Project Proposal Assignment: Impact of COVID-19 on e-Commerce Industry
Question
Task: Write an academic report on project proposal assignment addressing the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on e-commerce industry.
Answer
Background
The power of retail advisory group survey outcomes on Australian online retailers has projected the fact that while more of the retailers have face important minimizations in foot traffic as well as revenue, almost 20 percent are technically facing a development in sales (contevo.com.au, 2020). The communalisolation and the requirement of isolation have created customers more based on technologies for their rudimentary operations such as cost comparisons, keeping contact with others and shopping-retailers who could use e-commerce as well as the digital marketing are in the state for surviving, if not thrive, at the time of pandemic.
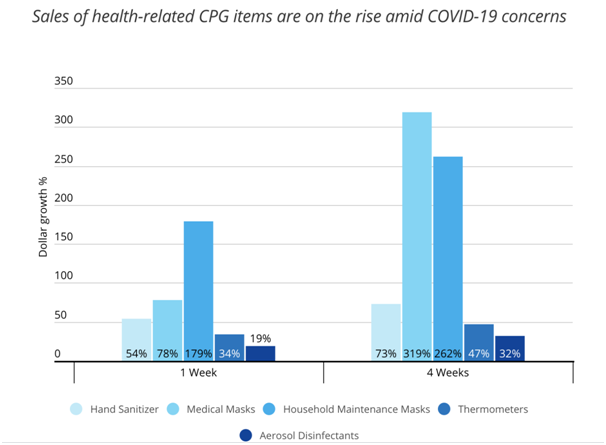
(Source: contevo.com.au, 2020)
Prior the increase in demands, grocery online shopping only created up around 4 to 5 percent of sales value. However, Coles and Woolsworth have accounted increasing entire capability in Hike with the distributionspace for Melbourne and Sydney stopped for a total week (contevo.com.au, 2020). The superstore chain has provided a click-and-gather opportunity as asubstitute. Both the supermarket is currently raging on e-commerce and recreatingdistribution operations for ensuring separated and important Australians remain to get important materials as more organizations are closed and customers are being made to stay at homes for limit the blowout of the virus (contevo.com.au, 2020).

(Source: contevo.com.au, 2020)
Research problem
Physical retailing would face its decrease continue at a more rapid pace than priorly. Mass outlet closings have already started over the world as an outcome of security and health worries along with a dip in footfall (TAYLOR, 2020). The noticeable contractions in physical retails suggest huge increase online. There would be limited term and longer level influences on customer characteristic, however this is prominent from earlier times of disorder, which new characteristic tends to stick. Physical retails have their attractions; however, this was broken. The trade- disaster has had limited to do with customers spending low, only where they were purchasing. E-commerce has resolved physical retail’s challenges, however; was confined through inertia in customer characteristics (Meyer, 2020). In Australia over than markets like the USA and China. Electronic commerce accounts limitless passageway profusion, customized and sufficient experiences, huge convenience and contact to data.
Cutting-edge store is applying information and intelligent inventories suggestions for tailoring varieties at the retail level, for anticipating alterations in consumer traffic, as well as for determining ultimate supply ways and developing the consumer experiences and increasing unit economics (TAYLOR, 2020). This function underlines whether the order must be satisfied from a retail or from a centralproduction centre. In order to be precise, the process will help retailers ensuring real-time fulfilment decisions, which increase expected profits (Columbus, 2020). Retail directors must constantly evaluate their savings in information and analytics for making sure that they are coming with new visions to the largest organizational difficulties.
Aim of the research
To identify definite changes in the e-commerce industry due to the current COVID-19 situations and underline the future trends
Research objectives
- To identify the changes, happen in the e-commerce industry operations due to COVID-19 situations
- To underline if the e-commerce behaviours of customers will have an impact on retail trends in future
Research Questions
- What are the changes happened in the e-commerce industry operations due to COVID-19 situations?
- What are the current trends and changes in customer behaviours in e-commerce retailing?
- How the e-commerce behaviours of customers will have an impact on retail trends in future?
Conceptual framework
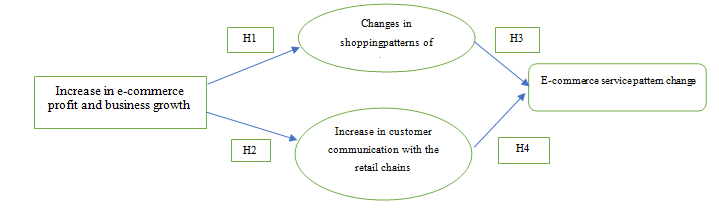
(Source: Created by the researcher)
Hypotheses
H1: There is a significant development in e-commerce sales and customer traffic
H2: The customer satisfaction level with certain retail services have decreased
H3: Australian retail has face important development in e-commerce business growth
H4: The customer buying patterns and habits have changes
Literature review
COVID-19 impact on e-commerce shopping behaviour
As this turn into even more strong just how transmittable COVID-19 is, some customers have developed concerns regarding the security of getting their online products. It has been found out that the virus could exist on the exteriors from 3 hours to up 3 days, reliant on the product. As a result of current surveys, it has been identified that customers found that around 96 percent of G Zs and Millennials are thinking regarding the pandemic as well as its influence on the economy (Meyer, 2020). This type of concerns is directing them to change their purchasing behaviour more drastically than other generation of customers that involves minimizing the spending level, stocking up on products and spending low on experiences. While research information displays that females are more likely to be thoughtful regarding the impacts of pandemic, this also focuses that men are likely to have this influence their spending behaviours (Dai, 2020). One-third of them, against to 25 percent of female consumers, accounted the epidemic impacting on how often and much they spend on items (Kim, 2020).
