the supply chain which is attractive and which can control the dynamics of the market is compulsory, due to technological advancement, the automotive industry is undergoing a rapid change; To help remove the issues in the automobile sector's supply chains; frameworks are being developed to help management to create safeguard against loopholes in their systems related to the supply chains in their respective firms. The managing of the supply chains amidst the various increasing amount of risks is regarded as a calculated choice for the automobile industry players(Ansari & Kant, 2017).
1.2 Scope
The scope for SCM awareness in the automotive industries needs serious attention; there is an increasing demand for cars in the automobile industry, there are demands explicitly made according to the geography of areas. The problem in supply chains is the number of suppliers that number thousands that are from single focal points which makes it massive and thus the problems are unending as a result of these supplies.
Thus secondary research is being conducted to analyze the risks involved in the automotive industry’s supply chains. The United Kingdom’s automobile sector is regarded as one of the most significant industries in the world, the industry is also always at risks with its supply chain which could either be inner or outer such as disruptions in the machinery and some problems related to computerized information’s as well as natural calamities or problems caused by man(Arunachalam, et al., 2018). The most common risk that is associated with the supply chains are the interim qualms of many assured procedures; those can be categorized as risks related to productivity like the failure of pieces of equipment, documents not being appropriately provided to comprehensible procedures, troubles in the value as a result of too much turnover of employees, the manufacture being halted or people not being in charge(Aven, 2016).
1.3 Relevance
SCRM has high relevance in the supply chain processes across the globe today, it deals with financial risks, problems incapacity, and no flexibility in production, there are risks in SCM which emanates from management like taking wrong decisions in choosing inappropriate associates, causing lag in production. When there is involvement of more number of companies, then the system becomes more significant as well as multifarious, so unless the companies that come later can be relied on, depended upon as well as be responsible, the entire chain may confront the risk of distributor’s supply(Burtonshaw-Gunn, 2017). There are also unique supply chain risks such as disruptions in the production; transportation risks are also involved as well as demand and infrastructure risks. Some systems are developed to reduce the risk factor; the methods of AHP, as well as TOPSIS, are applied to assign the weight to the risk factors as well as the ranking members to identify the hazardous issues in the chain. Four classes, namely the risks associated with supplying, risks in processing, the various hazards related to the environment and lastly the risks involved in the demands (Cagliano, et al., 2015). A framework which is adequately integrated was proposed for the risks in the management of the supplying chains where the unclear inference system is being used for calculating the total risk score; it was applied in the server manufacturing environment case study. Sustainable risks from sub-suppliers are also considered, the AHP approach, which consists of two steps for a sustainable worldwide selection of supplies, was developed too (Cai, et al., 2016).
A theory of ABC method for the trader’s choice is used for risk evaluation. Additionally, the ANP method is developed that is applied for multi-objective programming. This programming decides the supplier selection using the risk factors as well. A decision-making model is being proposed to improve measure and evaluate the supply chain risk management performance by using the analytic hierarchy process [AHP] and structural equation modelling[SEM]. An unclear supply chain network under uncertain conditions using a mean risk optimization method is developed to reduce the unexpected costs. The benefits include a high-efficiency rate, which means the business is capable of incorporating innovation of the product, better supply chains and logistics are integrated better.
There will be better strategies for innovation of the product and will be in a high position to not only predict the demand but also to act accordingly. It decreases the cost in several areas which improves the relationships with both the vendor as well as the distributor, improves the response of the system to the requirements of the customer (Coyle, et al., 2016). It also adjusts the space of storage to keep the finished goods which help in deleting the resources which are damaged, hereby improving the coordination and the collaboration with the various companies that provide transport and shipping. It improves the communication medium, which will help in better negotiation with distributors and the vendors, which indirectly helps in lowering the delayed processes.
Firstly, it is to ensure that the supply chain provides the necessary products and required services under problems, it is also for catching the various loopholes, vulnerabilities, suspicions and risks in the various supply chains (Dubey, et al., 2017). The use of technological programs or software for detecting the problems in the supplying process and lastly to achieve the top level of security system so that no treats are capable of bypassing the security. There are certain risks from the automotive industries such as the competition in the industry is quite high, there is instability in demand, there are risks in the exchange rates, the price of the raw materials are of a concern as well, frequent disruptions occur in the supply chain, there are instability problems in the economy, and there are hidden risks (Dubey, et al., 2017).
In the process, several techniques are developed to minimize the risk involved in the chain of traders, which in the industry of automobiles. By minimizing known, unknown risks in the automobile sector's trader's chain procedure there can be a list of benefits that will be of use for the various corporations that are in the business in linkage with the chain of suppliers in the automobile industry.
1.4 Objectives
- Identification of potential failure points
- Map the entire supply chain to determine interdependencies
- Identify and prioritize critical business elements
- To analyze the weakness in Supply Chains in automotive industries and accompanying problems
1.5 Research questions
- What are suitable methods for risk mitigation as well as risk valuation?
- How to enhance risk management capability of Supply Chains in automotive industries?
- What is different analyse practices as well as tools used for risk analysis in project management?
- What is the weakness in Supply Chains in automotive industries and accompanying problems?
Chapter 2
Introduction:
It is very important for the researcher to recognize the difference between a research method and research design. In this study, research method is used for conducting research study and the research design provides the plan which is a tool to carry out the study. This research study has been done with proper justification followed by the research methodology.
In the research study, execution and designing is a very crucial part. The researcher develops a plan by this method. The developing methods and design are essential for the researcher to select a various approach; theories, methods and it also help to execute the research design. This method assists the researcher to recognize the dissimilarity between the methods as well as design(Fahimnia & Jabbarzadeh, 2016). The investigate way conducts a research study. On the other hand, the study design is an arrangement, which developed to perform in this study.
The researcher used the pragmatic approach to accomplish the analytic research study. Due to this study, it aids the researcher to apply both interpretivism and positivism approach. In this investigation, the investigator also used deductive research approach, which helps to deduce the results from the collected data. It has to keep in mind, from the analysis when the results were deduced, and this approach is used by the researcher(Gopal & Thakkar, 2016). In this study, the researchers used the random sampling method.
Research Onion:
"Research Onion" is an integral part of the research methodology. It was established by Saunders et al. in 2007. According to this study, the researcher will be capable of knowing the systemic study from each layer of the research onion. In research methodology, the research onion is a progressive method. It helps to execute the systemic plan for the research study. This method can not only help for a systemic plan, but it also helps to implement the research design. This method is also used by the individual researcher to achieve accurate results.
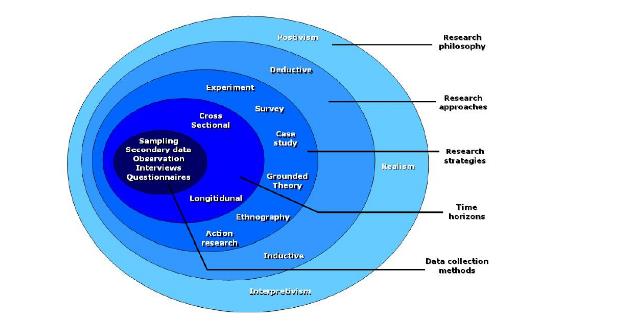
Figure 1
Saunders et al.2007
2.1 Research philosophy:
In this model, Research Philosophy is the first stage. The research philosophy has four vital parts. These are Pragmatism, positivism, Realism, Interpretivism. In the current research study, pragmatism is chosen by the researcher. This approach helps the research to deduce the results. Due to this study, Research philosophy describes the developing capacity. Logical reasoning involvement is also a part of this philosophy. Positivism, as well as Interpretivism both, is included in the research philosophy. Deductive and Inductive is a part of this philosophy. The research questions carry the essential part of pragmatism philosophy. In this philosophy, the researcher has to analyse the data(Govindan & Fattahi, 2017). This approach needs not just a scientific study, but also it can discover the factors of the investigation. Primary and secondary data collection also includes this topic.
Justification: In this study, the Pragmatism research philosophy is used by the researcher. Pragmatism philosophy is highly justified in this study. In this study the researcher needs to analysis data from the angle of company’s approach as well as the customers. This approach helps to deduce the results. The positive philosophy method cannot help the researcher for their present study. This philosophy is highly structured and has large samples. Pragmatism philosophy describes the developing capacity but the other philosophy cannot describe this. Due to this philosophy the researcher can identify the factors of this study.
2.2 Research approach:
The research approach is mainly an execution strategy. In the research, beginning the data collection to analysis of the data, these planning strategies are executed by the user of this approach. Here the researcher chose the deductive approach. This approach permits the investigator to simplify and devise the interconnection. To find the deduced exact ending from the generalized data; the researcher has used this approach. It is also used for evolution. It evaluated the confirmation and correction of the deducted connection. Interpretation, data analysis, data collection are the three main elements of this approach. In Deductive research approach, property and conclusion have to be true(Gunasekaran, et al., 2015). It carried mainly generalized data. Hypothesis, evaluate data collection also indicates the theory. Due to the lack of period, there could be errors in the research. Deductive research is used for controlling the errors. The Deductive research approach takes a limited time period. In this reason, the researcher chose this approach.
