mental health care assignment on strategies nurses can use to manage young adult addition management and care
Question
Task: how can nursing staff use mental health care assignment research techniques to improve young adult addition management and care skills
Answer
1. Introduction or Background
This mental health care assignmentexamines addiction among young adults. Abuse of alcohol, illicit drugs, and legal medications poses a serious threat to public health across the world. There were an estimated 27 million people, or 0.6% of the world’s young adult population, who were considered to be problem drug users in 2010, according to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). It is estimated that every year, 2.5 million people die from alcohol-related causes, and that between 0.1 and 0.2 million people die from the abuse of opiates, cocaine, and other medicines. Opioid dependence treatment is a societal burden since it leads to substantial morbidity, which in turn contributes to death. According to the UNODC, it will cost between $200 and $250 billion, or 0.3% to 0.4% of global GDP, to combat drug and alcohol abuse worldwide (UNODC, 2018).
Recent mental health care assignmentresearch studies (Bassionyet al., 2015; Salas-Wright, Vaughn & González, 2017; Winters et al., 2018; UNODC, 2018) have found a strong correlation between adolescents’ substance usage and continued substance abuse as an adult; this suggests that some drug problems serve as a gateway to early drug use. Drug and alcohol use is a major contributor to both unintentional and intentional mortality among those aged 15–24. Adolescent substance abuse is strongly associated with negative outcomes such poor academic performance, criminal behavior, unplanned pregnancies, and mental health issues (Salas-Wright, Vaughn & González, 2017). Some of these studies with a focus on prevention argued that negative health outcomes, such as opioid addiction, may be prevented by measures like lowering risk and increasing security.
2. mental health care assignmentAim or Purpose
This mental health care assignmentaims to investigate the illicit drug use in adolescents and how it affects their mental health.
3. mental health care assignmentMethod
Search Strategy
The mental health care assignmentresearcher has mostly utilized google search engine to acquire secondary data sources related to the issue. As a result, numerous databases like PubMed, NCBI, ProQuest, Google Scholar, etc. have been used to gather more reliable and relevant data. The research has used various binary connectives, like “AND,”“OR,”“IN” etc. The literature search included a wide range of terms and concepts, including “illicit drug abuse,”“Adolescent drug abusers’ mental health,”“health effect of illicit drug abuse in youngers,”“illicit drug misuse and engagement of 15-17 year aged,” etc. Themental health care assignment review did not include any search results or case studies that dealt with the effects of drug misuse or drug abusers specifically targeting the elderly population. The evaluation only includes studies that focus on the effects of drug usage on adolescents’ mental health.
Quality Appraisal Tool
In this mental health care assignmentstudy, CASP (Quality Appraisal Tool) has been used as a Quality Appraisal Tool. As a universal instrument, the CASP tool may be used to evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of any specific qualitative research approach. The instrument’s 10 questions probe several facets of qualitative research methodology. The instrument asks the researcher to think about the validity of their research techniques and the clarity with which they express their findings (Long, French & Brooks, 2020).
