Presenting A New Service Development For Hotel 41
Question
Task: Develop an idea for a new service for an Organisation of your choice and show how it is consistent with the existing brand and how it will add value for customers.
Write a 2000 word report using these headings a as a guide and refer to services theory as appropriate to underpin your work:
1. Analysis of the organisation’s environment and of similar existing services provided by competitors in their market sector using critical application of PEST and Porter’s Five Forces to justify the added value the proposed new service idea will bring.
To answer this you will need to complete some market research into the organisation and its market competitors using various sources, for example, Mintel and Marketline. The PEST and Porter’s Five Forces should be applied thoroughly and critiqued as part of their application and the added value the service will bring should help to justify why it is needed.
2. Application of the components within the New Service Development (NSD) process and development of a service Blueprint for the new service idea.
Here you will apply the various applicable components of the NSD process to your new service idea and highlight any particular areas which are of interest. A detailed Blueprint for the service using the front stage and back stage approach should be presented.
3. Application of the five ‘Features/Characteristics of Services’ (intangibility, perishability, variability, inseparability and rental/access) to identify the amount of impact each one of these will have on the new service idea.
You will need consider the impact of the features/characteristics of services (intangibility, perishability, variability, inseparability and rental/access) and how your service might minimise the impact of each of these.
The report should include an Executive Summary (excluded from the word count) plus a short introduction (briefly outlining the main areas of the report and stating what the new service is) and a conclusion to draw together your main points from the report content.
The assignment is worth 50% of the marks for the module and assesses these learning outcomes:
1. identify and critically evaluate factors in the business environment of service organisations that act as drivers for new service development
2. apply theoretical and methodological frameworks for new service development at each stage of the NSD process
Answer
Executive summary
The report below is based on the new service development for the renowned hotel in the UK, Hotel 41. The new service proposed in the report is the offering of an aircraft or balloon ride around the heritage places, lakes and other beautiful places in London and the surrounding area. Regarding the application of the new service, the external environment of the business has been analyzed with the help of PEST and Porter's five forces models. The process of New Service Development (NSD) has been applied and a service blueprint has been prepared.
Introduction
Despite the contribution of the innovative efforts in organizations in the new service development, the majority of the organizations in the service industry struggle to take innovative approaches. In the UK hospitality industry, the development of effective and efficient service is imperative as this industry is one of the major sources of foreign exchange (Jaakkolaet al., 2017). The present reports develop an idea regarding the development of a new service in Hotel 41, a five-star boutique hotel in the UK. The report analyses the external business environment of the UK hotel industry and justifies how the use of the new service, special aircraft and balloon ride to the clients, can benefit the organization in dealing with the market forces. The report also applies the elements of the new service development process and generates a service blueprint. The ability of the new service in minimizing the effects of different characteristics of services are also highlighted in the report.
Analysis of organizational environment and similar existing services provided by competitors in their market sector
PEST analysis
|
Political factors |
· The political instability of the UK caused by Brexit has introduced several uncertainties to the hotel industry in the UK (French, 2018). · The Hotel industry gains immense support from the government. · The hotel industry of the UK is highly influenced by political activities and therefore election activities can have a major impact on the business. · According to Bauer and Borodako (2019), environmental law and trade restrictions supported by the government will impact the hotel business. |
|
Economical factors |
· The UK hotel industry is a major attraction of foreign direct investments. · The increasing unemployment rate in the UK can have a negative influence on the hotel industry by a reduction in sales and profitability. · The expectation of the employees regarding the enhancement of the wages can be a negative influence on the business (Filimonau and Mika, 2019). |
|
Social factors |
· The trend of society toward travelling has greatly influenced the business of Hotel 41. · The increasing trend of people regarding having a unique experience while travelling has greatly influenced the hotel industry by forcing organizations to innovate service offerings (Eissner and Gannon, 2018). · The changes in cultural diversity, lifestyles, demography, values and beliefs have led to the changes in consumer behaviour that reduces the effectiveness of the old service offerings. |
|
Technological factors |
· The growing culture of social media among the people has influenced changes in consumer behaviour toward the existing services offered by the hotels. · Technological advancements in new services offered by the competitors have reduced the profitability of Hotel 41 to some extent. |
Table.1: PEST analysis
(Source: Created by the learner)
Porter’s five forces
Competitive rivalry (High)
Hotel 41 offers five-star boutique accommodation services to the elite and business class people in London. The organization faces a strong force from the top competitors in London such as London Marriott Hotel, The London EDITION, Boutique Hotel Knightsbridge, The Curtain, The Chesterfield Mayfair and Covent Garden Hotel. These hotels implement service innovations to offer the customers unique experiences during their travel or visit to gain a competitive advantage in the market (Mendes et al., 2017). The insufficient differentiation of services in Hotel 41 has resulted in a low market share in the UK. The rivalry within the hotel industry has been intense due to the differentiation in cost of services and products. However, the growth of the respective business is known to be required for maintaining high capital costs. Nevertheless, there are similar other competitors of the concerned organisation such as four seasons hotel; the royal hotel and rudding park hotel as well. These hotels are also known to provide hang gliding; ballooning and paragliding experience to the customers which have been a good competition for the concerned company.
