Implementing Electronic Human Resource Management In UK Workforce
Question
Task: Write a research report illustrating the qualitative analysis of the role in technology readiness for adopting electronic human resource management among the workforce in UK.
Answer
1. Introduction
1.1 Background
Electronic Human Resource Management (e-HRM)is defined as the integration of all the HR functions and activities by the use of “web-based technologies”. Traditional HRM processes mainly rely on offline processes or face-to-face conversations. However, e-HRM mainly focusses on the use of technologies and the internet to implement their goals and managing their activities. E-HRM helps in managing all the functions in anintegratedway and thus, helps the HR managers to take decisions effectively (Berber, orevi, & Milanovi, 2018).In the process of e-HRM practice, the HRM professionals can easily resolve their jobs with the help of internet and digitalization.It helps them to achieve their regular professional objectives efficientlyand lead them in making effective decisions on a particular situation.
e-HRM has been divided into three major parts namely- Operational e-HRM, Transformational e-HRM and Relational e-HRM (Njoku, Ruël, Rowlands, Evans, & Murdoch, 2019). The parts are also interlinked with each other. Firstly, Operational e-HRM mainly deals with the operations of HR like analysing the employee data and their performance, increasing the payroll and many more. Secondly, Relational e-HRM deals with supporting "businesses processes" like training and recruitment of the newcomers on the Company. It also includes initial support to the newcomers on the companies.And lastly, the transformational e-HRM emphasized on ‘knowledge management,’ strategicre-orientation’ and adjust themselves with the organizational environment.
The e-HRM helps to implement technological methods on the system and thus, provide idea to implement effective methods of the system. Currently, the workforce from the UK is focusing on the e-HRM methods as it has been proved to be effective for improving the Company’s growth (Thite, 2018).The UK workforce has been improved in recent years through the ways of e-HRM methods.
Electronic human resource managementhas employed sustainability in the UK workforce. In today's dynamic changing environment, sustainability has become an essential element in the operations of e-HRM. The digitalization of HRM operations through the implementation of e-HRM has engaged sustainability in the system. E-HRM has helped the workforce from the UKto increase their growth by 5.6% in two years (Njoku, Ruël, Rowlands, Evans, & Murdoch, 2019). The process has been made faster and smoother to introduce new technology in the system. The implementation of practices from e-HRM helps in making the HRM processes cost-efficientand consistent to improve the existing practice with utmost sustainability.
1.2 Research Objectives
The objectives of this study is to provide an understanding of technology readiness of e-HRM at the UK workforce are,
- To specify the role of the e-HRM’s technology readiness within the UK workforce
- To measure the capability among the e-HRM’s technology readiness within the UK workforce
- To identify the sustainability in adopting new technologies by expressing technology readiness within the UK workforce
- To understand the challenges of adopting technology readiness in working witheffective electronic human resource managementamongthe UK workforce
1.3 Research Questions
The quantitative analysis in understanding the technology readiness of e-HRM at the UK workforce is based on the following questions,
- What is the specification of e-HRM’s technology readiness within the UK workforce?
- How to measure the capability of e-HRM’s technology readiness within the UK workforce?
- What is the identification of the sustainability factor in adopting new technologies to express technology readiness within the UK workforce?
- How to understand the challenges underlying in adopting technology readiness in practicing effective e-HRM among the UK workforce?
1.4 Rationale
Electronic human resource managementis already implemented on the UK companies but still, it has been observed that many technologies cannot be adopted by the companies. The reason behind this is lack of knowledge in e-HRM and flaws in employee management. Thus, e-HRM is not used by the HR managers properly. It is creating many issues within the system that can be only solved by practicing appropriate technology readiness.
The above problem hasraised a serious issue because many of the technologies cannot be implemented due to lack of proper e-HRM knowledge.The understanding of e-HRM functions and practices will strengthen the technology readiness among the workforce of the UK. The current research process will be focusing on the technology readiness factor with the knowledge of e-HRM requirements. As a result, companies are facing lots of troubles in implementing various methods. It is affecting the growth of the company and thus,harm the country's economy.
The capacity of electronic human resource managementneeds to be known so that technological methods can be applied to UK companies. Without having proper knowledge of e-HRM capacity it is getting difficult to implement the effective technological processes on the system. Thus, the research will focus on the issue of e-HRM capacity in being technological readiness.
The research will analyse the capacity of e-HRM on technological readiness through quantitative analysis. The study will focus on the UK workforce and their operations related to e-HRM on technological readiness. The research will discuss the challenges based on the e-HRM and their possible mitigation ways to provide an idea on effective theories for workforce growth.
1.5 Problem Statement
The contemporary organizations are unable to incorporate e-HRM in the place of their traditional HRM processes.Thus, e-HRM has been implemented by the UK workforce to adopt new technologies and effective goals by HRM. However, the capacity of e-HRM in adopting new technology has not been measured so far.Proper knowledge on e-HRM has become important criteria for the UK companies. They are also not sure about their capacity and thus, they are lagging in several respects. The research focusses on mitigating the problem and improves the firm performance of the UK workforce.
1.6 Significance
The research will provide an idea of e-HRM capacity and its practical implementation in the UK workforce. It will help to suggest ways in building more effective integrated system on the UK workforce. The HRM professionals from the UK workforce can develop new technological techniques for managing the employees within the system. The research will suggest ideas to mitigate the challenges related to the electronic human resource managementand provide ways for maintaining sustainability on the system.The current research paper will be analysing the current practices and perspective of the HRM professionals from the UK workforce, which will enable the future researcher to work on this field with a more in-depth approach. It will help to build sustainability in the system. Thus, the results of the research can be used in another similar research.
2. Literature Review
2.1 Implementation of the electronic human resource managementin being technology readiness within the UK workforce
The new internet revolution has transformed the basic force condition in the job sector. The data access has become simple with the e-logistics which itself has influenced the human resource management as a whole (Al Haziazi, 2019). HRM is one of the key aspects in the success of business enterprises. The trend of efficient management has accelerated within the large business blocks such as the European Union or EU. The employment legislation in the UK is higher due to the European Union. The unique aspect of the European Union is in its supra national legislation of twenty-five countries. The workforce therefore is much dynamic and diverse. It belongs from various countries, culture and class. The public spending share in the GDP is much higher in the UK. Due to the increasing influence of the e-business, the fundamental sector such as retailing, financial sector and knowledge management has transformed. Therefore, the transformation of the individual e-learning into organizational learning and management of knowledge, online based career management, creative management resources utilization and work flexibilities. The impact of the e-business has effectively challenged the traditional working methods of the HRM.
