Marketing Assignment: Literature Review On Marketing Across UK & USA Cultures
Question
Task:
The marketing assignment is an individual piece of work that requires you to evaluate the literature on the subject of Cross-Cultural Analysis (CCA) techniques, considering that all the mainstream techniques still referred to today originate from the largely pre-digital and lesser- globalised era of the 1980s.
Your task
- To identify, discuss and critically evaluate the key perspectives of three key traditional CCA techniques (40%). This section requires you to review and discuss critically the classic CCA techniques such as Hofstede, Hall and Hall, Wills et al, etc. Analyse the perspectives from which these different techniques approach the issue of culture and marketing.
- To compare and contrast these key perspectives (30%). Here you should seek to identify what key differences in approach are evident. Reference to additional writer and journal article views and findings is crucial.
- To make justified conclusions regarding the relevance today of the CCA techniques discussed, and make recommendations for the use of CCAs in the 21st century (30%).All views put forward must be justified via the use of academic writings, from books and journal articles etc.
Answer
Background of marketing assignment
Marketers must realise how a greater perception of cultural nuances will boost the outcomes in an increasingly integrated global business setting. Marketing culture examines, according to Usunier, Lee & Lee (2005), how multinational corporations can acknowledge and adapt to diversity atthe international level. Much of the conventional methods used to perform intercultural research derive in this sense essentially from the last two decades of the 20th century, when digitalisation and globalisation were not given priority to enterprises, based on the opinion of Brodowsky& Schuster (2020). This following literature review of scholarly articles and journals will evaluate the viability of some mainstream techniques for studying marketing across UK and USA cultures and justify the most relevant technique to be used in the present time.
Identification and Critical Evaluation of Traditional CCA Techniques
It is not enough to be knowledgeable of cultural variations in the marketing process. More multinational promotional strategies are experienced to ask from the domestic markets by rising mobility between people and global markets. Digital marketing has improved decisively and has helped render company's activities for marketing strategy more powerful and successful, by prominence and use. Research by Trompenaars &Woolliams (2020) exclaims that a marketing strategy that reconciles such discrepancies is increasingly required. On the other hand, Hofstede (2015) stated that in present-day, strategic management almost consistently engages cross-cultural components. That is why understanding this concept is more important now than ever before.
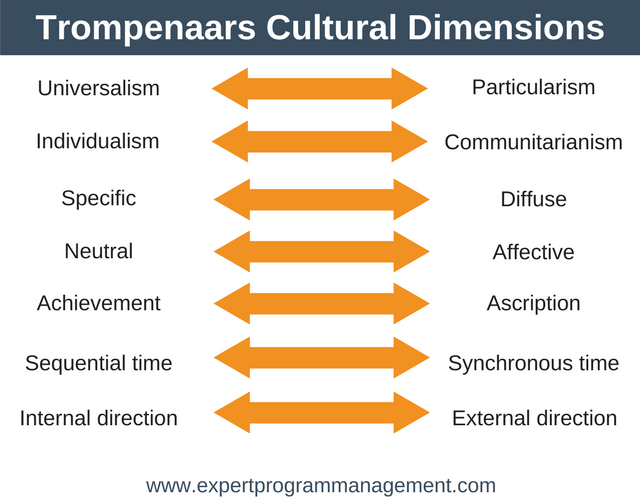
Hofstede Model of Cultural Dimension
The definition of culture should be based on a collective programme of the mind that discerns the members of the category of people or groups from others, according to Hofstede(2010). Geert Hofstede has suggested six cultural dimensionsto distinguish national cultures, their dimensions and the effect of the company (Hofstede, 2010):

Figure 1: Hofstede’s Culture Model
(Source: Hofstede, 2010)
The human resource related culture is used in business operation and marketing as it compare cultures to understand the human behaviour that helps marketers for effective campaign development. Each dimension in Hofstede model influences on one or more particular aspects of marketing, such as:
- Power Distance: adverstising appeals, service performance, behaviour of information exchange and innovativeness
- Uncertainty Avoidance: behaviour of information exchange, advertising appeals and innovations
- Collectivism: service performance, innovativeness and advertising appeals
- Masculinity vs. Femininity: sex role and service performance
- Long-Term Orientation: innovativeness
- Indulgence vs. Restraint: advertising appeals
Lewis Model of Cross-Cultural Dimensions
From the impression gathered from working in over 120 countries with different cultures, Lewis’ engagement through working, linguistics and travelling abroad has led him to develop his model of intercultural communication. As per Niemi (2019), Lewis’ model of intercultural communication divides the world into three extremes from a cultural perspective which all the nations and cultures belong to.

Figure 2: Lewis’ Culture Model
(Source: Niemi, 2019)
Leiws has proclaimed that the opinions which are the core beliefs of a nation, impose a crucial significance over culture as well as business and marketing,which is why it is necessary to understand the cultural differences while considering marketing for a particular region or country. However, it must be mentioned that no particular country should be thought of being purely neither linear-active nor reactive nor even multi-active since these characterizations are rather rough. Hence, a country or a culture, for example, can be linear-active as well as exhibiting some tendencies of reactive or multi-active. Niemi (2019) has further stated that it must be kept in consideration that such cultural variations are only averages and possibly not be true for every person in a nation, due to the existence of different attitudes rather than different regions only.
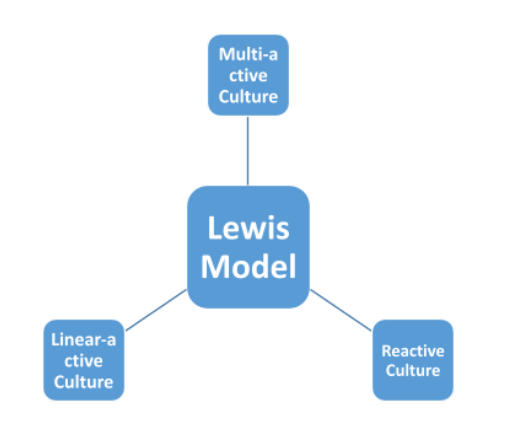
Trompenaars Cultural Dimensions
Several of the times as businesses collaborate with individuals from other culture, things go as planned. But Fons Trompenaars Cultural Dimensions Model will help if things don't go as expected and misconceptions occur. One of the most renowned economists in this field, Trompenaars began his study on the organisational pattern of the multiple cultures, stated by Carolina (2019). Trompenaars developed his model of cultural dimensions with seven dimensions:

Figure 3: Trompennaars’ Culture Model
(Source: Carolina, 2019)
Through the use of his theory, Trompennaars declared that cultural variations between organisations and cultures exist. Besides, this disparity has a direct effect on the way operations are carried out. He then felt that the approach in which a human community addresses challenges and settles dilemmas regarding marketing concners should be clarified by culture.
Comparison and Contrast of Key Perspectives of Hofstede Model
The Hofstede model of national culture has been proclaimed to be extremely popular by Minkov (2018) but is focused partially on faith. It was never replicated entirely and its statistical results were put into question. The author has evaluated the coherence and effectiveness of the paradigm and the results have strengthened individual collectivist operationalisations, indicating that it is a vigorous component of the culture at a national level.For several decades, Hofstede's theory continued, most definitely for its simplicity and complexity with management studies and his enthusiasm for sound bites that theory isn't simply easy to teach, but is easy to market, as Jackson claimed (2020). Yet this is precisely what has returned to droppings. Human culture is infinitely complicated and multifaceted. Positivist approaches and ideas offer a series of valuable insights into comparative philosophy but frequently struggle to grasp and justify the complexities, confusion and basic humanity of global community.
Therefore, a clarification is needed on the definition of the world market or global marketing. In general, the definition looks at the world as one market and is focused on cross-cultural similarities' recognition and targeting. Ghauri&Cateora (2009 ) claims that the global concept of marketing is focused on the assumption of cultural variations and is motivated by the assumption that each international market needs its own culturally relevant marketing strategies. As the economy expands internationally, it is profoundly important to consider marketing through cultures. As per Hofstede (2010), the definition of culture should be based on values and this is seen as basic elements of mental preparation and the focus of the defined meaning on the community may be the central trait of culture.
In this process, Hofstede describes six key concerns affecting all nations. The analysis between the UK and US in the appendix section (Appendix 4) will demonstrate the value of these six dimensions. The figure below indicates the percentage of each country in terms of each dimension. The prominent similarity between these two nations is seen to have a similar culture in terms of demonstrating their masculinity that drive individually. However, based on the ranking information obtained from Hofstede Insights (2020), this drive is not normally seen on the surface, and the reason behind the difference is the reflection of a higher ranking score of the US on the dimension of uncertainty avoidance than that of the UK. Stated otherwise, both societies contain same drive except USA citizens are open about it while it is a matter of surprise from UK citizens.
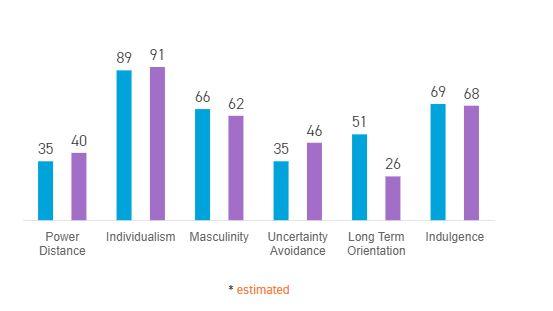
Figure 4: Difference in Six Cultural Dimensions between UK and USA
(Source:Hofstede Insights, 2020)
Relevance, Recommendations and Conclusion
Relevance of Hofstede Model to Marketing
The positivism within which Hofstede's' theory is based is not deeply relevant and recommended in the critical management circles. However, it is currently uninteresting to compare national cultures based on a few values or other dimensions. The cultural dimension of Hofstede is not only unimaginable but also a poor representation of reality as independent variables. Indeed, as De Mooij (2015) suggested, culture is not an element of the people, but it rather embraces several people, who have had the same educational and experience in life. Nevertheless, there is no global value to the motive for purchasing beneath. Hofstede has without any doubt established the cultural paradigm which was most useful and realistic, even useful in these days, but belonging to a pre-digital era before the trend of globalisation started, it loses its viability at many stages.
Recommendation for Marketers
As explained by Hermann (2020), brands predict the success of promotional activities, for which the significance of considering customers’ cultural attitudes and their interest in an online purchase is imperative. The essence of Hofstede’s concept is that culture is shared by its adherents from the point of view of a social phenomenon and that those cultural activities are to be found on the foreign market, which is why this model is still being used by MNC managers. Hofstede cultural model can be recommended because it is the most practical and renowned to comprehend the management of a nation. His cross-cultural comparison technique gives a possibility for understanding the type of organisations or individuals people have to work or collaborate with.
Conclusion
Over the years, cross-cultural marketing analysis has progressed from documenting cultural differences to defining significant and appropriate dimensions of cultural variation. These dimensions were then used to establish innovative theoretical trends which foresee and explain recorded differences. This study undeniably put culture on the marketing map. The cultural disparities, as discussed between UK and USA for example, affect the messages brands would provide to the consumers and can be especially successful at driving online shopping conversion rates at different times in the journey.
References
Brodowsky, G.H. and Schuster, C.P. eds., 2020. Handbook on Cross-Cultural Marketing. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Carolina, ?., 2019. Dimensions of National Culture–Cross-cultural Theories. Studies in Business and Economics, 14(3), pp.220-230.
De Mooij, M., 2015. Cross-cultural research in international marketing: clearing up some of the confusion. International Marketing Review.
Ghauri, P. and Cateora, P., 2009. International Marketing. Edinburgh Business School, Heriot-Watt University.
Hermann, Rico. 2020. Consumers' Perception of Online Video Advertising. 10.13140/RG.2.2.21754.11203.
Hofstede, G. (2010). Geert hofstede. National cultural dimensions, 2-7.
Hofstede, G. J. 2015. Culture’s causes: the next challenge. Marketing assignment Cross Cultural Management. pp.1
Jackson, T. 2020. The legacy of Geert Hofstede.
Minkov, M., 2018. A revision of Hofstede's model of national culture: Old evidence and new data from 56 countries. Cross Cultural & Strategic Management, 25, 231-256.
Niemi, R., 2019. With regard to programmatic advertising, are Lewis' findings on cultural dimensions still valid for millennials in the 21st century?, pp.1
Trompenaars, F. and Woolliams, P., 2020. Marketing research across cultures. In Handbook on Cross-Cultural Marketing. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Usunier, J.C., Lee, J.A. and Lee, J., 2005. Marketing across cultures. Pearson Education.
Appendix
Appendix 1: Hofstede Model of Cultural Dimensions
Appendix 2: Lewis Model of Cross-cultural Communication
Appendix 3: Trompenaars Cultural Dimensions
Appendix 4: Hofstede’s Six Dimensions Analysis of UK and USA
|
Dimension |
United Kingdom |
United States |
|
Power Distance |
|
|
|
Individualism |
|
|
|
Masculinity |
|
High score, reflects in behavioural pattern Combination of high masculinity and individualistic drives Showing success based on a precise setting for a target is a greater motivator than achieving success Dynamism in the society Gain higher status based on monetary reward Preference of fancy neighbourhood after each substantial promotion Several court cases and polarisation due to the belief of a certain level of conflict bringing best of individuals Endangered democracy due to rising inequality |
|
Uncertainty Avoidance |
|
|
|
Long Term Orientation |
|
|
|
Indulgence |
|
|