Flow Chart of The Literature Search
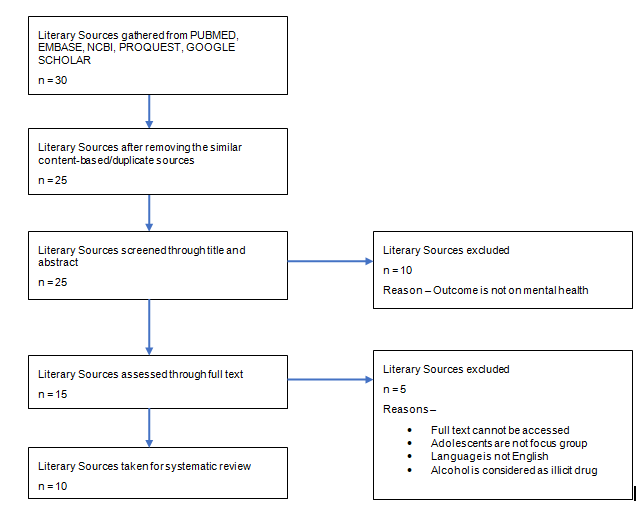
4. Results
Summary Table of Selected literature
|
Authors |
Year |
Country |
Method |
Participants |
Key Findings |
|
James White, Steven Bell and G David Batty |
2020 |
United Kingdom |
The mental health care assignment research analyses data of women from 1970 British Birth Cohort Study regarding the illicit drug usage and how it causes socio-economic disadvantages. |
14,082 participants (6999 women) from 1970 British Birth Cohort Study. |
A total of 20.3% of 16-year-olds reported having tried an illicit drug, and 7.2% reported using over the previous 12 months. There was a dose-response relationship between drug use at age 16 and recent drug use among teenagers, even after controlling for socioeconomic status and mental health difficulties in childhood, as well as for repeated testing. |
|
TorkelRichert,MatsAnderbergand Mikael Dahlberg |
2020 |
Sweden |
With the use of structured interviews, 1970 young people throughout 11 cities in Sweden are being studied. Chi-square testing, multivariate logistic regression, and averages were used to analyse the data. |
1970 young people from 11 cities of Sweden |
The majority of the young people who participated in the survey reported experiencing mental health issues. Problems with focus, insomnia, anxiety, and/or sadness were reported by 34–54 percent of the sample. |
|
V. Herz, N. Franzin, J. Huemer, D. Mairhofer, J. Philipp, and K. Skala |
2018 |
Austria |
Self-report measures were used to gather data on lifetime use, initiation, frequency, and amount of drug use, as well as sociodemographic, familial, and academic information. Substance abuse disorders were identified using CAGE. |
Twenty-five children and adolescents between the ages of 12 and 17 were selected from an Austrian child and adolescent psychiatric unit. |
76% of people have used drugs at some point in their lives, and 32% of those people use drugs regularly. |
|
Elizabeth Brownlie, Joseph H. Beitchman, Gloria Chaim, MSW, David A. Wolfe,Brian Rush, andJoannaHenderson, |
2019 |
Canada |
The mental health care assignmentresearch utilises a survey on mental health and drug use that students fill out in class. |
1360 students in grades 7 and 8 from four different areas of Ontario, Canada took part. |
More over 30% of people exhibited symptoms that surpassed the threshold for internalising and/or externalising difficulties, yet less than half had sought help for their mental health issues in the previous 12 months. Substance abuse was connected with an elevated risk of issues both inside and outside of oneself, as well as higher distress. |
|
Jens ChristofferSkogen, Børge Sivertsen,Astri J Lundervold, Kjell Morten Stormark, Reidar Jakobsen, Mari Hysing |
2014 |
Norway |
The mental health care assignment research uses a Cross-sectional study. |
Those residing in Hordaland County, Norway, between the ages of 17 and 19 were asked to take part. |
Alcohol and drug use initiation were both linked to the onset of depressive, impulsive, and hyperactive symptoms, but drug use initiation was the sole factor in the development of anxiety. |
|
Brian A. Feinstein, Blair C. Turner, Lauren B. Beach, Aaron K. Korpak, and Gregory Phillips II |
2019 |
Not Stated |
Youth Risk Behaviour Survey information collected at the local level was combined with data from other areas and years (2011–2015) |
There were 18,515 bisexual youth from various racial and cultural backgrounds. |
Bisexual youth of colour, particularly “black and Hispanic youth, were less likely to report being bullied in person or online than their White counterparts. Furthermore, as compared to bisexual kids of White, Hispanic, and Other racial/ethnic backgrounds”, Black bisexual youth were less likely to express feelings of sadness/hopelessness and thoughts of suicide. When compared to White bisexual female adolescents, Black bisexual female youth were less likely to report engaging in risky behaviours including smoking, binge drinking, and drug use. |
|
Jon E. Grant, Katherine Lust, Daniel J. Fridberg, Andrea C. Kingand Samuel R. Chamberlain |
2019 |
United States of America |
“The usage of e-cigarettes, alcohol and drug abuse, mental health difficulties, and impulsive and compulsive tendencies are evaluated using a 156-item anonymous online survey”. |
9,449 university students |
“Those with a history of e-cigarette and illegal drug use were more likely to have been diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, a gambling problem, anxiety, have poor self-esteem, and be impulsive”. |
|
Anthony Idowu Ajayi and OluwaseyiDolapoSomefun |
2020 |
Nigeria |
Using a stratified random sampling technique, “784 male and female university” students were included in a cross-sectional survey performed in February and March of 2018. Using binary logistic regression, we were able to uncover important determinants of both past and present drug usage. |
