International Trade Assignment Analysing Structure of World Economy
Question
Task: You are supposed to write an international trade assignment on the topic “The International Trade Structure”.
Answer
1. Introduction
The growth of international trade is significant for the economies of the countries in the world as it impacts the financial development of the nations that participate in global business. In this report, the prominence and significance of international trade for the world economy are described with theories and structures. International trade and its concept are evaluated with accurate facts and data concerning the current situation in the global business of companies. The primary objective of this paper is to analyze the structure of the world economy with respect to the business operations that influences the economy of the countries around the world. Moreover, this report also examines the theories that are related to international trade and the approaches that are done by the companies, whichare innovative and creative.The backdrops of international trade that are faced by the company, which is challenging for the economy can be mitigated with effective strategies. In this report, recommendations are also made with respect to thechallenges that are faced by global companies for the future development of the international business.
2. Concept of International Trade
The concept of international trade can be explained as the exchange of goods, services and capital across the border of a country. International trade contributes immensely to the world economy and the national economy of any country (Vale, Perobelli and Chimeli, 2018). Initially, international trade began with the need for goods and commodities, whichwerein scarcity in a country but were in abundance in another country. This led countries to exchange products and services to meet demands. Traditionally there are only two types of international trade, export and import, but currently, a new type has been seen entrepot trade. Products and services of one country rendered by another country are referred to as exports of the former country, and the opposite is called import. Entrepot trade takes place when a certain product or service has been exported to one country, and it is further exported to another country after adding some external cost to it, by the receiving country (Tang et al., 2017). This trade is also known as re-export. Through these both import and export relations, the balance of payments is maintained. The open market for international trade has given the opportunity for all kinds of business to promote themselves in international markets and opportunities of the domestic market to access products available in other countries. A total of $39.7 trillion worth of trade was generated in 2018, that is, $18.9 trillion in imports and $20.8 trillion in exports. This contributed 46 per cent to the global economic activity(Falkowski, 2017).
For example, the concept of Comprehensive and Economic Trade Agreement (CETA) is a deal between Canada and EU in which the agreement helps the industries in both the countries to grow and develop in the market. Moreover, the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) is an agreement that was signed by the United States and European Union, which enhances job opportunities for the population of both the countries and provides products that are of low price.
International trade mostly deals with electronics and machinery such as boilers, computers, mobile phones, transformers and other scientific instruments (Wiedmann and Lenzen, 2018). This constitutes almost one-fourth of the total trade. Moreover, around 12 per cent of the trade deals with automobiles,which is followed by petroleum and other chemicals. Pharmaceuticals come next with 10 per cent of the trade. Through international trade, the transfer of knowledge and technology has also been observed. However, it leaves a risk of compromising with security and threatens the uniqueness of a brand.
The advantages of international trade outweigh the disadvantages strongly, but the disadvantages are considerable. A few private and central banks facilitate monetary transactions in international trade.
3. Structure of the World Economy
The world economy is the aggregate of economic activities of all the countries separately (Falkowski, 2017). Import, export and entrepot have contributed to the world economy largely. Almost 50 per cent of the world trade constitutes international trade. Through globalisation, not only international trade takes place but also a transfer of culture and ideas. The advent of international trade has led to an economic revolution, which went on to have a lasting effect on the global economy, due to which, the economic culture of every country has grown out of its bounds. Access to the global market has positively affected the growth of a country.
Domestic industries have grown due to the open global market. With the help of international trade, many countries have prospered with their indigenous products (Zhang et al., 2017). The external demands have created an opportunity for these countries to use their surplus. The open global market has provided several opportunities for third world countries to grow their economy. A constant cash flow has been generated through international trade. Through this cash flow, an exchange of currency takes place. The value of the currency in nations like USA, UK, France and other first world countries are much more than the value of the currency in countries like India, Africa, Sri Lanka and other developing and underdeveloped countries. Therefore, the export from the developing and underdeveloped countries to the developed nations have resulted in a larger profit. This, in turn, boosts the economy of the concerned country (Feenstra, 2018). Moreover, the demand for a particular product or service in the global market boosts the reputation of the country, which can consequently increase the demand forother products and services provided by the country. It has also been seen that a particular product which is of a reduced value in the respective country due to larger competition, has been able to gain massive popularity and demand in the other country where there is a scarcity.
