Information Assurance & Risk Management Assignment: Analysis On Cerious Cybernetics Corp
Question
Task:
The risk management assignment requires you to engage with a scenario which sees you commissioned by ‘Cerious Cybernetics Corp.’ a private cybernetics research and development company to identify fit- for-purpose, robust and comprehensive information assurance and risk management policies, procedures and practices which will ensure successful information assurance for their business via cutting edge and relevant risk assessment, treatment and management both in the current climate and also, for future provision.
Cerious Cybernetics Corp. has its headquarters in London, England, employing a total of 60 full time staff and at any given time upwards of 20 agency staff. The headquarters is the location for the core business functions such as Human Resources, Finance, IT, data governance, legal resources and service level agreements (including those for customers and with the agencies supplying staff). Cerious Cybernetics Corp. currently has a number of ongoing research and development contracts, including the UK Ministry of Defence and the United States Department of Defence.
Cerious Cybernetics Corp. evaluates about every aspect of information assurance (from a combined, managerial, organisational and technical perspective) and risk management (from an organisational context). The white paper should aim to aid Cerious Cybernetics Corp.’s understanding and ultimately, ability to make a decision on which policies, procedures need developing and implementing within the organisation and also ensure any associated resource implications can be successfully supported.
The Cerious Cybernetics Corp. executive has further requested that you produce a sample Service Improvement Plan (SIP) within your white paper as part of the wider review (although this would normally be a discrete document, please integrate it for the purposes of this assessment); specifically, they want the detailed explanation to focus on the scenario of ransomware (please see the following article for an example https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2016/feb/17/los- angeles-hospital-hacked-ransom-bitcoin-hollywood-presbyterian-medical-center. Cerious Cybernetics Corp. is keen to establish improvements or initiatives which will ensure their IT function including infrastructure and data is kept secure.
Answer
Executive Summary
This risk management assignment covers the information assurance and risk management program for Cerious Cybernetics Corp. Information security and management is the primary concern of the organization. It deals with sensitive and critical information and the exposure of such information sets can cause massive damages to the organization and its stakeholders. The security standards and framework developed are applied to CCC to ensure that information properties are safeguarded and protected at all times. These properties include confidentiality, integrity, and availability, commonly referred as CIA triad. The security frameworks and standards identified for CCC include NIST FISMA, Cybersecurity framework NIST, and ISO/IEC 27001:2013. Information assurance and risk management are the ongoing activities that involve several steps and stages to achieve the desired outcomes. It is essential that these activities are dynamic in nature and are continuously conducted to keep the information sets and the applications protected.
Introduction
Information assurance can be defined as the set of processes, practices, and methods implemented to protect the information sets from any of the information associated risks. It applies to the use, sharing, and storage of the information sets.
Risk management can be defined as the mechanism to handle the risks associated with a particular system, application, project, or organization. There are several phases present in the risk management framework to ensure that the risks do not occur. Some of these include identification, assessment, treatment, and closure of the risks (Armenia et al., 2018). The risk management policy and framework shall be effectively designed to make sure that the risks can be controlled and prevented.
The paper covers the challenges and objectives of CCC followed by the details of standards and frameworks. Risk management details, information assurance program, ransomware and service improvement plan, resource details, and post-implementation process is covered thereafter.
CIA Triad
CIA triad refers to the essential information properties that must be safeguarded at all times. It stands for confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
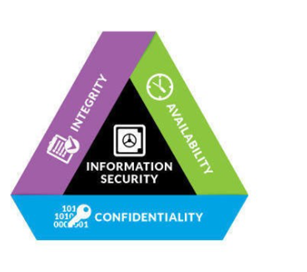
CIA Triad (Libicki et al., 2015)
To ensure that the information security is maintained, there are certain information properties that shall be protected. The first is confidentiality. It refers to the access of the information sets to only those users that are authorized to access the information. If the unauthorized users gain access to the confidential information then the confidentiality is violated. Integrity refers to the authorized modification of the data by the entities permitted to make changes. If the malicious entities make changes in the data sets then the integrity is violated. Availability is the information property that ensures access to the data sets at any time (Calderon & Gao, 2020). . The inability to access the information as an outcome of a security attack results in the compromise of information availability.