“784 male and female university students” |
The data found that 24.5 percent of the student body reported using drugs recreationally at some point in their lives, and that 17.5 percent are active users at the present time. Current drug users have used their substance of choice on average every six days in the last month. In the multivariable analyses, staying in the same home as one's mother, appropriate family support and regular attendance of religious fellowships were substantially related with a decreased chance of recreational drug use. However, male sex was related with increased likelihood of recreational drug usage. |
|
Louisa Degenhardt, Chrianna Bharat, Meyer D. Glantz, et al |
2020 |
Worldwide |
Cross-National Data Analysis |
90027 respondents from the “World Mental Health Surveys” |
According to the findings, an individual's risk of making a drug use transition depends on their own personal history of substance use as well as the drug and alcohol use histories of their age cohort. After accounting for demographic and it is rationalized that remission disorder and frequent drug use is more prevalent among the affected personals. |
|
Daise Fernanda Santos Souza Escobar, Priscilla Rayanne e Silva Noll, Thaís Ferreira de Jesus and Matias Noll |
2020 |
Brazil |
This mental health care assignmentResearch examined the connection between high-risk behaviours and three indicators of mental health problems using data from the National School Health Survey and multivariate analysis is performed. |
There were 102,072 Brazilian students, ages 11 to 19, included in the sample. |
Students exhibiting signs of mental health concerns were more likely to engage in high-risk activities, such as drug use and unsafe sex, according to the research. Thus, risky activities may contribute to or worsen the effects of mental illness. |
Quality appraisal scores
Refer to Appendix 1, associating CASP Analysis of study, that illustrates the overall quality appraisal of the study.
mental health care assignmentKey findings
As per themental health care assignment analysis of the selected studies, it can be implied that there is greater prevalence between the younger populace and drug usage as per the research of White, Bell & Batty(2020). While it was also conceptualised that the aspects of illicit drug usage largely consequential towards conditions such as insomnia, sadness, anxiety etc as per Richert, Anderberg& Dahlberg, (2020). These aspects thus overall leads to the prospects of elevated health risk issues and risky behaviours driven by higher level of distress caused by drug usage. Some of these risky behaviours include hyperactivity, acute depression, unsafe sex and so on.
Some other influential factors that variate the mental health conditions of young people includes religion, colour and sexual orientation and psychologies according to the analytics of the selected studies.
5. Discussion
Findings Of the Articles and Any Commonalities or Themes Identified Between Them
As identified in the articles/secondary sources, illicit drug abuse of adolescents has been seen to pose a huge detrimental effect on their mental health. White, Bell & Batty (2020), illicit drug abuse of adolescents can result criminal and anti-social behaviour in their later life. Richert, Anderberg& Dahlberg (2020) have identified that adolescents drug abuse can cause various mental illness like concentration difficulties, sleeping difficulties, anxiety and depression. Herzet al. (2018) have surveyed and identified that drug abusing adolescents were subject of academic failure, school absenteeism, behavioral problems and suicidal intentions. Brownlieet al. (2019) have achieved poor-rated mental health in self-analysis of adolescent participants who were substance abusers.
Skogenet al. (2014), in similar to Richert, Anderberg& Dahlberg (2020) and Herzet al. (2018), have identified depression, inattention andhyperactivity in adolescents as impacts of illicit drug abuse. Feinsteinet al. (2019) have identified various health disparities in young females because of substance abuse. Grantet al. (2019) have identified “ADHD, PTSD, gambling disorder, and anxiety, report low self-esteem, and endorse traits of impulsivity in adolescents as mental illness results of regular drug abuse”. Ajayi &Somefun(2020), in their cross-sectional study, have obtained anti-social behaviors among university students who were abusing substances. Degenhardtet al. (2019) also identified drug use disorders in the adolescent participants of their study. Also, Escobar, Jesus& Noll (2020)have identified various risky behaviors of students who were subjected to abusing drugs.