Justification: In this case study the researcher use deductive research approach. This topic itself points in the direction of deduction of a particular relation between the customer and the concept. It has been highly justified with limited time period used in the study. The research conducts this study within limited time span, and it helps to the research to avoid risks in the time of research. If the researcher uses inductive research approach, then the researcher faces many issues. This process is lengthy, cannot control the errors. Due to this reason, deductive approach is more justified.
2.3 Research design:
Research design mainly provides a plan. It assists the entire research study. Research design is mainly based on analytical research and explanatory research. This analytical research helps the researcher to recognize why as well as how characteristics. The implementation of various methods and execution strategy are done by the explanatory research design. The cause influence interconnection analyses are also done by the graphic design. Co-relation research design, a diagnostic research design is also a part of this(Hahn & Packowski, 2015).
The topic throws some light on the reason for this study. Due to this, the researcher will integrate different apparatus, and the whole strategy is consistent and logical way. It has no hidden controller. It also helps the researcher to find out the complex problems. There are four characteristics seen in this design. These are generalization, reliability, neutrality, validity. The scope of error in the research can be the provision of biased data.
Justification: In this study, the researcher uses explanatory research design. It gives plans for the study. This design indicates the purpose of this study. Through this design the researcher will integrate different apparatus in logical way. The researcher can find the complex problems by this design. If the researcher uses analytical researcher design, they cannot integrate in logical way, and they cannot find any complex problem. Due to this reason the explanatory redesign which is used by the researcher is highly justified.
2.4 Data collection method:
According to the discussion, primary as well as secondary data collection method is included in data collections method(Hazen, et al., 2016). Surveys and interviews are parts of primary data collection methods. Alternatively, secondary data collection methods permit the investigator to study the earlier research prepared on the same topic. The researcher can search the internet, reading books, articles, journals or something related to the topic. The researcher gets the data from the newspapers. There was no exact collecting process. The research will be able to utilize the external as well as internal sources. They can follow business journals, social books, sales reports, magazines, libraries. It is mainly a process to gather information from the relevant sources. It also helps to find out the solution. It also tests the Hypothesis and calculation of the results. It also works for discovering the trends. It assists in resolving the issues. The audience is segmented into the different customer groups. Gathering and measuring process it also includes the process(Hohenstein, et al., 2015).
Secondary data is readily available. It requires less time to assemble information. Comparatively, it is less expensive from primary data collection method. It is not always possible for the researcher to obtain specific data, but still, it shall be done.
Justification: In this study the researcher choose secondary data collection method and it is highly justified for this study. In this study, the investigator follows social books, previous case study, business journals, reports and magazines. If the researchers use primary data collection method, they face some problems. Primary data collection method includes survey and interviews, it consumes high time, and it is expensive. This research was done in previous in this case present researcher get more documents on this topic from many sources, it is less expensive and it consume less time. Due to this secondary data collection method is highly justified.
2.5 Sampling technique:
The sampling method is an integral part of the research study. The success of the research depends on selecting the exact sampling method. It permits the researcher to collect data about the population. Probability and non-probability are the two main parts of this method. In this study, the researcher is chosen as the non-probability sampling method. The convenience sampling method is also liked by the researcher. This method is straightforward. In this reason, it is acceptable to the researcher. Results should be useful for the investigator. Sampling methods could not find any errors. These methods do not help assess faults. Purposive sampling is applied in the non-probability sampling method(Ivanov, et al., 2016).
Purposive sampling method can be extremely appropriate. Sometimes it provides biased data. Create an accurate sample, Reduces sample bias, diverse population is the three main parts of the sampling method. Non –probability method is a sampling method, which includes the group of response depends on the researcher. Non-probability sampling is a very effective sampling method. This sampling method based on random selection and subjective decision. It also based on non-random sampling method. Arbitrary selection, exploratory nature also defines this method. It determines the correct of the results(Kaufmann & Gaeckler, 2015). Some or other common characteristics are involved in the population. Elements number is called population size.
Justification: The researcher chooses non-probability sampling method for this study. It is a straight forward sampling method which gives useful result. Based on this method the researcher can take random selection. Subjective decision is also very easy to take for researcher. The researcher cannot use probability sampling method because this method does not give useful results; it is not effective for the study, it is not a straight forward method. Due to this reason non-probability sampling method is highly justified.
2.6 Data analysis:
In the Research, Pragmatism research philosophy is chosen by the researcher. It is mainly a roadmap, for finding and analyses the survey data. The explanation of the research and the various steps are included in the analysis plan. It should maintain a targeted manner. Firstly the research questions need to devise within the analysis. The first important step for the purpose of conducting statistical analysis is known as the process of descriptive analysis; the analysis gives an idea of the data distribution and helps in detecting the type errors and the outliners. It identifies the variables associations as well as prepares for conducting later analysis(Khalid, et al., 2015). With the many available graphical types and approaches, in summary, it becomes confusing as to which data should be analyzed, thus ending in doing many analyses, thus wasting time.
In data analysis research questions and analysis are revised by the researcher. In this method, explorative data is achievable. Outcomes, population, comparison, Intervention is also included in this method.
2.7 Ethical consideration:
In the research methodology, ethical consideration is the most crucial part. In 2007 Bryman and bell established this(Liou, et al., 2016). Research time cannot harm any subject; they main their dignity, they should be prioritized, participate gives their full consent over their study. Participates should maintain their privacy for their research topic. They should handle their research data confidently. Participate have to declared for affiliation. They should avoid any type of confusing information. They should be communicated with each other and maintain their honesty and transparency. From any stage of the study, participants have to withdraw forms right. Based on informed contents, there should be the participation of respondents. Sufficient information and assurances are provided by the researchers. While pursuing the research, it is essential to see that such research is done in appearance to all laws pertaining to it(Maier, et al., 2017). This law maintains the privacy of the United Kingdom. As per this law despite the fact that was handling sensitive information about ethnic background, religious principles, political opinions, health condition, and criminal records must be taken extra care. The researcher should take care of the emotion, feelings, and sentiments of the others participate. The researcher should take special care not to mess up any things. They do not force anyone to join their group. There is a difference between Future population and best participating in a trial. Cookbook solution is included in ethical consideration. The planning of the trail each group is considered one by one. The reason for the arising ethical issue depends on challenging sets of values. Health issues are treated as unethical (Marshall, et al., 2015).
Summary: This chapter includes different thoughts of research techniques and methodologies that are working for execute the research. Along with that the researcher indentifying different research techniques and methodological justification is also provide for each and every tools for their significance.
Chapter 3
Introduction:
In this study, the researcher analysis the supply chain risk management process. Supply chain risk management process is an implementation of the strategy for managing exceptional risk as well as everyday risk. This process based on continuous risk assessment with ensuring continuity and reducing vulnerability. The supply chain risk management challenge has been improve by globalization, where sensitive inventions like defence system use raw materials, related components, and circuit board have originated in countries where the manufacturer did not know the supply chain. This complexity brings extra potential failure points and high level risk. In the new scenario supply of risk, chain management has become a popular topic. According to the report, in the last decades, the SCRM management has left a remarkable impression on the managing sector. Despite any other industries, automotive industries became the world's most important economic sector. It also left a good impression on the revenues and employment. An automotive supply chain is a complex of automobile parts. Automobile industries have multiple layers.
3. Literature Review:
The automotive supply chain is not only but a sophisticated form of industry stakeholder; multiple suppliers associated with supply chain network in case of automobile parts. In this supply chain, it is essential to coordinate with information, coordination of materials, to maintain the financial flow(Mohammaddust, et al., 2017). In many cases, it also seems that repeatedly stricken of natural disaster or manmade disaster left a complete loss in the manufacturing of the automotive supply chain. This research provides a comprehension literature review of extending research work on SCRM and management. Space of discussing an area of literature review in this content is limited.
The review will provide and summarized and also classified the supply chain risk management resources in the industries of automotive. In the automobile industries, the two most crucial mathematical model is developed in research and concentrating on the supply chain(Mohr & Khan, 2015). Development research locates manufacture cooperation in this chain. In this model or chain, it is said that the capabilities and the performances of the supplier must be improved day by day. OME's also donate a reasonable sum of money for the improvement of the employees. It is also essential to allocate the investment among the suppliers for minimizing the risks as low as possible.
In many cases, the acceptable return level becomes a critical issue. This mathematical model or the non-linear investment model has more acceptability in supply chain risk management methodology. Development in the research model is a satisfactory contract for the development of the new product with all-risk consideration in automobile industries. Through this review, it will investigate how would be decided supplier’s capabilities and manufacture’s order to reduce losses and maximized profit. The two major swing factors in automobile industries are demand and regulation.
Project management theory:
In this case study the researcher introduces kraljic matrix. This model guide the managers, they can formulated strategies and identify the weakness of their organization and guide the co-workers against supplies disruption. Purchasing has to transfer into supply management. The kraljic matrix is one the most valuable models for determining supply strategy.
