Mitigation Plan Assignment: Risk Assessment for Singapore Sun Cable Project
Question
Task:
You are a project analyst at a large construction company. You have been asked to develop a risk analysis and mitigation plan for:
Singapore Sun Cable: https://www.suncable.sg/
Also see: • https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2019/jul/14/just-a-matter-of-when-the-20bnplan-to-power-singapore-with-australian-solar
https://www.straitstimes.com/business/economy/20b-plan-to-supply-solar-power-fromaustralia-to-spore
Your mitigation plan assignment should cover the three parts as detailed below:
Part A: Project Overview
For each student’s allocated case study students must be able to identify the following information through their own research:
- The overall budget for the project (real or projected)
- Social and economic rationale: Including benefits and drawbacks for the project
- Key Statistics: Provide key information about the project:
- Scope and Size
- Budget and estimated cost
- Time required to complete the project
- Key construction elements or phases (e.g. if you are building a toll road one key element may be the tunnel segment or bridge segment)
- Environmental costs or benefits
- Funding mechanisms: How the project makes money or provides return to its promoters
- Identify the Key Stakeholders in the project
Part B: Risk Analysis
In this part students develop a risk assessment analysis in which they use both qualitative and quantitative measures to identify potential risks in the project and determine how they should be weighted.
The risk analysis should draw upon principles outlined in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) and material discussed in class in weeks 1 -5. Students would be expected to produce a risk matrix where the likelihood of potential risks events are mapped against their possible consequences. Other risk assessment and analysis activities might focus on a range of financial measures associated with the project.
Part C: Risk Mitigation Plan
In this part students will use the information collected and analyzed in the previous two parts to develop a risk mitigation plan and strategy. Based on information identified in the risk analysis students will be expected to develop a plan for how they deal with the various identified risks. The mitigation plan should outline which risks need to be address and in what order. The plan should also identify and potential risks that they believe do not require attention.
The plan should then explain how risks might be addressed and by what means. Where possible places should include the reference to time and resource (costs) implications. Students need to take into account commercial considerations when constructing the plan and identify whether the plan is cost effective or has any implementation issues.
Answer
Mitigation Plan Assignment Part A: Project Overview
Sun Cable is building the world's biggest solar energy network, which will enable clean energy to power Australia, Singapore and other ASEAN markets. The project also aims to provide interconnection transmission of solar energy across the countries. This initiative would make it easier to electrify existing and growing sectors, thus promoting large-scale industrial growth and lowering carbon pollution (Sun Cable 2021). The primary goal of Sun Cable intends to construct the world’s largest intercontinental electricity network, linking Australia to Singapore and supplying clean energy 24 hours a day and seven days a week.The Sun Cable project intends to create a massive solar power plant throughout central Australia, coupled with energy processing and then link everything to Singapore through an undersea cable, mostly on unparalleled scale.
Overall Budget
The mega solar power project that is being constructed by the Sun Cable is estimated to be completed with an overall budget of A$22 billion.
Social and Economic Rationale
Sun Cable has decided to construct a mega project that will focus on providing solar energy through Australia to Singapore and will also promote cleaner environment (Nwaigwe, Mutabilwa and Dintwa 2019). This is considered as the world’s largest project which will focus on providing solar energy to Singapore 24*7 hours. However, there are certain benefits and drawbacks are associated with the construction of solar power by Sun Cable.
Benefits
The new Sun Cable project will pose importance on reducing greenhouse gases and emissions and at the same time will focus on the development of large scale of economies with ASEAN markets.
An optimistic export strategy could produce huge sums of money and place Australia as the center of reduced energy in a potential zero-carbon environment. It's projected that the Sun Cable project would put throughout the region's development up to $8 billion, and will also 1,500 employment to be generated and 350 permanent vacancies at service start-ups(Sun Cable 2021). Once within service, the AAPL is expected to generate solar power to the value of $1 billion annually. With the completion of the project, the residents would have access to sustainable, safe, and clean energy.