Challenges for Cerious Cybernetics
One of the major challenges for Cerious Cybernetics is the legal compliance in the area of information security. The organization must comply with the legislations applicable in the UK as it has its headquarters in London. It develops for the Ministry of Defence (MoD). It also needs to maintain compliance with the legislation followed in the USA. This is because it develops under contract with the Department of Defense (DoD).
Due to these legislations and regulations, it is possible that the issues of non-compliance occur. The organization also operates is the domain of military research and development. It leads to inclusion of an additional layer of governance and regulation.
It will be essential to meet the security requirements as per the CIA triad and it will also be necessary that the authenticity and authorization along with non-repudiation aspects are considered and reflected in the operations and activities (Libicki et al., 2015).
Objectives
- Prevent or mitigate the security risks and issues associated with the information sets
- To maintain consistency in the project deliveries and make sure information security risks are managed in all of these deliveries
- Maintenance of the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information for all the information sets including critical and non-critical data
- To identify and implement the security controls for physical and environmental security
- To develop and implement the detailed policies on information assurance and risk management
- To make sure that the employees are aware on the concepts and aspects of information security and privacy
- To make continuous improvements and changes in information assurance and risk management aspects as per the latest trends so that the violation of information properties does not occur (Peterson et al., 2018)
Standards and Frameworks applicable
There are a number of frameworks and standards applicable for Cerious Cybernetics Corp (CCC).
ISO/IEC 27001:2013
The security standard comes under the ISO/IEC 27001 family and covers the specific security requirements that must be met to ensure effective information security risk management. The other standards in the family are based on the security controls along with the guidelines on risk management, information auditing, and others.
The standard will be beneficial for CCC as it is applicable internationally and makes use of Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle. The cycle is followed from initiation till the end to make sure continuous assessment and improvement is possible (Iso, 2015).
NIST Framework
National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST has come up with a number of standards associated with information security. These standards come under Federal Information Security Management Act, FISMA. NIST came up with a comprehensive framework for management of the risks. The framework is developed using the NIST standards and guidelines along with the Federal Information Publications, FIPS. The RMF process covered under NIST framework include six steps. The first step is based on the categorization of the information assets (Nist, 2018). It is then followed by selection of an initial security baseline to manage the information sets. Security controls are implemented thereafter followed by the assessment of security controls. The system operations are authorized next followed by necessary monitoring and assessment.
Cyber Security Framework
Cybersecurity framework is also one of the programs under NIST and it was developed to enhance the critical infrastructure associated with cybersecurity. The framework also comprises of a specific set of industry standards and procedures to assist the organizations in the management of cybersecurity. The entire program is classified in three major stages beginning with the framework core (Gordon et al., 2020). The common activities and references are covered in the core. The next is the framework profile. The profile covers the guidelines for developing the program for specific organization. The last is the framework implementation tiers. The organization approach to manage the cybersecurity risks and attacks is portrayed in this part. The framework was originally developed for use in the organizations associated with US critical infrastructure. It can now be used by other organizations too.
Implementing the aforementioned Frameworks / Standards
Implementing ISO/IEC 27001:2013
- The first step in the implementation of the standard shall include the gathering of the background information on ISO/IEC 27001 standard to understand the need to implement it in the organization
- CCC shall then come up with a dedicated team to implement the security standard and initiate the process in the organization
- There are currently several security gaps in the organization. Detailed gap analysis shall be performed to understand the existing loopholes and the changes that shall be made
- Defining the scope of risk management and information assurance procedures as part of the standard will be necessary. The in-scope and out-of-scope items shall be adequately defined
- High-level policies for information assurance and risk management shall be developed thereafter to include the specific actions and steps to follow
- Risk assessment shall be carried out in the next step and it will comprise of sub-stages. The information shall be gathered first to identify the risks associated with CCC. The next steps shall involve assessment of the risks followed by treatment and control processes
- The security controls as per the best practices under the ISO/IEC 27001:2013 standard shall be developed and mapped with the specific procedures and risks
- The essential documentation, such as risk treatment plan, statement of applicability, etc. shall be developed so that effective risk management and information assurance is in place
- Staff awareness training shall be conducted to share the details of the best practices and norms with the staff members
- Internal audits shall be performed to assess and review the risk details and come up with the security mechanisms to implement
Implementing FISMA (NIST)
- The first step towards FISMA compliance shall include risk categorization. In this step, the information systems associated with CCC shall be categorized as per the security objectives in order to maintain essential security compliance. The categorization of the risks shall be performed based on the risk level with sensitive information placed at the highest level.
