Market Structure Analysis Essay: Monopoly In Indian Railways
Question
Task:
a) Briefly describe and contrast four market structures. (Hints: Use features of each market structure such as number of siellers, type of product, entry conditions, profits and losses in the short and long run, advertising, research and development and appropriate diagrams to answer this question. While your textbook is your first point of reference, you should consult other references in order to receive full marks. Use real life examples to support your discussion).
b) Choose an industry from your home country representing monopoly. Explain why it is a monopoly based on the characteristics of market structures outlined in part a). Analyse price and output decisions made by this monopoly using economic theory and illustrate it on a diagram. (Hint: this is your case study that you need to describe in details, provide relevant information, use table, diagrams where appropriate. You should use real data as much as possible).
c) Using your case study, evaluate the efficiency of your chosen monopoly. Explain it using economic theory and illustrate it on a diagram. (Hint: compare the allocation of resources and market outcomes between your chosen industry and perfectly competitive market structure using theory and real data from your case study).
d) Provide the case for or against the monopoly in your case study. Would you suggest to break up this monopoly into oligopoly? Explain using economic theory and diagrams. (Hint: use real life data from your case study. For example, if the monopoly has been investing in research and development, provide evidence with supporting references).
Answer
Introduction
The market structure analysis essay analyzes the four market structure that operates in the real market environment such as perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly and monopolistic market structure. Further, the paper analyzes the monopoly market of India by focusing on the rail industry that represent a strong monopoly. Moreover, the paper present a comparison of allocative efficiency between monopoly industry and perfect competitive market to conclude the efficiency power of the monopoly case presented. Lastly, the essay suggests for and against point of the chosen monopoly and suggest whether to break the monopoly into oligopoly or not.
Discussion
Types of Market Structure:
Perfect competition can be regarded as such a market where there is lack of competition among the firms. There is no such industry in India that exhibits market competition.
The model of perfect competition depends on the below mentioned assumptions:
- Large number of buyers and sellers: his industry includes large number of consumers and suppliers so that the single firm has the capacity to manage the goods supplied. Further, there are different buyers in the market and there exists no monopsonistic power so that it affects the functioning of the market. Therefore, in a perfectly competitive market, the firms alone cannot affect the price by changing the output decisions in the market.
- Product homogeneity: It can be said that an industry in a perfectly competitive market is defined as the group of firm that produces homogenous product in the market. The buyers cannot differentiate the products in the market and if the products are differentiated, there should be some type of discretion in the market. This is considered to be the ex hypothesi rule in perfect competition.
- Free entry and exit: There exist no such obstacle to entry as well as exit in the firm. Although the exit and entry might require some time, the firms has the liberty of movement within and outside the industry. Further, the total firms might also be reduced if barriers exist.
- Profit maximisation: The objective of the firm in the perfect competition is profit maximization.
- Lack of government regulation: There exists no government regulation in a perfectly competitive market. This assumption is considered to be sufficient in order to make the firm price taker and thus the demand curve is considered to be infinite elastic demand curve.
- Perfect knowledge: The factors of production mentioned in this market structure analysis essay are considered to travel from one company to another. The workers can also changes their jobs and thus it suggests that the skills can be easily captured. Labour is not considered to be unionised and the raw materials and the other related factors are not monopolised. Therefore, there is perfect competition in the market for factors of production
- Perfect mobility of different factors of production: The suppliers and the consumers must have comprehensive knowledge of the firm that is operating in the economy. This knowledge is necessary in order to know the prevailing market conditions in this present period and thus the condition of uncertainty about the future development in the market has been diverted (Gans, King & Mankiw, 2011).