The transforming methods in the workforce arena have led major changes in the management strategies. The transforming strategies require important strategic arearrangements and re-ordering (Al Shobaki M. , Naser, El Talla, & Amuna, 2017). Impacts of the electronic management of human resources are the main object for this research paper. Researchers I this research used the analytical approach to achieve the objectives and as a study toll used the questionnaire.The question of the job design and performance management has crucially transformed in UK with the introduction of the technological updates. The improvisation of the updated technological aspects is necessary due to overall changing working patterns.
The government legislation in UK outlawed the age wise discrimination in the workplace. The demands of the technological handling ability are essential for job market in the present scenariofor being proactive demands better digital marketing strategies and technological assistance (Al Shobaki M. , Naser, Amuna, & El Talla, 2017). The e-business methods are making organizational strategies easy and efficient.
Without including the younger generation into the senior management and Human Resource Management, their digital efficiency cannot be utilized on the optimum level(Al Shobaki et al., 2017). The age gap is major factor in the improvisation of the digital knowledge and creative management planning. The influx of young blood into the marketing management stream is providing better possibilities of digital capabilities and technical capabilities. The increasing educational standards in the EU have led to better and efficiently skilled student trainings. This ultimately is developing the management capabilities and marketing opportunities in the UK.
The major influence of the EU in the UK workforce is its variation of cultural sectors which ultimately leads to varied approaches to the introduction of the electronic human resource managementfacility. The variety of workforce in the UK includes its migrant, domestic and outsourced labours. It provides a huge contradicting variety in imbibing the digital up gradation. The aspect of performance management is crucial in the HRM and it therefore, focuses on performance standards, orientations and appraisals. The migrating sections from different part of the European Union are trained in different ways of primary and education. Therefore, the aspect of the digital improvisation remains a major challenge in organising the workforce into a single unit. The importance therefore is on the essential introduction of the digital methods through interactive methods and organized ways.
HR aspect of training and development is crucial and ultimately decides the possibilities of the implementation of the aims and objective outlined by the management strategy. Implementation of the digitally informed methods transforms the working patterns and outcome as a whole (Blom, Du Plessis, & Kazeroony, 2019). The variety of cultural background possesses a better opportunity of utilising various specialised skills with a proper management strategy. The efficient management skills can ensure a proper integration of the various workforces and therefore develop and train them accordingly. The strategic orientation of the HR changes the approach of employee training and development. The methods of skill development are essential in determining the utilisation of the resources in making the e-HRM possible.
The increasing technological efficiency of the workforce in UK is making the emergence of the relevance of electronic human resource managementrelevant. With the help of the individual coaches to managers, the efficiency of the workforce is developing. The digitally capable and technologically sound workforce in UK has increased 13% in one year. The constant development of the Information Technology and Digital training facilities, the user capacity has increased. UK has introduced digitalised education system as well as certain government facilities which not only makes the system efficient and fast, but also helps in making the citizens getting technologically sound and capable. The workforce enhancement in a digital orientation is possible by introducing technical knowledge from primary levels. The e-HRM facility enables the HR team to interact easily and communicate properly.
The workers with different abilities of utilising the IT applications are improving with this interdependence and efficient co-ordination of the HRM. The human resource management teams are utilising the modern techniques of HR portals, employee/managers self-service etc to develop its resource database of support decisions, user connection and adaptability improvement. It is crucial for the developing workforce to increasingly improvise the digital skills in order to strategize effective management plans and implement them accordingly. Fostering leadership abilities need better working environment and improved team work skills. The newly introduced management techniques are being further improve by the digital knowledge and technical development (Bondarouk, Harms, & Lepak, Does e-HRM lead to better HRM service?, 2017). The increasing technical ability is a major positive aspect of the UK making the possibility of the implementation of electronic human resource managementpossible.
2.2 Frameworks to bring sustainability in the UK workforce
The value of skilled labourers is increasing and other skill developing trainings areproducing
a major skilled manufacturing workforce. The workforce sustainability is effectively contributing in the development of various components of the market. The importance
of the sustainability is increasing in the UK job sector in order to deliver the expected income
through expected outcomes of employment. These policies then make staying unemployed less attractive relative to working by (i) decreasing the income expectation of the unemployed through the receiving a sanction possibility, and (ii) increasing required search level, which is costly to the unemployed (Bondarouk, Parry, & Furtmueller, Electronic HRM: four decades of research on adoption and consequences, 2017).
The community factor is essential in developing a strong and connective working force for the job market. The important factor of the community standards development is essential in delivering the expected return from the labour economy. The community factor strongly influences the working methods of the labour team and hence the expected return increases. The improving skill standards are important in developing the market returns as well building majorly effective business plans. The conditions of the connectivity development depend both on the effective management strategy and efficient human resource planning. The development of the IT sector and its increasing influence is leading to the major development of the community factor.
The community spirit is essential in delivering an effective and efficient team work, which guarantees the maximum profit securing and returns. The community basis is crucial tothe sustainable management plan which in turn provides efficient returns (Bos-Nehles, Bondarouk, & Smit-Methorst, 2019). It is therefore important to chalk out a sustainable plan of management strategy to strengthen the workforce community. The community standard improves performance and effective capabilities of the workforce that aims to chalk out a sustainable management plan. The effective capacity of the community standard improvement requires an overall development.
The sustainability of performance management is crucial in securing an effective overturn. Performance increase rate through various activities lead to the effective implementation of the aims and plans of the company. The strategic objectives of the management team are an essential framework in mapping out effective plans and strategies. The quality service to the clients can be enhanced with the qualitative development of the workforce performance (Škudien?, Vezeliene, & Stangej, 2020). Therefore, basic training and skill developments are essential in developing the performance management. To make the workforce effectively yielding and extensively productive, the plans of basic interactive developments must be developed. The importance of introducing communicative and interactive work space environment ensures the delivery of performance skills and necessary values.
The internal evaluation is essential in this aspect of developing the skills and performing capabilities of the workforce community. To establish an effective eco-innovation strategy, one requires the particular firms to change the dynamic environment and for its adaptation (Salim, Ab Rahman and Abd Wahab, 2019). Sharing of good practices and monetary incentives are effective ways of boosting the performance capabilities of the workforce. The inclusion of the better performing training experts is indispensable. The training expert enhances the skills of the workforce that is otherwise not utilized and remains a hurdle in the expansion of the company. The effective training standards ensure better performance capabilities. The importance of performance standards is effectively seen during the companies’ feedback evaluation period. The performance enhancement ensures better skills and workspace adaptabilities along with strong leadership qualities (Ziebell, Albors-Garrigos, Schoeneberg, & Perello-Martin, e-HRM in a Cloud Environment: Implementation and its Adoption: A Literature Review, 2019). It is important in making the business strategy sustainable and efficient.