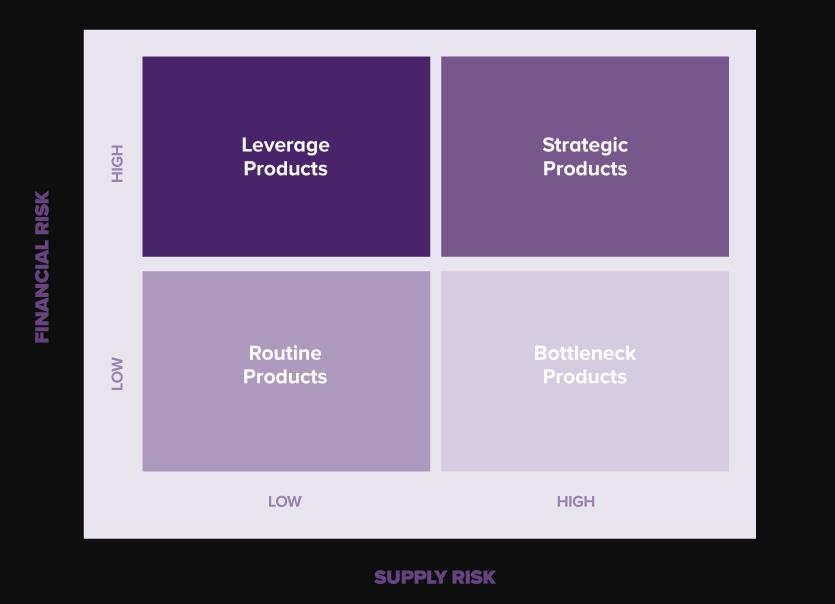
Figure 2
It is the biggest challenge as well as the role of automotive suppliers to control the changing facts associated with the risk involved. Administrative and legal constraints are a significant hindrance for suppliers and manufacturers. NAFTA has a considerable contribution in case of controlling and monitoring the automobile industry and associated stakeholders. In many countries, it is also be seen that rules and regulations change overnight. Thousands of suppliers who are trying to create their manufacturing model are being defected. In the last decades, a considerable number of organisations have been shaken by unforeseen delivery chains leading to the recall of a hundred million dollars from pharmaceuticals to electronics as well as automotive. Such as, multiple public organizations or private organization has been struggling with cyber securities branches due to losing intellectual property failures. In this situation, the heart of the crises is a common theme(Oliva, 2016).
Risk management definition:
In supply chain risk management, the challenge of risk enhances by globalization. It is also noticed that many manufacturing companies have a supply chain in sensitive products like circuit boards, raw materials, but they do not even know about that. In modern supply chains, the supply base transparency is next to impossible. In the supply chain process, thousands of suppliers contribute their products to a single project(Rajesh & Ravi, 2015). Even hardly know about the raw material sources. The scope of intimidating and the probability of risks is ascertained so that it is challenging to address the quantity. In sophisticated products, one or two suppliers may consider their supplier chain to be proprietary, purchase limitation. Supply chain risk management is a theory where is to manage the implementation of strategies and risks.
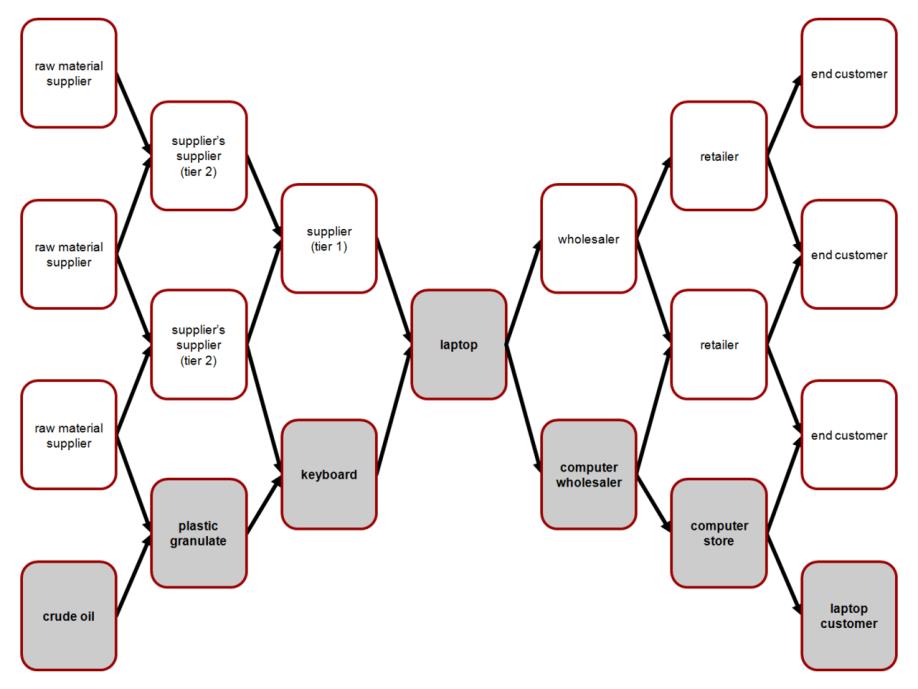
Figure: internal and external costs
(Ross, 2015)
SCRM issues: According to BCI’s report [2011], 559 companies across the 65 countries found over 85 per cent of the companies had suffered from at least one supply chain problem during the year. It is also respondent that 40 per cent distribution originated by sub-tier suppliers(Sasson & Johnson, 2016).
Risks:
There are so many ways to accepts risk levels to the engineer. Among them, one crucial point is managing stock in case of supply chain management risk. There are so many ways to accept risk levels to the engineers associated with the automobile industry. Among them, one crucial point is managing stock. Supply chain management [SCM] organized warehousing as well as efficient planning strategies. Effective supply chain management allows handling complex processes for productivity as well as it also minimises the business or liability risks.
In this content provide that novices, recruits, specialists as well as executives training to ensure proficient professional of critical business planning(Savino, et al., 2015). Supply chain risk management [SCRM] is the area of emerging from the growing appreciation to supply the chain risk by the practitioners and researchers. However, there belongs a diverse perception of the search for supplying.
3.1 Supply chain management
Always it has to be remembered that, on investment, there are two sides, one side is profit, and the other side is risks. In investment returns have no guarantees. As an example, in the long term process, one business profits a lot but no one can predict the future, after running in profit line with a reasonable amount of time the company can drop out. There would be no assurance to get back the money on time. An investor may also lose money due to risk involved and production inadequacy. There are many reasons for stock management issues in case of supply chain risk management associated with the automotive industry. An investor should make his or her mind about the losses that can be arrived in future. It is also be noticed that in many cases, the short time investment loses more than long term investment, so that, the investor should set mind about the causes(Alotaibi & Mehmood, 2017).
Risk identification:
The planned supply chain risk management process is a device that provides strategically useful information to the management regarding the numerous risks associated with the chain of supply in that point of time, which is opposite to the conventional method based on the estimations of a single point. The SCRMS makes sure that the supply chain managers adopt strategic ways like proper decisions to estimate options for improving the supply chain process; they provide efficient ways to handle the correct decisions(Cai, et al., 2016). Many researchers attempted to understand and measure the common risks related to the supply chain process, a supply network opportunity package was developed to estimate the scheduling as well as planning for the SCRMS projects.
A linear programming model was also developed for measuring the costs of risk-based upon the present monetary amount of activities; an analysis network for disruption was also created to calculate the impact done by changes caused by disruption on the supply chains. There were specific techniques applied as well like the algorithms of genetics, the artificial method of bee colony and optimization on swarm particles to correctly classify the risk factors. A hybrid method named Petri-net was proposed for evaluating the performance and assessing the risks which can threaten a supply chain.
Risk assessment:
There was a suggestion that practices in the purchase and sourcing from the delivery could affect in an unhelpful way on the strictness of the halts in the supply chain, managing knowledge is useful for improving the flexibility of the supply chain. Much vulnerability was assessed in the supply chain network, and it was also decided that if the mangers were more capable of managing and adequately measuring the weakness than more halts could be prevented. The more vulnerability that is prevented in the system also allows for understanding more strong versions in less cost, and much data is needed to calculate the factors which affect the chain networks(Burtonshaw-Gunn, 2017).
Many works were done to reduce the risk in the supply chains; supply failure is a common problem in the process which can be easily solved by management techniques based on behaviour. It is believed that a two-way sourcing approach is always better than a single source, but the benefits are not noteworthy. The number of suppliers does not bring the desired profits as the thought of; the supplier’s cost has much more influence on the order than the failure of the supply. The risk factors in the supply have the highest number of risk types, so it gets the most consideration, while others don't receive the same consideration due to the risks being negligible especially the risks related to the infrastructure(Cai, et al., 2016).
Organizations face up to five different types of risks in their chain supplies, and some are not that serious while holds great importance and cannot be avoided. Investigating the total impacts of all these risks, can lead to risk management in a better way and be able to treat each risk singly. There is increasing research being done in the SCRM areas which are mostly speculative like, for instance, there are many varieties of management in SCRM, and also several types of frameworks that have come out.