Changes in e-commerce in pandemic
As per the Australian Post study in May reported that product packages are importantly different. In the week coming up to Mother’s Day, arts, beauty items, fashion deliveries all have developed by around 140%. This combines with other information, which outlines specific sectors would benefit from electronic-commerce over others-particularly groceries, cosmetics, homeware products and liquors (Yigitcanlaret al., 2020). Obviously, the effectiveness of electronic commerce waves depends on various businesses quickly increasing their online platforms. Some organization would find it easy than others, however either process; this is going to be a rough way. Current online organizations in Australia would have to develop their production and safe supply-chains, while the bricks-and-mortar outlets would require to invest important capital analytically, not to underscore up-skilling on the fly(Columbus, 2020).
However, even retail stores, which do not sell health-based products and household goods still face the benefit from their robust e-commerce policy during COVID-19 (Singh,2020). Underlined precautions and exponential demands have stressed retail distribution process, with customers seeing empty shelves and cost increase (Akpan et al., 2020). Against this, more customers would turn to new online platforms and DTC organizations, which include mainly of minor, domestic companies with assured source, and that supply to niche customer requirements (Tran, 2020).
The future of e-commerce in an after COVID-19 age
It is significant to mention that the skills of ML and AI are straight dependent on the scope, qualities and activation of the information powering this-suggesting that information alone, is not effective (Devon, 2020). Retailers could apply augmented reality for ensuring browsing procedure for consumers more customized and assist them make more informed decisions (Bhattiet al., 2020). For instance, consumers would be capable in uploading their own photos to the application for seeing how a cloth will look on them or any beauty product right before buying them. Mobile shopping is important in Australia and has played a huge role in the pandemic. It has been predicted that by 2021, this is expected that e-commerce sales will increase to 73% on a mobile device (Kannappan, 2020).
Methodology
The researcher will apply a deductive approach, like the objectives are set previously for initialising the research analysis for performing as well as making this research effective. The analysis will also apply primary quantitative testing tools and data as study will be concentrating on numerical or calculative knowledge based on the research hypotheses. The information collected applying this method will be reviewed through SPSS and graphical process, which the future research practitioners would easily understand and apply. The research design will be informative, as all the data is available, so that the future researchers will be capable in finding the results in the study report in care of uncertainty. The researcher here will include primary data for processing of information from the respondents identified in this study. The primary data collection process will include survey of 50 employees from the Australian retail industry. The survey will be held online and a questionnaire of 10 questions will be provided to the respondents and online data collection will be done by the researcher. The probability sampling technique will be applied here. The secondary data will be included in the literature review section from the journals, news and annual retail reports. Hypotheses will be tested through SPSS method.
References
Akpan, I.J., Udoh, E.A.P. and Adebisi, B., 2020. Small business awareness and adoption of state-of-the-art technologies in emerging and developing markets, and lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, pp.1-18.
Bhatti, A., Akram, H., Basit, H.M., Khan, A.U., Raza, S.M. and Naqvi, M.B., 2020. E-commerce trends during COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking, Vol. 13, No. 2, 2020 pp.1449-1452
Columbus, L., 2020. How COVID-19 Is Transforming E-Commerce. [online] Forbes. Available at:
Contevo. 2020. How COVID-19 Is Affecting Retail And Ecommerce In Australia - Contevo. [online] Available at:
Dai, C., 2020, November. The Disruptive Effects of COVID-19 on the Aviation Industry, Food Industry, and E-commerce Industry. In 2020 2nd International Conference on Economic Management and Cultural Industry (ICEMCI2020) (pp. 61-64). Atlantis Press.
Devon, E., 2020. The Future Of Ecommerce In A Post COVID-19 World. [online] Retail World. Available at:
Kannappan, S., 2020. Marketing agility and E-Commerce agility in the light of COVID-19 pandemic: A study with reference to fast fashion brands. Asian Journal of Interdisciplinary Research, 3(4), pp.1-13.https://doi.org/10.34256/ajir2041
Kim, R.Y., 2020. The Impact of COVID-19 on Consumers: Preparing for Digital Sales. IEEE Engineering Management Review. 10.1109/EMR.2020.2990115
Meyer, S., 2020. Understanding The COVID-19 Effect On Ecommerce. [online] The BigCommerce Blog. Available at:
Singh, Gunjan.(2020). E-Readiness and Customer Perception about the E-Commerce during Lockdown: Covid 19 Perspectives.Indian Economy After Covid 19,Potential Threats, Challenges and Remedies.Edited Book Volume 2. SwaranjaliPublication.NRJP 2020.ISBN NO.:978-93-90110-53-7., Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3694279 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3694279
TAYLOR, J., 2020. This Crisis Is Different: E-Commerce, Coronavirus And The Looming Recession - Smartcompany. [online] SmartCompany. Available at:
Tran, L.T.T., 2020. Managing the effectiveness of e-commerce platforms in a pandemic. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 58, p.102287.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102287
Yigitcanlar, T., Kankanamge, N., Preston, A., Gill, P.S., Rezayee, M., Ostadnia, M., Xia, B. and Ioppolo, G., 2020. How can social media analytics assist authorities in pandemic-related policy decisions? Insights from Australian states and territories. Health Information Science and Systems, 8(1), pp.1-21.