The improvement of the management in order to sketch an effective strategy can effectively transform the working capabilities of the workforce. The development of the management effectively depends on the efficient market analysis, ability to improvise constantly developing technology and effective human resource management. The improving aspects of the digital capabilities of the management workforce can effectively make the sustainable returns. The sustainability of the market depends on the efficient handling of the products and its proper logistics. It is crucial for the logistical sector to improve in order to prove mobility of the workforce. The mobility of the workforce is essential in improving the sustainability of the management strategy. The mobility provides improvement in the performance capability of the skilled workforce which effectively utilizes the dynamics of the market and overturns the profit returns.
The diversity and inclusion is another major framework in providing sustainability to the workforce in the UK considering electronic human resource management. The involvement of various skills and knowledge is crucial in building a diverse workforce. The workforce essentially incudes shared knowledge and values to improve the performance ability. The diverse knowledge and values regarding sustainability improves the communicative interactions within the sector. The sector is provided ample opportunities of utilizing workers knowledge and skills and hence outlines an effective planning of the sustainable marketing techniques. The importance of the diversified views and approaches lies in the general development of the demands of efficient and easy services. The sustainability transforms overall aspects of the workforce in terms of its handling, processing and delivery of the work. The diversified workforce needs to be integrated into the market standards through performance development and infrastructural developments. The importance of the infrastructural development ensures effective integration of the diversified workforce and varied groups of the people.
The diversified groups of the UK workforce are essential in utilising the shared knowledge prevailing in different regions of the European Union. The diversified workforce includes varied working capacities and enhances human resource management which ultimately develops the sustainability. The sustainability of the workforce remains crucial in mobilising it to increase market activities and production sector development (Winarto, 2018). The essential characteristics of the integration involve efficient technical training and mobilisation of the workforce to aim strategically orientation and market goals. The importance of the sustainability is crucial in improving profit accumulation.
2.2 Efficiency of Workforce structure in adopting new technologies on UK companies
The new technological innovation of the IT developments is bringing efficiency in the workforce structure in the UK. The involvement of technologically developed applications is transforming the workforce structure. The organisational strategy development is crucial in developing the overall management strategy. The organisational strategy is improved by improvisation of new interface-based technologies which enhanced the leadership qualities and team work interactions.
The communication strategy is crucial in the development of the workforce quality. Without effective exchanges between the team members, the structure of the management workforce cannot be enhanced. The importance of the structural development of the management team is effective in the overall development of the workforce. The importance workforce development is crucial in developing the overall market performance of the UK companies. The effective utilisation of the new digital platforms and technological applications are improving the overall performance of the workforce. The introduction of the digital applications in the workspace is making the major workforce sectors like retails more efficient and customer serving. The importance of online app based online purchasing and surfing is increasing the dependency of the customers on the efficiency of technology and effective communication. The importance of the digital transaction is demanding workers skill in handling of the virtual transactions and exchanges.
The development of the user interface software has created increasing demands of the efficient service by the retail sector. The other sectors also have considerably improved the technology handling and its implementation. The importance of the software-based communication has increased demands for efficient virtual assistance and infrastructure. The logistical development has greatly improved with that of the adoption of technological innovations and high-performance machineries. The improvement of the heavy working sectors such as mining and transportation has effectively transformed with the introduction of the high-performance machinery and improved logistical assistance.
The workforce members have imbibed the knowledge gained from the elementary learning of the technological usage. The competency capacities have improved due to the improving skills and increasing efficiency of implementing it. The goals and achievement strategy have improved with the improvement of the greater changes in the organisational methods. The workforce efficiency has enhanced with the improvement of the digital efficiency and technological knowledge. Importance of the innovative technological changes lies in the improvement of the working condition and facility (Waheed, Xiaoming, Waheed, Ahmad, & Tian-tian, 2020). The effective transformation of the competency capabilities and marketing strategies has led to overall changes in the working strategy.
The improvisation of sustainable management strategy is essential in determining the efficiency of the workforce. The overall transformation of the UK workforce has resulted into major hike in the profit accumulation in the market and also company performance in the market. The increasing penetration of the Information Technology is essential in changing the working capacities of the workforce structure. The digital influence has effectively introduced structural changes in the UK job market.
The sustainability of the market depends on the efficient handling of the products and its proper logistics. It is crucial for the logistical sector to improve in order to prove mobility of the workforce. The mobility of the workforce is essential in improving the sustainability of the management strategy. The major factor determining the community spirit development is the efficient communication and effective interaction. The team development is crucial in providing a sustainable workforce for the maximum profit gains (Waheed, Waheed, Karamat, Ahmad, & Majeed, 2017). The improvement of the community basis is necessary in proving a productive, resilient and healthy workforce. The research tends to summarize the lessons from the research on the effectiveness of the UK organization that can be implemented for improving or developing workforce structure
The importance of the diversified views and approaches lies in the general development of the demands of efficient and easy services. The sustainability transforms overall aspects of the workforce in terms of its handling, processing and delivery of the work. The diversified workforce needs to be integrated into the market standards through performance development and infrastructural developments.
The variety of workforce in the UK includes its migrant, domestic and outsourced labours. It provides a huge contradicting variety in imbibing the digital upgradation. The aspect of performance management is crucial in the electronic human resource managementand it therefore, focuses on performance standards, orientations and appraisals. The migrating sections from different part of the European Union are trained in different ways of primary and education. The type of consequences focusses literally on the changed effects of operationalization, in terms of relational and transformational outcomes. The research paper emphasizes on the discussion regarding the shifts along with the implication of changes by the electronic human resource managementinto the organizations of UK for the enhancement of workforce.
The research paper examines the function of the information technology in a direct way on the one central perspective of work structure in the recent times. It impacts on the HRM itself. The research paper emphasizes on interpreting a more comprehensive as well as contextualized view of the HRM, an integrated structure of the stakeholders, and a wider approach to deal with the outcomes. Applying the principles on the IT literature, HRM helps in identifying and clarifying both the merits and demerits to the various stakeholders of the intersection between technology and HRM. It can be seen that the rapid developments in the technological infrastructure offers an updated, digital, and smart context for the practices of HRM along with a better quality of the data of HRM in enabling a strong ownership of the HRM by the stakeholders (Umar, Yammama, & Shaibu, 2020).