Drawbacks
Though the project will provide numerous advantages, there are certain disadvantages like, the project will take longer time to complete the overall construction.
The budget can also get exceed as it requires high capital expenses to set up the area.
Key Statistics and Features
Scope and Size- The scope of this project is to construct the world’s largest solar energy framework which will focus on providing solar energy from Australia to Singapore. The new project also emphasizes on implementing innovative features like a 10-gigatonne-capacity series of panels would be distributed over 15,000 hectares and will also be supported through battery storage to guarantee continuous supply of energy.
Budget and estimated cost- To complete the Sun Cable project, the budget required is $22 billion which has been funded by a tech billionaire and also by a resource billionaire.
Time required to complete the project- It has been estimated that the Sun Cable’s largest solar project will provide sunshine to one-third of Singapore by 2030.
Key construction elements or phases- Key elements required to construct the project is the solar cell or the photovoltaic cell constructed of semi-conductor component that helped in the process of automated conversion of sunlight into electricity (Rosales-Asensioet al. 2017).
Environmental benefits- The project will help to reduce carbon pollution from the environment. It will also focus on eliminating wastage of water and will also support in fighting against climate change (Guerin 2017).
Funding Mechanisms
The project has been funded by two different billionaires who act as the key sponsors of the project. Once the project is completed, it will promote various local businesses and at the same time will help in renewing international links that would be beneficial for all the stakeholders involved with the project.
Key Stakeholders
|
Role |
Category |
Interest |
Influence |
Responsibilities |
|
CEO |
Internal |
High |
High |
He is responsible for looking after the overall finding for the project. |
|
Project Manager |
Internal |
High |
High |
The project Manager is responsible for monitoring the overall construction of the project (Kivilä, Martinsuo and Vuorinen 2017). He is also accountable to share the progress report with the client.
|
|
Developers |
Internal |
High |
High |
The developers are responsible for the efficient deployment of the project. |
Part B: Risk Analysis
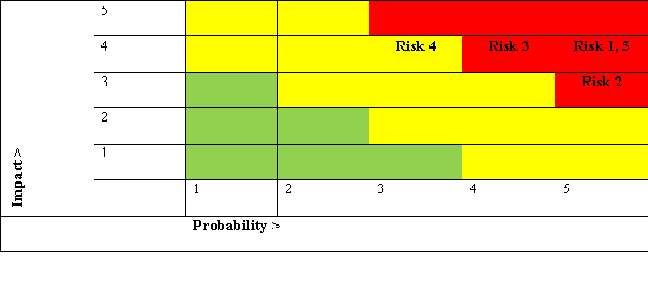
Risk assessment is actually a central integrated framework that allows defining threats and developing strategies for project mitigation. Risks impair the efficiency or value of a proposed solution in construction project. In this solar panel construction project, the threats can interrupt project plans and also budget estimates. The success of this project depends upon the risk assessment level implemented by developers to reduce designing risks.
