Northern Rock Case Study Analysis on Change Intervention Ideas
Question
Task: Use the Northern Rock case study and prepare a written assessment. Based on less than perfect information supplied about the Northern Rock problem statement, you are now required to continue your external change advice to the Board.This assignment requires you to apply change intervention ideas to solve the company’s range of change issues. However, if needed, add additional relationship and behavioural assumptions based on less than perfect information as follows:
1. Based on Readings McFillen et al. 2013 (Reading 11), Rafferty et al. 2013 (Reading 12) and Barratt-Pugh et al. 2013 (Reading 13)compare and contrast the relationship between change readiness and change agents? Please use examples from the Northern Rock case to support your answer.
2. Using Kotter’s Integrative model of Organisational Dynamics Chapter 7, Figure 7.4 (Hayes, 2018 p.130), redraw and adapt this Figure to suit your analysis of Northern Rock. Now using facts from the problem statement plus your own assumptions from the case study, explain your analysis using the short, medium and long term as described in Chapter 7 (700 words)
3. Based on Hayes (2018) Chapter 9 and Battilana et al (Reading 16)identify, discuss and explain appropriate leadership approaches and competencies when implementing planned organisational change at Northern Rock. (600 words)
Answer
Relationship between change readiness and change agents
Change is an inevitable part of an organization and the ability of organizations to be flexible has become paramount. Readiness to change is an imperative element for the successful implementation of organizational change. When readiness to change exists, it becomes easier for organizations to embrace change and reduce resistance. Every organization faces development issues and requires improvements in the loopholes being identified within the business operations. Consequently, readiness to change can facilitate initiatives to reduce business risks and attain productive performances. As opined by Rafferty, Jimmieson and Armenakis (2013), change and development have continued to exist within organizations allowing them to make efforts to achieve their intended organizational objectives. However, they also state that many organizations have failed to implement planned changes due to factors like employees’ attitude towards change. As identified in the case of Northern Rock, the company had strong intention to bring changes in their business operation, however, failed to overlook the potential threats. The failure to identify external changes could consequently get negative responses from stakeholders. Rafferty, Jimmieson and Armenakis (2013) also identified that there is a lack of research on adoption of multilevel approach which is critical to comprehend the individual and organizational implications of change readiness. In contrast, change agents are the individuals from internal and external sources of the organization that assists businesses to transform themselves. The case of Northern Rock depicts that the organization was a risk taker but failed to access the external threats. The major focus of change agents is to follow change in market trends, technological changes, structural modifications and maintain crucial relationships within the organization.
According to McFillen, et. al. (2013), change readiness is backed up by organizational diagnosis that plays an important role in taking change initiatives. According to the author, previous researchers have not gone deeper in deconstructing the organizational diagnosis process resulting in failure of change initiatives. It is important that changes initiated are properly planned and executed to derive the desired results. However, the consideration of internal and external factors to change and resistance is important. McFillen, et. al. (2013) identified that an organization can never understand the root cause of underlying organizational problems.Conversely, Rafferty, Jimmieson and Armenakis (2013) suggest that organizations still have limited knowledge on change readiness and therefore are unable to identify the importance of change agents. Change agents help identify which components of change are weak or strong. Barratt-Pugh, et.al (2013) in their article have stated that role of managers in initiating changes within the organization through utilizing formal and informal agencies of change in their managerial roles. The author suggests that change and readiness are related as they require creation of the right culture in the organization so that employees accept the change. Organizations must strategically plan their change initiatives and ensure that employees believe in the change. As in the case of Northern Rock, the company has implemented changes that helped it to expand its business operations, however, these changes must be informed to the stakeholders to avoid any problems in the future. Barratt-Pugh, et.al (2013) also suggested that the resources must be available to make the employees ready to accept the new changes. At Northern Rock, the resources were well-preserved and the management risked to invest the resources on the ongoing changes such as implementing financial changes within the organizations.