The strengths of international trade are massive, but there are certain weaknesses. Availability of products and services in the global market has made it possible for anyone to copy the technology or idea, whichcan also be referred to as intellectual theft (Zhang et al., 2017). The thought behind a product or service, which makes it unique and increases its demand in other countries are often observed to have been copied within a few months of its advent. Moreover, customer information is also asked as a mandatory step in the process of buying from other countries, which threatens privacy and security. A hefty shipping charge across country boundaries is also an issue faced by consumers, which has caused many customers to refuse to buy from other countries. Furthermore, cultural and language difference has created hindrance in the smooth running of international trade.
4. Theoryof International Trade
The concept of trade is to exchange services and goods among two entities or individuals. In international trade, the exchange of goods and services are done in between the entities of two different nations (Krugman, Obstfeld and Melitz, 2018). International trade is carried out for the benefit of two or more different countries. It is an agreement among the government of the countries that are participating in international trade to facilitate each other with finances or other services. Moreover, in international trade, there are deals that are done based on the policies, theories and strategies in the business environment (Suttle, 2017). The economists in the current generation are focused on the theories that are helpful in enhancing international trade for the development of the economy, especially in the underdeveloped and developing countries. Trade theories are not new terms that the countries are acknowledging (Prystupaet al., 2019). The theories are existing from the historical period as earlier the trades used to take place to belong to the hierarchies of the states or the countries. One of the most prominent trade theory of the historical period is the classical or country-based trade theories.
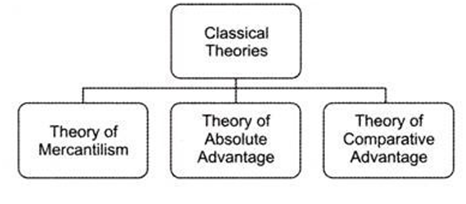
Figure.1: Trade Theories
(Source: Görgün, 2019)
4.1 Mercantilism
Mercantilism was developed in the sixteenth century, and it is the first effort that was made to develop and improve an economic theory. According to this theory, a country was termed established by determining the amount of gold and silver the nation possess (Feenstra, 2018). In this theory, the countries that were wealthy used to discourage imports and promoted exports for economic benefit. The aims and goals of the countries were to collect a considerable amount of gold or silver in return of the services they used to provide to other nations, which was known as trade surplus (Viner, 2016).With the increase in exports, the rulers of the countries used to make sure that the region is flourishing and benefitting from the strategies that are formed for the development of the economy. Restrictions were imposed on imports, as the rulers at that time wanted to collect gold for the country, which is termed as protectionism. The strategy of protectionism is still in use, as many countries follow the classical theories of trade.
However, some weaknesseswere noticed in this theory, as in many countries, there were limited supply of products and services. The nations that opposed import faced specific challenges, as they were unable to produce the products, which became a major problem in earlier times.
4.2 Comparative Advantage
Comparative advantage came right after mercantilism as the business transactions observed extensive challenges with the historical approaches. The countries that are producing goods are an advantage for the economy according to the comparative advantage theory (Cohen, 2019). As per the theory of comparative advantage, if there are two countries that are better at producing the goods that are unavailable in the opponent nation, there was an exchange of products between the two entities (Görgün, 2019). The theory of comparative advantage primarily focuses on productivity differences with definite improvements in business transactions. The agreement between the countries is based on the exchange of products that are available in huge quantity. Through this method, the policy of trade agreements was based on legal regulations as the countries agreed to serve the nations that were unable to produce any productive services or goods (Barua, 2019). This theory is related simply to the “give and take”policy. Furthermore, this theory of comparative advantage is still in use in recent times, especially in developing countries.