The threat of new entrants (low to moderate)
There are many barriers to the entry of new hotels in the UK. It has been evidenced that financial resources are one of the major barriers for new organizations to enter and compete with existing businesses. On the other hand, the differentiation of the products is another potential barrier to entry (Kitsios and Kamariotou, 2018). However, the presence of the string communication channels promotes the entry of the new business in the sector resulting in a low to moderate force on the existing businesses like Hotel 41. Based on the threat of new entrants, tariffs can be determined regarding the differentiation within management; location and guest ratios as well. However, the new entrants can be at disadvantage for limited best locations within the metropolitan cities.
Bargaining power of the customers (High)
The ability of the consumers to search online for best hotels that can provide more attractive services in the UK has enhanced the power to many folds. According to Biemanset al. (2016), the customers of the five-star hotels are not much affected by the price of the services but on the type of services provided. The service innovations of the competitors and the availability of substitute products have greatly increased the bargaining power of the customers. Based on the concern of business travellers, the differentiation tends to be significant and this makes the organisation and similar other competitors to be under pressure for keeping their brand unique in the eyes of those customers.
Bargaining power of the suppliers (Low)
As stated by Armstrong and Matters (2016), the power of the suppliers in the hotel industry is very low. The hotel 41 depends on several suppliers that supply goods based on which guests are provided with services, such as textile, furniture, food and beverages, and entertainment. The greater cooperation of Hotel 41 with its suppliers increases its potential to gain a competitive advantage in the industry. For being within the leading league as compared to other hotels, the respective company needs to maintain an advantage of cost over the rivals along with being innovative regarding the differentiation of its own self through ts strategic group.
The threat of substitute products (low to moderate)
According to Biemanset al. (2016), the availability of five-star guesthouses, restaurants and hotel chains in the UK can have a weak pressure on the hotel businesses. The alternative options of food and beverages have also reduced the performance of the restaurant segment of Hotel 41. However for accommodation of larger group based on the people of travelling along with business travellers, the respective company might not face any threat over the substitute. Nevertheless, it can face a moderate competition based on differentiation.
Justification of the added value the new service development will bring
According to Burton et al. (2017), the changing trends of society toward travel and tourism has a great impact on the changing patterns of the services. People are now directed to make their travel more advantageous and exciting. On the other hand, a fiercely competitive environment of Hotel 41 pressurizes it to implement service innovation that can provide the customers, a new experience while their visit to the hotel. The implementation of the new service, an aircraft or balloon ride around the best places in London will enhance the experience of the customers. The implementation of this new service is justified based on the changing business environment as it can provide a greater competitive advantage and gain support from the government and the advanced technologies (Reports.mintel.com. 2020).
Application of the components within the New Service Development (NSD) process and development of a service Blueprint for the new service development
According to Yang et al. (2016), New service development can be defined as the end-to-end process to develop and launch a new service that can enhance the value provided to the customers. The development of new service highly depends on the market research, customers' needs and experiences, and service strategy. New service development includes several stages and in each stage of the process, some components that are important to be assessed to ensure the quality of the service. Ateetananet al., (2017) have provided a model of NSD that includes three major activities that are the development of service concepts, development of service system and the development of the service process. The first activity includes a range of other activities such as the generation of strategy and objectives, idea generation and screening of the ideas, development of concept and testing. Therefore, in this stage of the NSD, Hotel 41 is required to carry out detailed market research to identify the needs of the customers, trends of the market, competitive forces and the other external factors based on which objectives and strategies can be formulated. As the idea regarding the aircraft or balloon rides has generated hotel business is needed to screen the effectiveness of the idea in meeting the demands of the market and develop a concept regarding the service. Once the concept is developed, Hotel 41 can test the concept by using survey methods to collect the response of the customers regarding the demand for the aircraft or balloon rides during travelling.