Risk management:
There are useful tools of mathematics that is needed for understanding the best chain risk management process; they attract a lot of attention due to the vulnerabilities that they have to offer. Though the studies are mostly of high quality, they are also practical, and there are researches based on the model as well(Dubey, et al., 2017). A mixed-gender programming model is also being implemented, which as well is used for determining most exceptional supplier relationship; stimulation models are also being implemented for the purpose. It is to seek the uncertainty of the demand and the reliability of the supply process in relationship and design.
The process of risk management has three stages which are the identification; evaluation and finally the mitigation process, and there are two stages of risk evaluation which are the measurement and assessment of risk. The assessments cannot be predicted as the future of it is unknown; it is regarded as a dynamic process, so it should be revised and overseen all the time. The most crucial stage is always regarded as the identification of the risks in the risk management process; the risk associated with every one of them can be identified singularly(Rajesh & Ravi, 2015).
There is a list of factors that leads to better capability in the supply chains the management of risk. They are critical factors for the risk management process in the automotive industry in the UK. Various companies can match their practices as well as decisions with those factors to analyse the level of their capabilities. The advancement of the capabilities depends upon the level of the practices. These factors are considered as a crucial parameter in the governance of risks which means having the presence of fitting processes as well as structures.
Risk monitoring:
Better resilience in the process and network architectures implies having the right amount of suppleness and redundancy in the automotive industry. The better coalition between the partners and the supply chain drives better alignment in supply chain risk management. In the identification of new patterns and advancing towards it, better integration of the supply chain risk management is required. Better coalition and incorporation within the business leads towards demanding and ensuing combination of the supply chain that was implying better and visible teamwork. Arrangement and amalgamation between the risk management functions can develop alignment between the various actions on a company level, involved management and operation. The inside and outside process integrating techniques are also regarded as necessary as well as the governance of risks.
The operations related to the supply chain and management of risk processes go side by side and balance one another very well, in the lower levels both the processes go alone, but in the higher levels, they operate together. For the development and the setting up of capabilities in an effective manner, the supply chain being highly sophisticated is a must need. The maturity of the supply chains and management of risk process can be divided into four phases(Cagliano, et al., 2015).
3.2 How to reduce risks
The manager has to identify and access the risks. Quantify the risk, and then develop the mitigation strategy by increasing visibility into supply chain operations. There are so many ways to accepts risk levels to the engineer. Among them, one crucial point is managing stock.
3.3 Business risks
With a lack of good fundamentals are not able to deliver good growth. As a result in many cases, it is also have seemed that, due to companies' reduced scale of growth, scarcity of sales growth as well as reduced margins and inefficient margins(Schenkel, et al., 2015). It also is noticed that lack of business capital is also can be created by companies' poor performances. In a short turn, it can be possible temporary returns in substandard business, but in a long time, the performances of the company affected stock returns.
3.4 Valuation risks
Risks mean when the stock became overpriced than fair value. It left an impression on the return of investment. Overvaluation can also be judged as a temporary phenomenon.
3.5 Liquidity risks
Market when a product has no value or buyers, it is difficult to sell products or stock quickly. In this kind of case, it also is noticed that the managing department washout the stock at a low price as much as they can(Schenkel, et al., 2015). It can be a public sector or even small companies, for companies for this type of situation it is better to remove that kind of stock immediately. Will be discussed ten kinds of stock risks that face a company.
3.6 Risks for commodities price
Price risk is nothing but the swing of the product prices. This kind of risk affected the business. In the case of arising prices, it is related to companies' profit and vice-versa. It proved that many big companies also suffered when prices drop. It is also be seen that even those companies that have no relation to the commodities factor have suffered due to the changing form of commodities(Touboulic & Walker, 2015). By changing the prices, it affected the whole economy as well as the service economy.
3.7 Headline risks
Risk is also known as media risk. The media run over their channels or paper can affect the image of a business. It is not only for a small company but also applicable to many big national companies. Media has a significant impact on society; in many cases, it has also seemed that with verify the truth media published a fake story that would be left a wrong impression of a business. In 2011 the Fukushima nuclear crisis was a great example of headline risks (Subramanian & Gunasekaran, 2015).
3.8 Rating risks
Whenever business rates there achieve or loss in number is called rating. Credit rating is essential for any business. In business financing, credit ration plays an important role. The business rating has a physiological impact on the market.
3.9 Dictation risks
Here another form of risks is called dictation risks. In dictation risks, the authority fails to dictate the employees about the process of the program. No companies are free from risks. It may be private sector or public sector.
3.10.1 The management of the supply chain and provisional risk management
The integration of the supply chain is not proper though the process is organized correctly; there is a high level of duplicity in their activities, and they are disconnected in and out. There is a lack of effort in the partnering and supplying activities, the design of the product is done independently, and not much activity can be seen between the partners and the suppliers. The capacity is of a reduced level leading to unsatisfied customers, and the total rate becomes more, there is not much light thrown in the sources of the supplying process. The amount of threats and vulnerabilities that are detected is low as well; there is no proper response being given to the threats(Ansari & Kant, 2017).
3.10.2 The integration of the supply chain internally and the intended positions of buffers to avoid the roadblocks
The supply chains are organized in a cross-functional way; the processes of the inside are integrated, and there is proper sharing of information and have better visibility. There is a joint management of the resources, and there is a right level of configuration between the several objectives pertaining to performance. There is a proper integration planning which is being executed at many levels, and all this leads to a singular plan which is executable by the company. The processes of risk management are appropriately acknowledged and included inside; the various leakages and lurking threats are properly evaluated(Aven, 2016).
3.10.3 The supply chains are collaborated externally and give a good risk response.
There are alliances of supply chains across the enterprises, there is a good sharing of information, and it has excellent visibility as well. The designing of products and managing of inventories are included between the partners of the supply chains; the internal planners add the inputs which are external into their activities. The standards of the interfaces are increased, and the products, as well as the processes, are reorganized to avoid difficulty, the sharing of information and its visibility for checking the levels of resiliency and the continuation plans of businesses are made. Outside of the corporation is subjugated for setting up sensors as well as predictors related to variables and change for the positioning of the response mechanisms. Many methodologies of quantitative proportions are introduced for the purpose of risk management; there are also the conductions of sensitive study(Cagliano, et al., 2015). There is monitoring of the suppliers and the partners
3.10.4 The adaptation of supply chain that is dynamic which are quick to respond in terms of risk
The partners of the supply chain and the companies are quite united with each other on the variety of dimensions across the venture. The common goals guide the strategies of the individuals, the supply chains can work across different types of environment, the new patterns of the value chain that are born from the interaction are identified and probed so that in the process equilibrium points of high value is achieved. In order to match the propositions of customers, the supply chain is being built, real-time analysis and monitoring support the various risk and prediction sensors. There is full elasticity in the supply chain product as a result of these operations.
The capabilities of a company are evaluated in a framework, and as per the various surveys most of the companies have an undeveloped supply of chain operations as well as the risk evaluations, the distribution of the supply chain risk management have to encounter blockades which adds to the business and financial stability of the company. Companies faced many disruption issues during the process of the supply chain(Arunachalam, et al., 2018).
Supply chain management is a simple form of controlling the goods flow and the services that involve the live streaming of the business's side supply activities. This theory would be applied to gain maximum profits in case of supply chain and automobile industry in the UK. It also very important is to gain a competitive advantage in the UK market. In this chain management, the retailer preferred to evolve in this management. Most of the time, the retailer's involvement helps to control product qualities, timing, and expenses. As an example, the Walgreens Boots Alliance Inc. company is the second-largest company in the US. This company has to manage its chain and there supply so that they stay ahead to there future goals.
In every business, it needs a leader in the place. A leader needs to find out the problems and set a small team to engage in the supply chain. The employees must have a sense of the "big picture" of marketing if needed the professional tanning should give them. There must be a difference between non-professional and professional staff. Professionalism makes a job best. So, the leader should be adequately trained. Infield, the manager, should have the controlling power towards the workforce(Burtonshaw-Gunn, 2017).
Figure: supply chain system
(Kaufmann & Gaeckler, 2015)
The sound output of the supply chain risk management strategies depends on the information and data. The real-time reports are also available in all times that will be provided with valuable insight through the supply chain on the excellent manufacturing business. A software which is called ERP allows both users and management for the ability to instantly access, for the production and purchasing of data for the critical decision.
Summary:
In this chapter the literature review explains the important and the necessity of supply chain risk management and the steps represent the management process. This literature review also explains how to manage this problem and how to overcome these issues. In this chapter the researcher identified the problem which can be taken into consideration in the time of research. In this chapter the researcher introduce a new management theory named Kraljic matrix which is appropriate for this research study. It is a technique for manage supply risks. This model should develop the effectiveness of automotive suppliers in managing risk. This risk is very important for automotive suppliers.
Chapter 4
4. Data Collection, analysis and discussion:
Introduction: This chapter will explain the data analysis and interpretation which is collected from the previous case study, business journals, social books, reports and magazines. The data analysis will achieve the answers throughout the research questions that will help the researcher to found the aim of the research. The researcher analysis the research questions first. From this analysis the researcher gets ideas of distribution and how to find the errors.