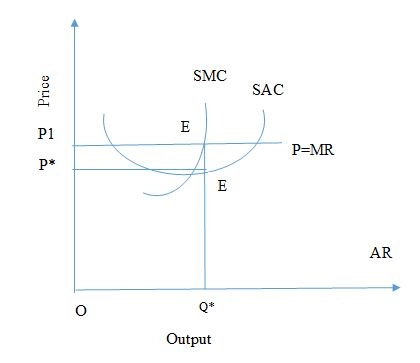
Fig: Equilibrium of the firm under perfect competition
From the above figure mentioned within this market structure analysis essay, it can be seen that the SMC curve intersects the P=MR curve at point E. At this point, SMC=MR. Point E is considered to be the point of equilibrium. Further at OQ level of output, the first and the second conditions of profit maximisation is fulfilled. The profit level is maximum at point OQ and thus it is regarded as the equilibrium output. The pure profit of firm is shown by the area P1EE*P* where P1P*is the per unit supernormal profit at output OQ*.
Monopoly can be regarded as such a market where there is sole seller with no close substitutes of the commodity and barriers to entry. The railway sector in India is an example of monopoly. The different features of monopoly are discussed below within this market structure analysis essay:
- There is provision of ownership of the strategic raw materials and thus the monopolist has exclusive knowledge of the different production techniques.
- There exists patent rights for the products involved in the production process
- The provision of government licensing as well as the obligation of foreign trade barriers excludes the foreign competitors.
- The scope of the market is such that it is sufficient to exhibit the economies of scale.
- The existing firm will try to adopt limiting pricing policy and thus this pricing policy aims at the prevention of entry of new firms (Hansen, 2013).
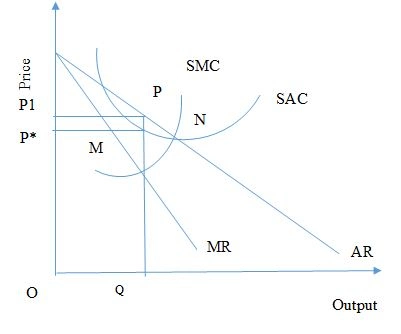
Fig: Equilibrium of the firm in monopoly
It can be seen from the above figure within this market structure analysis essay that the MR and the MC curve intersects at point N. This point N satisfies two conditions of profit maximisation. The equilibrium output is OQ. The per unit monopoly profit is PM. Therefore, the total monopoly profit is P1PMP*.
Oligopoly is such a market where there are a few sellers in the marketplace trading similar or differentiated products. The automobile market in India is an example of oligopolistic market. The features of oligopoly market are discussed below:
- There are small number of sellers in the market. This number of seller is so small that an individual firm faces difficulty in influencing the market price and the business strategy.
- There is independence of the business decisions in an oligopoly firm. Since, there are only a small number of firms, the strategy and the business decisions evokes retaliatory actions. This is known as the interdependence of the oligopoly firm.
- The barriers to entry in an oligopolistic firm might arise due to huge investment requirement, absolute cost advantage and economies of scale, improved consumer loyalty and resistance by the established firms.
- There is interdeterminateness of the price and the output in an oligopolistic market. However, the output and the price is found to be determinate in case of collusive oligopoly. This is explained below in the figure (Hansen, 2013).
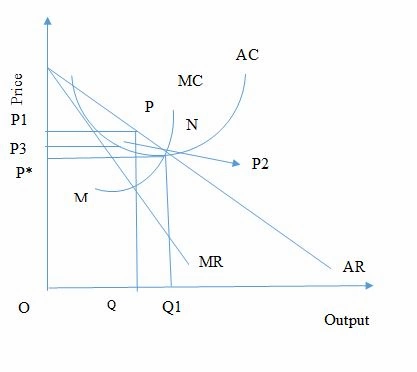
Fig: Equilibrium of the firm in collusive monopoly
In the above figure, the quantity Q can be distributed between different cartels in the firms. The supernormal profit of the firm is determined by P1PP2P3. The deadweight welfare loss is PNM.
Monopolistic competition refers to the market structure where there many sellers in the market selling differentiated products with no close substitutes. The toothpaste industry in India is an example of monopolistic competition.
The features of monopolistic competition illustrated in this market structure analysis essay are:
- There is countless number of sellers in the monopolistic industry.