The above suggestions from authors it can be analyzed that change readiness can be measured by an organization’s financial, human, material and informational resources that are applied to the change and the willingness of employees to accept the change. Change agents include managers, executives, hired consultants or any other external person. The importance of change agents is not limited to assessing the changes within the organization but also to formulate how the change will happen and what outcomes will it generate. Therefore, the relationship between a readiness to change and change agents within an organization is that when employees are ready to accept the significant changes, change agents will be able to communicate the ideas better, take their suggestions and initiate the change process smoothly. However, it is required for change agents to smooth resistance to change and address the issues before derailing an initiative. Kotter’s Integrative model of Organizational Dynamics
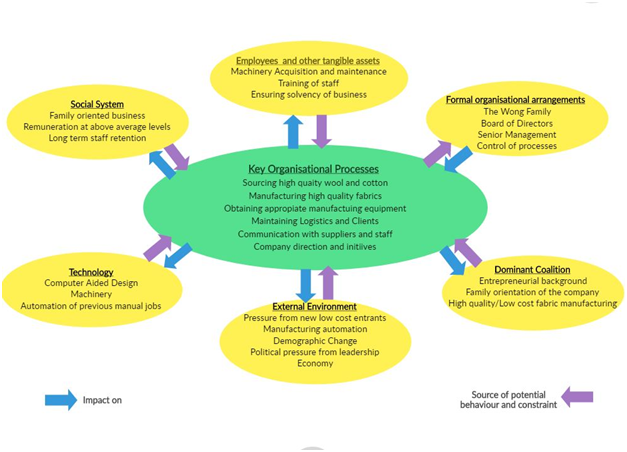
According to Hayes (2018), Change depends on the internal and external factors of an organization. These factors include technological, social, demographic, human resources, managerial and cultural changes that help decide an organization to initiate the changes within its business operations. There are many models and theories of change.According to Teixeira, Gregory and Austin (2017), Kotter has devised a model of change which states that when an organization fails to meet certain conditions, it becomes difficult to initiate and implement the process of change. Kotter believes that leadership and a good management act as change agent within an organization. In the case Northern Rock, the leadership and management were strong that led to implement changes to improve the financial condition of the company. The company implemented changes in their business model that gained immense support from its customer base. They provided surplus funds to its customers to fulfill their needs and desires. Although this strategy of lending higher risk mortgages and making the loans available to a wider customer base, there lies a risk of resistance from customers who believe in traditional methods. Northern Rock is in need of new adaptation changes. The basis of adaptation may help to assess the surroundings and the intellectual strategy might facilitate transformation or change the organization. Consequently, the adaptation of the transformation will support development of the organization.
According to Hayes (2018), Open systems theories highlight that changes in any of the internal or external factors of an organization can affect the other related factors. It is important to understand that all the factors or elements of an organization are interconnected. The Kotter’s Integrative Model of Organizational Dynamics has seven major elements where one set related to conversion of energy and the other related to gathering information and communication. According the Kotter’s model, there are six structural elements (Hongand Park,2020). The external environment assesses the external factors such as political systems and responses from public. In the case of Northern Rock, the external factors and threats are seen to be just overlooked by the company. Northern Rock had confidence in its strategies that did not allow to assess the impact of the potential threats from the external environment. Northern Rock has faced international issues which can be mitigated by cooperation with other banks. The employees and other tangible assets element include land, building, inventories, cash. Being a financial company, Northern Rock deals with cash and solvent enough to run the business operations. The availability of funding sources has allowed Northern Rock to expand its operations. The formal structures include the hierarchy, and job design. Northern Rock has always tried to focus on developing its own staff. The major decisions are taken by the senior management who control the processes. The social system includes the culture an organization holds and its social structure. Northern Rock as a bank has a diversified culture which connects to variety of customers. The company socializes and associates with local sports clubs and events to enhance its social image. The technology elements include the core technologies utilized by an organization in its business operations. In the year 2007, Northern Rock start declining from its position and technologically they did not have an upper hand. Although they invested in enhancing their website but failed to deliver the desired results. However, Northern Rock had contingency plans to cover the issues and ensure customers of a safer transaction. The dominant coalition element involves the organizational objectives or objectives of people who control decision making.
Short term
In short term, Norther Rock’s decision-making policies can be changed that aligns with the interests of the clients that still follow the traditional ways of banking. If the company brings changes in its operations, it has to consider the current market trends, analyze the strategies used by competitors and select the best idea to implement the change.