4.1 Data collection:
In the operating supply chain, Risk management plays an essential part. Risk management depends on uncertainties. Mitigating risk, areas of defining, operationalising is included in the risk management system, which is focused by the researcher. Supply chain risk management is also called research profiling on the theme. After 2012, supply chain risk represents the" essential expression" theme. Significance in the logistic area is gaining by SCRM. Risk assessment, risk identification, treatment and monitoring are included in the SCRM. Complete definition and theoretical framework are developed by SCRM. It helps to assess theory and identify future research instructions. Many industries, as well as outsourcing, supply base reduction and product life cycle, is increased in supply chain risk. Man-made problems or natural calamities can have a significant part in this process.
Operational problems, as well as financial troubles, are also included in this process. Researchers depend on the complicated and compound nature of this process. The systemic review is needed for this process. The making of SCRM strategies the researcher uses the vital definition and implementation. External coordination, collaboration, Internal implementation is also essential parts for making SCRM strategies. Save-cost and cash-flow managements are also involved in SCRM. Build the capability and reduce the liability and make sure business stability is the aim of this process.
SCRM goals not only reducing the cost but also maintain, liability, business stability, continuity, continuity. This process is Multi-Faceted. Many researchers define SCRM in different ways. The objective of SCRM and pathway do not pay apparent concentration. Uncertain events can affect SCRM. Transformation, facility location, inventory positioning, supplier selection, design are also involved in this process. SCRM based on cost, location, quality, lead-time, reputation, capacity(Aven, 2016).
This research involves risk factor identification, supply chain risk, Industrial risk, and delivery infrastructure risk. SCRM also depends on process risk, environmental risk, and demand risk. Supply chain disruption is included in this model. In this research study, some risk factors are identified by the researcher. These are customer risk, supplier risk, commodity risk and technology risk. Reduce the crash of the risk by building a model for identity, ease risk, and access. Many government and private organization have faced a problem named SCRM. Lack of identification and manage problem help to growing up SCRM. It is also the world-wise interconnected. It has taken part in globalization. Thousands of suppliers can give a single product in modern SC. Identifying the raw material sources is a time taking process.
A known risk is located easily and possible to manage, but Unknown risk cannot identify quickly. In this reason, it is tough to manage. Identification process mainly based on plants, suppliers, transport route, and warehouse. It is an ongoing process, risk entered and then it is registered and then it is tracked by one. Due to this previous reason, all data are collected and recorded for further investigation. For accessing all risk, this process includes scoring methodology. I t is very vital design. Depends on organizations requirements the monitoring risk management system is adapted. Improving the flexibility and capability of supply chain risk; mitigating action is defined by the SCRM(Liou, et al., 2016). An Analysis of project supply chain Risk management in the automotive industry.
4.2 Analysis:
SCRM studies are utilized for finding the sources of risks, risk topology, and reviewing the topic. The time of chain implementation manage strategy and network-level are benefited by the SCRM. It is not the only risk, but only the uncertainties make the SCRM challenging to manage. Risk has taken part in the supply chain. It is an essential part. High-performing and secured supply chain are introduced by the supply leaders. The risk factor is minimized by this(Alotaibi & Mehmood, 2017). It is also added good value in the business relationship. In contracting management, efficiency and innovation are the central part. Limitations of liability, indemnification, Supplier insurance strategy also take part in this process. Financial stability of the suppliers is viewed by this process.
There are two major types of supply chain risk associated with automotive industry such as internal chain risk and external chain risk. The internal risk is consisting of Contingency risk, planning and control risk, cultural risk, business risk, planning risk. On the other hand, external risk involves physical plant risk, demand risk, environmental risk, demand risk. Demand risk is established on random customer demands(Ansari & Kant, 2017). Environmental risk is related to various factors such as social, climate factors, economic, governmental, and terrorism. Physical plant risk depends on physical stability and regularity of suppliers.
Manufacturing risk is established on the disturbance of the in-house process. Business process, key person, management, communication with sellers and clients with buyers, reporting construction is included in the business risk. Planning and control risk is involved in insufficient planning and unsuccessful management system(Arunachalam, et al., 2018). Contingency risk is based on not adding an excellent alternative solution where something incorrect. The cultural risk depends on hiding negative information by organization.
There are many kinds of risk, and these are: strategic, organizational, operational, commercial. Lack of understanding creates risk in stakeholder management and business functionality. It depends on buying and selling prices and fund allocation process. Risk is also created by Trade practice. Logistic service provider, component sources, logistics infrastructure are the three critical components of the supply chain. The management, collection, analysis of data of this process should be automated(Aven, 2016). Errors cannot be determined by human eyes, but the system can find it accurately, it is called automation. Many potential queries create an impact on the supply chain, whereas dangerous operation and profitability are assessing by the executive. The core focus is named cybersecurity.
The level of risk management is increasing day by day — digitalization and globalization in supply chain management create great opportunity for success and growth for many companies. SCRM is a sub-process and integrated process of an operating system of the automobile industry. SCRM co-ordinate with the risk identification, goal definition, risk management, risk analysis, controls the efficiency of the system, monitoring, and measuring the key elements. Developing a corporate strategy protective phase is involved in this process. In the case of the unsafe event, the objectives define the delivery capability. SCRM maintain the dynamic balance between the required capacity and managing supply interval and disruption susceptibility in the supply chain(Burtonshaw-Gunn, 2017). More than Tier 1 supplier covers transparency is involves for generating risk- connected transparency for the supply chain. The supplier based on the non- linear chain and a network. The trigger of the massive supply of disruption is based on Tier 3 suppliers.
SCRM depends on world economy changing process. SCRM assess exposure using data, mapping and analytics. Identification, measures, single points of failures, and prioritized mutually dependent risk are included in the SCRM. In SCRM, transfer approach and develops the modified risk mitigation is depends on business objectives. The details mapping of product, information flow and cash are provided by the SCRM(Cagliano, et al., 2015). Physical assets, internal and external resources, technology, and relationship create the importance for the organization. SCRM helps to control the balance between resiliency and efficiency.
A relationship model established between business process and critical business activities created by SCRM. Based on SCRM, many organizations shut down its supply chain for a certain period. In the automotive industry, risk can be based on missed production target, vehicle recalls, and safety incidents(Cai, et al., 2016). Security, safety dangers can create lousy impact for the organization. Revenue, employees, vehicles quality, customers, plants, and intellectual property also creates an adverse impact on the organizations. For preventing the risk organization should focus on their reach point and controlled the infrastructure of industrial automation. For improving the risk management system, organizations should focus on their four key areas. These are obsolescence, safety, quality and security
4.3 Discussion:
Industrial safety process is an important part of the automotive organization. Quality should high always. It could not compromise for any situation if workforces and Production targets increased. It can control quality with time.
The researcher companies identified the problems. These are: they should control over the critical process, loss of control over inventory, track and trace issues, and yield.
The company should investigate their increasing risk due to problems, which is seen. They should notice their partner's performance. They should identify the person who is responsible for uncertainty and impurity. They should control the problems with their partner's relationship(Hahn & Packowski, 2015). The process is always not asymmetrical with business objectives and functional activities. The information system will be based on the capabilities of the stakeholders and operational management methodologies. The uncertainty and performance are recognized as vital problems for the automobile industry and associated stakeholders.
SCRM is a new methodology that recognized the operations as well as financial features of decision-making. SCRM is a new concept for developing countries. Inadequate communication and departmental structure should control by the organization(Liou, et al., 2016). The suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers and logistic providers are involved in the organization's network. They should help their organization to fulfil its aims. They create a network to deliver the products to the customers.
Collaboration and coordination are including the supply chain risk management process. Marketing, sales, productions, logistics, information and finance are an integral part of managment functionality. Supply and Demand is the primary of the SCRM. On the other hand, political, environment, security and process risks are also involved in SCRM. Security risk has more priority level should control by the SCRM(Hazen, et al., 2016).
The reduce of loss and damages in the supply chain management process, incorporating SCRM is beneficial for automobile stakeholders. In the automobile industry, the inadequacy of quality supplies is a vital problem. Production delay also creates functional delay and declining productivity. Fraud and abuse become a prevalent issue in SCRM. Proactive risk management is a cost-effective approach. The company should control the risk from starting to end. Due to this reason, companies maintain their brand reputations, gain competitive advantages.
The risk management system is an essential part of the business. The organization should maintain its stability and expand the rate by this risk management system. This practice helps the organization to identify their problems, track, evaluate, and mitigate the risk. This practice should beused by the all kind of business like small, big. Small business takes this practice informally(Kaufmann & Gaeckler, 2015).
Enterprise risk management deals with the environmental, operational, market, regulatory, financial, and another risk. For software solution, ERM is most preferable practice. The organization have faced huge loses if risk management is absent. This practice should tell about the operating environment of the business who deal with the pre-emptively system. Action that is needed to be performed is included in the structured of the risk management process.
