International Finance Assignment: Impact of Negative Rate of Interest on Finland’s Economy
Question
Task
In recent decades, some major economies and regions, including Japan, the Eurozone, and a few others, have adopted zero and then negative interest rates; a historically unconventional monetary policy response. This international finance assignment requires that you investigate Finland’s adoption of a negative interest rate policy and the implications for its currency’s value and develop an essay on this topic. In this essay you will need to explain why any noticeable volatility in the currency’s exchange rate against the US dollar occurred, giving adequate reference to knowledge learnt during the course. You need to cite appropriate references from academic journals, government announcements and publications, newspapers, institutional reports, etc., to support your argument.
Answer
Introduction
A negative rate of interest, discussed in the international finance assignment, occurs when the rate of nominal interest drops below 0% for some specific zone in the economy. It also shows that the financial firms and banks had to pay and keep the excess reserves get stored within the central bank instead of receiving positive income from interest. In this study, the main discussion is based on the negative rate of interest on Finland’s economy and its impact on livelihood. It will discuss the negative effect on the monetary value and exchange rate. Moreover, the study will also discuss both the disadvantages and advantages of the negative interest rate of the policy.
Define monetary policy
Monetary policy is said to be a set of many tools used by the central bank of the nation which is available to promote economic growth in sustainability through controlling the money supply overall, which is available for the businesses, nation's banks, and consumers. As stated by Thornton and Vasilakis (2019), the main goal of monetary policy is to keep the nation's economy humming at a certain rate. It is considered to be the main weapon for the disposal of the nation's money. The central bank also plays an important role in setting the rate that it charges for loan money, especially to the banks of the nation. During the high and low rates, all the financial institutions the rates tweak that is being charged on customers by big businesses that have been borrowing money from the bank for major projects and applying for mortgages. Monetary policies are broadly classified into contradictory or expansionary. As opined by Bongiovanni et al. (2021), the tools that are being included for revising the rate of interest up and down are direct lending of cash to some banks and also changing the reserve requirements of the bank. On managing the supply of money, the aim of the central bank is mainly to influence the factors of macroeconomic which include consumption rate, overall liquidity, inflation, and economic growth.
Implications of having a negative rate of interest
A negative rate of interest is a form of policy of monetary which looks at the rate of interest falling below 0%. Regulators and central banks mostly use this as a policy tool during the strong signs at times of deflation. Further charges are made by central banks on reserves of commercial banks for incentivizing the effort on spreading instead of hoarding cash positions. A negative rate of interest is regarded to be a form of policy in monetary value that looks at the interest rate falling below would change most of the financial aspects on a personal level which is as follows:
- Loans: Nordea Bank, which is based in Finland, has been offering mortgages for 20 years at the rate of 0% interest for last year. Moreover, it sounds incredible since most of the analysts warn banks that an extremely lower rate of interest given on mortgages drives the prices of housing higher. As discussed by Corneille et al. (2021), with a higher price in housing, the borrowings become cheaper, and demand increases subsequently. Apart from that, with a higher price on every product, the purchasing power of an individual also gets disturbed, and they tend to purchase less. Furthermore, the rise in the interest rate on providing loans may hamper the banks, which allow them few customers to take loans.
- Products and Savings account: Savings account yields would get crushed by the negative rate of interest. As discussed by Grasselli and Lipton (2019), the main function of a negative rate of interest is on encouraging spending rather than keeping money fixed away into an account. Moreover, it is believed that a high-yield of savings account can result in a distant memory. It is believed that big savers are more prone to hit hard through negative rates of interest. A negative rate leads to create more accounts paying 0%; hence, the deposit value will further get eroded through inflation. However, wealthy savers can face charges on holding sums with a large amount of money with deposits.
- Credit Cards: Negative rate of interest certainly depress the rate of interest for credit cards. As quoted by Hameed, and Rose (2018), the negative rate of interstate it has a minimum impact on debt of credit card, overdrafts, or personal loans. Moreover, the cost of borrowing will remain the same since the lender's rate of interest charged will continue to be as earlier. It has been seen that a negative rate of interest may pull it lower since it seems to be unrealistic to expect on getting paid for most of the time on swiping up the credit card. As stated by Thornton, and Vasilakis (2019), hence the credit card faces major consequences due to a negative rate of interest that may affect the consumer acquiring lending rate. Therefore, the country also has to face negative impacts with lower interest rates or negative interest rates for credit cards.
Effect of the negative rate of interest on the time value of money
An ambience of a negative interest rate commences in situations when the nominal rate of interest is below 0% for a particular economic zone. This efficiently implies that financial firms and banks have to make payments to retain their extra reserves warehoused in the central bank instead of receipt of interest income that is positive in nature. The interest rate that is negative is referred to the payment of interest to borrowers instead of making it to the lenders. It is found that commercial banks are charged by Central Bank in a natural course on their reserves in the form of unfurling monetary policy of non-traditional nature instead of crediting those (Nucera et al., 2017). This is an uncommon scenario that usually takes place during the situation of profound economic recession when market forces and monetary efforts have pushed rates of interest to their minimal zero bound. This policy is implied to motivate spending, lending and investment instead of hoarding cash, which is bound to lose worth deposit rates of negative nature.
The rate of interest is normally known as the borrowing cost. This implies that interest is charged on the borrowers by the lenders in case of any kind of debt, such as a mortgage or loan. In the situation of a negative interest rate, the lenders don't charge from borrowers; instead, they pay the interest so that they don't hold on to their spending or investment in the market. The time value of money can be referred to as the level in the available cash in the present time is valued more than equal amount at some situation in the forthcoming period because of its probability for growth (Goodfriend, 2016). The rate of interest is the chief quantifiable representation of the economic worth of money. While making an investment in bonds, for instance, the rate of interest enhances the worth of deposited cash with time if left without being invested. Hence, it is said that bonds of low risks cannot always offer the investors the needed return anticipated on their amount of investment through the appreciation of assets with time because of numerous factors of risk intrinsic in rates of interest such as inflation.
In recessionary ambience, and at situations when a circumstance of expected, risk-free assets are demanded more (reduction in efficient yield and brash up the price) as the return security they offer becomes more highly worth. The assets can even straight influence the rate of interest on any kind of investment replicated in the time period to liquidity, default risks and maturity of that bond (Lilley and Rogoff, 2019). Essentially, it can be said that the interest rate of negative nature interrupts the time value of money. Hence, the aim is on the role of the Central Bank in pursuing the policy of a negative rate of interest is to interrupt the time value of money. Hence, it can be like $1 that has the receipt in the current situation would have less worth than $1 that has been received in the forthcoming year.
Defining noticeable volatility on the exchange rate of currency against US dollars
The significant volatility of the currency exchange rate (Euro) against the USD occurs by the factors that influence the value of EUR/USD and other currencies. For this reason, the differential interest rate between the ECB and Fed affects the values of both the currencies when compared with one another. For instance, when the federal bank interferes in the open market operations with an aim to make USD stronger, the value of EUR/USD cross declines due to the strengthening of USD as against the Euro (BA?ARIR, 2018). Poor economic reform in the EU economy results in noticeable volatility in the currency exchange rate as compared to USD.
The Federal Bank policy is responsible for bringing in massive currency exchange risk for Euro as compared to the USD. For instance, the hike in the interest rate was first announced by the Federal Reserve In December 2015. That target increase for the federal funds ranges from 0.25% to 0.5%, from the last range of 0% to 0.25%. Moreover, the Fed Policy ceased the purchase of bonds in late 2014. The two policies led to a sharp decline in the Euro in comparison to the USD that was used by ECB. The Greek crisis caused a depreciation of the Euro after the parliament approved the financial budget involving 5.7 billion Euros to be made for public spending. Despite the frequent reduction of 500 million Euros in defence and 1.8 billion Euros from a pension, Greece recorded a deficit budget for the year 2016 that surpassed its previous year's record (Bahmani-Oskooee et al., 2020).
The monetary policy implemented by ECB with regards to interest rate policy is another major factor that led to currency risk for Euros. In 2014, ECB imposed a negative interest rate of 0.1% on the deposits that it was holding (Quoreshi et al., 2019). Further, the rate lowered by ECB in September 2014 t -0.2%. The frequent downfall of interest rates affects the exchange rate risk for the country. Although, ECB implemented a negative interest rate to positively affect the economy by giving the people the allowance to borrow to offer more money to the organization and consumers at lower interest rates. In addition to this, trade speculation by investors affects the worldwide forex market probing a high risk on the currency risk volatility. In recent times, Euro has gained substantial interest among global investors.
Why did Finland adopt the policy of a negative interest rate and its implications on currency value?
Negative interest rates on the economy are used by the country's central bank to increase lending during an economic recession. The provision of negative interest rates by the central bank reduces the economic cost of credit, which aims to stimulate economic activity through increased investment and consumer spending. In 2014, the European Central Bank, or ECB, became the first central bank in history to adopt a negative interest rate policy to address the crisis in the euro area (Smith, 2021). The ECB cut the deposit rate to -0.10% in 204 to end deflation and free the economic bloc from prolonged downtime. The current ECB deposit rate is -0.5%, the lowest ever. The Bank of Finland has introduced negative interest rates in Finland as a subsector of the Eurosystem as part of its monetary policy. The financial operations of the Bank of Finland reflect the balance sheet results, which consist of assets acquired and deposits on loans with banks operating in the country.
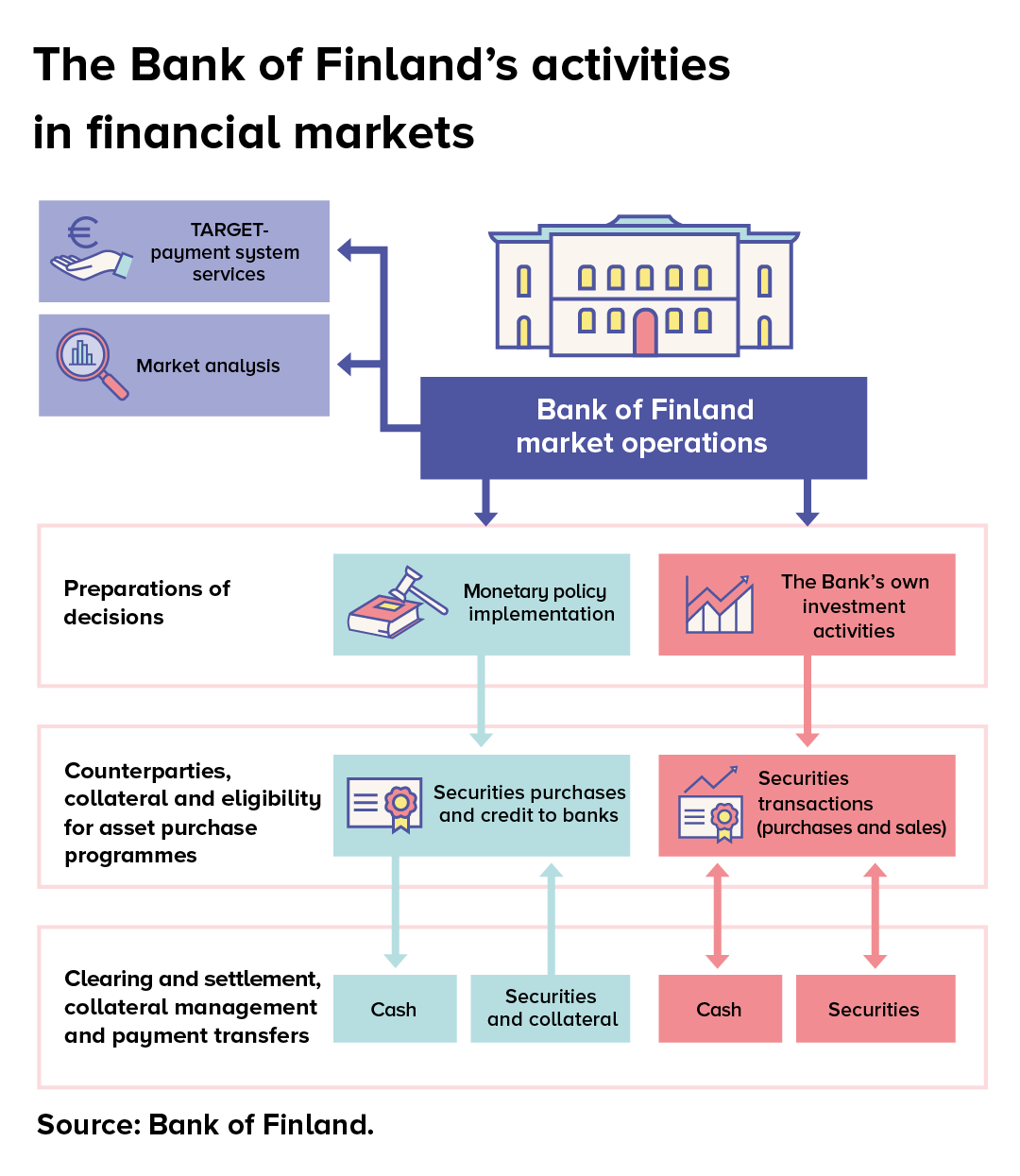
Figure 1: The Bank of Finland’s activities in the financial market
(Source: Välimäki et al., 2020)
The graph above shows how the Bank of Finland manages its net financial assets in the financial markets. The main reason for introducing negative interest is to achieve price stability. Negative interest rates keep inflation stable by boosting economic growth and employment, and preventing unexpected disparities in wealth and income. The ECB also aims to limit the annual inflation rate in Europe between 0% and 2% in the medium term. The three economic crises that Finland has faced over the past three decades are the reasons for introducing negative interest rates in the country. In the early 1990s, with the fall of the Soviet Union as its largest export market, Finland was faced with a banking crisis and losses. The global financial crisis, which was followed by the European sovereign debt crisis, caused the economy to lose a decade of growth between 2007 and 2017 (Suerf.org, 2021). Lastly, the ongoing Covid-19 presents Finland with an economic challenge by decreasing demand for goods in overseas markets.
The introduction of interest rates negatively affected the value of the Finnish currency and financial position.
Loans: Europe has a big impact on lending due to negative interest rates. For example, Nordea Bank in Finland offers a 20-year mortgage at 0% interest. Jyske Bank in Denmark serves 10-year loans at -0.5% annual interest. On the other hand, mortgage rates that are too low lead to higher property prices because loans become cheaper and demand is high. Credit Cards: Negative interest rates reduce credit card interest. The average credit card interest rate was 16.61% based on data from the Federal Reserve for the first quarter. Lowering interest rates further would be an unrealistic situation for everyone as it is impossible to get paid every time someone shows their credit card.
Currency Value: Low or negative interest rates mean foreign investors get lower returns on investment. This leads to a devaluation of the currency, which leads to lower demand for the domestic currency. A negative interest rate lowers the exchange rate, which encourages unnecessary competition between countries that export homogeneous goods and with exchange rate fluctuations that are often undesirable.
Advantages and disadvantages of negative interest rate policy
The policy of a negative rate of interest brings extra undoing of monetary policies that can improvise the macroeconomic viewpoint. Improvised prospects for the real economy should decrease boosting of the profitability of banks and impaired loans. The consequential enhancement should be sufficient to counterbalance the influence from the decreased income of interest. Numerous industrial nations such as Denmark, Sweden and Japan have employed them to offshoot their economies and last to apply them. Amidst the cluster of Euro, countries have been negative since the year 2014.
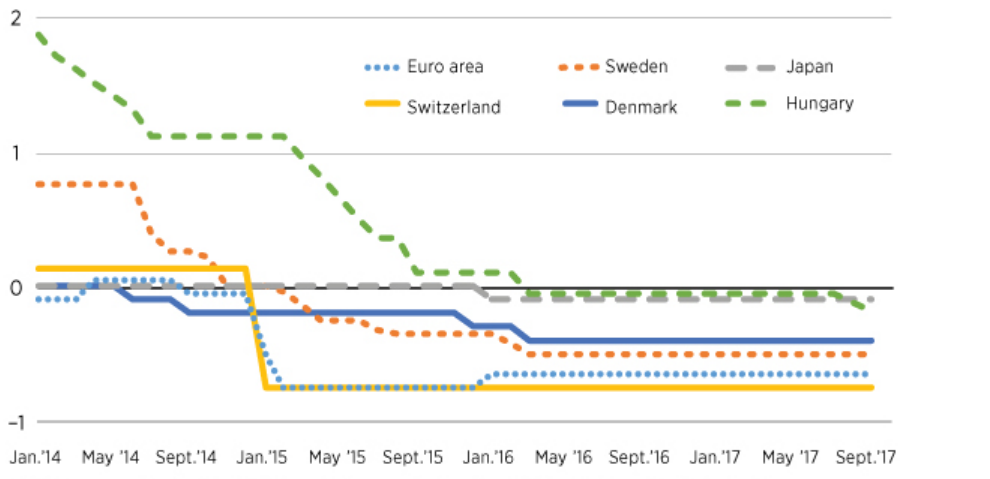
Figure 2: The policy of Central Bank of Interest rates
(Source: Palley, 2016)
The advantages of Negative Interest Rate
Many countries experience an actual negative rate of interest for a longer duration of time. Basically, anyone who has been saving in a typical current account would have been the witness of the worth of their dropping down due to interest rates of nominal nature are lower than the inflation level (Wuand Xia, 2020). This has been the scenario in the case of household deposits government debts over the time of the previous ten years. If the nominal interest rates turn negative, there is the possibility of the savers losing out further. Hence, there lies psychological benefit in such type of situation.
The nominal or negative rate of interest would be a witness of depreciation in the situation of exchange rate because the investors of international origin would dispose of the assets of UK origin in case the rates of interest go negative (Palley, 2016). In this way, there would be a boost to the manufacturing sector as a weaker currency rate would turn the exports cheaper. Because banks feel it easy to lend to corporations or businesses, their certain sheets get improvised, and the profitability is enhanced.
In this way, the improvised prospects for the actual economy lead to the reduction of impaired loans by enhancing the profit of the bank. However, there is a flip side of the negative rate of interest can also be the reduced lending from the bank, specifically if there is worry regarding the ratios of capital. When the economic activity reduces, there is a rise in unemployment; losses on existing loans of the bank can even possibly be picked up. Hence, employing the policy of negative interest rate can be considered less efficient in offering spur to the economy.
The disadvantages of Negative Interest Rates
Hence, even if a negative interest rate is employed for the purpose of fighting the situation of deflation but it can be a disadvantage for the ones who are savers. In the situation of an economic downturn, people basically keep their money and wait to observe this is as an improvisation before they can rise for spending. As a consequence, the situation of deflation can be rooted in the economy (David-Pur et al., 2020). People stop themselves from spending, declining the demand, prices of services and goods decrease, and people take time and wait for a further decline in the prices. The negative rate of interest puts up a fight against the situation of deflation by turning it more costly and by keeping a hold onto the money, thereby perking up the spending. Supposedly, a negative rate of interest makes it less tempting to store cash in the bank. However, the bigger issue is rather than producing interest on the amount of savings; the depositors have to bear the charge by the bank of a holding fee. This can lead up to a situation where the people would withdraw their savings from the bank and might choose to save it under their bedsheets.
Conclusion
Based on the study, it can be concluded that the study mainly discussed the negative impact of interest rates on Finland's economy and exchange rate. It discussed the impact it had on a savings account, credit cards, products, and loans. Moreover, the study also discussed the effect it may have on the time value of the money. Monetary policy was defined to be a tool that needs to be maintained to provide a certain rate for the banks to provide loans and other benefits. Apart from that, it also discussed both the negative and positive aspects of the negative rate of interest policy on the nations' economy, livelihood, and banks. In addition to that, it discussed the noticeable volatility that had on exchange rate currency against the US dollars. Furthermore, it provided reasons for Finland's adoption of a policy on the negative rate of interest and its implications faced on currency value. Hence, the main objective of the study is to examine the consequences faced by the nation and banks on having a negative rate of interest.
Reference
Bahmani-Oskooee, M., Nouira, R. and Saafi, S., 2020. Exchange-rate volatility and commodity trade between the US and Germany: asymmetry analysis. International Economics and Economic Policy, 17(1), pp.67-124.
BA?ARIR, Ç., 2018. Volatility structure of stock price index and exchange rates: Casuality analysis for Turkey. Gümü?hane Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Elektronik Dergisi, 9(24), pp.330-349.
Bongiovanni, A., Reghezza, A., Santamaria, R. and Williams, J., 2021. Do negative interest rates affect bank risk-taking?. Journal of Empirical Finance, 63, pp.350-364.
Corneille, O., D’Hondt, C., De Winne, R., Efendic, E. and Todorovic, A., 2021. What leads people to tolerate negative interest rates on their savings?. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, 93, p.101714.
David-Pur, L., Galil, K. and Rosenboim, M., 2020. To decrease or not to decrease: The impact of zero and negative interest rates on investment decisions. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, 87, p.101571.
Finland and monetary policy through three crises, SUERF Policy Notes .:. SUERF - The European Money and Finance Forum (2021). Available at: https://www.suerf.org/policynotes/15831/finland-and-monetary-policy-through-three-crises (Accessed: 3 October 2021).
Goodfriend, M., 2016. The case for unencumbering interest rate policy at the zero bound. Designing Resilient Monetary Policy Frameworks for the Future, pp.127-160. Grasselli, M.R. and Lipton, A., 2019. On the normality of negative interest rates. Review of Keynesian Economics, 7(2), pp.201-219.
Hameed, A. and Rose, A.K., 2018. Exchange rate behaviour with negative interest rates: Some early negative observations. International finance assignment Pacific Economic Review, 23(1), pp.27-42.
Lilley, A. and Rogoff, K., 2019. The case for implementing effective negative interest rate policy. Available at SSRN 3427388.
Nucera, F., Lucas, A., Schaumburg, J. and Schwaab, B., 2017. Do negative interest rates make banks less safe?. Economics Letters, 159, pp.112-115.
Palley, T.I., 2016. Why negative interest rate policy (NIRP) is ineffective and dangerous. Real-world economics review, 76(30), pp.5-15.
Qureshi, A.M.M., Uddin, R. and Jienwatcharamongkhol, V., 2019. Equity market contagion in return volatility during Euro Zone and Global Financial Crises: Evidence from FIMACH model. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 12(2), p.94.
Smith, K. (2021) Negative Interest Rates Explained: How Could They Affect You?, Forbes. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/advisor/2020/05/18/negative-interest-rates-explained-how-could-they-affect-you/?sh=3cd930377b46 (Accessed: 3 October 2021).
Thornton, J. and Vasilakis, C., 2019. Negative policy interest rates and exchange rate behavior: Further results. Finance Research Letters, 29, pp.61-67.
Välimäki, T. et al. (2020) Recent economic crises have modified the Bank of Finland's market operations – Bank of Finland Bulletin, Bank of Finland Bulletin. Available at: https://www.bofbulletin.fi/en/2020/4/recent-economic-crises-have-modified-the-bank-of-finland-s-market-operations/ (Accessed: 3 October 2021).
Wu, J.C. and Xia, F.D., 2020. Negative interest rate policy and the yield curve. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 35(6), pp.653-672.