- Minimum baseline controls for CCC shall be selected next. It is not essential to meet and include all the security controls mentioned. The security control relevant to the organization and its systems shall be included in the baseline.
- Security controls shall be listed and described in the formal system security plan. The plan shall include the details of all the information systems, information sets, interfaces, and hardware components. The baseline controls shall be used and mentioned in the document to maintain the security.
- Risk assessment procedure shall be followed to improve and enhance the security controls. This shall be performed in order to validate the security controls and to make sure if the controls mapped are sufficient or any changes are required. The effectiveness of the controls implemented shall be tested after the implementation is complete.
- CCC shall carry out annual security reviews by the experts in order to obtain the certification and accreditation.
- Continuous monitoring of the security controls shall be carried out and accredited systems must be used to perform the monitoring. It will enable the organization to provide quick response to the data breaches and include the changes made to the security controls. Continuous monitoring of the security controls shall focus on the status reporting along with the configuration management
Implementing Cyber Security Framework
- The first step that shall be included in implementing the NIST framework is to define the organizational goals associated with data security. The goals shall be based on the risks associated with CCC along with the current gaps, levels of the risks, and the associated priorities.
- Detailed risk profile shall be developed as per the business needs to make improvements in the risk management aspects accordingly. The framework comprises of the implementation tiers that can help in the identified of the business needs and the essential improvements. Four such tiers are defined in the framework as tier 1 – partial, tier 2 – risk informed, tier 3 – repeatable, and tier 4 – adaptive.
- Current position shall be determined by CCC to understand the existing position in the aspects of information assurance and risk management. There are automated software tools that can be used to provide scores on the security efforts. Security measures along with the training aspects shall be determined accordingly (Takahashi et al., 2017).
- The next step shall include analysis of the gaps to determine the suitable actions to be taken. The security scores assigned can be shared with CCC stakeholders to come up with the information on the gaps and actions to be taken to resolve these gaps
- Implementation of the plan must be the next step using the plan, gaps, and the control measures. The plan shall be continuously improved to make sure that the security vulnerabilities do not cause adverse implications on the systems and applications.
- NIST resources shall be approaches to navigate the overall framework implementation process. They will assist in the determination of the best practices and guidelines to implement for the business (Keller, 2019).
Risk Management
Information risk management is one of the crucial aspects of the information assurance program. It includes the systematic assessment of the security threats and issues related with specific information assets to come up with the specific controls and countermeasures for managing the risks.
The entire risk management process is primarily classified in four steps.
- Risk identification: The first step includes the identification of the possible risks with CCC. These risks can be classified in different categories based on the CIA triad.
- Risk Analysis: The second step is the analysis of the risk. The risks associated with CCC will have varying degree of impact. These impacts can be in the range as low, medium, or high. The probability levels of the risks will also vary and these can also have the levels as low, medium, or high (Ganin et al., 2017). The analysis processes shall include the determination of these aspects along with the analysis of the risk controls in place.
- Risk treatment: The treatment strategies associated with the risks shall be defined and it must include the outcomes of the analysis phase. Based on the risk impact and likelihood, the treatment mechanisms and methods shall be implemented.
- Risk monitoring: The monitoring processes shall be implemented to mitigate and manage the risks. The changes in the risk level and status shall be tracked continuously.
The information assets associated with CCC can have more than one identified risk. There can be multiple threats and vulnerabilities associated with a system or an application. A risk assessment table shall be developed including the details of the overall risk management process. The table shall include the list of the risks CCC systems will be exposed to. The table shall include the description of these risks along with the probability and impact levels of the risks. The risk score or level shall be calculated accordingly and mapped with the risk. The risk treatment strategy shall be mentioned against the risks and the risk status (Insua et al., 2019).
Risk management is a dynamic process that shall be continuously carried out. This is because the status and level of the risks can change continuously.
INFORMATION ASSURANCE PROGRAMS
There are two major approaches present to develop and implement the Information Assurance programs. The first is the compliance-based approach and the second is the risk-based approach. The compliance-based approach is the one that is centrally controlled and managed. The approach has structured guidelines and the procedures under it are enforced for all the users. The approach associated with the program is utilized by the US DoD. These programs provide clear requirements to ensure protection to the national security data.
