Nursing Essay: Older Adults Receiving In-Home Care in Australia
Question
Task: ‘Good nursing practice is based on evidence and assessment. A community health assessment is a means to providing the evidence to guide community nursing practice’.
Guzys, D., Brown, R., Halcomb, E. & Whitehead, D. (Eds.). (2021). An introduction to community and primary health care. (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
You are a community health nurse working in a community receiving IN HOME CARE. Write a 1400 word nursing essay to describe and discuss your understanding of the principles and processes involved in performing a community health assessment for your chosen community. In your discussion it will be necessary to consider the following: epidemiological data; health issues; social determinants as well as the identified community needs.
Answer
Introduction
The nursing essaysheds light on a community which is often referred to as the concept of a group of people with common interest, community services work towards identifying the gaps that prevail in community health and hence work towards addressing the same (Mwanriet al. 2018). The community that has been identified for this essay is that of older adults who are receiving in-home care in the urban area. This essay will highlight the issues experienced by older adults residing in the urban parts of Australia (Seymour, 2018). The objective is to identify the prevalent health issues and hence find the key factors that can be held responsible for the occurrence of these health issues within this community.
Demographics
As per Australian Institute of Health and Welfareapproximately 3.8 million Australians belong the age group of 65 and above. The population of Australia is increasing rapidly and so is the number of people belonging to the older adult age group. In the year of 1999 the proportion of the population belonging to the age group of 65 was 12.3% however; in the year of 2019 it increased to 15.9% (McKechnieet al., 2019). Considering the advancements in the medical field it can be stated that the life expectancy of people is increasing which will further contribute towards the increase in older adult population all around the world.
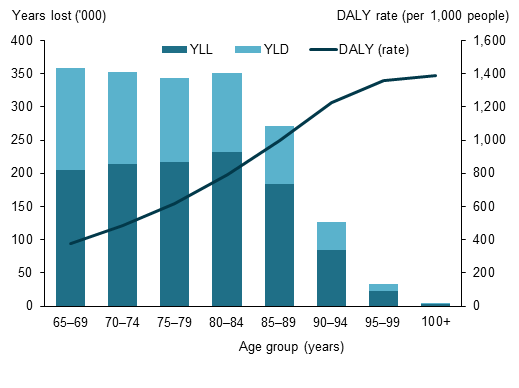
The sex ratio of the total population in Australia back in the year of 2019 was 98.4%ofmale per 100 females. About 58% of the older age group population is female. However, the percentage of women belonging to the age group of 64-75 is 51% and 63% for people belonging to the age group of 85 and above. It is evident that the number of female is greater than the number of males. It has been observed that the Australian population is increasing rapidly and population of older adults is increasing as well (Munasinghe et al., 2020). The graph in appendix 1 shows the fatal and the non-fatal cases classified on the basis of age group and it has been found that the fatality rate for the older adult groups is decreasing which further suggests that they experience a number of age related complications (Taylor& Haintz, 2018).
Health issues
Ageing exposes people to a large number of health related issues which includes coronary heart diseases, dementia, stroke and a number of other health related complications. On analysing the epidemiological data it has been found that cardiovascular diseases and cancer are some of the leading health issues among the older adults. Neurological disorders, musculoskeletal issues and different conditions associated with respiration. Cancer is common in males and a cardiovascular disease is common in women (Dorsey et al., 2018).
The focus will be on the neurological issues like Parkinson’s and Dementia. These issues force the concerned individual to be dependent on others to perform their daily tasks. The aspect of accessibility will be assessed and the role of community health workers will be analysed as well. Parkinson’s and Dementia are health issues that do not have any cure as of yet. It is hence important for these patients to take necessary steps to maintain their quality of life. Quality of life is dependent on mental, physical as well as social health of an individual.
Parkinson’s and Dementia are progressive diseases and the only way to deal with it is by continuing medication that helps to slow down the progression. The initial symptoms include tremors and slowing down of movement. However, these symptoms progress with time. It is hence necessary to diagnose this disease at the earliest and ensure that the correct medication is started immediately. These health issues generally occur in older adults however, it can occur in younger people as well.
It has been observed that people dealing with Parkinson’s experience clinical depression and anxiety as they fail to accept that they will have to be dependent on others for basic activities like eating or walking (Armstrong & Okun, 2020). The family members of the people experiencing Parkinson’s and Dementia experience challenges as well. There are other challenges as well which includes the side effects associated with the medication for these issues. People often lose trust in healthcare system due to the side effects that occur from the medication associated with these health issues.
The needs of this specific group are different from the other age groups as they need person-centred care that will help them to get treated with utmost care and dignity (Yashadhanaet al., 2020). The healthcare needs demand a multidisciplinary team that will include a neurologist, a dietician, nurse, physiotherapist and a psychologist. The community healthcare options will be able to offer them with necessary care that they need from time to time. The community healthcare workers are easily accessible and the community healthcare workers can help the patients to cope with the symptoms in a structured way.
There is no specific reason for the occurrence of these kind of diseases and hence it gets challenging for the patients and their families to accept it. Further, lack of awareness of these diseases will contribute towards the delay in the treatment process which will further impact the overall process of slowing down the progression (Liu et al., 2021). It is evident that the health related needs of these patients is uniquely different from others. The healthcare system in Australia offers the citizens with rehab programs and other facilities that help the patients in their respective treatment procedure.
Social determinants of health
There are a number of factors that contribute towards the treatment process of an individual. Social determinants of health are a concept that highlights the factors that impact the health of an individual. This section will identify three social determinants of health that impact the health conditions in people dealing with Parkinson’s and Dementia in specific.