There are five primary steps. Those are: firstly, identifying risk, then analyzed the risk, after that risk is prioritized, implement the solution and monitored the risk. The administration and documents involved in the manual risk management system. In identifying process environment risk, legal risk, regulatory risk, and market risk are involves(Cai, et al., 2016).
In the analyzed process, risk should be analyzed when the risk is identified. Risk should be determined. The organization should understand the link between the factors and the risk. It is essential to know how many business factors are affected by risk. Environment analysis is done manually in the manual process. The time of implementation, procedures, policies, business process and different documents is taking the critical part. Risk should be ranked and prioritized. Depending on the seriousness of this risk, there are different types of the risk management system. Every risk should be eliminated as early as possible.
For avoid, the risk cliff is the most natural way, which is used by the organization. The organization should prevent the risk when it is happing. They should control this for their own project. The company can mitigate the problem when they could not find the risk. The transfer is a constructive way of controlling the risk. It is a dealing process. The company deals with someone for avoiding the risk(Cagliano, et al., 2015).
It is impossible to avoid, mitigate and transfer the risk then the company should be accepting the risk. The companies should know the access process of the risk, identify the responsible persons, and the planning. There are some technical risk includes component issue, which is very hard to use. Depends on the weather, transform of the market is an obvious problem. All risk is not equal. After identifying the risk, the organization should evaluate each risk depends on its probability. Risk breakdown structure creates the risk, which is categorized by a table format(Maier, et al., 2017). Reliable sully chain is developing and maintaining by the organization. It is a vital part to achieve the success for business in the economy of present days. In many companies, the risk managers should work together for identifying the risk and evaluate this.
Chapter 5
5. Critical Evaluation of performance and conduct
5.1 Risk analysis: With time, the various supply chains have extended immediately with the goals of increasing overall production, decreasing the costs and fulfilling the various demands in the growing markets. The increasing amount of difficulties in the supply chain halts the process reducing visibility and makes it difficult to control the process. Various cases are showing the disruptions faced by companies in their supply chains, and when not under control, it can affect other members of the process.
The various difficulties, as well as assimilations, pose a significant threat to the supply chain risk management process, it becomes challenging to identify the threats as the supply chain processing is handled by the external service providers and cannot be seen much. The proper identification of the threats depends upon the place of the corporations in the chain and also depends on the investigation of the threats carried out by them(Maier, et al., 2017).
Thus the supply chains need to be protected at all costs to maintain the proper results of the system in such adverse situations; they should be managed efficiently to avoid risks in the process.
There are some classifications of the supply chain risks-
- The risks that cannot be controlled
- The risks which are influencing
- The controllable risks
Those risks can be categorized as –
- Financial risks
- Operational risks
Financial risks
The financial risks in the supply chains can be determined by the sales, debt fairness ratio of the supplier as well as the working capital management. In the supply chain, risk occurs whilst rendering supply of a product or service to the customer about the price, proper delivery in time and the impact on the image. The risk affects an extensive range of shareholders, the ones engaged in the supply chain shares are:
- The ones who produce
- The consumers
- The retailers
- The one who strategizes
- The financers
Operational risks
The various organizations are dependent on machines for the function of their supply chain process; the machines can suffer from obstructions or disruptions in the middle of the supply chain process which can indirectly affect the other branches of the ongoing process.
External/ Internal risks
There are external risks in the supply chain as well, and those risks cannot be influenced by the business, political situations or the global landscapes. The external, as well as the internal risks associated with the supply chain, has a significant impact on the financial markets and the rates of interest, which ultimately affects one in business decisions.
Assessing the risks or uncertainties in the process means determining the probability of those risk factors. The risks can be analyzed by the objective information provided and prospect distribution for the significant supply chain risks where the results are derivable. However, if there is no availability of the objective information, then the personal information's and judgment can be used to estimate shares. The techniques such as the Delphi method or the expert groups can help in finding the sources of the probability; there are other ways like five-point estimating, parameter estimations, probability encoding or the stimulation of Monte Carlo.
The internal, as well as external risks in the supply chain process that causes problems in the system, is a matter to think about(Liou, et al., 2016).
Internal Risks of Supply Chain Management
The internal risks of supply chain risk management are as follows:
- Planning and control risks: The problem arises due to insufficient planning and analyzing, which leads to inefficient management.
- Risks related to business: This occurs due to the changes in the procedures of the business, management area, and processes in the business.
- Risk related to manufacturing: It occurs when there are halts or blockades in the internal processes of the system.
- Contingency and improvement risks: This happens when there is no alternate solution for problems occurring now and then.
- Risks of culture: This occurs when business tends to avoid or hide the negative information obtained, in such a case, the company cannot react in time to sudden failures.
External Risks of The Supply Chain Management
The external risks of supply chain risk management are:
- Risks related to the demand: This happens when the customer is confused or when the demands exceed to great length in mind typically a case of misunderstanding.
- Risks of supply: These are caused due to the various halts or interruptions in the internal processing of the system.
- Risks of the environment: There are environmental factors which do not deal with the supply chain like climatic conditions, threats from terrorists as well as economic and political reasons.
- Risks in doing business: The risks involved in this are related to the financial problems of the suppliers, purchase problems or sale problems related to the companies of the suppliers.
- Risks of the physical plant: This risk is caused due to the instability of the physical facility of the supplier and the dogmatic compliance.
The probability category of each risk is given a probability index of risk which will help find the exposure values of the risk. The risk analysis methods have many drawbacks when it is tested globally, and across-the-board unidentified situations, the quality of assessing the risk depends upon the actual information being available including the risk analyser’s experience in handling it. The risks are generally analyzed and calculated by a relatively small amount of people who do not possess much global experience and information on the topic. Therefore it is tough to evaluate such circumstances and adequately prepare for urgent situations.
Since it is not possible to properly decide the correct perception of risk, multiple viewpoints should be included and surveyed with continuity. The usual approaches of putting up an objective and deducting actions often fail here since they are not applicable for use in sudden, alarming situations. The ideas based on High-Reliability organizations [HRO] pertain to emergencies due to the integration of many stakeholders in the decision-making process(Cai, et al., 2016).
5.2 Gantt Chart
Refer to Appendix
5.3 Work Breakdown structure
Refer to Appendix
5.4 Critical Path:
Refer to Appendix
Chapter 6
Introduction:
As per the above discussion it can be depicted that the research shows the betterment step of the organization in supply chain risk management. In this study, the researcher wants to develop the relationship between the third party desire and the organizations. In this chapter the researcher find out the solution for risk management. In the previous chapter the investigator identified the risk then they analysis the problems and find the solution for overcome this problem. It is very important to know that, the globalization creates the supply chain more challenging and the new demands of the customer make it complicated. Supply and demands should be in same order. Or else the insufficiency of the product or the demand for the product can be affected.
6.1 Solution:
Nowadays, the automobile industry has become one of the largest industries as well as the most complex world. Automobile manufactures big vehicles like cars, trucks etcetera. It has a global reach. Globalization makes the supply chain industry more difficult. It also creates a demand for practical solutions for a vehicle from manufacturers and brands. This is also very important to know that, not only the globalization create the supply chain more challenging but also the new demands of the customer make it complicated. Supply and demands must be in the same order. Otherwise, the scarcity of the product or the demand for the product can be affected.
The supply chain has the target to get the maximum profit at minimum costs. A manager also has to control the supply chain so that, the product can be distributed in the right origination at the right time. In this context, the solution factures will be discussed in some steps.
Step 1: Poor Visibility and result [Challenge]
Any vehicles are the complex form of many parts. According to the report, a vehicle has around three thousand isolated parts. The report says that parts can be imported or it can be house made of the organization. Most of the time, the third party delivered the parts because it is difficult to provide all in one organization. So, in the case of supply chain risk management, this is very important to continue the whole supply chain in the same order. If any associated organization delay their product to deliver can be a significant loss for the organization itself. The production line, as well as the supply line, can de down for the delay of any individual supplier. It is also essential for the automobile manager to perform well in thousands of other managers that, he or she can have that knowledge of the competition.
Optimization of Parts Visibilities [Solution]
It is complicated for a manager to optimize the parts of the automobile's visibilities in routing management. Here some points how a manager can control his or her sector of the supply chain. Every supply chain must have a law and Oder for the supplying system. It should be obeyed for each of the supplier insane orders. The positive and negative results must be controlled by the central board. A manager has to control the negative issued by addressing correctly. The manager has identified the problem as soon as possible. The very next duty will be for a manager to take steps to rectify the problem unless it can be caused a great deal for an organization.
A manager has to track the IoT. IoT is a monitoring system interconnected by all the supply chain. In this monitoring system, the data or information can be shared with another system. This system is essential because it can show the personal progress and the location of the product. So, a manager can identify the location where the system is delaying delivering the product.