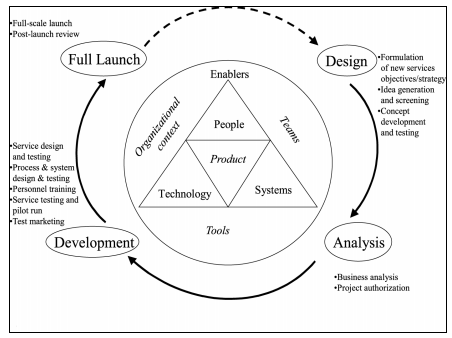
Figure.1: NSD process cycle
(Source: Glöckneret al., 2017)
In the next stage, service system development, Hotel 41 will require to develop the infrastructure that is essential for the delivery of the service. The important resources are aircraft, balloons, highly trained pilots and balloon operators, tour guides, and engineers. In the last stage of the NSD, Hotel 41 is needed to build interfaces among the departments, suppliers and customers. According to Go and Kim (2018), service system development includes several activities such as service testing and pilot run, personnel training, system designing, and test marketing. In this stage, the organisation can launch the service at full-scale and collect the review after the launch for improving the service.
Service Blueprint for the new service development
According to Ali and Garg (2017), service design is an important tool for explaining how a service can function. A service blueprint is one of the widely accepted tools for service designing that explains the journey of service. Service blueprint of the new aircraft or balloon service of Hotel 41 provides details and specifications of the relationship among the different aspects of the service along a timeline. The service blueprint also includes the actions of the customers and the company including the onstage and backstage aspects.
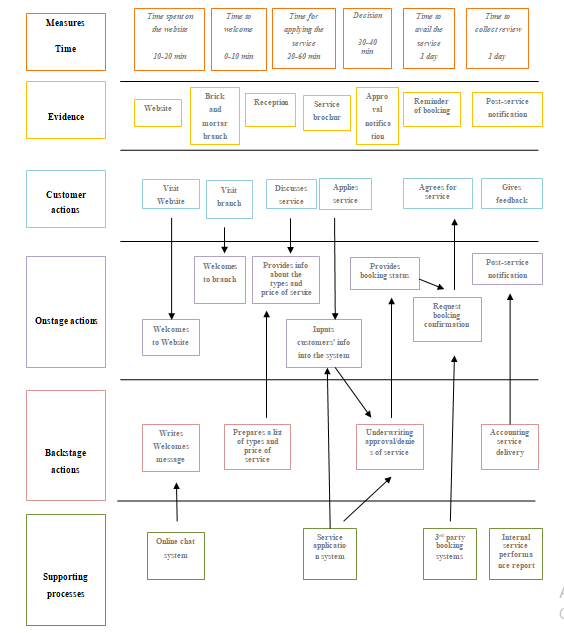
Figure.2: Service blueprint for the aircraft or balloon ride for Hotel 41
(Source: Created by the learner)
What is the application of the five ‘Features/Characteristics of Services’ to identify their impact on the new service development?
According to Sethi (2017), there are different distinct characteristics or features of services. Among the major characteristics of services, inseparability, perishability, intangibility, variability, and access are the most commonly discussed characteristics.
Inseparability
As opined by Chivandiet al. (2019), the inseparability factor of the service tends to localize the development and marketing of the new services offered by an organization. Therefore, inseparability can quantitatively limit the market. The new aircraft or balloon ride service that would be offered by Hotel 41 will minimize the impact of insuperability on restricting the geographical limits of the service.
Perishability
Perishability is the characteristics of those services that cannot be inventoried or stored. However, the new aircraft or balloon ride service that would be offered by Hotel 41 is based on the infrastructure that can be maintained by the organization and therefore can minimize the impact of the perishability characteristics of services.
Intangibility
The intangibility of the services relates to the fact that some services are untouchable as they cannot be felt, seen, heard or tasted before their purchase (Dikmen and Bozda?lar, 2017). Although the new service to be offered by Hotel 41 is an intangible experience, the Hotel management can offer the customers willing to purchase the service a view of the service. In this case, the customers would be offered to see other customers who are taking the ride before their purchase. In this way, the new service development can counteract the negative impact of intangibility.
Variability
According to Del Chiappa and Dall’Aglio (2016), variability is a major characteristic of services that explains the quality of the service can be different based on the nature of the service provider and the time of the service provision. The aircraft and balloon riding experience highly depend on the skills and knowledge of the pilot and the operators and therefore the organization have to ensure to hire efficient and skilled professionals for these functions so that the negative influence of this feature can be mitigated. In this way, the organization can maintain the quality of the service delivered to each customer.