4.3 Modern and Firm-based Trade Theories
After World War II, modern-based theories came into effect, which is contrasting, to the classical theories. This theory was developed by business school professors and not by economists. The evolution of the firm-based theories is mostly related to the multinational companies as these firms are growing largely in the international business (van Aaken and Kurtz, 2019). Firm-based theories are currently in use by the international firms as it provides the intended economic support to the countries(Allen, Noseworthy and Ormsby, 2017). The new approach has been adopted by most of the firms in the global domain because the country-based theories were inadequate to address the expansion and improvement of the interindustry trade or MNCs (Hung, 2020).This kind of trade is carried out between two nations that produce goods in the same industry. As for example, Germany exports Mercedes-Benz to Japan, and in return, it imports Toyota from Japan. In addition, firm-based theories highlight the incorporation of service and product factors, which includes customer and brand loyalty, quality, technology in order to understand the flow in the trade, especially in the international market.
4.4 Porter’s National Competitive Advantage Theory
The international trade theories are continuing to evolve with time as the global firms are applying effective and efficient strategies to survive and sustain in the market. Michael Porter from Harvard Business School developed this business modelin the year 1990. The theory stated that the competitiveness of a country in a firm depends on the industry’s capacity to upgrade and innovate itself in the market (Król, 2019). The primary focus of this theory is to analyse the advantages a nation gains in the international market. There are four determinants that in this theory that are explained by Michael Porter which are (1) domestic market capabilities and resources, (2) demands in the local markets, (3) complimentary industries and domestic suppliers and (4) characteristics of local firms.
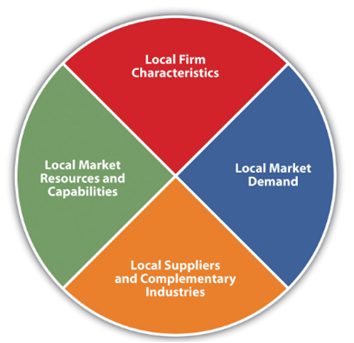
Figure.2: Theory of Porter’s National Competitive Advantage
(Source:Görgün, 2019)
The international trade theories that are explained in this section have helped thegovernments, economists and businesses to acknowledge the strategies of international trade in order to promote, manage and regulate it. Thus, the theories that are formed regarding international trade are influential in the development of the world economy in a significant manner.
5. Innovative and Creative Approach in Global Trade
The industries that are carrying out their business all over the world are adopting methods that are creative and innovative as the customers around the world get attracted by experimentation and innovation. The creative economy is understood as a catalyst that acts significantly in becoming a contributor to the domestic products that are also sold in the global markets. Innovation in the global business has transferred creativity and knowledge across many sectors of the economies that are developed as well as in the underdeveloped entities (Antonelli, 2019). In order to develop the sector's creativity is regarded as a strategy that is effective in managing to attract customers from all over the world(Gorgoni, Amighini and Smith, 2018).Moreover, the businesses that take creativity as an approach to improve the business gains cultural and commercial value in the global domain. The governments worldwide are recognising the value of innovation in the business ideas to develop and expand the businesses (Shafi, Sarker and Junrong, 2019). Creativity also provides a competitive advantage in the global markets for the companies so that they are able to sustain for an extensive period of time, which includes making better connections with traders from other nations and creating a diversified route of trading goods at a lower cost.
The companies make most of the approaches in the creative segments by analysing the global trends in the markets. Customers are always fond of the products that have a brand image in the market and is of high value. The international brands are opting for digital advantages, as the customers are more inclined towards the internet for their products (Jackson, 2020). The companies do the delivery of services and products in any region of the world so that they are able to hold customers loyalty and emerge internationally in the market. This has been possible primarily because of the innovation of technologies as technology is effective in attracting customers from all over the world.
The companies adopt technological innovation so that they are able to analyse the demands of the customers in order to retain them. Global trade has become easier after the introduction of technology. The companies are also interacting with the customers through digital platforms by making their approach creative towards the customers (Abbasi, Vassilopoulou and Stergioulas, 2017). Creativity is aligned with the engagement of the customers with the brands that are done by the employees of the companies. Thus, innovation, along with creativity, has played a significant role in supporting the companies that are operating in international trade.