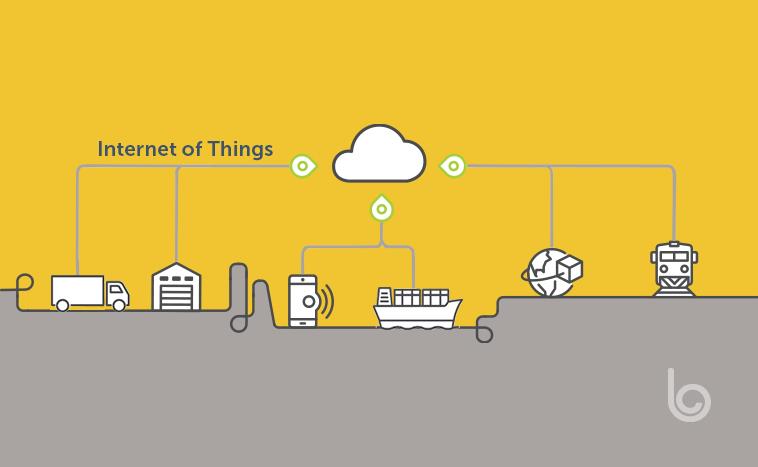
Figure: Use of IoT
(Burtonshaw-Gunn, 2017)
The connection between suppler and organization is significant for the better performances of an organization as well as a supply chain. It is also essential to maintain the connection between the supplier or the managing department of an organization to the third parties. There must be a stem line between organizations and suppliers. It helps to improve the process quickly.
Customer demands research is very important for any of the organizations. Customer demands increasing day by day. Sometimes it can be challenging to fulfil the expectation of the customer. So, it is the practice of a manager in monitoring the demands chart.
Step 2: Impact of The External Factor and Disrupts [challenge]
In market place or the other sector, the global nature of the automotive industry makes the economy, environmental status political, market place and other sectors very sensitive. Tariffs and another external cost for the import and the export of the parts can leave an impact on the supply chain. In many cases, it is also be seen that political pressure and corruption are also a reason for the supply chain risk management. The environmental disaster is can also be left an impact on the supply chain. It is also undeniable that, that environmental issues are not located earlier but it also a duty of a manager to take steps on that situation carefully. The changing trends in customer demand are shifting. It is complicated in tandem with the demands.
Use ERM For Potential Issues [solution]
Sometimes it becomes very difficult to manage the automobile chain system in the same order. Here will be discussing some steps that will help an organization to control its disputes. Firstly, the managers have to identify the problem that arises in the supply chain; then, a manager must draw lists to rectify the problem. Risk identification is essential to control risk management. The risk might be "high" or "low". A manager has to decide the risk according to their nature and the demand. Contingency and RMP [Risks Management Plan]can be applied to the supplier and manufacturer. It is also essential to identify customer changing demands. Supply depends on demand so; an organization must have a clear view of the market demands. The manager has to give a clear strategy to their employees that can help to develop the status of the organization.
Step 3: Cost and Visibility Problem [challenge]
In the automobile industry, cost problems are a big issue. Cost may be variable or fixed. Machinery investment is a significant part of an organization. Stuff salaries can be a big issue just because of unionization. After retirements, the pension process can be a cost issue. For the betterment of the company, it is essential to draw a plan. For the plan, in many cases, I can be seen that the organization arranges some research process. This is also an external cost. Machinery maintenance cost can be high, but it is essential to maintain the machinery for the better performances and the healthy environment.
Deep Visibility with Control System [solution]
The cost problem can be controlled by the right agreements or by the right method. For the controlling cost, the manager must deal with internal and external contrast. Always have to take advice manager to the financial department. In case of deficiency, the variable cost must be controlled. The audit process is also essential for an organization to understand its financial status.
Linking with objectives:
Linking objective 1:Identification of potential failure points: In this chapter proper identification of potential issues has been properly determined and accordingly the measures are taken to resolve these issues. The researcher identified the problems. These are insufficient planning and analyzing, procedure changes of the management and business, manufacturing issues, contingency risk, cultural issues, demand risk, supply risk, and environmental issues.
Linking objective 2:Map the entire supply chain to determine interdependencies: After the identification of the potential risk then the researcher determines the supply chain map and also determines interdependencies. In the above discussion the researcher determine the interdependencies of the supply chain. It includes buyers and suppliers, personal contacts and relations with partners, resource alternatives, resources important, buyer’s freedom etcetera. Interdependences based on supplier’s relationship with organizations. The main ingredient of a successful business is how strong the interdependence between its various sectors are. Collaboration and coordination of process and the activities of the different function are also includes in interdependence of the supply chain.
Linking objective 3:Identify and prioritize critical business elements: In this discussion the researcher prioritizes the critical business elements. Tariffs and another external cost for the import and the export are important parts of this problem. The political pressure and corruption are also a reason for the supply chain management. The environmental disaster is can create an impact on the supply chain. The changing trends in customer demand are shifting. It is complicated in tandem with the demands. The researcher finds out the solution for overcome this situation.
Linking objective 4:To analyze the weakness in Supply Chains in automotive industries and accompanying problems: The third party delivered the parts for the reason that it is difficult to provide all in one organization. In supply chain risk management, this is very important to continue the whole supply chain in the same order. If any organization delays their product to deliver, that can be a significant loss for the organization itself. The production line and the supply line, down for the delay of any individual supplier. It is also essential for the automobile manager to perform well in thousands of other managers that, he or she can have that knowledge of the competition. In this discussion the researcher finds out the weakness and they also find out the solution to overcome this problem
6.2 Recommendation
The risks in the supply chains take birth from many areas like natural or man-made calamities, acts of war or terrorism, the financial instability of the supplier, leakages in data, system damages. There is an occurrence of at least one obstruction in the companies in their supply chain business which can affect the company in the wrong way. Thus proper steps should be taken, and plans should be prepared to avoid these risks which occur due to these disruptions. There are recommendations as to how these risks in the supply chain can be improved:
1. Identifying and calculating the ongoing risks
The business should be analysed accurately, and the areas with maximum exposure to risks should be identified, the various potential scenarios of supply chain obstructions should be appropriately identified.
2. More priority should be given to risks with more impact and probability
Going through every risk is virtually not possible, so the risks with more chances to happen should be given more priority. The estimation for the financial impact should be analysed, and then improvement plans should be executed.
3. The quality of the supplier should be assured
The reputation of a company depends upon the suppliers, so the suppliers should be chosen wisely as to how customers are treated by them and the source of their supplies.
4. Expand suppliers
There should not be a single source for the products, as the supply chain becomes endangered if the goods can't be delivered timely, so the establishment of secondary supplies in various regions is necessary to reduce the vulnerability.
5. There should be partners during the planning of risks
There should be interaction with the suppliers, shipping carriers and data managing centre to know if they have the recovery for disasters and business plans that matches yours. The involvement with them strengthens your relationship with them as a partner and their role in improving the risks increases.
6. Having more visibility with THE associates
Information on the business, such as the changes in designs and plans should be shared with the allies, which helps the supplier to have the proper materials available to them. If there are drop-in sales, then that too should be shared with the partners, thereby improving the bonds.
7. Insurances in trade should be considered
The consumers who do not pay the price end up affecting the working capital of the income, therefore credit insurance in trade can protect the fundamental aspects of the business and can help in getting better finance options from those who lend.
8. The risks should be sorted out occasionally
The risk scenarios should be analyzed systematically, and the changes in the supply chain should be acknowledged, preparing for the risks as early as possible is the best way to safeguard the company and its products from intrusions in supply chains.
6.3 Conclusion
It would be concluded that this research shows steps for the betterment of the organization in the management of risks supply chain. Through this research, it can develop the relationships between the organization and the third parties according to the customers’ desire. This paper will help to draw the risk factors and implementation. Notably, this study has pointed out the research questions. In this study, anyone can understand how to handle the situation in case of manmade or environmental loses. Through the understanding of the relationships between the organizations to the customer, any organization can know to control the supply chain. Customer demands and technology are rising day by day in the field of automobile technologies. A customer always had a demand for a high-quality product at a minimum of cost. According to research, the management always wants to minimize the external cost. An organization has to identify the right supplier.
In the field of supply chain management, it also seemed that the machinery left a significant issue on the environmental. So, the industry or the organization must take steps for eco-friendly technologies. Low pollution-based battery vehicles can be used to reduce pollution. In the case of betterment for the companies, it is also essential for proper training for both the manager and the employees. This is also very important for an organization to continue the study about the
scenario of world demands as well as their target audience. According to data, the internal risks are driving the force in the supply chain. Although "increasing the material prices" is considered as the most critical consequences. It is essential to identify and to analyze the barriers, and according to the rectification theory, the manager must control the whole project. Work field politic can affect supply chain management risk mitigation.
Limitations of Research:
There are various limitations indentified in this study as the research work progress to the conclusion. The primary restriction have been identified in the progress is a lack of the time. According to the researcher if more time was available then the research could have been done in a better way. Another shortcoming in the research is that during the process of data analysis, there is bias of data. Various obstructions have occurred while doing research in the form of time and financial resources.
Future Scope:
Supply chain management solution plays a vital role in automotive industries. These industries needs supply chain management solutions for operation flow and inventory management. This risk management procedure helps to the automotive industry for reduce their risks. In future they apply the risk management process for their better achievement. The organizations are focusing to utilize the technology and internally cut costs in the best path. The growth of automotive industry is directly related to the current economic environment and the development of international trade flow. Based on this research study next research will be better for the researcher. Based on this study the future researcher will be able to overcome these limitations.