|
Risk |
Probability |
Impact |
Risk Score (P*I) |
|
1.Construction risk in project- This is the most common risk associated with majority of the construction project. Construction risk mainly pops out, when there is no fixed plan in continuing the project. Another risk associated with the development of solar panel is that, sometimes the workers are not provided with safety equipment and resources that lead to accidents and injuries among the workers (Chen, Lu and Zhao 2020). Shortage of workers is another problem that can prevent the construction of the solar panel project. |
5 |
4 |
20 |
|
2.Financial Risk-In Australia, the expense of solar power development is significantly greater than that of power generation and solar energy persists to be an unsure and expensive power storage option. A broad variety of benefits, including feed-in duties, production opportunities, Renewable Purchasing obligations (RPO), centre and regional asset incentives and revenue stimulus. The absence of management and collaboration between the business and the Government means that contractors find it impossible to pursue a competitive strategy to achieve their objectives (Jimmy and Falianty 2021). |
5 |
3 |
15 |
|
3.Subcontractor risk-A big risk element for subcontractors in solar power building infrastructure projects has been to negotiate with the supplier who does not work on the project Whenever an insolvent sub-contractor fails to fulfill its contractual commitments, the project plan and also the gross profit will be totally destroyed. Schedule disruptions will also affect others as well as lead to expensive reprocessing. This will contribute easily to financial hardships if developers overreach with too much overtime or through delaying payments on other programs. |
4 |
4 |
16 |
|
4. Change orders risk in the project-Change orders represent an unavoidable aspect of the building process and could be a significant risk attribute if not managed correctly. A change order constitutes merely an addition or modification to the initial project agreement or scope of the project. They could be started by the founder, the contractor, or one of the subcontractors. They often necessitate further work due to oversights or discrepancies in the initial project scope or unclear design sketches.Poorly managed change orders will result in higher operating expenses, missed contract deadlines, distractions in operation, and failure to complete a project on track. |
3 |
4 |
12 |
|
5.Technical Risk in the Project-Solar designers also necessitates the use of extremely precise engineering tools including parabolic lenses and transmitter tubing that are not readily available in local markets. Due to various insufficient field expertise, data, method accuracy, and product specifications are inconsistent, with each provider implementing their own framework. Due to the extreme degree of customization, the solar equipment must be implemented on a project-by-project schedule, prohibiting businesses from extracting income from increased productivity. This possibility arises as a consequence of the shortage of skills and almost no expertise of asset stimulation (Razi, Ali and Ramli 2021). Another major risk in solar infrastructure development is the unavailability of sufficient grid network facilities. In addition, it is highly probable that the project concept never reaches its level of implementation, so the plan could be deemed unfeasible or economically unprofitable.There is a fairly high chance of delay and cost overrun and even has relatively high effects of these provisions. |
5 |
4 |
20 |
Part C: Risk Mitigation Plan
Risk management involves an act that enables individuals and organisations, by identifying a system to store fundamental capital, to cope with uncertainty. In overseeing infrastructure projects, designers need to adopt a particular strategy to accomplish the objective of delivering a successful project. Project managers can accomplish their objectives with a decent performance, great budget and with a good timetable.The advantages of project risk management entail risk identification and analysis, and improved management procedures for development projects and the efficient utilization of capital.The effects of risk and instability on infrastructure projects can be disastrous (Bingham and Gibson Jr. 2017). As a result, risk identification and assessment are still important aspects of construction industry to deal successfully with complexity and unforeseen incidents and gain project completion.
In case of construction risk in the deployment of solar infrastructure project, there are few types of threats that are related with construction risk. To deploy the infrastructure project successfully and efficiently, the project manager should implement a well-planned strategy beforehand and all the stakeholders should be involved while preparing the project execution strategy. It is also necessary for the project team to ensure that the workers working in the project site are equipped with well protected kits and hand gloves(Muriana and Vizzini 2017). They should also get access to proper mask and gloves while dealing with harmful chemicals. It is much less expensive to spend in training, work instructions, and personal protective equipment (PPE) to deter injuries than to live with the fallout whenever something happens. Prior to actually starting work, the project manager should ensure that the subcontractors acknowledge the dedication to safety and offer instruction to their workers.
In mitigating financial risk in this particular project, allowing Certified Construction Auditors (CCAs) to check the agreement before this formally becomes operational has been the most efficient strategies for handling financial risks throughout a construction project. These experts would verify that all parties possess the resources necessary to achieve the project's progress. Development arrangements must have guidance for all sides on matters including contract modification, orders and contingent liabilities. Furthermore, the project manager should monitor thoroughly the cash flow for different activities related to the project.
To minimize the risk associated with subcontractors throughout the implementation of solar infrastructure, it is important to remain vigilant in tracking the subcontractors if the project head thinks things are going in the wrong direction (Gunduz and Elsherbeny 2020). A rapid reduction with in subcontractor's manpower on the worksite, overdue inventory orders, and inability to reimburse their subcontractors or vendors on schedule are common warning signs and this will also help in mitigating the above-mentioned risk.To assure that the subcontractors accomplish their job financially and physically, it is necessary to prequalify them. The project manager should also make sure, that the subcontractor is providing a weekly report regarding the progress of the project.