6. Practical Recommendations for International Trade
6.1 Customs
There are at least two custom interventions during international trade, which are import and export. To develop a smooth flow of goods and commodities across custom, both the parties should consult about their exchange and increase coordination and for a faster and more efficient process. Better policies should be formed by the government for the smooth working of custom. Through the authorities of customs, governments need to consult with the parties that are interested, to define corporate objectives for customs. The corporate objectivescan be published for a long-term plan to achieve these objectives. The use of information technology can be increased to assist customs in the performance of their duties. All the countries need to develop computer applications for the customs processing of financial and commercial transactions. The program of UNCTAD should be taken into consideration for implementing the Automated System for Customs Data in customs reform and computerisation. The interfaces of customs, including the electronic submission of manifests, goods declarations and others need to be developed to make it available for international traders.
6.2 Banking and Insurance
Payment and risk management products are determined to be the critical elements in the development of international trade in the world. The development is required due to the availability of current finance that is related to trade. The efficiency of trade in financial services has influenced the performance of medium and small-sized companies. The participation of these firms in international trade with the exporters of other nations has been impacted (Shousha, 2019). The growth of markets for the services regarding finance will enable improved global trade in services and products, which will further enhance the levelsofproductivity. Besides, addressing the aspects regarding the structure of the market for the financial services of trade furtherformulates policies in the regulation area. Policymakers need to consider the indirect along with the direct financial impact of the limitations that are affecting the economic services regarding trade. The recent regulations and laws, which are affecting international payments, trade finance and insurance in the international market, need to be reviewed to assure global practices.
6.3 Transport
Transport is directly related to international trade, which is an essential aspect of successful trading in the global market. There is a demand for the implementation of trade efficiency measures in the transport industry for the growth of international trade. Governments need to support the international growth of trade by reviewing the laws and regulations of current transport. In addition, governments need to encourage the adoption of commercial practices in the transportation investment and chain by foreign as well as domestic investors. Governments can implement specific operations for improving transport. It can include the formation of block train services and the development of multinational transport operations. Additionally, governments can provide rules to update commercial insurance and banking practices that have been recommended by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). Subregional cooperation projects concerning the coordination of the policies of legal regimes and transport regulatory to identify global solutions of these problems. The establishment of sub-regional databases on transportation needs to be encouraged by the government.
7. Conclusion
International trade among various countries exists from an extensive period. The world economy withstands on international businesses, as it is a source of financial support for the countries worldwide.International trade and its concept relyon the agreements that are among various countries for the achievement of benefits and facilities, especially regarding the economy. The structure of the world economy determines the advantages and disadvantages, along with the weaknesses of international trade. In this report, international trade theories are explained that aligns with the business deals between the countries. Moreover, the strategies that are adopted by the international companies for trade are innovative and creative in nature, which attracts the customers, are evaluated in detail in this report.
References List
Abbasi, M., Vassilopoulou, P. and Stergioulas, L., (2017).Technology roadmap for the creative industries. Creative Industries Journal, 10(1), pp.40-58.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17510694.2016.1247627
Allen, E., Noseworthy, M. and Ormsby, M., (2017).Phytosanitary measures to reduce the movement of forest pests with the international trade of wood products. Biological invasions, 19(11), pp.3365-3376.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10530-017-1515-0 Antonelli, C., (2019). The creative response and international trade.https://iris.unito.it/handle/2318/1717421
Barua, A., (2019). POSTIVE THEORY OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE.http://ris.org.in/others/Exim%20Summer%20school/Summer_%20School%202019/10-06-2019/Mr%20Alokesh%20Barua.pdf
Cohen, H.G., (2019). What is International Trade Law For?. American Journal of International Law, 113(2), pp.326-346.https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/american-journal-of-international-law/article/what-is-international-trade-law-for/F8C98A6B262B92A3C97632E402D01EDC
Falkowski, K., (2017). Long-term comparative advantages of the Eurasian Economic Union member states in international trade. International Journal of Management and Economics, 53(4), pp.27-49.https://content.sciendo.com/view/journals/ijme/53/4/article-p27.xml Feenstra, R.C., (2018). Alternative sources of the gains from international trade: Variety, creative destruction, and markups. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 32(2), pp.25-46.https://www.aeaweb.org/articles?id=10.1257/jep.32.2.25
Gorgoni, S., Amighini, A. and Smith, M., (2018). Automotive international trade networks: A comparative analysis over the last two decades. Network Science, 6(4), pp.571-606.https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/network-science/article/automotive-international-trade-networks-a-comparative-analysis-over-the-last-two-decades/5EDFCE13AAF00B5F52886308D9E33B40
Görgün, M.R., (2019). CLAssICAL INTERNATIONAL TRADE THEORIEs. RECENT ECONOMIC APPROACHES & FINANCIAL CORPORATE POLICY, p.247.https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=oqLEDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA247&dq=theory+of+international+trade,+pdf&ots= 8Yj4OJGfJi&sig=CekgyOPiRKdEI3g0_EHrGJ-wisQ
Hung, H.F., (2020). Trade Battles: Activism and the Politicisation of International Trade Policy.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0094306119889962s Jackson, E.A., (2020). Fostering sustainable innovation through creative destruction theory.https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/id/eprint/102174
Król, K., (2019). Trade Theory in International Economics. International Journal of Tax Economics and Management.https://journals.seagullpublications.com/ijtem/archive/f_IJ0620190550.pdf
Krugman, P.R., Obstfeld, M. and Melitz, M.J., (2018). International trade: theory & policy. Pearson Education Limited.http://103.227.140.9/handle/123456789/18291
Prystupa, L., Koval, V., Kvach, I. and Hrymalyuk, A., (2019), September.Transformation of cycles of state regulation in international trade.In Strategies, Models and Technologies of Economic Systems Management (SMTESM 2019).Atlantis Press.https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/smtesm-19/125917662
Shafi, M., Sarker, M.N.I. and Junrong, L., (2019).Social network of small creative firms and its effects on innovation in developing countries. SAGE Open, 9(4), p.2158244019898248.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/2158244019898248
Shousha, S., (2019). The dollar and emerging market economies: financial vulnerabilities meet the international trade system. FRB International Finance Discussion Paper, (1258).https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3473069
Suttle, O., (2017). Distributive justice and world trade law: a political theory of international trade regulation (Vol. 36). Cambridge University Press.https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=1-w0DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR15&dq=theory+of+international+trade,+pdf&ots=kxsREu2JBW&sig =8zF5qK_G45qIcsQe5IkB8Gt-B4E
Tang, X., Jin, Y., Wang, X., Wang, J. and McLellan, B.C., (2017). Will China’s trade restructuring reduce CO2 emissions embodied in international exports?. Journal of Cleaner Production, 161, pp.1094-1103.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652617310004
Vale, V.A., Perobelli, F.S. and Chimeli, A.B., (2018). International trade, pollution, and economic structure: evidence on CO2 emissions for the North and the South. Economic Systems Research, 30(1), pp.1-17.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09535314.2017.1361907
vanAaken, A. and Kurtz, J., (2019). Beyond rational choice: international trade law and the behavioral political economy of protectionism. Journal of international economic law, 22(4), pp.601-628.https://academic.oup.com/jiel/article-abstract/22/4/601/5695631 Viner, J., (2016). Studies in the theory of international trade.Routledge.https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=Q1duDQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT12&dq=theory+of+international+trade,+pdf&ots=L6oBpAeqCo&sig=TsdrjJ7aP7YP5EH6zRNTCKo080I
Wiedmann, T. and Lenzen, M., (2018).Environmental and social footprints of international trade. Nature Geoscience, 11(5), pp.314-321.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-018-0113-9
Zhang, L., Chen, T., Yang, J., Cai, Z., Sheng, H., Yuan, Z. and Wu, H., (2017). Characterising copper flows in international trade of China, 1975–2015. Science of The Total Environment, 601, pp.1238-1246.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969717313232
Zhang, Q., Jiang, X., Tong, D., Davis, S.J., Zhao, H., Geng, G., Feng, T., Zheng, B., Lu, Z., Streets, D.G. and Ni, R., (2017).Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature, 543(7647), pp.705-709.https://www.nature.com/articles/nature21712?fbclid=IwAR18vzsqXjECFfNK7Cn5Buvttwf_P7OY4qNGYh3lmR60Q11bqW5xsQTc4PM