The second is the risk-based approach associated with information assurance. In this approach, the responsibility is applied to identify the threats associated with the processing environment. The risk appetite of the organization is then determined to understand the risks that can be accepted (Trappe & Straub, 2018). Under this approach, it is essential that the risks associated with the specific functions or departments are identified and listed. The alternatives to risk management are then evaluated to make cost-effective decisions.
The information assurance programs do not intend to eliminate the risks. Rather, these programs aim to come up with a logical methodology that shall be consistent with good systems engineering mechanisms so that effective risk management is possible. The risks are analysed and ranked as per the priority so that risk reduction is possible. Information assurance shall not be a separate activity rather it shall be synced with the existing lifecycle to witness the best results (Willett, 2019).
There are a total of nine components of a risk-based information assurance program. These include policy, assessment of responsibilities, associated procedures and set of guidelines, systems engineering techniques, IT personnel security, end-user trainings, incident management, and management review.
Policy
It refers to the statement provided by the senior management or leadership to define the expectations in the organization. The section defined for CCC shall not describe the process of expectations to be discharged or success measurement.
Assignment of Responsibilities
The second step involved is to determine the resources responsible for the implementation of the policy. The primary responsibility of implementation and management is on the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). There are other resources also assigned to the security team and shall be assigned with the roles and tasks.
Associated Procedures and Set of Guidelines
In this step, the specific procedures and the set of guidelines shall be defined in association with the methodological approaches to implement and maintain the information assurance program. There are various aspects that shall be focussed upon in this step. Systems engineering process shall be developed and the specific data sets and applications must be developed based on the respective categories. The testing approaches and mechanisms shall be defined for the security requirements and the steps involved in the maintenance of the security controls shall also be listed (Ahmad et al., 2019).
Technology plays an important role in ensuring that the information security is managed and maintained. The IT procedures shall be developed to make sure that the information properties and systems are safeguarded. The procedures and methods shall be defined to assess the security risks associated with the IT infrastructure. The definition and development of the specific plans and protocols shall be developed as an outcome.
Personnel security procedures shall be defined and established to make sure background checks are made properly and the access to the information sets is distributed accordingly. The mechanisms shall also be implemented to record and avoid unacceptable actions by the security personnel (Ulven & Wangen, 2021).
Awareness and training procedures shall be included for the resources in the organizations. It is often seen that the security violations and attacks occur due to the negligence or lack of awareness of the users. The training and awareness sessions must focus on the end-user training to avoid any of the adverse impacts of the user practices on the information security. The training processes shall aim to mitigate the security risks and threats associated with the system, data sets, and the applications.
There can be numerous security incidents that may occur in spite of the security controls and measures adopted. The incident recording, response, and resolution shall be effective. The procedures must be adopted to report the specific incidents so that the suitable actions are taken. The adequate monitoring and review processes shall also be in place to manage the security incidents.
Management review is also an important aspect of information assurance program. The senior management has a major role to play in ensuring that the security risks and events do not occur. The periodic review and audit processes shall be conducted to make sure that the security plans are properly implemented. The training programs shall also be executed to determine the security status of the systems.
Ransomware and Service Improvement Plan
There are specific measures and actions that shall be followed to mitigate and prevent the ransomware attacks. Also, service improvement in the organization shall be supported with a detailed plan. Incident response lifecycle is crucial to follow to control and prevent the issues.
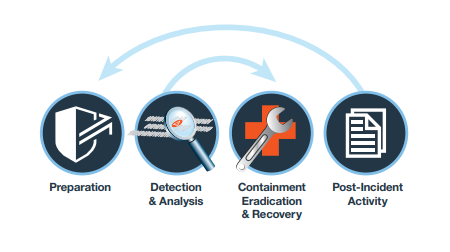
Incident Response Lifecycle (Ibm, 2020)
The first step in the lifecycle is preparation. It is the phase that includes preparing the organization to manage the security events and incidents. The phase shall also include the determination of the probability and impact of the security events that may occur. It is necessary to make use of defense-in-depth strategy to confront ransomware and make sure that such an attack never occurs in the organization environment.