- There is differentiation of the firm’s product in monopolistic industry.
- In a monopolistic industry, there are no such restrictions to entry of the new firms as well as exit of the old firms in the industry.
- The firms in monopolistic competition try to make heavy expenditure on advertisement and thus this distinguishes monopoly and perfect competition from monopolistic market.
- The firms faces downward sloping demand curve in a monopolistic market (Varian, 2014).
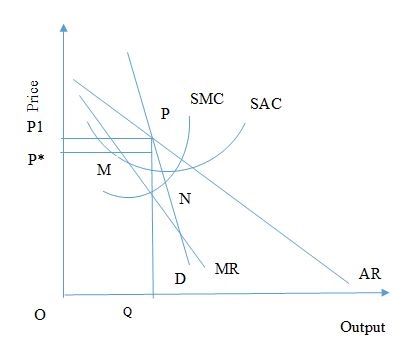
ig: Equilibrium of the firm in monopolistic competition
In the above figure, it has been found that MR=MC intersects at point N. The individual firm produces at OQ and at price P1. At this level of output and price, there is profit maximisation of the firm in the short run. In the short run, the equilibrium point will be considered at N. Therefore, the maximum profit of the firm will be P1PMP*.
Price and output Decision of Monopoly within the market structure analysis essay
The chosen industry that represents a monopoly in India is rail industry that is owned by a single government firm in the industry that is Indian Railways. Indian Railways is the only company that operates in the rail industry of India and is a state owned railway company. Indian Railway is seen to be a sole seller of rail services to the passengers in India. In addition to this there are other sources of market power such as Indian Railways has a separate capital intensive venture that is budget every year and economies of scale that restricts new entrant from entering the company. Indian railway is seen to hold 4th position as the largest railway network in the world after US and carry approximately 20 million passengers and 2 million tons freight daily (Pushpavanam, 2019). This characteristics of Indian railways aligns with that of monopoly market features such as single seller in the market with no close substitutes and high barriers to entry being a highly government regulated industry. Indian railway is seen to be the only seller of rail services in the country and go beyond brand identity and cannot be replaced easily by any other mode of transport for long journey. Indian Railway also holds the characteristics of a monopoly that is a price taker because they set the price for the rail routes and destination by themselves and is not impacted demand and supply in the market. Further, they also show high price discrimination for the service they sell such as selling different rates of prices for online tickets and counter tickets. Further, ticket prices also differs due to block price such as ticket charges reduces as one travels longer. Similarly, fares differs according to demographic attributes as well such as age (Goyal, 2008). This show that Indian rail industry faces all the three types of price discrimination that is first, second and third.
The price and output decision made by the rail industry in India depends on the distance of travel. It is seen that the more the distance the people travel the less is the price of the ticket. This means the more the quantity of service purchased the lesser the price of the service. This represents the characteristics of second price discrimination of monopoly where the price varies according to the quantity sold. This can be seen from the table below that show the more the distance travelled the less is the price for the ticket for Rajdhani 1st class AC fares.
|
|
Bangalore to Delhi |
Bangalore to Nagpur |
Nagpur to Delhi |
|
Rajdhani 1st AC fares |
4555 |
3245 |
2845 |
The table provided in this market structure analysis essay shows that the more the distance the less the ticket fare. The train fare for the Rajdhani 1st class AC from Bangalore to Delhi is comparatively less than the ticket rate from Bangalore to Nagpur or Nagpur to Delhi. This can be linked with the downward sloping demand curve and MR curve faced by a monopoly firm. This means the more the distance the lesser is the price burden felt by the passenger according to the service they are taking that is the service quantity from Bangalore to Delhi is huge and comparatively price is reasonable. However, service quantity from Bangalore to Nagpur is very less and comparatively price is only less by marginal amount.