The socioeconomic position impacts the health condition of people. It is essential for every individual to have access to economic sources that will help them address the financial needs associated with health related issues. As per the AIHW reports published in 2017-18, it has been found that 10.5% of the entire population in Australia lives in low income households (Taylor & Haintz, 2018). The treatment process of Parkinson’s and Dementia demands medication, physiotherapy, and psycho-therapy and proper diet. Poor socioeconomic position of an individual will severely impact the treatment process which will impact the health of the concerned individual.
The second issue that has been highlighted is that of family relationships. It is significantly necessary for the concerned individual to have a great bonding with their families. The treatment process here demands the active participation of the family members and hence it benefits the treatment process. The function and support of the families impact the treatment process. Neglect and abuse from the families have a negative impact on the health and wellbeing of the concerned individual (Chan et al., 2021). The support from the family members further contributes towards the effectivity of the treatment process as well.
The third issue that has been identified is that of social support and exclusion. The social connectedness impacts the health and wellbeing of an individual. It further helps people suffering from these issues to cope with the situation effectively. Often people with Parkinson’s and Dementia experience social exclusion which has a significantly negative impact on the wellbeing of these individuals. Living a normal life demands maintaining a normal social life as well, lack of a social life will make it challenging for the individual to maintain their desired quality of life (Mohanty&Niyonsenga, 2019).
Identified needs
As per Bradshaw’s four kinds of needs, the felt needs are the need of proper awareness of these diseases in all age groups (Reeveet al., 2018). Expressed needs are the ability of the patient to overcome the social stigmatisation and have complete faith on the healthcare system and approach them for help. It is evident that many people refuse to take professional medical help due to the fear of social stigmatization. Lack of awareness causes this issue, community health workers can work towards conducting awareness camps that will help to promote health and wellbeing and will further provide people with all the relevant information that will help the public understand these diseases better.
Conclusion
It can be hence concluded that there are a number of issues experienced by people belonging to different age groups. There is always scope for further development and it is essential to highlight the aspects that can be improved. It has been observed that the healthcare system within Australia provides the older adult groups with a number of facilities that contributes towards the health and wellbeing of the individual. However, the social determinants of health are the key factors that impact the treatment process and hence it is necessary to focus on these aspects and address them to ensure that the common people have access to all the healthcare facilities that they need to treat the health related issues.
Reference list
Armstrong, M. J., & Okun, M. S. (2020). Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. Jama, 323(6), 548-560.https://www.amedeolucente.it/public/Diagnosis%20and%20Treatment%20of%20Parkinson%20Disease.pdf
Chan, G., Chiu, V., Sun, T., Connor, J. P., Hall, W. D., & Leung, J. (2021). Age-related trends in cannabis use in Australia. Findings from a series of large nationally representative surveys. Addictive behaviors, 107059.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306460321002446
Dorsey, E., Sherer, T., Okun, M. S., & Bloem, B. R. (2018). The emerging evidence of the Parkinson pandemic. Journal of Parkinson's disease, 8(s1), S3-S8.https://content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-parkinsons-disease/jpd181474
Liu, S., Hong, Y., Gallois, C., Haslam, C., Jetten, J., Tran, T. L. N., & Dane, S. (2021). Contributors to social well-being from the perspective of older migrants in Australia. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies, 1-17.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tran-Tran-11/publication/353519529_Contributors_to_social_well-being_from_the_perspective_of_older_migrants_in_Australia/links/6103b5d31ca20f6f86ea56f8/Contributors-to-social-well-being-from-the-perspective-of-older-migrants-in-Australia.pdf
McKechnie, D., Pryor, J., Fisher, M. J., & Alexander, T. (2019). Examination of the dependency and complexity of patients admitted to in-patient rehabilitation in Australia. Australian Health Review, 44(1), 143-152.https://www.publish.csiro.au/ah/AH18073
Mohanty, I., &Niyonsenga, T. (2019). A longitudinal analysis of mental and general health status of informal carers in Australia. BMC public health, 19(1), 1-16.https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-019-7816-8
Munasinghe, S., Page, A., Mannan, H., Ferdousi, S., & Peek, B. (2020). Determinants of treatment non-attendance among those referred to primary mental health care services in Western Sydney, Australia: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ open, 10(10), e039858.https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/10/10/e039858.abstract
Mwanri, L., Okyere, E., &Pulvirenti, M. (2018). Intergenerational conflicts, cultural restraints and suicide: Experiences of young african people in adelaide, south australia. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 20(2), 479-484. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10903-017-0557-9
Reeve, E., Wolff, J. L., Skehan, M., Bayliss, E. A., Hilmer, S. N., & Boyd, C. M. (2018). Assessment of attitudes toward deprescribing in older Medicare beneficiaries in the United States. JAMA internal medicine, 178(12), 1673-1680.https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/article-abstract/2706177
Seymour, K. (2018). "Respect for each gender": Gender, equity and backlash in australia's male health policy.Nursing essay Australian Journal of Social Issues, 53(2), 123-138. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ajs4.37 Taylor, J., & Haintz, G. L. (2018). Influence of the social determinants of health on access to healthcare services among refugees in Australia. Australian journal of primary health, 24(1), 14-28.https://www.publish.csiro.au/py/py16147
Yashadhana, A., Fields, T., Blitner, G., Stanley, R., & Zwi, A. B. (2020). Trust, culture and communication: determinants of eye health and care among Indigenous people with diabetes in Australia. BMJ global health, 5(1), e001999.https://gh.bmj.com/content/5/1/e001999?fbclid=IwAR3QrUG_y-_XhNaP_QM7e_NZSuzvrRNKOrqimf56ioDqqaz2Xi_kBp4yUis&utm_term=consumer&utm_content=012021&utm_campaign=usage&utm_medium=cpc&utm_source=trendmd
Appendices
Appendix 1: Fatal and non-fatal composition classified on the basis of age group