Limitation of the Review
The systematic review conducted for this study has only included secondary sources. Therefore, the results if this review is totally dependent on the reliability and validity of the outcomes of the selected secondary data. Any unidentified discrepancy in the secondary sources has been supported and cited in this study. Therefore, the credibility of this mental health care assignmentwas not in control of the author.
Recommendations for Future Work
In future, this topic can be addressed through primary research, where the researcher will conduct cross-sectional or cohort studies on adolescents or their families or mental health centers to identify the mental health impact on the adolescents for abusing illicit drugs.
6. Conclusion
By focusing on raising awareness, interventions can recognize the potential role of social learning mechanisms in the development of adolescent drug abuse. Furthermore, the research acknowledged that adolescents with poor individual and societal standards are more sensitive to substance abuse concerns. In addition, the young individuals may be more inclined to turn to substance abuse in lieu of more healthy coping techniques. The usage of drugs has contributed to enormous youth morbidity and death across the world. Many of these young individuals are likely to waste their lives in drug addiction, and many are predicted to convert into regular consumers of narcotics. The mental health care assignment findings show Adolescent drug addiction is a widespread and complex problem, but there are effective solutions that may be used by doctors, community leaders, and educators to reduce the epidemic’s prevalence.
7. Reference list
Ajayi, A. I., &Somefun, O. D. (2020). Recreational drug use among Nigerian university students: Prevalence, correlates and frequency of use. Plos one,mental health care assignment 15(5), e0232964.
Bassiony, M. M., Salah El-Deen, G. M., Yousef, U., Raya, Y., Abdel-Ghani, M. M., El-Gohari, H., &Atwa, S. A. (2015). Adolescent tramadol use and abuse in Egypt. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 41(3), 206-211.
Brownlie, E., Beitchman, J. H., Chaim, G., Wolfe, D. A., Rush, B., & Henderson, J. (2019). Early adolescent substance use and mental health problems and service utilisation in a school-based sample. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, mental health care assignment64(2), 116-125.
Degenhardt, L., Bharat, C., Glantz, M. D., Sampson, N. A., Al-Hamzawi, A., Alonso, J., ... & WHO World Mental Health Survey Collaborators. (2019). Association of Cohort and Individual Substance use with Risk of transitioning to drug use, drug use disorder, and remission from disorder: findings from the world mental health surveys. JAMA psychiatry, 76(7), 708-720.
Escobar, D. F. S. S., Jesus, T. F. D., & Noll, M. (2020). Assessing the mental health of Brazilian students involved in risky behaviors. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(10), 3647.
Feinstein, B. A., Turner, B. C., Beach, L. B., Korpak, A. K., & Phillips, G. (2019). Racial/ethnic differences in mental health, substance use, and bullying victimization among self-identified bisexual high school-aged youth. LGBT health, mental health care assignment6(4), 174-183.
Grant, J. E., Lust, K., Fridberg, D. J., King, A. C., & Chamberlain, S. R. (2019). E-cigarette use (vaping) is associated with illicit drug use, mental health problems, and impulsivity in university students. Annals of clinical psychiatry: official journal of the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, 31(1), 27.
Herz, V., Franzin, N., Huemer, J., Mairhofer, D., Philipp, J., & Skala, K. (2018). Substance use and misuse among children and youth with mental illness. neuropsychiatrie, 32(1), 18-25.
Long, H. A., French, D. P., & Brooks, J. M. (2020). Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Research Methods in Medicine & Health Sciences, 1(1), 31-42.
Richert, T., Anderberg, M., & Dahlberg, M. (2020). Mental health problems among young people in substance abuse treatment in Sweden. Substance abuse treatment, prevention, and policy, 15(1), 1-10.
