International business assignment on competence of South Korean multinationals in the international markets
Question
Task: Can you write an international business assignment on to what extent have South Korean multinationals competed successfully in different international markets, and which major factors explain these achievements and shortcomings?
Answer
Introduction to the international business assignment
Today South Korea has transformed its image as it was before 1997 and has put itself among one of the world's largest economies (Kim et al. 2018). The Asian financial crisis in the 90s has allowed the country to use foreign capital for strategic and non-strategic businesses. Business regulations were eased attracting foreign companies to do business in the country. The Government tactically used its geographical location as a central hub for logistics in the Northeastern region. Today as per the international business assignment, South Korea is well known for its advancement in digital technology, automobiles and infrastructure. In electronics, home companies are competing and ruling the world market. America is a big market for South Korean in smartphones and automobiles. The international business assignmentwill critically analyse the factors of success and areas of shortcomings in terms of industry and other countries in the region.
Factors behind the success of South Korean Industries
Foreign policies and trade relations mainly focus on four countries United States, China, Russia and Japan. The Government understood that without changing foreign perceptions South Korea's economic revival is not possible. Ease in foreign investments and trade regulations become the first stage in the international business assignment, allowing favourable conditions to attract global companies to choose Korea as their regional headquarters. Special Economic Zones were created in Youngjong, Gimpo and Songdo to promote business (Jung, 2020). However, the government agenda under president Roh's rule became to use foreign investment in the growth of local business(Jung, 2020). Support from the government and a preferable environment allowed local companies to flourish rapidly and soon establish their business offshore as per the findings of the international business assignment. Strong business ties with the US became one of the major factors for South Korean companies to establish their brand globally where the US became one of their biggest markets. China on the other hand became a major trader in automobiles. Investment to develop the ports and transport system helped a lot in the business. During its initial period, the country used foreign investments in educating the next generation with heavy investments made in developing research centres (Jung, 2020). It is found in the international business assignmentthat the Korean Steel business gained momentum in a few years with low-cost labour, dollar rate and fuel being the primary reasons for the industry to grow. The Koreans used this opportunity and soon jumped into building automobiles, ships, electronics and more. Korean steel being of good quality and low price soon captured the world market with China becoming one of the prominent traders.
No rivalry with other countries as per the international business assignment
As per the international business assignment, South Korea in the last few decades has not involved itself in any major conflicts, making it one of the favourable nations to trade globally. The rising economy of the South East Asian region has been one of the other reasons to gain market. China has remained a bigger market than South Korea where demand for products in electronics and automobiles has increased consistently (Xu and Sim, 2018). The data from the international business assignment reveal that the recent tension between US and China has provided an opportunity for South Korea to tap the American market with its electronic product and services.
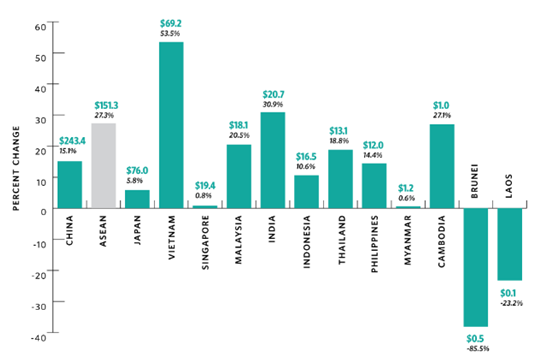
Figure1.Trade Statistics by Country, 2019
(Source: Botto, 2021)
On the other hand of this international business assignment, recently the government is working on (NNP) New Northern Policy, to strengthen relationships with Russia, and European Countries where (NSP) is designed to focus its trade relations with South East Asian countries including Bangladesh and the growing market of India (Hauge, 2019).
Issues for South Korean companies in the International market
Most South Korean companies are run and controlled by families, thus these companies find it difficult in establishing business outside with foreign partners under different terms. Korea has not been able to portray itself as providing a free business environment as happened in the case of Singapore and Hong Kong as per the analysis from the international business assignment. Both the countries manage to pull better infrastructure with all designed city plans to have better transport and connectivity. On the other hand, South Korea took time to gain economical stability. Even now a huge difference is observed between rural mass and city dwellers in terms of living. It is found in the international business assignment that the South Korean companies are highly dependent on the USA market and while the US provides military aid to the country companies suffer economical decision autonomy (Prasanna et al. 2019). In recent periods business with China and Russia has largely impacted South Korea over rising tension with the USA with the two strong powers. The country has largely developed itself in technology, automobiles, and shipbuilding, textile and entertainment sectors. However, they lack in seizing market opportunities as the Chinese group does (He et al. 2019). It is because they still are unable to take over the highly growing Indian market despite the favourable condition it has.
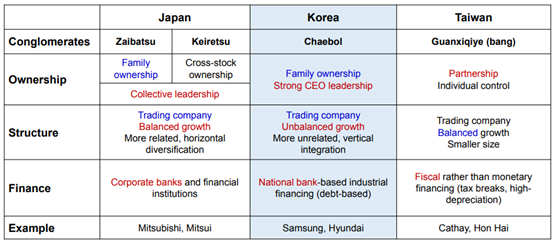
Figure2: Comparing Conglomerates of Japan, Korea and Taiwan
(Source: Mun and Moon, 2016)
Most South Korean companies as per the international business assignmentare under immense pressure after the UN go green movement for making a transition to a cleaner and greener approach. The conglomerates are not able to cope with the new industry standards put by US and European countries. Including high tariffs and price pressure. On the other hand, the Korean market is not as per US markets making US global companies face difficulty to perform business in the region. For instance, in the case of smartphones, Samsung is getting strong competition from Chinese brands in the North and South Asian regions. Other than that Chinese brands have created strong repute in European regions restraining Samsung to revise its strategy. Apart from that growing market complexities and Covid19 have impacted global business immensely making South Korean companies difficult to make larger investments in new regions.
Figure3. Comparison of Foure Asian Tigers
(Source: Mun and Moon, 2016)
AS per the international business assignment, Korea follows restricted trade policies and cannot enjoy autonomy as China or Russia does further because large conglomerate businesses' growth strategy remains unbalanced in which SMEs are affected largely. The Country over these years has developed itself in manufacturing and technology. However, has failed to infuse sustainable business strategies so that less carbon and wastage is produced.
International business assignmentexplaining change in the paradigm to attract FDI
Between 1998-2001 during the Asian financial crisis, South Korean policies attracted USD 52 billion in FDI. The government opened its passage for free trade allowing European companies to use the route in marketing in eastern countries. As per the data of the international business assignment, the investments were used to strengthen local industry while reframing human force. Singapore and Malaysia started developing during the same period however, both came out as a centre for finance and investments to become regional heads of global companies, whereas South Korea flourished in the area of manufacturing and technology. Korean companies evaluated the opportunities present in automobiles and the booming market of mobile phones. Companies such as Hyundai Motors soon positioned themselves in the world market with their quality automobiles at economic prices. On the other hand of this international business assignment, Samsung has eventually developed its business group and has become one of the largest exporters of electronic products globally (Luo and Zheng, 2018). Daewoo electronics are the other name that eventually made global branding in a few years for providing quality products. Hyundai also made its mark in the shipbuilding industry under (HHI) Hyundai Heavy Industry. Growing multinational was one of the strong reasons for gaining FDI and marking the country as the next growing nation. Korean companies soon started overshadowing other companies in terms of price, quality and variety. Gaining global recognition allowed changing the western perception of performing business in the country (Oktenet al. 2019). Over the recent period as found in the international business assignment, Seoul has become one of the favourite places for a business centre in the global market.
The government tactically used Capital Market Theory during the Asian financial crisis and managed to pull US$52 billion during the period. It allowed the country to flourish its local business as interest rates remain low and the source country as in this case the USA provided all possible aids to support the business structure. However it is found in this international business assignment, more interest in inwards investment is shown by the government attracting global companies from other countries to perform their business in the region in the recent period. The use of the Eclectic paradigm is observed where home companies are gaining control in the business over other companies. The use of correct business and political moves by the country has allowed growing its reputation in the world and it immensely affected the FDI approaches.
One of the strongest reasons for South Korean companies flourishing and withstanding global competitors as per the international business assignmentis their approach to delivering quality material while maintaining the price point. It has been possible because of the initial steps taken in developing human force as well as providing a basic structure to produce in-house products. In the last few years, Korean companies have invested heavily in research which allowed them to fulfil growing market demands (Benmamounet al. 2018). However, the country has not been able to establish itself as a hub for international companies. The country has not been able to project itself as Hong Kong or Singapore have, in a foreign business-friendly environment. The country though home to many global companies is still dependent on a few major countries for its economy. However, in a recent period, a gradual shift in global strategy is observed. The government is working to elevate relations with other countries to minimise dependency on a few nations especially after suffering business over growing tensions between the USA, China and Russia. For this agreeing to (ASEAN) Association of Southeast Asian Nations building cooperation over culture, economy, politics and security is considered. Under new policies as mentioned in the international business assignment, the country is seeking to stand as a middle power in the region while diversifying economic and strategic relationships.
Reasons for South Korean companies gaining global recognition
South Korean companies propel to go big in the market during the '90s when the new government understood the opportunities present after globalization. International trade relations were formed which helped local companies to gain the proper infrastructure and finances required to perform. As per the findings of the international business assignment, Korean companies took help from Japanese companies in terms of technology for instance Hyundai Heavy Industries took help from Mitsubishi for Shipbuilding. During the period foreign business environments were favoured where Russia lifted blocks and China opened business doors (Park and Lee, 2021). However, the financial crisis period between 97 and 2007 put a halt to business paddles. After which loans from IMF helped in business with new conditions of improving transparency, capital structure, maintaining a strong relationship with SMEs and raising shareholders. The government under the new rules as per the international business assignmentadopted new accounting and auditing rules followed internationally. Other than that change in working practices with the rise in the right to workers, along with structural help to fit in the international market by 104 trillion values of bonds were rose by the government (Driffield et al. 2021). South Korean companies get further assistance in terms of technology which allowed them to shift business into advanced working models and thus reduce the margin of errors.
As per the findings from the international business assignment, production and operations were made hi-tech, which allowed fewer communication gaps and errors in the work. Korean companies soon evolved their auto manufacturing setups which allowed companies such as Samsung and Hyundai to scale their production and feed the global market. The government over the years worked a lot and has strengthened logistics making it easier for the local companies to market their products in a new region (Luo and Zheng, 2018). Global companies use the advanced supply chain to reduce costs in the process while at the same time minimising wastage and production of carbon. Companies in the country are mostly supervised and controlled by conglomerates which make the OLI framework fit better when going for partnership or making new arrangements.
South Korean government continuously pushes its citizen to try new and for this in the last few years, huge investment in the research sector is observed in the private and public sections. As per the new regulations mentioned in the international business assignment, South Korean companies require to reduce carbon production and adopt global supply chain policies. South Korean companies unlike Chinese aggressive marketing policies place products to fit the market requirement. Korean companies gel with the local needs and practices well in the region where marketing takes place and it strengthens relations with the local consumers. MNEs focus more on service and quality over quantity and it helps them to build a brand and sustain it for longer (Park and Lee, 2021). MNEs partner with local traders and marketers for the distribution and it allows them to increase their reach in new territory.
South Korean companies usually follow Chaebol and so the heads or decision maker always remains from the family. However, MNEs hire global talents in a significant position to report and handle business. AS per the international business assignment, South Korean business practices are much likely as Japanese firms. However, many changes are made in the recent period to fit with global practices. Companies do provide in-house training and management skills. South Korean Companies working global follow the new global working culture. Each region where MNEs are situated has their regional head who is responsible for the business in the region. However, business heads regularly make a close look at the performance to evaluate the business in the region. It is found in this international business assignment, that the Korean companies are well supported by the government and so Chaebols' presence in prominent government positions is common in the region. Companies such as Hyundai, Samsung and Daewoo experience loans at low interest. However, these Chaebols are major contributors to the country's economy. However, the government has a strong influence on the purchase of resources.
South Korea's existing regional relations and diverting interests are prime reasons for MNEs to move their interest into South East Asian countries (Botto, 2021). The favourable relationship of India with the US has allowed flourishing business and extending ties with the country. However, China still remains the largest purchaser of Korean products in Asia. The country needs to tactfully recalibrate its business ties and make strong regional relations. This shift of operational parts as done by Samsung is a strong move to strengthen ties with other countries. South Korea has increased its trade relation with Vietnam for a continuous flow of raw supplies and finished goods (Botto, 2021). Shifting of operations under regionalization is thus observed in this international business assignment. An increase in the involvement of locals by global companies is largely observed. The Eclectic paradigm or OLI framework is used to gain control over ownership, choice of location and internationalization methods however, the economy is heavily influenced by the government as it is Chaebol dominated economy.
Over recent years the government of South Korea is making continuous efforts to stimulate the inward economy by making global investors perform their business in the country. The government plan is to revive local business in the region. The political economy in the region is the voice of conglomerates which influence decision-making in the country.
Conclusion
It is found in this international business assignment, that the Korean companies are focussed to produce quality products and bring innovations that are useful making them competitive and demandable in Europe and US markets. However, their focus remains more on service enhancement. Japanese unlike Koreans are more experimental in terms of approach, whereas Chinese counterparts believe in capturing the market with the number of products and intense distribution. Other than that Japanese companies grow horizontally by expanding parent businesses to different regions. According to the international business assignment, Koreans are more known for diversification in which companies manufacture different products to target mass consumers.
References
Benmamoun, M., Singh, N., Lehnert, K. and Lee, S.B., (2018). Internationalization of e-commerce corporations (ECCs): Advanced vs emerging markets ECCs. Multinational Business Review in the international business assignment, 27(4), pp.317-338. Available at: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/MBR-02-2018-0010/full/html [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Botto, K., 2021. South Korea Beyond Northeast Asia: How Seoul Is Deepening Ties With India and ASEAN. Available at: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/1850549/south-korea-beyond-northeast-asia/2597458/ [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Driffield, N., Jones, C., Kim, J.Y. and Temouri, Y., (2021). FDI motives and the use of tax havens: Evidence from South Korea in the international business assignment. Journal of Business Research, 135, pp.644-662. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296321004720 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Hauge, J., (2019). Should the African lion learn from the Asian tigers? A comparative-historical study of FDI-oriented industrial policy in Ethiopia, South Korea and Taiwan. Third World Quarterly, 40(11), pp.2071-2091. Available at: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01436597.2019.1629816 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
He, S., Khan, Z., Lew, Y.K. and Fallon, G., (2019). Technological innovation as a source of Chinese multinationals’ firm-specific advantages and internationalization. International Journal of Emerging Markets. Available at: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJOEM-02-2017-0059/full/html [Accessed on: 14.07.2022] Jung, J., (2020). The fourth industrial revolution in the international business assignment, knowledge production and higher education in South Korea. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 42(2), pp.134-156. Available at: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1360080X.2019.1660047 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Kim, B., Kim, H. and Jeon, Y., (2018). Critical success factors of a design startup business. Sustainability, 10(9), p.2981. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/330086 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Knoerich, J., 2018. Re-orienting the paradigm: path dependence in FDI theory and the emerging multinationals. International Journal of Emerging Markets. Available at: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJoEM-04-2017-0123/full/html [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Lee, M. and Kim, H.J., (2022). Exploring determinants of digital music success in South Korea. Electronic Commerce Research, pp.1-22. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10660-022-09573-5 [Accessed on: 14.7.2022]
Luo, X. and Zheng, Q., (2018). How firm internationalization is recognized by outsiders in the international business assignment: The response of financial analysts. Journal of Business Research, 90, pp.87-106. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0148296318302066 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Mun, H.C. and Moon, H.C., (2016). The strategy for Korea's economic success. Oxford University Press.
Ökten, N.Z., Okan, E.Y., Arslan, Ü. and Güngör, M.Ö., (2019). The effect of brand value on economic growth: A multinational analysis. European research on management and business economics, 25(1), pp.1-7. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2444883418301153 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Park, B.I. and Lee, J.Y., (2021). The survival of the fittest in the global markets: multinational corporation challenge, evolution and decline. Management Decision. Available at: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/MD-01-2021-081 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Prasanna, R.P.I.R., Jayasundara, J.M.S.B., Naradda Gamage, S.K., Ekanayake, E.M.S., Rajapakshe, P.S.K. and Abeyrathne, G.A.K.N.J., (2019). Sustainability of SMEs in the competition: A systemic review on technological challenges and SME performance. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 5(4), p.100. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/594730 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]
Xu, J. and Sim, J.W., (2018). Characteristics of corporate R&D investment in emerging markets and international business assignment: Evidence from manufacturing industry in China and South Korea. Sustainability, 10(9), p.3002. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/331036 [Accessed on: 14.07.2022]