The research paper emphasizes on the discussion regarding the shifts along with the implication of changes by the electronic human resource managementinto the organizations of UK for the enhancement of workforce. The aspect of performance management is crucial in the HRM and it therefore, focuses on performance standards, orientations and appraisals (Thite, 2018). The migrating sections from different part of the European Union are trained in different ways of primary and education. Therefore, the aspect of the digital improvisation remains a major challenge in organising the workforce into a single unit. The community factor strongly influences the working methods of the labour team and hence the expected return increases. The improving skill standards are important in developing the market returns as well building majorly effective business plans. The conditions of the connectivity development depend both on the effective management strategy and efficient human resource planning.
2.3 Implementation of HRM goals to bring effective changes on the UK workforce
The implementation of electronic human resource managementgoals is important in bringing out effective changes on the UK workforce. It emphasizes on interpreting effectiveness of workforce through the acquisition of human resources and the development of human capital. Among the lot of essential elements in the complicated alchemy of effectiveness within organizations is a greatly motivated, capable, and adaptive workforce (Iqbal, Ahmad, Raziq, & Borini, 2019). For accomplishing the research objectives, the organization should navigate the complicacies, dynamics, and uncertainties of its external environment through counteracting and outperforming the adversaries to become innovative. They must create a unique and capable workforce, and then must leverage its specific talents. It can be accomplished through the development of a strategy for meeting the research objectives and aligning the internal organization in terms of leadership, work procedures, structure of administration, and management of human resources for supporting the execution of the strategy.
Building and acquiring an efficient workforce is predicted in terms of providing the organization with special capabilities and enabling it for meeting the objectives of itsstrategically conquests for simultaneously making it difficult for its adversaries to get successful. The research purpose is concerned with describing the behavioural science theory and the findings of research from the psychology of the organization and the electronic human resource managementunderpinning the development of workforce in terms of implementing the human resource management. There are several strategic goals in terms of establishing capable workforce by the implementation of the human resource management. They are discussed in the following.
2.4 The intelligence community as an UK organization
It is likely to assert that the intelligence community is not exactly like other organizations, but it is similar to the organization in many ways. Keeping in mind the differences, various key factors are identified that make the institutions of public and the IC which is the Intelligence Community lesser sensitive to the pressures of adaptation that are faced by the commercial firms (Rahman, Mordi, & Nwagbara, 2018).The research tends to summarize the lessons from the research on the effectiveness of the UK organization that can be implemented for improving or developing workforce structure along with the learning of IC within the organization.
2.5 Diversities in terms of individual differences
The management of human resources focus on the various diversities that are linked with various differences among people. At many workplaces the diversity and the individual differences do not allow the HR to practice their principles at the workplace (Yadav and Katiyar, 2017). It is collection of workforces comprising the pool of human resource for an UK organization. There are two types of individual differences. They are stable and malleable.
2.6 Human capital and human resources
Human capital and human resources provide a base for understanding the diversities in the endowments of resources and the aggregated capabilities distinguishing the organizations those are competing within a particular background of environment(Roumpi, Magrizos and Nicolopoulou, 2019). The HRM practices are targeted to be designed for the enhancement of the ability of workforce for the UK organization. Some of the practices such as the selection, recruitment, training, compensation, and management of performance are used for empirical linking of the HRM practices to the effectiveness of the UK organizations.
2.7 Developing an effective workforce
Although many varying practices of HRM are utilized by the organizations, the research provides a discussion on four core clusters of practices (PrabaDevi). They are the selection and recruitment, the training and improvement, the management of incentives and performances, and the teamwork and work designing. It focuses on the consistency of the strategic architecture of electronic human resource managementimplementation as they are based on the methodologies that are well-developed and possesses an extensive foundation of research.
2.8 Overcoming resistances
Although the resistance of the employees is a natural reaction to the widespread changes of the UK organization, one can overcome the resistance through emphasizing on various strategical factors. Firstly, it includes clear and consistent communication about the changes before its implementation (Iqbal, Ahmad, Allen, & Raziq, Does e-HRM improve labour productivity? A study of commercial bank workplaces in Pakistan, 2018). Secondly, it includes helping the employees for understanding the requirement for change in better ways and the rationale behind the decisions lie in affecting the situation of the workplace by incorporating changes. Thirdly, it must ensure that the management team incorporating changes can help in spreading positive messages about the change along with taking the temperature of the reactions of the employees to the change. Lastly, it includes a provision for supporting the changing environment for ensuring the managers with required information and training for answering the questions of the employees.
2.9 Engagement of employees
The employees who are engaged into the change are more inclined to put their individual efforts in helping necessary implementation of the change and ensuring a positive outcome for the UK organization(Mohanty, 2018). Help creates higher level of engaging employees during the process of change through various factors. Firstly, a team approach must be developed including the perspectives of the employees from a variety of departmental levels. Secondly, it includes clarifying and assigning roles and tasks (Panos & Bellou, 2016). Thirdly, it increases the focus of the organization on the workers. Fourthly, it includes resistance of the leaders in the processes of change for helping to overcome pushbacks from the employees. Lastly, it involves understanding of each employee’s motivational factors.
2.10 Implementation of change in phases
For the UK companies who are planning an important initiative regarding change, taking a phased approach helps in ensuring that the transition to the updated process or system is very seamless and smooth. Leading of the management of the change by the UK firms constitutes preparation, management, and reinforcement. The electronic human resource managementpractices are targeted to be designed for the enhancement of the ability of workforce for the UK organization. For accomplishing the research objectives, the organization should navigate the complicacies, dynamics, and uncertainties of its external environment through counteracting and outperforming the adversaries to become innovative.
2.11 Communication of the change
Failure in telling the employees in advance regarding the changes within the organization may increase the misconduct of the employees. An essential part of every basic stage of the processes through which the changes are managed, communication should be a two-directional way for ensuring the success of the change implementation within the UK organization.
Firstly, the pre and post feedbacks and surveys must be done before implementing the change and it will enhance the overall procedures of the human resource management. Secondly, it must engage the resistors in one-on-one session before the implementation of the solution for allowing them to provide their inputs (Omran & Anan, 2018). Thirdly, it must include being cleared, explicit, and consistent in handling responsibilities. Fourthly, both informal and formal approaches of communication must be used involving intranet, email, in-person meetings, voice mails etc. Fifthly, it must offer opportunity to the employees for providing feedbacks into the processes of bringing out a change in particular. Lastly, it involves gathering of employees for exploring the worst-case scenarios and developing the strategies for addressing them.
Although the implementation of the organizational changes is very complex, it does not possess the ability of affect the performance of the UK companies in terms of a negative orientation (Iqbal, Ahmad, & Allen, Unveiling the relationship between e-HRM, impersonal trust and employee productivity, 2019). One can minimize the organizational disruptions through the beginning the communication and planning processes for creating the foundation for a successful implementation. The research purpose is concerned with describing the behavioural science theory and the findings of research from the psychology of the organization and the electronic human resource managementunderpinning the development of workforce in terms of implementing the human resource management (Obeidat, 2016). The research paper provides a review of the various decades of researching in this area with the aim of providing a summary and an integrated framework as a base for any future researches concerning the topic. The research aimed at finding out the factors that are affecting the adoption of electronic human resource managementwithin the UK organizations for enhancing the effectiveness of the workforces.
2.12 Literature gap and Summary
Despite of the existing recent reviews on the researches of e-HRM, the literature gap comprises the lack of a comprehensive understanding of the factors that affects the consequences and adoption of e-HRM within the UK organizational structure for enhancing the efficient workforce. The research paper provides a review of the various decades of researching in this area with the aim of providing a summary and an integrated framework as a base for any future researches concerning the topic. The research aimed at finding out the factors that are affecting the adoption of e-HRM within the UK organizations for enhancing the effectiveness of the workforces. Among the lot of essential elements in the complicated alchemy of effectiveness within organizations is a greatly motivated, capable, and adaptive workforce (NAGESWARI). For accomplishing the research objectives, the organization should navigate the complicacies, dynamics, and uncertainties of its external environment through counteracting and outperforming the adversaries to become innovative.
Also, the type of consequences focusses literally on the changed effects of operationalization, in terms of relational and transformational outcomes. The research paper emphasizes on the discussion regarding the shifts along with the implication of changes by the electronic human resource managementinto the organizations of UK for the enhancement of workforce. It is concerned with describing the behavioural science theory and the findings of research from the psychology of the organization and the HRM underpinning the development of workforce.
3. Research Methodology
3.1 Research Philosophy
The methodology is the heart of a research paper where the researcher expresses about the method in which the research process is expecting in gathering data, documenting the information data, and derives towards the research result and discussion. The current research paper is based on the positivism philosophy that requires an extensive amount of factual knowledge and data to make a research process trustworthy and broad observation. It enables a researcher in working with a limited set of data. In the current research process, it is related to the survey process among the 100-150 participants from various companies in the UK in understanding the role and possibility of electronic human resource management. The research process has conducted an elaborate ‘literature review’ from the existing research paper to make the research philosophy true to its research background.
3.2 Conceptual Framework
The conceptual framework of the current research process has been started from developing an understanding of the research topic to make research objectives and appropriate survey questionnaire. It helped in the further development of the research process with an elaborate ‘literature review’ and introduction. Then it expresses the research methodological concepts in which the research has been taken place. Further, it was carried out with the research result acquired from the survey process and continues with the discussion section. The current research paper has concluded with the research summary, future research possibilities, and recommendations.
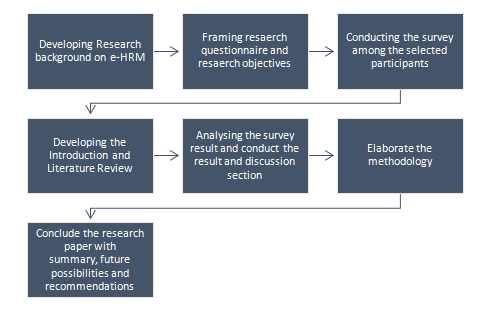
Fig: Conceptual framework in conducting the current research process (created by the author)
3.3 Research Design
The research design of the research paper includes the entire process in which the researcher “conceptualizes” the problems, gathers proper data by conducting primary methods, analyses and interprets the data and finally develops the results. The current research hasapplied the same process in developing the study (Meyers, Gamst, & Guarino, 2016). They have conducted a research survey on 50-150 participants among UK companies in various sectors. Then, they have analysed the data to develop the results. It has helped them to evaluate the research questions and reach to the effective results (Meyers, Gamst, & Guarino, 2016). In recent years, the popularity of e-HRM has been engraving the market and it is providing effective results to the Company. Most of the UK companies have implemented electronic human resource managementon their system and have git effective result (Meyers, Gamst, & Guarino, 2016). Thus, they decided to measure the capacity of e-HRM in being technology readiness and developing a greater number of technological methods on the system.
The research paper is mainly based on the quantitative analysis collected from the primary data. The primary data has been collected in the form of survey responses to develop the results authentically (Schoonenboom & Johnson, 2017). Later, some of the existing literature has been taken for the reviews and the theoretical background of the research has been developed from the existing literature papers. The responses provide a clear overview of UK workforce success factors and its sustainability by developing electronic human resource managementon their system (Schoonenboom & Johnson, 2017). The current study has reviewed the significant factors and variables related to e-HRM through the use of existing pieces of literature (Schoonenboom & Johnson, 2017). The existing literature papers have been acquired from online sources and have not violated any copyright issues.
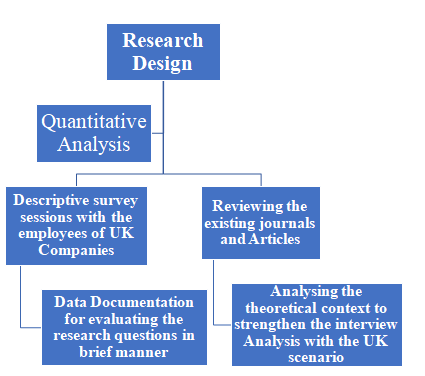
Figure: Diagram showing the research design process of quantitative analysis of the role technology readiness plays with e-HRM adoption in a UK workforce (created by the author)
3.4 Research Method
The current research has approached the primary research method with a quantitative approach. The reason behind the quantitative approach is that the survey has been taken from the employees related with various UK companies on different sectors and they have submitted their response through the numeric value (Beins, 2017). It has helped the researchers to study the actual scenario of electronic human resource managementon the UK workforce. The sustainability rate has also been measured through the responses and its applicability has also been determined (Wildemuth, 2016). The responses have been strictly collected from the UK companies to determine their workforce culture and role of e-HRM on their work culture.
The research has also worked with the “deductive” approach for analysing the documented data and develops a hypothesis from the existing theories. The quantitative analysis helps in retrieving information in a deep precise form (Wildemuth, 2016). It has resulted in building the realistic conclusion from the research.
On the other hand, research has been conducted with the existing pieces of literature for drawing a theoretical context on the research background. It will help in analysing the consistency with the survey answers (Wildemuth, 2016). Moreover, existing pieces of literature has been focused on the significant variables related to the topic and discusses the relationship between them (Beins, 2017). It has provided authenticity to the research.
3.5 Data Collection& Sampling Process
The data collection has been done on the form of survey responses from UK companies. The UK companies have already implemented the e-HRM on their system but still yet not know it (Moser & Korstjens, 2018). They don’t know the e-HRM capacity and thus, lagging on the practical implementation of it. The data will be sampled from the selected participants that have given completely on the questionnaire. The identified country is one of the most influential places where the electronic human resource management has been applied and sustainability has also been achieved (Moser & Korstjens, 2018). However, the problem arises when a new technology has been implemented on the processes. Due to lack of knowledge on e-HRM by the HR managers, the company face many uncertainties on the system (Stieglitz, Mirbabaie, Ross, & Neuberger, 2018). They failed to implement the latest technological tools on the system.
The current research has chosen a population of 50-150 participants which includes employees from both essential sectors and non-essential sectors. The data has been collected in a combined manner and suggests that the responses are authentic at its best. A sampling of data can be done through another process but the reason behind doing it through quantitatively is that it helps in providing authentic responses (Stieglitz, Mirbabaie, Ross, & Neuberger, 2018). The responses have been taken from such employees those are related to the UK companies for many years and know the improvement after the application of e-HRM on the system (Stieglitz, Mirbabaie, Ross, & Neuberger, 2018). It helps the researchers to build their network on UK companies and retrieve authentic data effectively.
3.6 Data Analysis
Data has been analysed based on the coded questionnaire forms and authorized files. The code has been taken in the form of a numeric value and it has been analysed thematically (Agresti, 2018). The questionnaire is strictly related to the electronic human resource managementapplications and its capacity on technological readiness. Technology readiness has become an essential part of recent years among UK companies (Agresti, 2018). The reason behind this is that the system is going digitalized and thus, needs upgradation on the operations. The process of recruitment and selection must involve technological tools so that it can be more improved performance in the system (Heeringa, West, & Berglund, 2017). The recruitment can be done in the bulk form if proper methods of e-HRM have been applied. The questionnaire suggests that the responses have shed light on the e-HRM capacity and capability on improving the sustainability of the system (Heeringa, West, & Berglund, 2017). UK companies will get an idea about improving the methods of electronic human resource managementon their Company.
Results by analysing the coded data will help the companies to implement effective ways according to their feasibility and work structure of the system. It has been noted that the work structure of the companies is not the same and it varies according to the policies (Heeringa, West, & Berglund, 2017). Thus, the research has been studied in a general overview to provide solutions to various companies from different sectors. Thus, the research will also help future studies to develop technological tools according to the capacity of e-HRM on the workforce culture (Heeringa, West, & Berglund, 2017). The reason behind choosing the UK as the research case study because being a first world country, it implements technological tools on the first go. Thus, helps to determine the e-HRM capacity on the system.
3.7 Research Ethics
The main purpose of maintaining 'research ethics' in a research process while conducting a survey is to protect the participants from experiencing any fraud activity while disseminating valuable information (Sobo?an, Bertotti, & Strom-Gottfried, 2019). The current research process will provide an authentic ‘consent form’ to every participant before starting disseminating answers. The participants need to understand the research background and provide relevant information that will help in developing the analysis section. The involvement of 'social science' research process requires 'field-based' research to strengthen the research practice (Brittain, et al., 2020). Poor research practice cannot generate accurate data in the research process.
In the current research process, the survey research with 'quantitative' analysis is the appropriate process in understanding the current trend among electronic human resource managementin the UK workforce and analysing its various elements with accurate data. The 'ethical' guidelines in a research process require consent form in any research background related to human interference (Clark-Kazak, 2019). It is proof for participants on the authentication of the current research process. It is also important to give credit to the contents retrieved from the existing research paper and journals that helped in developing the background of the current research. The survey process did not document any personal information from the participants and prevent any discrimination against race, gender, and ethnicity. The current research process has also ensured the authentication of used contents and references to avoid any misleading information.
3.8 Time Horizon
The time horizon in a research process indicates the specific time that the researcher took to collect their information from a particular time. The current research paper has taken two to two and a half months to collect the required data through the survey process among the electronic human resource management sector under the UK workforce. The advanced research process and a brief understanding of the changing research strategies and 'dynamics' are dependable on the allocated time for conducting every research elements (Kunisch, Bartunek, Mueller, & Huy, 2017). The current research process has implemented a 'cross-sectional' research process that targeted a specific period to collect the required data through the survey process. The advancement of digital processes and activities in conducting social or management researches helps the researchers to save their time and effort in considering the manual process.
The conceptualization and development of proper timing help the researcher to develop an efficient study on the taken topic. In the current research paper, the researcher has taken the step of conducting the survey process among various industries to understand their characteristics and capability of adopting new technologies and enhancing the 'technology' readiness. To understand a systematic research process with specific data and information with a 'cross-sectional' study with descriptive and analytical results (Zangirolami-Raimundo, Echeimberg, & Leone, 2018). It will help the current research to understand the current status of 'e-HRM' in the UK and its future sustainability in adopting new technologies. The analysis process in different industries will express different patterns to recognize the weakest and strongest areas in the UK workforce. The 'cross-sectional' study will restrict the survey's period in a specific time that will generate results in an equal environment.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1 Results and Discussion of the Survey Question-Answers
Question Number 1:
1. Do you think the industry is aware of technology readiness among the electronic human resource managementfrom the UK workforce?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
86.00 |
129 |
150 |
|
Agree |
13.33 |
20 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
0.67 |
1 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
0.00 |
0 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
0.00 |
0 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
56.00 |
Table 4.1: The industry awareness of technology readiness among the electronic human resource managementfrom the UK workforce
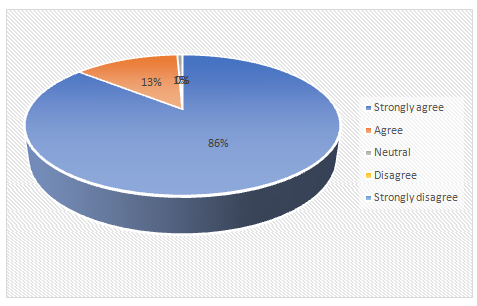
Chart 4.1: The industry awareness of technology readiness among the e-HRM from the UK workforce
Analysis for Question Number 1:
Most of the participants from the survey procedure were aware of the usage and implementation of e-HRM and their capability of technology readiness. It provides an understanding that most of the employees under HRM have a desire of developing the business structure with the help of technology.The existing relevant literature of the current research process has also provided an extensive understanding on the usage and mechanism of electronic human resource managementamong various countries. It might be the lack of understanding and resources in adopting the e-HRM techniques by expressing the technology readiness with the new technologies in the UK workforce.
Question Number 2:
2. Do you think technology readiness can sustain the work processes among the UK workforce?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
59.33 |
89 |
150 |
|
Agree |
26.00 |
39 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
7.33 |
11 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
4.67 |
7 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
2.67 |
4 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
11.00 |
#N/A |
35.81 |
Table 4.2:Sustenance of the work processes among the UK workforce due to technology readiness
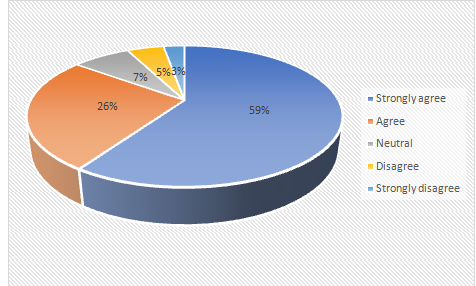
Chart 4.2: Sustenance of the work processes among the UK workforce due to technology readiness
Analysis for Question Number 2:
More than half of the participants (59.33%) were agreed with the fact that technology readiness is one of the vital and crucial factors in achieving sustainability among the HRM activities in the UK workforce. It has been also understood from the works of literature related to the electronic human resource managementand its activities that the advanced technologies are capable of providing sustainability among the workforce in the UK.
Question Number 3:
3. Do you think the UK workforce has already adopted technology readiness?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
43.33 |
65 |
150 |
|
Agree |
18.00 |
27 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
20.67 |
31 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
11.33 |
17 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
6.67 |
10 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
27.00 |
#N/A |
21.24 |
Table 4.3: Adoption of technology readiness in UK workforce
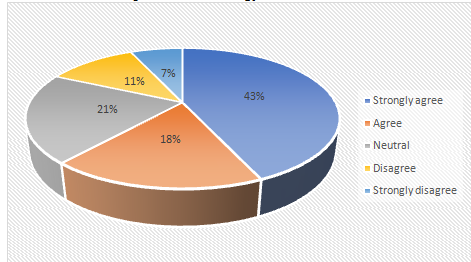
Chart 4.3: Adoption of technology readiness in UK workforce
Analysis for Question Number 3:
Although the knowledge dissemination of appropriate usage of electronic human resource managementis still unknown, 43% participants believed that the industry has already adopted technology readiness to enable the HRM activities in acquiring new technologies into the current scenario.However, the current advancement in various industries in the UK and the knowledge on current practices observed by various researchers has established a clearer picture on the possibilities and opportunities that will be acquired by the management if they start enhancing their technology readiness.
Question Number 4:
4. Do you think that the UK workforce is facing challenges while adopting technology readiness?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
39.33 |
59 |
150 |
|
Agree |
14.00 |
21 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
19.33 |
29 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
14.00 |
21 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
13.33 |
20 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
21.00 |
21.00 |
16.61 |
Table 4.1: Challenges faced by UK workforce while adopting technology readiness
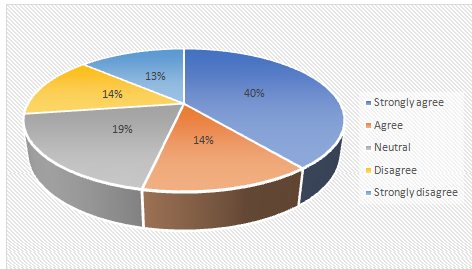
Chart 4.4: Challenges faced by UK workforce while adopting technology readiness
Analysis for Question Number 4:
The relevant literature has pointed out that the challenges associated with adopting technology readiness are the lack of knowledge on electronic human resource managementand usage of technologies by various industries in the UK.This particular answer makes it clear that the UK workforce is facing challenges in adopting technology readiness in their existing HRM system. It can indicate the lack of knowledge and understanding over the new technologies.
Question Number 5:
5. Do you think technology readiness is the future of e-HRM of the UK workforce?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
37.33 |
56 |
150 |
|
Agree |
45.33 |
68 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
2.67 |
4 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
8.67 |
13 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
6.00 |
9 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
13.00 |
#N/A |
29.69 |
Table 4.5: Technology readiness as the future of e-HRM of the UK workforce
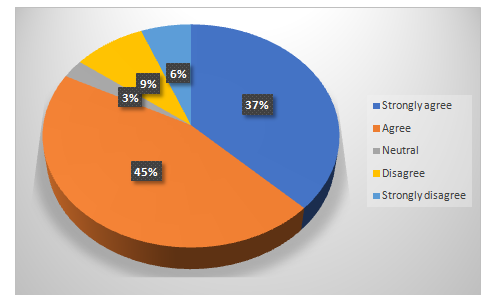
Chart 4.5: Technology readiness as the future of e-HRM of the UK workforce
Analysis for Question Number 5:
There is no undeniable factor that the enhancement of technology readiness will make an enormous different in the HRM practice in making it more cost-effective, sustaining, and efficient.Almost 37% and 45% strongly agreed and agreed that the technology readiness is the future of HRM industry among the UK workforce. It indicates the knowledge in adopting technological aspect in the electronic human resource managementworking process gradually.
Question Number 6:
6. Do you think technology readiness is important for sustaining the current HRM works?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
20.00 |
30 |
150 |
|
Agree |
37.33 |
56 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
17.33 |
26 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
9.33 |
14 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
16.00 |
24 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
26.00 |
#N/A |
15.68 |
Table 4.6: Technology readiness as important for sustaining the current HRM works
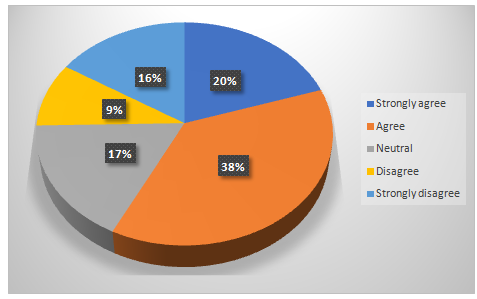
Chart 4.6: Technology readiness as important for sustaining the current HRM works
Analysis for Question Number6:
Technology readiness is the only bridge between adopting the functions of e-HRM effectively among the UK workforce.The traditional HRM activities are changing increasingly after getting used to with various technologies. More than half of the participants were agreed with the sustainability of electronic human resource managementwith the technology readiness.