Salas-Wright, C. P., Vaughn, M. G., & González, J. M. R. (2017). Drug abuse and antisocial behavior: A biosocial life course approach. Springer.
Skogen, J. C., Sivertsen, B., Lundervold, A. J., Stormark, K. M., Jakobsen, R., &Hysing, M. (2014). Alcohol and drug use among adolescents: and the co-occurrence of mental health problems. Ung@ hordaland, a population-based study. BMJ open, mental health care assignment4(9), e005357.
UNODC.(2018). DRUGS AND AGE: Drugs and associated issues among young people and older people. World Drug Report. UNODC Research. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.unodc.org/wdr2018/prelaunch/WDR18_Booklet_4_YOUTH.pdf. [Accessed on 29.08.2022].
White, J., Bell, S., & Batty, G. D. (2020). Association of illicit drug use in adolescence with socioeconomic and criminal justice outcomes in adulthood: prospective findings from a UK national birth cohort. J Epidemiol Community Health, 74(9), 705-709.
Winters, K. C., Botzet, A. M., Stinchfield, R., Gonzales-Castaneda, R., Finch, A. J., Piehler, T. F., ... &Hemze, A. (2018). Adolescent substance abuse treatment: A review of evidence-based research.mental health care assignment Adolescent substance abuse, 141-171.
Appendix
CASP Analysis of the Study
Section A: Are the results of the review valid
|
Section A: Are the results of the review valid |
||||
|
|
||||
|
1. Did thereviewaddress a clearlyfocused question
|
Yes |
|
||
|
Can’t Tell |
|
|||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: The research prospectively addresses the key effects of illicit drug usage on the adolescent populace’s mental health.
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
2. Did theauthors look fortheright typeofpapers |
Yes |
|
||
|
Can’t Tell |
|
|||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: The research evaluated experimental, cohort, large-sample data analysis and pilot studies associated with the effect of illicit drug usage on the mental health of young adults.
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
Is it worth continuing |
||||
|
|
||||
|
3. Do you think all the important, relevant mental health care assignmentstudies were included |
Yes |
|
||
|
Can’t Tell |
|
|||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: Majorities of studies collected from credible sources and journal publications all related to mental health and illicit drug usage of young population.
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
4. Did the review’s authors do enough to assess quality of the included studies |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Can’t Tell |
|
|||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: Each of the study’s methods, key results and prospective contribution and relevancy is assessed by means of inclusion criteria to maintain sufficient relevancy and quality of the systematic mental health care assignmentreview. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
5. If the results of the review have been combined, was it reasonable to do so |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Can’t Tell |
|
|||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: All the data and prospective results are rationalised based on the interrelation of each paper with other’s findings based on key themes, findings and relevancy which is ultimately combined to attain sufficient outlook on the research.
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
Section B: What are the results |
||||
|
|
||||
|
6. What are the overall results of the review |
|
|||
|
Comments: The overall result of the study is detrimental effects of illicit substance usage on the mental health condition of young people which includes acute depression, anxiety, risky behaviour as well as socio-economic effects.
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
7. How precise are the results
|
|
|||
|
Comments: The results are fairly accurate and largely based on cross-national effects of illicit drug usage on the young population. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Section C: Will the results help locally |
||||
|
|
||||
|
8. Can the mental health care assignment results be applied to the local population |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Can’t Tell |
|
|||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: The results will help to identify the patterns of illicit drug usage that can be recognised from the ill behaviours witnessed from their daily conduct, thereby, proper actions can be taken in this behalf. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
9. Were all important outcomes considered |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Can’t Tell |
||||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: The mental health care assignmentresearch does evaluate range of outcomes that includes phycological degradation, behavioural issues and socio-economic problem, but aspects of all outcomes are uncertain in consideration.
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
10. Are the benefits worth the harms and costs |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Can’t Tell |
|
|||
|
No |
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
Comments: Since, the mental health care assignmentresearch only identifies the key causes of illicit drug usage it is not certain whether all the harms are worth the cost or not. |
||||