References
Alotaibi, S. & Mehmood, R., 2017. Big data-enabled healthcare supply chain management: opportunities and challenges. s.l., Springer, pp. 207-215.
Ansari, Z. N. & Kant, R., 2017. A state-of-art literature review reflecting 15 years of focus on sustainable supply chain management. Journal of cleaner production, Volume 142, pp. 2524-2543.
Arunachalam, D., Kumar, N. & Kawalek, J. P., 2018. Understanding significant data analytics capabilities in supply chain management: Unravelling the issues, challenges and implications for practice. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, Volume 114, pp. 416-436.
Aven, T., 2016. Risk assessment and risk management: Review of recent advances on their foundation. European Journal of Operational Research, 253(1), pp. 1-13.
Burtonshaw-Gunn, S. A., 2017. Risk and financial management in construction. s.l.:Routledge.
Cagliano, A. C., Grimaldi, S. & Rafele, C., 2015. Choosing project risk management techniques. A theoretical framework. Journal of Risk Research, 18(2), pp. 232-248.
Cai, Z., Huang, Q., Liu, H. & Liang, L., 2016. The moderating role of information technology capability in the relationship between supply chain collaboration and organizational responsiveness: evidence from China. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 36(10), pp. 1247-1271.
Coyle, J. J., Langley, C. J., Novack, R. A. & Gibson, B., 2016. Supply chain management: a logistics perspective. s.l.:Nelson Education.
Dubey, R. et al., 2017. Explaining the impact of reconfigurable manufacturing systems on environmental performance: The role of top management and organizational culture. Journal of cleaner production, Volume 141, pp. 56-66.
Dubey, R., Gunasekaran, A. & Papadopoulos, T., 2017. Green supply chain management: theoretical framework and further research directions. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 24(1), pp. 184-218.
Fahimnia, B. & Jabbarzadeh, A., 2016. Marrying supply chain sustainability and resilience: A match made in heaven. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, Volume 91, pp. 306-324.
Gopal, P. R. C. & Thakkar, J., 2016. Sustainable supply chain practices: an empirical investigation on Indian automobile industry. Production Planning & Control, 27(1), pp. 49-64.
Govindan, K. & Fattahi, M., 2017. Investigating risk and robustness measures for supply chain network design under demand uncertainty: A case study of glass supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, Volume 183, pp. 680-699.
Govindan, K., Soleimani, H. & Kannan, D., 2015. Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain: A comprehensive review to explore the future. European Journal of Operational Research, 240(3), pp. 603-626.
Gunasekaran, A., Subramanian, N. & Rahman, S., 2015. Supply chain resilience: role of complexities and strategies. s.l.:Taylor & Francis.
Hahn, G. J. & Packowski, J., 2015. A perspective on applications of in-memory analytics in supply chain management. Decision Support Systems, Volume 76, pp. 45-52.
Hazen, B. T., Skipper, J. B., Ezell, J. D. & Boone, C. A., 2016. Big Data and predictive analytics for supply chain sustainability: A theory-driven research agenda. Computers & Industrial Engineering, Volume 101, pp. 592-598.
Hohenstein, N.-O., Feisel, E., Hartmann, E. & Giunipero, L., 2015. Research on the phenomenon of supply chain resilience: a systematic review and paths for further investigation. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 45(1/2), pp. 90-117.
Ivanov, D. et al., 2016. Disruption-driven supply chain (re)-planning and performance impact assessment with consideration of pro-active and recovery policies. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, Volume 90, pp. 7-24.
Kaufmann, L. & Gaeckler, J., 2015. A structured review of partial least squares in supply chain management research. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 21(4), pp. 259-272.
Khalid, R. U. et al., 2015. Putting sustainable supply chain management into base of the pyramid research. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 20(6), pp. 681-696.
Liou, J. J. H., Tamošaitien?, J., Zavadskas, E. K. & Tzeng, G.-H., 2016. New hybrid COPRAS-G MADM Model for improving and selecting suppliers in green supply chain management. International Journal of Production Research, 54(1), pp. 114-134.
Maier, A. et al., 2017. DS 87-3 Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED 17) Vol 3: Product, Services and Systems Design. s.l., Design Society.
Marshall, D., McCarthy, L., McGrath, P. & Claudy, M., 2015. Going above and beyond: how sustainability culture and entrepreneurial orientation drive social sustainability supply chain practice adoption. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 20(4), pp. 434-454.
Mohammaddust, F. et al., 2017. Developing lean and responsive supply chains: A robust model for alternative risk mitigation strategies in supply chain designs. International Journal of Production Economics, Volume 183, pp. 632-653.
Mohr, S. & Khan, O., 2015. 3D printing and its disruptive impacts on supply chains of the future. Technology Innovation Management Review, 5(11), p. 20.
Oliva, F. L., 2016. A maturity model for enterprise risk management. International Journal of Production Economics, Volume 173, pp. 66-79.
Rajesh, R. & Ravi, V., 2015. Supplier selection in resilient supply chains: a grey relational analysis approach. Journal of cleaner production, Volume 86, pp. 343-359.
Ross, D. F., 2015. Distribution Planning and control: managing in the era of supply chain management. s.l.:Springer.
Sasson, A. & Johnson, J. C., 2016. The 3D printing order: variability, supercenters and supply chain reconfigurations. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 46(1), pp. 82-94.
Savino, M. M., Manzini, R. & Mazza, A., 2015. Environmental and economic assessment of fresh fruit supply chain through value chain analysis. A case study in chestnuts industry. Production Planning & Control, 26(1), pp. 1-18.
Schenkel, M., Krikke, H., Caniëls, M. C. J. & van der Laan, E., 2015. Creating integral value for stakeholders in closed loop supply chains. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 21(3), pp. 155-166.
Subramanian, N. & Gunasekaran, A., 2015. Cleaner supply-chain management practices for twenty-first-century organizational competitiveness: Practice-performance framework and research propositions. International Journal of Production Economics, Volume 164, pp. 216-233.
Touboulic, A. & Walker, H., 2015. Theories in sustainable supply chain management: a structured literature review. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 45(1/2), pp. 16-42.
Appendix
Gantt Chart
Work Breakdown structure
|
WBS |
Task Mode |
Task Name |
Duration |
Start |
Finish |
|
1 |
Manually Scheduled |
Supply Chain Risk management in the automotive industry |
Seven days? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Tue 26-11-19 |
|
1.1 |
Auto Scheduled |
Risk Identification |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.1.1 |
Auto Scheduled |
Investigation |
1 day |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.1.2 |
Auto Scheduled |
Classification Risks |
1 day |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.1.3 |
Auto Scheduled |
External risk identification |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.1.4 |
Auto Scheduled |
Internal Risk identification |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.1.5 |
Auto Scheduled |
Finalising Documentation |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.2 |
Auto Scheduled |
Risk Assessment |
3 days? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Wed 20-11-19 |
|
1.2.1 |
Auto Scheduled |
Analysis Risk |
1 day? |
Tue 19-11-19 |
Tue 19-11-19 |
|
1.2.2 |
Auto Scheduled |
Case Study Based Analysis |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.2.3 |
Auto Scheduled |
Perception Based Analysis |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.2.4 |
Auto Scheduled |
Risk assessment documentation |
1 day? |
Wed 20-11-19 |
Wed 20-11-19 |
|
1.3 |
Auto Scheduled |
Selection of Proper Risk Management Process |
5 days? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Fri 22-11-19 |
|
1.3.1 |
Auto Scheduled |
Strategy Proposal for Risk Management Process |
1 day? |
Fri 22-11-19 |
Fri 22-11-19 |
|
1.3.2 |
Auto Scheduled |
Evaluation Challenges for Risk Management Process |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.3.3 |
Auto Scheduled |
Evaluation Advantage for Risk Management Process |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.3.4 |
Auto Scheduled |
Finalising Risk Management Process |
1 day? |
Thu 21-11-19 |
Thu 21-11-19 |
|
1.4 |
Auto Scheduled |
Implementation |
6 days? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 25-11-19 |
|
1.4.1 |
Auto Scheduled |
Complexity management |
1 day? |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.4.2 |
Auto Scheduled |
Organisational learning |
1 day |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.4.3 |
Auto Scheduled |
Information technology support |
1 day |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.4.4 |
Auto Scheduled |
Performance metrics evaluation |
1 day |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
|
1.4.5 |
Auto Scheduled |
Risk management steps evaluation |
1 day? |
Mon 25-11-19 |
Mon 25-11-19 |
|
1.5 |
Auto Scheduled |
Mitigation of supply chain risk |
7 days |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Tue 26-11-19 |
|
1.5.1 |
Auto Scheduled |
Project closure |
1 day |
Tue 26-11-19 |
Tue 26-11-19 |
|
1.5.2 |
Auto Scheduled |
Evaluation recommendation for further risk management |
1 day |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Mon 18-11-19 |
Critical Path: