Innovating Business models assignment for Saint Peter Restaurant: Navigating Disruption in the Global Hospitality Industry
Question
Task: How can Saint Peter restaurant in Sydney, Australia, leverage innovative business models assignment to navigate and thrive in the disrupted global hospitality industry amidst the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic?
Answer
Summary
The advent of the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the functioning of the hospitality industry, on a global scale in recent years. Characterised by high mortality rates the outbreak became impossible for health professionals to control its spread among civilians. This caused many Governments to close down the travel routes which caused a major impact on the hospitality industry (Khan et al., 2021). The dine-out and restaurants throughout the globe were heavily impacted by the pandemic.
At present, this industry has changed its way of functioning in various ways to prevent outbreaks in the future. The dine-out location shave reduced the number of their deals in the location. Online food delivery services also gained popularity, as they allowed restaurants to reach out to consumers with less contact (Hong et al., 2021). The following report analyses the case study of Saint Peter restaurant. It aims to assess the business and present three models for better functioning.
Introduction
Saint Peter is a fine dining restaurant, located in Sydney Australia. It was established by Chef Josh Niland and Julie Niland in mid-2016. The restaurant offers a fine dining experience and specialises in serving seafood of the highest quality (Rodell, 2018). It is also well known for its high-quality raw materials sourced from the locality. Chef Josh is also known as the chef of "gill-to-fin", a name he earned by implementing his knowledge of Japanese culinary expertise in the presentation of his dishes. The restaurant prides itself in being able to produce dished and use the whole fish without creating much waste. Chef Josh claims to use 90% of each fish he purchases to produce recipes including eyes, scales and the liver (AL-BASSAM, 2023). At present the restaurant faces the situation of limited setting arrangements and adapting to the online delivery services. However, it has made no compromise on the quality of its food. The report presents the situation of the Saint Peter restaurant and aims to identify three business models assignment assignment for its improvement
Business background
The restaurant is one of the finest restaurants in Australia which serves fresh seafood, particularly various fish items. The pandemic created a deep impact on the overall hospitality industry in the country. However, the founder and owner of the restaurant Josh Niland took a brave step in the pandemic by relaunching the restaurant in Paddington. He introduced a full-on take-home menu from the Fish Butchery and also reduced the capacity of the restaurant from 34 to 20 in the year 2020 (Durack, 2020). The new setup depicted the dining tables on one side and on the other side the area of the chefs who prepared the dishes through the concept of an open live kitchen
Business models assignment assignment
Considering the significance of local and loyal customers in the recovery from the crisis, it is crucial to consider that consumers value the innovations of hospitality organisations. Hospitality organisations are themselves wary that their consumers expect constant innovation and thereby strive to constantly innovate to be capable of competing in the market(Breier et al., 2021). Following are three innovative business models assignment assignment that can be implemented by hospitality businesses such as Saint Peter to deal with the contemporary business landscape:
Servitisation Business Model
Under this business model consumer’s pay for a service as opposed to acquiring products outright, an amplifying number of businesses are moving towards this business model. The model sturdily incentivises the owner of the equipment which is the service provider. The provider by facilitating state-of-the-art maintenance can reduce operating charges, particularly energy use which is the biggest cost constituent over the life cycle of the tool(Karamitsos et al., 2020).
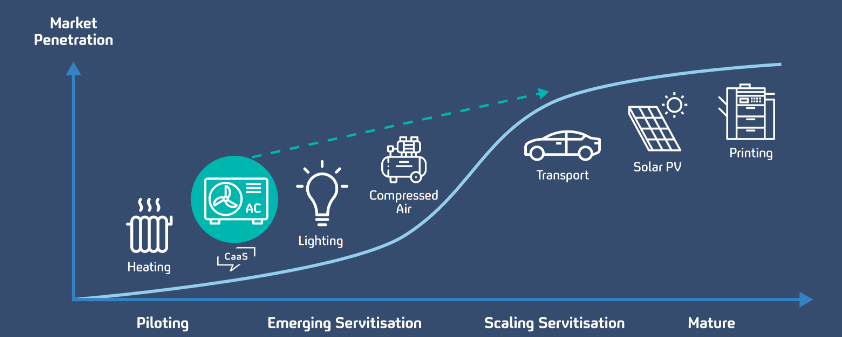
Figure 1: Servitisation Model
Source: (Karamitsos et al., 2020).
The model of servitization is a chief provider of the systemic efficiency strategy to acquire international energy decarbonisation. Servitization sturdily emphasises innovation. This model endorses efficiency as a corporate prospect and assists cash-constrained organisations to regain momentum while minimising operating expenditures and climate impact. These innovative approaches can take several forms like rethinking system design, enhanced preventive maintenance, incorporation of AI and IoT technologies and utilising a systematic approach while serving consumers.
Dematerialised Business Model
A business model that endorses renting products as opposed to purchasing them outright plays into the amplifying trend of dematerialisation. Under this model, organisations deliver the same service or products they always have but utilise fewer physical resources. This trend is being accelerated in part by an amplifying awareness of sustainability concerns in both organisations and their consumers.
Overconsumption along with the amplifying international population and the limited amount of primary materials on Earth has produced a circumstance where the planet’s sustainability is at stake (Petrides et al., 2018). Dematerialisation is everything that constitutes the circular economy. Businesses under this model ask how they can either eradicate the production of waste or whether specific waste items can be utilised somewhere else. The concept of dematerialisation has resulted in a remarkable disparity between the older generation's items compared to the current generation. Development in technical performance tends to amplify the overall usage of the product which can thereby lead to an overall surge of energy needs, resource usage and material usage. The additional usage of resources that eradicates a full or part of the potential savings projected from the technical enhancements is known as the rebound effect. If an experience is unique at least locally and it matches with the concept of the hotel then it can be monetized adequately to bring value to the business (Sawerschel, 2023).

Figure 2: Dematerialisation Example of Hotel Outlet
Source: (Sawerschel, 2023).
Through the integration of this model, the organisation can ensure the provision of operational excellence and service quality. Relying on the hotel location and its target customers, pairing back the guest experience is the chief constituent in being a winning strategy.
Virtual Business Model
Virtualisation is a crucial means of business model innovation as technologies such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality and the metaverse become more pervasive. Virtualisation comprises creating virtual as opposed to physical services and products. Unlike digitalisation which shifts from prevailing physical services into the digital realm, virtualisation has the probability to make virtual products and brand new services. The approach of virtualisation encompasses producing a comprehensive industry space or ecosystem in the virtual world. However, it is crucial for businesses to still ask customers what their problems are and then work accordingly in describing a value chain. Virtual business models assignment assignment are considered to be a significant type of business model that can be implemented within the hospitality industry. It is mainly related to and associated with the adoption of technology by the entity to conduct the majority of its operations. This business model does not have a physical infrastructure or premise which makes it entirely operational and functional with the help of technical innovations and tools (Fernando, 2020). The model can be initiated within the restaurant by following certain steps which can assure the proper implementation plan. Mobilizing the hospitality employees and teams along with understanding the competitive environment are the two main steps of the adoption and implementation stage.
The assistance of the business models assignment assignment
The servitization business model is a significant paradigm shift that can help in allowing restaurant management to create revenue streams through the innovation aspects and adding value to the products and services offered. This model significantly helps the business organization in enhancing its overall competitive advantage within a disrupted market. It mainly offers a connected operations solution to the business which can help in enhancing operational efficiency in times of market disruption and adversity (Ebel, Bretschneider and Leimester, 2016). The dematerialization model helps in converting the physical shares and assets of the company into digital or electronic forms. It can enable the smoothening of the overall process of purchase and can help in transferring or holding the shares. The business model is considered to be cost-effective in terms of the hospitality industry as the restaurant has faced business disruption due to the pandemic (Kohtamäki et al., 2019). In the virtual business model, the organization can utilize financial resources through product competency which can help achieve cost-effectiveness in times of market disruption as the one faced by the restaurant during the pandemic. This type of business model is particularly suitable for smaller business organizations and startup companies that can leverage their business operations through the digitalization mode.
Characteristics of the models
The servitization model can significantly improve customer satisfaction levels in terms of the hospitality industry and increase the market power and capacity of the restaurant. However, this business model can be considered time-consuming and costly for the restaurant as it involves a complex procedure that needs to be incorporated into the value chain. The dematerialization business model can significantly reduce the risk of physical damage to the establishment, infrastructure, and property which can be considered an advantage to the hospitality industry and the restaurant in times of market and economic disruption like the pandemic. However, there are various charges on account of the maintenance of the infrastructure which can increase the overhead costs of the restaurant (Rha and Lee, 2022). Virtual business models assignment assignment on the other hand can be less cohesive and can allow the teams to fragment the operations according to the job responsibilities. Technological issues can be faced by the restaurant during the implementation of this model during the market disruption which can further lead to the escalation of other operational issues within the restaurant.
Implications
The suggested business models assignment assignment for the Saint Peter restaurant are the servitization business model, dematerialized business model and virtual business model. The servitization business model adds value to the production of a finished product. The implementation of this model allows the manufacturers or the owners to gain more profits from their products. Saint Peter is a fine dining restaurant, thus by implementing this model it can gain more profits. This is because it takes care to produce dishes that require a lot of time and effort in formulation. This model also helps increase the long-term customer loyalty of a business (Ruiz de la Torre and Sanchez, 2022).
The dematerialised business model involves the consistent delivery of goods and services but with lower use of resources. By implementing this Saint Peter can focus on lowering the use of expensive raw materials and increasing its products. The virtual business model allows businesses to employ the means of electronic transactions. This may allow the business to interact with consumers on a larger scale and gain more knowledge regarding the feedback of the consumers. The model also allows businesses to present more services and products to their customers. This may also be very profitable for the functioning of the restaurant.
Conclusion
The following report has presented the problem faced by the hospitality industry due to the COVID-19 pandemic. It assesses and identifies the problems based on Saint Peter restaurant and also presents an overview of its background. Based on the analysis, the report has identified three different business models assignment assignment that can source profits for the restaurant if implemented. The suggested business models assignment assignment for the Saint Peter restaurant are the servitization business model, dematerialized business model and virtual business model. Each of the models has its unique feature but allows the business to improve its functioning.
The report found that the servitization business model helps the business organization in enhancing its overall competitive advantage within a disrupted market. It also found that the dematerialized business model helps in converting the physical shares and assets of the company into digital or electronic forms. Lastly, it has been found that businesses can utilize financial resources through product competency and achieve cost-effectiveness in times of market disruption with the implementation of a virtual business model.
Reference
AL-BASSAM, S. (2023).Meet Josh Niland, the Australian chef who started a fish revolution. [online] nationalgeographic.com. Available at: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/travel/article/josh-niland-sydney-fish [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Breier, M., Kallmuenzer, A., Clauss, T., Gast, J., Kraus, S. and Tiberius, V. (2021). The Role of Business Model Innovation in the hospitality industry during the COVID-19 crisis. International Journal of Hospitality Management, [online] 92(92), p.102723.doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102723.
Durack, T. (2020).Brave Relaunch of Paddington’s Saint Peter. [online] Good Food. Available at: https://www.smh.com.au/goodfood/eating-out/brave-relaunch-of-paddingtons-saint-peter-20200728-h1pn1u.html [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Ebel, P., Bretschneider, U. and Leimester, J.M. (2016).Leveraging Virtual Business Model innovation: a Framework for Designing Business Model Development Tools. [online] www.researchgate.net. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/292949042_Leveraging_virtual_business_model_innovation _A_framework_for_designing_business_model_development_tools [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Fernando, E. (2020). Virtual Business models assignment assignment: The Next Big Thing? [online] Medium. Available at: https://medium.com/@eshanfernando8/virtual-business-models-the-next-big-thing-d4ec0d0f6499 [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Hong, C., Choi, H. (Hailey), Choi, E.-K. (Cindy) and Joung, H.-W. (David) (2021). Factors affecting customer intention to use online food delivery services before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, [online] 48, pp.509–518. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1447677021001339 [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Karamitsos, D., Motmans, T., Corno, V. and Maggiora, C.D. (2020).What is servitization, and how can it help save the planet? [online] World Economic Forum. Available at: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/11/what-is-servitization-and-how-can-it-help-save-the-planet/#:~:text=With%20a%20servitization%20model%2C%20the%20customer%20pays%20a [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Khan, K.I., Niazi, A., Nasir, A., Hussain, M. and Khan, M.I. (2021). The Effect of COVID-19 on the Hospitality Industry: The Implication for Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, [online] 7(1), p.30. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2199-8531/7/1/30 [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Kohtamäki, M., Parida, V., Oghazi, P., Gebauer, H. and Baines, T. (2019). DigitalServitization Business models assignment assignment in ecosystems: a Theory of the Firm. Journal of Business Research, [online] 104(7). Available at: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1362739/FULLTEXT01.pdf [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Petrides, D., Papacharalampopoulos, A., Stavropoulos, P. and Chryssolouris, G. (2018). Dematerialization and Environmental Sustainability: Challenges and Rebound Effects. Procedia CIRP, [online] 72, pp.845–849. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212827118302889 [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Rha, J.S. and Lee, H.-H. (2022). Research Trends in Digital Transformation in the Service sector: a Review Based on Network Text Analysis. Service Business, [online] 16(1), pp.77–98. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11628-022-00481-0 [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Rodell, B. (2018). Saint Peter in Sydney, Australia. [online] nytimes.com. Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/01/04/dining/saint-peter-review-seafood-sydney.html [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023].
Ruiz de la Torre, A. and Sanchez, D. (2022). Evolution of Servitization: new business model opportunities. International Journal of Production Management and Engineering, [online] 10(1), pp.77–90. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358246035_Evolution_of_Servitization_new_business_model _opportunities [Accessed 8 Mar. 2022].
Sawerschel, Y. (2023). The impacts of dematerialization on the Hospitality Industry. [online] hospitalityinsights.ehl.edu. Available at: https://hospitalityinsights.ehl.edu/what-is-dematerialization-hospitality-industry [Accessed 20 Nov. 2023]