Medium Term
According to Kotter’s model, misalignment in changes can impact all the elements as they are interconnected. If Northern Rock has strategies but lack of knowledge of the current trends, the dominant coalition and external factors are misaligned. In the medium term, Northern Rock can ensure that all the elements are appropriately aligned.
Long term
Long term strategies determine the survival, growth of an organization and ability to adapt to the external changes. Northern Rock may have to take decisions of structural changes or creating a long term for survival.
Role of Leadership in organizational change
According to Be?liu (2018), in the 21st century, change has become an important part of every organization. The fast pace of the changing environment has put organizations under the pressure to adapt to the changes. Changes can vary from cultural, technological or social changes that can either have positive or negative impact on an organization. However, leaders see and manage foresee the changes that can improve the present condition of their organizations. As it is stated that not all changes are successful, but with proper planning and careful execution, changes can bring significant impact within an organization. The responsibility of leaders is to measure the impact and outcome of the changes before derailing the changes (Wulandari, et.al., 2020). Leaders act as communicators that help employees to be aware of the changes made and how it will affect their work. Leaders act as advocates for change which means that they first need to be onboard for the change before they can support their subordinates. Leaders act as coaches to support employees through the process of change. The core competency required here is the ability to transform employee skills and behavior, and reinforce the change to sustain in long run. Leaders must be able to persuade and transform employees that resist to change by making them understand the importance of the necessary changes.
Northern Rock has been unstable in terms of its business operations requiring strategic changes that can be implemented by its leaders. The leadership of Northern Rock has been strong but decisions of buying in international money markets rather than using customer deposits as source of funds to lend out was not suitable. The banking crisis also contributed to the ill-fate of Northern Rock. The decisions of retaining the business could not be successful due to ongoing recession and loss of jobs. Northern Rock could have taken wise decisions of making up to the loss of the foundation. Since stakeholders are up for claiming profits, the decision making the bank nationalized could have been re-thought. A small group of shareholders were under the claim that their life savings were lost after Northern Rock was nationalized. The leaders could have understood the underlying issues and take strategic decisions to settle the claims of its customers. Leaders could have refloated the bank as an individual business or completely closing it down. Leaders had an opportunity to exert their power and persuade the Treasury that the bank can be sold as a going concern (Computerweekly.com, 2007). In Northern Rock, the leaders need to have effective communication skills and have a clear leadership structure. The changing environment of the financial market must be assessed by the leaders to understand the current financial trends, rates and changes in the financial systems. The rationale here is that leaders act as advocates of change. Therefore, when they are onboard for changes, they can easily communicate such changes to the employees. The support from leaders to move the company ahead is huge but the lack of support can decline the position of the company.
Reference List
Rafferty, A.E., Jimmieson, N.L. and Armenakis, A.A., 2013. Change readiness: A multilevel review. Journal of management, 39(1), pp.110-135.
McFillen, J.M., O'Neil, D.A., Balzer, W.K. and Varney, G.H., 2013. Organizational diagnosis: An evidence-based approach. Journal of Change Management, 13(2), pp.223-246. Barratt-Pugh, L., Bahn, S. and Gakere, E., 2013. Managers as change agents: Implications for human resource managers engaging with culture change. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 26(4), pp.748-764.
Hayes, J., 2018. The theory and practice of change management. Palgrave. Teixeira, B., Gregory, P.A. and Austin, Z., 2017. How are pharmacists in Ontario adapting to practice change? Results of a qualitative analysis using Kotter’s change management model. Canadian Pharmacists Journal/Revue des Pharmaciens du Canada, 150(3), pp.198-205.
Hong, S.H. and Park, M.J., 2020. Dynamics of marketing automation adoption for organisational marketing process transformation: the case of Microsoft. International Journal of Electronic Customer Relationship Management, 12(3), pp.205-224.
Be?liu, D.C., 2018. Institutional management of change resistance of the employees against organizational transformations. Scientific research and education in the air force, 20, pp.351-358.
Wulandari, R.D., Supriyanto, S., Qomaruddin, M.B., Damayanti, N.A. and Laksono, A.D., 2020. Role of leaders in building organizational readiness to change–case study at public health centers in Indonesia. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 18(3), p.1.
Computerweekly.com, 2007. Northern Rock website problems offer lessons. [online] Available at:












