Auditing Assignment: IT Audit Report Analysis Of Western Australian Auditor General
Question
Task:
This auditing assignment is designed to assess students’ ability to apply theoretical learning to practical, real world situations. In this assessment students are given an IT audit report conducted by the office of the Western Australian Auditor General and required to address the followings:
- Identify the audit focus and scope
- Describe audit findings in the Department of Health
- Describe audit findings in the Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety
- Describe audit findings in the Office of State Revenue
- Describe audit findings in the Western Australian Electoral Commission
- Describe audit findings in the KeyStart Housing Scheme Trust
- Discuss the professional, legal, and ethical responsibilities of an IT Auditor
Answer
Introduction
The key objective of this auditing assignment is to evaluate an individual aptitude to relate theoretical learning to convenient, real-world circumstances. For this study, the IT audit report performed by the office of the Western Australian Auditor General has been taken into considerations. Hence, the overall study will be focused on the IT audit report analysis by understanding relevant regulations, generally accepted auditing standards and ISACA's CORBIT framework. The report will assess the audit focus and scope, findings of the audit report in the Department of Health, Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety, Office of State Revenue, Western Australian Electoral Commission, KeyStart Housing Scheme Trust as well as legal, professional, and ethical responsibilities of an IT Auditor.
Furthermore, the IT audit report is based on Information Systems Audit Report 2018, wherein the report has been introduced for legislature under the Auditor General Act 2006, clauses of section 24 and 25. The audit report of information systems focuses on the computing terms of agencies to find out if these efficiently maintain the integrity, privacy and accessibility of the data they hold. Thus, the Information Systems Audit Report summarizes the outcomes of the 2017 annual cycle of audits as well as passwords examination and application reviews completed by the audit group information system since the previous years’ report.
Identification of audit focus and scope
The audit focus and scope generally reflects on the quantity of time and documentations that are concerned with an audit, which is an essential aspect in all auditing. The audit scope, eventually, creates how intensely an audit has been conducted by the auditor. Thus, it can vary from easy to entire, entailing all documents of a particular firm. Hence, within the Western Australian Auditor General’s Report on Information Systems Audit Report 2018, the audit focus and scope has been focused on the control applicability of audits and general computer and potential evaluations.
The audit focus and scope emphasizes the application reviews, findings per application and patient medical record system within the department of health. A review has been done within the applications of core business at 5 agencies and every execution seems to be essential to the functions of the agency and might affect a stakeholder that involves the public, in case the application and suitable processes are not organized properly. On the other hand, within the general computer controls and capability assessments, GCC audits has been conducted at 47 agencies with potential evaluation credentials by informing them to finalize and rewarding back at the end of the audit. Thus, a comparison has been done in the overall report that is based on the outcomes of GCC audits (Audit.wa.gov.au, 2018).
Discussion on audit findings in the Department of Health (DoH)
As per the report, it has been found that several hospitals in Western Australia use a record system for patient medical to make records for patient medical accessible digitally. Hence, it has been found that these applications record confidential information such as medical records and the identity of the patient. When analyzing the overall report, it has been found that the DoH is yet to determine if all records of medical health will be digitized within Western Australia. As per the figure below, it can be said that there is only 15% security of patient’s sensitive information and this can impact the comprehension of accepted effectiveness gains and developments in records of health care around the Heath system as of the execution of the application.
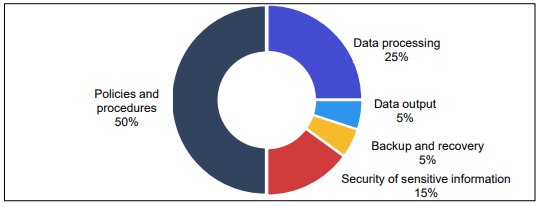
Fig 1- Patient Medical Record System- DoH
Sources- (Audit.wa.gov.au, 2018)
However, the audit findings in the DoH has been listed and discussed accordingly on the following grounds:
The need for digitisation strategy and not clear decision-making- A need for strategic track and functional supervision has affected the effective as well as the efficient application of the software application. Hence, it has been found that the DoH is not able to determine if all the records of the medical health can be digitized around Western Australia as the DoH are yet in the developing process for digital strategy. It has been found that the decisions concerning the design and use of Application are created at particular hospitals without concern of complete health needs. However, as per the audit findings, this enhances the threat that the application might not conduct against the purpose of minimizing the confidence in and value of holding a paper record, instant and synchronized access to records of medical as well as more effective practices of capture record.
The need for proper contract management- this generally means that the DoH cannot be determined if it is on budget and acquiring what it invest for. It has been identified that the DoH does not make out if the vendor contract and its cost are managed properly and effectively. Concerning this, a weakness has been identified in managing the vendor contract. Thus, a lack of responsibilities and roles for managing the vendor and no supervision of the contract cost has been identified.
Effective use of application- As per the DoH report, it can be said that the manual procedures could be inclusive of the effective usage of the software application. Hence, an opportunity for the DoH has been recognized to improve the application used by a better inclination to business workflows and functionality of report.
The threat of unauthorized access and misuse- It seems that there is a gap in the controls to protect the confidentiality of patients' records at threat of unauthorized access and misuse. Hence, the risk of improper access and misuse involves insufficient vulnerability management, the configuration of a weak password, ineffective management of user account, inadequate processes of continuity management, risks of application are not being officially managed etc.
Discussion of audit findings in the Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety
The Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety (DMIRS) uses the Tendency Bonds Management System (TBMS) to supervise the dealing out of residential and long-term tendency bonds.
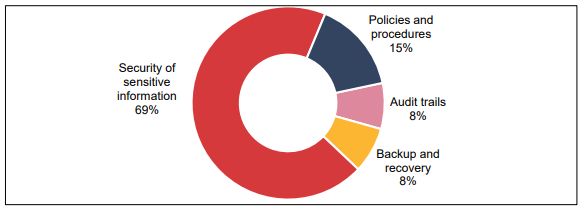
Fig 2- TBMS-Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety
Sources- (Audit.wa.gov.au, 2018)
Hence, the audit findings in the Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety have been discussed on the following grounds:
Risk of unauthorized access or misuse- Insufficient admittance controls raises the threat of unauthorized access or mishandling. Hence, within the TMBS, drawbacks have been identified with access controls by assuring users are properly authenticated and authorized is essential to the personal information security recorded within the application. Hence, some of the weaknesses that have been identified in the audit findings are:
- Configuration of weak password
- External user accounts are not managed well
- Insecure logins
Vulnerabilities of security are not organized- From the risk of cyber-attacks, DMIRS does not efficiently protect its system and the software vulnerabilities could be oppressed to acquire unauthorized access to data that is sensitive or interrupt the business of DMIRS. Hence, it can be said that it does not require frequent mending and vulnerability scans are significant for safeguarding systems as DMIRS do not possess a policy for management of vulnerability. Also, has not authorized, and is not maintaining its patch management process and is not utilizing the software of vulnerability scanning to conduct frequent scans to recognize vulnerabilities in its environment of IT to make sure that the patches are effectual.
Inadequate security controls- Due to a lack of insufficient security controls, sensitive data is at exposure risk. TBMS records personally recognizable data of owners and tenants that are more confidential. Hence, it has been found that DMIRS’ recent security controls are not effectual in securing the confidentiality, reliability and accessibility of information it records.
Inadequate Monitoring- It generally means unauthorized access or changes which neither are nor detected properly. A key activity in the TBMS is not monitored properly as DMIRS does not have official procedures or policies in place for supervision and logging. Thus, it can be said that without proper logging and supervision procedures and policy DMIRS might not be able to detect the access of unauthorized activity.
Discussion on audit findings in the Office of State Revenue (OSR)
The OSR uses the First Home Owner Grant Online system (FHOG Online) to conduct special payment for the eligible primary homeowner who is constructing or buying a new property. Hence, the system involves confidential private data about endowment applicants, involving the details of a bank.
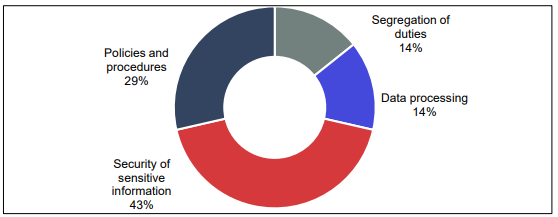
Fig 3- FHOG Online- Office of State Revenue
Sources- (Audit.wa.gov.au, 2018)
After analyzing the OSR, it can be said that the audit findings within this segment have been listed and discussed on the following grounds:
Inadequate security controls- Due to inadequate security controls, confidential data is at risk of unauthorized access wherein security controls of OSR are not effectual in securing the confidentiality, reliability and accessibility of the information it records.
Risk of grants and their inappropriate issuance- No proper allocation of duties increase the risk of grants and their inappropriate issuance. The Treasury Department has not allocated its processes of grant payment as it has been identified that the similar individual in Treasury processes grants payments and conducts settlements of payment. This is due to the lack of duties allocation that increases the risk of inappropriate grant payments.
Risk of errors- The manually executed processes is not effective and the risks of errors are mostly increased. The OSR depends on a considerable amount of manual processing to collect data in the system. Manual workflows are ineffective and augment the threat of errors in deciding the eligibility of applicants.
Discussion on Audit Findings of the Western Australian Electoral Commission
The election commission of West Australia is an authoritative institution that is responsible for managing and conducting an election in Western Australia. The Western Australian Electoral Commission manages the election-related information with the help is Election Management System WA. Following are the audit findings in the Western Australian Electoral Commission:
- Weak Security: The security system that is implemented to safeguard the data and information of the voters were found to be weak and exposed to various risks. This increases the risk of identity theft and the misuse of information related to voting. Security issues like insecure databases and weak personal information protection (Sear, 2018). Despite the policies that were implemented to secure the database it was found that these policies were not implemented. The general information of the voters is also extracted and used for other purposes without the consent of the voters.
- Absence of Recovery Process: The Western Australian Electoral Commission does not possess any kind of recovery process if the documents are destroyed. There is no IT Disaster Recovery Plan for giving details regarding the process through which the lost data can be recovered. Few recovery processes are being implemented but it is not fully approved or tested. This lack of recovery can hamper the elections and may cause a mass disturbance. The ethics and the integrity of the election process are questioned because the Western Australian Electoral Commission cannot recover the lost data.
- Presence of Manual Process: Several pieces of information and data are manually entered into the system. This increases the risk of error and misstatement because there is no machine intervention. The information of the legislative ballot is manually entered into the system. After the calculation of the election results, the results are again entered manually. The risk of error can be prevented if the Western Australian Electoral Commission automated the entry process.
- Tracking Changes: The Western Australian Electoral Commission uses an election management system and this system cannot identify the changes made to the information. The system fails to recognize whether the changes are authorized or unauthorized. This means that the person making the change can make some inappropriate changes in the information and the system will not detect any wrong activities.
Discussion on Audit Findings in the KeyStart Housing Scheme Trust
This scheme is operated with the help of the Keysmart system to manage and monitors inquiries related to home loans. Following is the audit findings in the KeySmart Housing Scheme Trust:
- Unauthorized Access: The first audit finding in the KeyStart Housing Scheme Trust is the unauthorized access to the information related to the loans. This is occurring because of insufficient management by the users who are setting up weak passwords. The Keysmart system stores all the confidential information of the consumers who are applying for a loan or who has already received the loan. Though the Keysmart system has a policy to safeguard the users' information the policy is not enough because it lacks application to a premium database system. 32 Keysmart system accounts were no longer in use for over 8 years and such unused accounts increase the risk of getting hacked. Through hacking a third party can extract all the information and make illegal used of that information. This can cause immense problems for the original account holder. Along with that, there were over 20 accounts that had passwords that were easy to guess. Passwords of many accounts were not changed and still had their default account. These default passwords are generally well known and easy to guess by other people. Moreover, there were 11 accounts whose password was not changed for many years.
- Updates and Configuration Settings: The accounts in the Keysmart system are exposed to hacking and other external harms because the system does not have robust configuration settings and advanced updates. Though the Keysmart system provides a management process for coping with the weakness, there are still issues in the servers of many workstations and its application. There were many weaknesses in the system that creates the risk of getting hacked and the hacker can have full access to the business information. Through access to the business information can hackers can disrupt the business process and the business can suffer immense loss. There were insufficient configuration settings that could make the security system of Keysmart robust. This security weakness hampers the confidentiality of the organization and makes the Keysmart system unreliable for implementation.
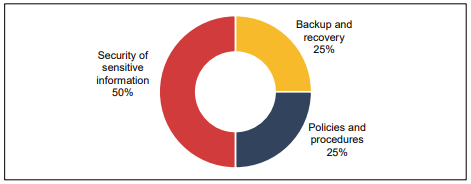
Figure 4: KeySmart System
Source: (Audit.wa.gov.au, 2018)
Discussion on Professional, Legal, and Ethical Responsibilities of an IT Auditor
Following are the professional responsibility of an IT Auditor:
- The very first professional responsibility of an IT Auditor is the preparation of an independent audit report. This report should be prepared by complying with all the given auditing standards.
- Making inquiries regarding the financial entries is another responsibility of an IT Auditor. The auditor is required to make inquiries wherever it is needed.
- IT Auditor is responsible for complying with all the Auditing Standards issued by the government. These standards provide guidelines to the auditors regarding the performance of their duties and responsibilities (Tuovila, 2019).
- If there is any kind of fraud in the financial report, it is the responsibility of an IT Auditor to report it to the appropriate authorities. Along with that an IT Auditor also needs to make an in-depth investigation regarding the fraud activity.
Following are the legal responsibility of an IT Auditor:
- The IT Auditor is responsible for ensuring that all the laws laid down by acts such as the Companies Act and Sarbanes Oxley Act are not violated while constructing a financial report.
- It is the responsibility of an IT Auditor to monitor and track the legal requirements that have to take into consideration for preparing a report.
- The legal responsibility of an IT Auditor allows him/her to take action against any kind of fraudulent activity detected after a proper investigation (Zager, Novak and Malis 2016).
Following are the ethical responsibilities of an IT Auditor
- The IT Auditor of an organization should have integrity and the clients expect that the auditor to respect and work according to their values and principles (Roy & Saha 2018).
- The reports prepared by an auditor should be free of any kind of influence and should not be biased. The relationship between the client and the auditor should not affect the outcome of the final report.
- The IT Auditor is not authorized to share their client's information with any party. The client's confidentiality should be maintained at all times and information should be shared with only the authorized participants.
- Continuous professional development needs to be done by the IT Auditors to improve their skill and techniques. With this, IT Auditors can improve their competency in executing their duties and responsibilities.
Conclusion
To conclude, it can be said that the overall report focuses on the confidentiality of an individual or patient and the technology that are secure enough to carry the stored data or information. The overall audit finding focuses on the weaknesses wherein each department require proper strategic guidance and supervision for an operation that has affected the effectiveness and efficiency of the management. Hence, there seems to be a weak configuration of password, insecure access to documents, unprotected individual information as well as poor IT controls.
References
Audit.wa.gov.au (2018). Western Australian Auditor General’s Report. [online] Available at: file:///C:/Users/USER/Downloads/wa-report_1318399503.pdf [Accessed 17 Mar. 2021].
Office of the Auditor-General 2018, Election Management System WA – Western Australian Electoral Commission, Office of the Auditor-General, viewed 17 March 2021,
Roy, MN and Saha, SS 2018, ‘Ethical Responsibility of Statutory Auditors in the Backdrop of Corporate Accounting Scandals: An Analysis of Respondents’ Perceptions’, Statutory Auditors’ Independence in Protecting Stakeholders’ Interest, pp. 287–354.
Sear, T 2018, If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it: Australia should stay away from electronic voting, UNSW Newsroom, viewed 17 March 2021,
Tuovila, 2019, Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS), Investopedia, viewed 17 March 2021,
Zager, L, Novak, A and Malis, SS 2016, (PDF) The Role and Responsibility of Auditors in Prevention and Detection of Fraudulent Financial Reporting, ResearchGate, viewed 17 March 2021,