The preparation phase shall a number of steps and activities. End-user education shall be covered in the initial phases (August et al., 2019). Many a times, it is observed that ransomware and other forms of security attacks occur due to the negligence of the end-users. The proper education and training of the users shall be ensured so that the security risks are prevented. In the ransomware attacks, the emails are often used as the infection vector. Mock phishing exercises shall be conducted to make sure that the end-users are aware of the possible malpractices that the attackers can adopt. The ransomware code may also be shared in the macros in the Word documents. The users are usually not aware of such a possibility and it leads to the occurrence of the ransomware attacks. The attackers also send the malicious files in the emails. When the users click on such ZIP files, the ransomware gets downloaded on the users’ machine. The preparatory phase shall focus on the adoption of some of the basic and necessary controls for preventing the ransomware attacks. The malware tools and programs shall be installed in the systems and applications to make sure that ransomware protection is enabled. The execution of the programs from the Temp folders shall also be restricted. It is necessary that the patch management policy and mechanism is up to date so that the updates are installed on the systems. It is also necessary to increase DNS visibility along with the web filtering capabilities to control and avoid the security attacks (Hayes, 2017).
It is observed that the ransomware attackers target the files and systems that are commonly used. The organizations must adopt the least privilege policy to control the access granted to the users and reduce the attack surface. Disabling Windows Scripting host and Flash can also lead to the avoidance of security. The detailed plan on information security and risk management shall also be present.
The next step included in the incident lifecycle management is detection. The organization must realize that they have been infected with the ransomware attack. The process of such realization can vary from one organization to the other. The primary focus shall be on the identification of the small to large systems that have been infected by the ransomware.
Once the issue and the damage caused by the issue are detected, the analysis of the ransomware attack shall be performed. The analysis phase can be classified in two major categories as analysis on the specific malware variant and determining the root cause behind the security attack. Security service providers and experts shall be contacted to provide assistance on the determination of the variant. The usual forms of entry of the ransomware in the organization are through the unsolicited emails or the web browser vulnerabilities. The analysis shall be performed to understand the entry point (Roldan-Molina et al., 2017).
The next step shall be containment. As soon as the infected systems are identified to contain ransomware, they shall be separated from the rest of the systems and networks. It will assist in controlling the spread of the ransomware to other systems. After containment of the infected systems, eradication processes shall begin. These shall focus on the removal of the malicious code from the system. Recovery processes shall be implemented thereafter to ensure such attacks and risks do not occur again in the future.
It is essential that the post-implementation measures are followed so that the security issues do not arise again. Patch management is one such aspect that shall be followed. There are frequent changes occurring in the security infrastructure. The patches and security updates must be released and launched in order to make significant improvements. The training processes shall also be carried out from time to time. The training procedures shall cover the norms for the end-users to make sure that the negligent practices are avoided. There may be new techniques developed by the attackers to launch the security attacks. These techniques shall be covered in the training to alert the users (Scala et al., 2019).
The lifecycle shall ensure that all the steps and phases are conducted properly with detailed focus applied on these phases. This will ensure that the overall risk management and service improvement is in place.
Resource Allocation and Staff training
It is essential that adequate resources are allocated to the information assurance program so as to control and manage the security risks and issues in CCC. The human resources will be significant and the entire program shall be headed by the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). Apart from CISO, the security team shall include the Security Architect, Security Advisor, Security Analysts, and security associates.
The non-human resources, such as workstations, integrated security management tools, project management tools, and reporting tools will also be needed to manage and maintain the security.
The staff training shall be arranged and conducted based on the gap analysis performed. The gap analysis will provide the information on the necessary skills. The trainings on the tools, legal compliance, and ethical compliance aspects will also be important (Peng et al., 2018).
Post implementation process
The post-implementation process of information assurance program shall focus on the following aspects:
- Continuous monitoring of the implementation of the information assurance program shall be performed
- The senior management and CISO shall review the program at regular intervals to determine and report the gaps. The review processes shall cover the security objectives and must identify the corrective and preventive actions to be implemented. The effectiveness of all of these actions shall also be determined.
- Periodic internal audits shall also be conducted to determine the progress and gaps. The outcomes shall be documented so that suitable prevention or corrective actions are taken.
Summary
Information assurance and risk management are critical aspects for CCC. There are various security standards and framework developed. Three such standards and framework as ISO/IEC 27001, NIST FISMA, and Cybersecurity framework shall be followed and implemented. These will provide the mechanism to determine the risks and make changes and implementations accordingly. The risk management process in the organization shall also be conducted in a series of steps. These shall include risk identification, analysis of the risks, risk treatment, and monitoring activities. The information assurance program will also cover a set of steps and activities. The procedures and guidelines around information technology, information security personnel, management reviews, end-user training, etc. will make sure that the overall security and privacy of the information sets and the applications is safeguarded. The information assurance program and risk management must aim at safeguarding and protecting the information properties mentioned in the CIA triad.