Access
Less access relates to the low level of authority to the customers to experience the service (Dikmen and Bozda?lar, 2017). In the new service development to be offered by Hotel 41, customers are given with moderate rights to access the ride while maintaining a greater level of customer satisfaction. However, the customers are not provided with the accessibility to operate the balloons or the aircraft during the ride to maintain the security issues.
Conclusion
From the above study, it has been evidenced that new service development is a complex procedure. For the new service development, it is important to carry out detailed research on market trends and competitors. Based on the proposed new service development for Hotel 41, UK, a service blueprint has been prepared and the ways to mitigate the negative influence of the service characteristics are highlighted.
References
Ali, I. and Garg, R.K., 2017. Marketing of Services: Challenges & Opportunities in the Context of the Globalization of Business. International Journal of Engineering and Management Research (IJEMR), 7(3), pp.522-526.
Armstrong, R. and Matters, R.T., 2016. Modern slavery: risks for the UK hospitality industry. Progress in Responsible Tourism, 5(1), pp.67-78.
Ateetanan, P., Usanavasin, S., Shirahada, K. and Supnithi, T., 2017, July. From Service Design to Enterprise Architecture: The Alignment of Service Blueprint and Business Architecture with Business Process Model and Notation. In International Conference on Serviceology (pp. 202-214).Springer, Cham.
Bauer, T. and Borodako, K., 2019.Trade show innovations–Organizers implementation of the new service development process. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 41, pp.197-207.
Biemans, W.G., Griffin, A. and Moenaert, R.K., 2016. Perspective: New service development: How the field developed, its current status and recommendations for moving the field forward. Journal of product innovation management, 33(4), pp.382-397.
Burton, J., Story, V.M., Raddats, C. and Zolkiewski, J., 2017. Overcoming the challenges that hinder new service development by manufacturers with diverse services strategies. International Journal of Production Economics, 192, pp.29-39.
Chivandi, A., Samuel, M.O. and Muchie, M., 2019. Expectancy Models and Work Related Service Innovation and Service Quality Orientation as a Business Strategic Tool in the Tourism Sector. In Tourism-Perspectives and Practices.IntechOpen.
Del Chiappa, G. and Dall’Aglio, S., 2016. 16 Do Negative Experiences of Hospitality Services Always Lead to Dissatisfaction?. Tourist Behaviour: An International Perspective, p.145.
Dikmen, F. and Bozda?lar, H., 2017.The Role of Service Culture in Hospitality Industry. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 8(5), pp.85-98.
Eissner, S. and Gannon, J., 2018.Experiences of mentoring in the UK hospitality sector. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality & Tourism, 17(3), pp.296-313.
Filimonau, V. and Mika, M., 2019. Return labour migration: an exploratory study of Polish migrant workers from the UK hospitality industry. Current Issues in Tourism, 22(3), pp.357-378.
French, S., 2018. Between globalisation and Brexit: Migration, pay and the road to modern slavery in the UK hospitality industry. Research in Hospitality Management, 8(1), pp.23-31.
Glöckner, M., Ludwig, A. and Franczyk, B., 2017, January. Go with the flow-design of cloud logistics service blueprints. In Proceedings of the 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences.
Go, M. and Kim, I., 2018. In-flight NCCI management by combining the Kano model with the service blueprint: A comparison of frequent and infrequent flyers. Tourism Management, 69, pp.471-486.
Jaakkola, E., Meiren, T., Witell, L., Edvardsson, B., Schäfer, A., Reynoso, J., Sebastiani, R. and Weitlaner, D., 2017. Does one size fit all? New service development across different types of services. Journal of Service Management.
Kitsios, F. and Kamariotou, M., 2018. Mapping new service development: a review and synthesis of literature. The Service Industries Journal, pp.1-23.
Mendes, G.H., Oliveira, M.G., Gomide, E.H. and Nantes, J.F.D., 2017. Uncovering the structures and maturity of the new service development research field through a bibliometric study (1984-2014). Journal of Service Management.
Reports.mintel.com. 2020. Hotels - UK - November 2018 - Market Research Report. Available at: https://reports.mintel.com/display/859767/# [Accessed 20 Feb. 2020].
Sethi, J.A., 2017. Service Marketing: An Overview. In Strategic Marketing Management and Tactics in the Service Industry (pp. 1-14). IGI Global.
Yang, Y., Lee, P.K. and Cheng, T.C.E., 2016. Continuous improvement competence, employee creativity, and new service development performance: A frontline employee perspective. International Journal of Production Economics, 171, pp.275-288.