As mentioned-above, change orders are also considered as a significant risk in the infrastructure project and therefore, proper mitigation strategy is required to deploy the project successfully and efficiently. The contract must explicitly specify the requirements for handling changes orders. The establishment of standards of initiation, authorisation, execution and payment of service demanded by changes can slow reduce the amount of unwanted changing requests and can also discourage needless applications. It ensures to find out who gets directives for changes. The deadline should always be listed as well as the value of predictability should also be reflected (Demeterioet al. 2019). An in-depth project analysis and even its reach will indicate that any ambiguities, mistakes or inconsistencies which may cause challenges are addressed.
Disruptions due to changes to documents are much less difficult and much less expensive to handle at the beginning of the project than changing after starting of the project.
Technical risk can be resolved in the construction project by providing adequate training to its existing employees to handle the technology successfully and efficiently. The project head should ensure on providing training to the employees to handle the project successfully(Galli 2017). Moreover, the deployment team should store all its important and confidential documents securely and safely in the company’s server. In addition to these risks, there are also certain risks that do not require attention for now and can be addressed at a later stage. Some of these risks include scope creep, future design changes or modifications, additional work and others. This is mainly because, although these risks have the potential to cause negative impacts, they might have some positive outcomes as well. Hence, they will be treated at a later stage once it is confirmed that these risks can offer any positive or negative impact on the overall project. ?
References
Bingham, E. and Gibson Jr, G.E., 2017. Infrastructure project scope definition using project definition rating index.Journal of management in engineering, 33(2), p.04016037.
Chen, L., Lu, Q. and Zhao, X., 2020. Rethinking the construction schedule risk of infrastructure projects based on dialectical systems and network theory. Journal of Management in Engineering, 36(5), p.04020066.
Demeterio, R.A.M., AnchetaJr, R.A., Ocampo, L.A., Capuyan, D.L. and Capuno, R.G., 2019. An investigation on the intralocality differences in health and safety implementation of construction industries.Recoletos multidisciplinary research journal, 7(1), pp.13-25.
Galli, B.J., 2017. The effective approach of managing risk in new product development (NPD).International Journal of Applied Management Sciences and Engineering (IJAMSE), 4(2), pp.27-40.
Guerin, T.F., 2017. Evaluating expected and comparing with observed risks on a large-scale solar photovoltaic construction project: A case for reducing the regulatory burden. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 74, pp.333-348.
Gunduz, M. and Elsherbeny, H.A., 2020.Construction contract administration performance assessment tool by using a fuzzy structural equation model.Sustainability, 12(2), p.523.
Jimmy, C. and Falianty, T.A., 2021. Managing leverage of infrastructure projects: Aggregate and sectoral risk effect. Journal of Asian Economics, 73, p.101284.
Kivilä, J., Martinsuo, M. and Vuorinen, L., 2017.Sustainable project management through project control in infrastructure projects.International Journal of Project Management, 35(6), pp.1167-1183.
Muriana, C. and Vizzini, G., 2017. Project risk management: A deterministic quantitative technique for assessment and mitigation. International Journal of Project Management, 35(3), pp.320-340.
Nwaigwe, K.N., Mutabilwa, P. and Dintwa, E., 2019. An overview of solar power (PV systems) integration into electricity grids.Materials Science for Energy Technologies, 2(3), pp.629-633.
Razi, P.Z., Ali, M.I. and Ramli, N.I., 2021, February. Exploring risk associated to public road infrastructure construction projects. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 682, No. 1, p. 012030). IOP Publishing. Rosales-Asensio, E., de Simón-Martín, M., Rosales, A.E. and Colmenar-Santos, A., 2021. Solar-plus-storage benefits for end-users placed at radial and meshed grids: An economic and resiliency analysis. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 128, p.106675.
Sun Cable. 2021. Sun Cable | The World’s Largest Solar Energy Infrastructure Project. [online] Available at: https://www.suncable.sg