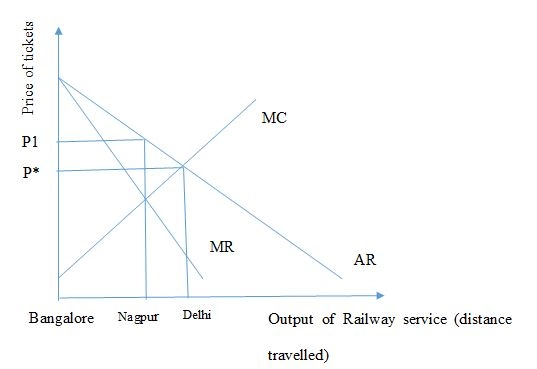
Figure- price and output decisions under monopoly
Sources- authors’ creation
From the above diagram given in this market structure analysis essay it can be seen that different price is charged for different quantity of rail service taken by the travelers. It is seen that when the traveler decides to travel from Bangalore that is at “0” to Delhi then they have to pay a price of P* and as the distance reduces from Bangalore to Nagpur then the price of the ticket increases from P* to P1. This shows that the more the distance of travel and the more far the destination is the lesser price is charged by rail industry in India under second price discrimination. Moreover, this also related to the downward sloping demand curve that shows a negative relationship between quantity of service charged and price for the service. This means that the output and price decision of Indian Railways being a monopoly firm is determined by discriminatory pricing policy especially taking in consideration second price discrimination
Efficiency of Chosen Monopoly
Monopoly market structure is not efficiently placed as the allocation of resources are not done in an efficient manner. It is considered as the most inefficient market structure of all the four types of market structure. The inefficiency in this market structure is due to the market control that the monopoly has over its price and quantity. Monopoly faces a negatively sloped demand curve and the price charged by them is greater than marginal cost. This inequality that occurs between the marginal cost and price is the way that makes a monopoly inefficient. In comparison to this the perfectly competitive firm allocates their resources efficiently at the point where their demand is equal to marginal cost. This shows that they have used their resources efficiently in producing that amount of good where demand has been able to be equal to their marginal cost. Further, monopoly is also stated to be inefficient because it produces a quantity at a price that is more than the marginal cost (Dang, 2016). This means that they are simply focusing on increasing profit by reducing their profit. however, competitive firms on the other hand is seen to charge price equal to the marginal cost and tries to absorb market efficiently. This shows that the inefficiency of monopoly market leads to a lower market outcome compared to perfectly competitive market.
This scenario of market structure analysis essay can be seen in Indian Railway also that acts like a monopoly in the rail industry of India. There are some instances of inefficiency of resource allocation and market outcomes seen in the context of this industry. There are some routes that lacks trains on a daily basis compared to the demand and traffic they face in that route. This shows the inefficiency that is created by Indian railways makes it charge high price compared to the rail service outcome and more than the marginal cost. For example the rail service from Bangalore to Delhi route, which is one of the busiest and longest route connecting many places lacks any daily trains and only have 9 weekly trains running from New Delhi to Bangalore (Cleartrip, 2019). This shows the inefficient market outcome of trains produced by Indian Railways due to inefficient allocation or use of its resources.

Figure- comparison of market efficiency between monopoly and perfect competition
Sources- authors’ creation
From the above diagram provided in this market structure analysis essay it can be seen that the total number of trains that is offered by Indian Railways as their service from Bangalore to Delhi is at 9 in which it is being able to charge a price of P1 due to negatively sloped demand curve AR. this price is more than the marginal cost of the service that the rail incur in rail maintenance, production and other services. In comparison to this being at perfectly competitive market would have allowed the rail industry to offer Q1 number of rail service in that route. This shows that in perfect competition the supply of rail service would have been more. Moreover, the price charged would also have been more in a perfectly competitive rail industry that is at P*. This shows that profit maximization production is efficient under perfect competition as it would have been equal to MC.