References
Ahmad, Z., Ong, T. S., Liew, T. H., & Norhashim, M. (2019). Security monitoring and information security assurance behaviour among employees. Information and Computer Security. https://doi.org/10.1108/ics-10-2017-0073
Armenia, S., Ferreira Franco, E., Nonino, F., Spagnoli, E., & Medaglia, C. M. (2018). Towards the Definition of a Dynamic and Systemic Assessment for Cybersecurity Risks. Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 36(4), 404–423. https://doi.org/10.1002/sres.2556
August, T., Dao, D., & Niculescu, M. F. (2019). Economics of Ransomware Attacks. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3351416
Calderon, T. G., & Gao, L. (2020). Cybersecurity risks disclosure and implied audit risks: Evidence from audit fees. International Journal of Auditing. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijau.12209
Ganin, A. A., Quach, P., Panwar, M., Collier, Z. A., Keisler, J. M., Marchese, D., & Linkov, I. (2017). Multicriteria Decision Framework for Cybersecurity Risk Assessment and Management. Risk Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.12891
Gordon, L. A., Loeb, M. P., & Zhou, L. (2020). Integrating cost–benefit analysis into the NIST Cybersecurity Framework via the Gordon–Loeb Model. Journal of Cybersecurity, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/cybsec/tyaa005
Hayes, J. (2017). Pay up - or else [ransomware attacks on industrial infrastructure]. Engineering & Technology, 12(4), 48–51. https://doi.org/10.1049/et.2017.0404
Ibm. (2020). Ransomware Response Guide IBM INCIDENT RESPONSE SERVICES. https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/233484/Open%20Systems%20Specialists/Content/Ransomware%20Response%20Guide.pdf?t=1507156230392
Insua, D. R., Couce?Vieira, A., Rubio, J. A., Pieters, W., Labunets, K., & G. Rasines, D. (2019). An Adversarial Risk Analysis Framework for Cybersecurity. Risk Analysis, 41(1), 16–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.13331
ISO. (2015). ISO/IEC 27001 Information security management. ISO. https://www.iso.org/isoiec-27001-information-security.html
Keller, N. (2019, July 8). Cybersecurity Framework. NIST. https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework
Libicki, M. C., Ablon, L., & Webb, T. (2015). The defender’s dilemma : charting a course toward cybersecurity. Rand.
Nist. (2018, June 12). Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) Implementation Project. NIST. https://www.nist.gov/programs-projects/federal-information-security-management-act-fisma-implementation-project
Peterson, D. C., Adams, A., Sanders, S., & Sanford, B. (2018). Assessing and Addressing Threats and Risks to Cybersecurity. Frontiers of Health Services Management, 35(1), 23–29. https://doi.org/10.1097/hap.0000000000000040
Peng, C., Xu, M., Xu, S., & Hu, T. (2018). Modeling multivariate cybersecurity risks. Journal of Applied Statistics, 45(15), 2718–2740. https://doi.org/10.1080/02664763.2018.1436701
Roldan-Molina, G., Almache-Cueva, M., Silva-Rabadão, C., Yevseyeva, I., & Basto-Fernandes, V. (2017). A Comparison of Cybersecurity Risk Analysis Tools. Procedia Computer Science, 121, 568–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.11.075
Scala, N. M., Reilly, A. C., Goethals, P. L., & Cukier, M. (2019). Risk and the Five Hard Problems of Cybersecurity. Risk Analysis, 39(10), 2119–2126. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.13309
Takahashi, T., Panta, B., Kadobayashi, Y., & Nakao, K. (2017). Web of cybersecurity: Linking, locating, and discovering structured cybersecurity information. International Journal of Communication Systems, 31(3), e3470. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.3470
Trappe, W., & Straub, J. (2018). Cybersecurity: A New Open Access Journal. Cybersecurity, Ulven, J. B., & Wangen, G. (2021). A Systematic Review of Cybersecurity Risks in Higher Education. Future Internet, 13(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi13020039