Break up of Monopoly
From the Indian Railways case study discussed in this market structure analysis essay it is seen that the railways has been able to improve the quality of rail service they offer by introducing superfast trains that are slightly increasing in speed. The rail company is investing in research to improve the speed of the trains for improving convenience and saving time of passengers. Further, the chances of getting Tatkal have increased over the years which means that the last minute travelers have benefitted from it. However, being in the monopoly market structure the company has been able to surge its prices. Without anyone noticing anything it is seen that the railway fares has hiked incredibly in the recent years. Further, the Special Railway Safety Fund was created for the passengers, however, instead of bearing the entire cost Indian Railways has levied some of its cost on the customers by adding it to the fare. Further, train fares are seen to increase incredibly nowadays depending on the time of travel, station to station charges, festival seasons and others (Pushpavanam, 2019). In addition to this, the rail has kept more percentage of ticket for tatkal and VIP quota ticket and this has left less seats for normal people that book ticket from advance. Through this policy the rail increases price.
From the above analysis within this market structure analysis essay it is seen that the number of positive points towards Indian Railways is less than the negative points. This is because increase in price is leading to huge inconvenience to the travelers and exploiting them in terms of their needs and demands. All the issues faced by the Indian Railway suggests that it is better to break up the monopoly power and introduce competition in the industry that is to make it an oligopoly so that the service is improved. This can be done by deregulating rail service and privatizing the service so that other companies can enter easily into the industry. Privatization will give more consumer choices, variety and better quality and price for trains. Indian Railways will offer better service and price with the fear of losing competition under oligopoly market (Ciliberto, Murry & Tamer, 2018). From the diagram it is seen that oligopoly will help in reducing the price from P1 to P and benefit the consumers highly at the same quantity of trains that is being offered by Indian Railways.
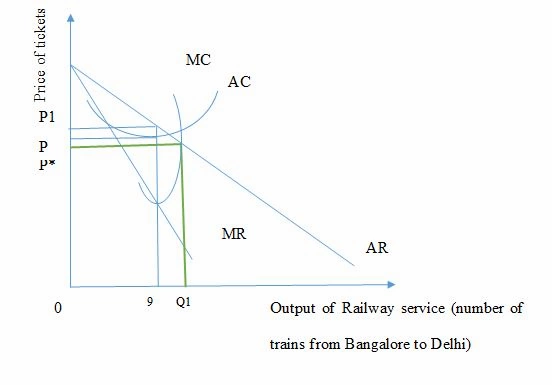
Figure- Movement from monopoly to oligopoly market structure
Sources- authors’ creation
Conclusion
From the above analysis within this market structure analysis essay it is concluded that monopoly has various negative impact on the society as seen from the data collected from Indian Railways which acts as a monopoly firm in the rail industry of India. It is seen that the monopoly offer inefficient market outcome and do not utilize its resources efficiently. The price increase and poor policy of IR is making it more prone to breakup and formation of oligopoly market in future.
Reference List
Ciliberto, F., Murry, C., & Tamer, E. T. (2018). Market structure and competition in airline markets. Available at SSRN 2777820.
Cleartrip. (2019). New Delhi to Bangalore Trains. Retrieved 24 August 2019, from https://www.cleartrip.com/tourism/train/routes/new-delhi-to-bangalore-trains.html/
Dang, C. H. E. N. (2016). Monopoly or competition: Market concentration of China's online games and policies. market structure analysis essay International Journal of Simulation--Systems, Science &Technology, 17(45), 1-4.
Gans, J., King, S., & Mankiw, N. G. (2011). Principles of microeconomics. Cengage Learning.
Goyal, A. (2008). Governance in India's public transport systems: Comparing Indian railways and airlines. Economic and Political Weekly, 119-127.
Hansen, M. (2013). Principles of microeconomics.
Pushpavanam, S. (2019). Privatise railways to break monopoly and encourage competition. Retrieved 24 August 2019, from https://www.ibef.org/industry/indian-railways.aspx
Varian, H. R. (2014). Intermediate Microeconomics: A Modern Approach: Ninth International Student Edition. WW Norton & Company.