Question Number 7:
7. Do you think the industry is aware of current best practices in the e-HRM for sustaining a business process?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
52.67 |
79 |
150 |
|
Agree |
27.33 |
41 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
3.33 |
5 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
14.00 |
21 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
2.67 |
4 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
21.00 |
#N/A |
31.24 |
Table 4.7: Awareness of the industry regarding current best practices in the e-HRM for sustaining a business process
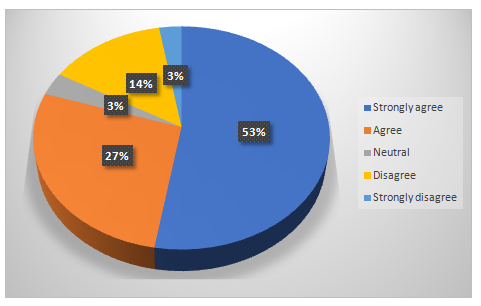
Chart 4.7: Awareness of the industry regarding current best practices in the e-HRM for sustaining a business process
Analysis for Question Number 7:
Despite of lack in widely adoption of the technology readiness among the HRM industry in the UK workforce, almost 70% of the participants were agreeing with the fact that the industry is already aware of the existing best practices in electronic human resource managementprocess.It is because of the fast-changing industries with the help of advanced technologies and globalization makes it obvious for the HRM professionals to have knowledge on electronic human resource managementand technology readiness.
Question Number 8:
8. Do you think the future is going to be fully digitalized in the HRM sector with the help technology readiness?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
72.67 |
109 |
150 |
|
Agree |
23.33 |
35 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
4.00 |
6 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
0.00 |
0 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
0.00 |
0 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
6.00 |
0.00 |
46.48 |
Table 4.8: The future as fully digitalized in the HRM sector with the help technology readiness
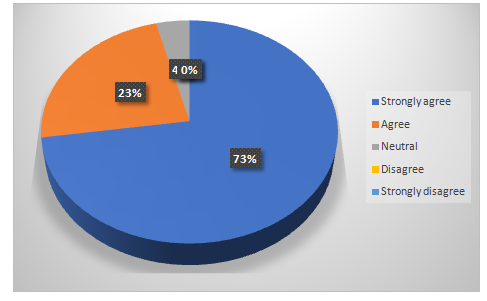
Chart 4.8: The future as fully digitalized in the HRM sector with the help technology readiness
Analysis for Question Number 8:
The future cannot be imagined without the implementation of digitalization. It has already been digitalized from a long-time and technology readiness will help in sustaining the process effectively.No matter how many people are still fond of the traditional contemporary activities under the HRM sector, most of them know that digitalization is our future. Almost all the participants were agreed on this specific question.
Question Number 9:
9. Do you think technology readiness is essential to implement in the electronic human resource managementof the UK workforce?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
32.67 |
49 |
150 |
|
Agree |
34.00 |
51 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
24.00 |
36 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
6.00 |
9 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
3.33 |
5 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
36.00 |
#N/A |
21.82 |
Table 4.9: Technology readiness as essential part to implement in the e-HRM of the UK workforce
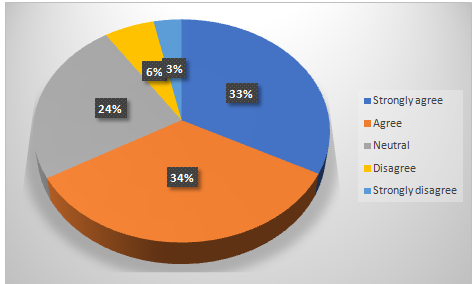
Chart 4.9: Technology readiness as essential part to implement in the e-HRM of the UK workforce
Analysis for Question Number 9:
It has discussed before that the technology readiness is the bridge between adopting e-HRM in various sectors. Technology readiness will generate a broader understanding on the requirements of electronic human resource management.The survey has received mix answer in this particular question. It is obvious that the e-HRM is all about technology implementation and working with the networks. It is important for the HRM industry to become technology readiness for sustaining their e-HRM activities. However, 24% participants remained neutral on this factor.
Question Number 10:
10. Do you think the acceptability of technology readiness among the electronic human resource managementis valid among the UK workforce?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
19.33 |
29 |
150 |
|
Agree |
22.00 |
33 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
34.67 |
52 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
11.33 |
17 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
12.67 |
19 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
29.00 |
#N/A |
14.00 |
Table 4.10: The acceptability of technology readiness among the e-HRM is valid among the UK workforce
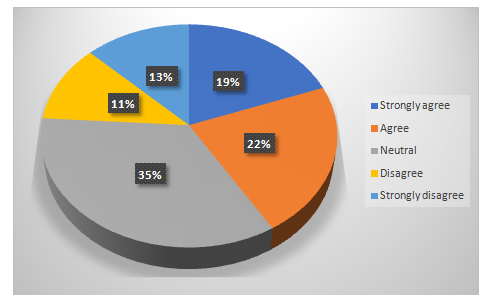
Chart 4.10: The acceptability of technology readiness among the e-HRM is valid among the UK workforce
Analysis for Question Number 10:
Participants were also in doubt with this question where it is important to understand the current validity in accepting the technology readiness among the UK workforce. However, 35% participants remained neutral as they did not want to make its clear about the underlying development in the UK workforce. Although, 41% of the participants were agreeing that there is validity in technology readiness adoption.However, it is needed to be understood that the professionals from the HRM industry in the UK workforce is ready to adopt technology readiness.
Question Number 11:
11. Do you think there is lack of knowledge behind adopting technology readiness among the electronic human resource managementin the UK workforce?
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
40.67 |
61 |
150 |
|
Agree |
18.67 |
28 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
32.00 |
48 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
2.67 |
4 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
6.00 |
9 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
28.00 |
#N/A |
24.53 |
Table 4.11: Lack of knowledge behind adopting technology readiness among the e-HRM in the UK workforce
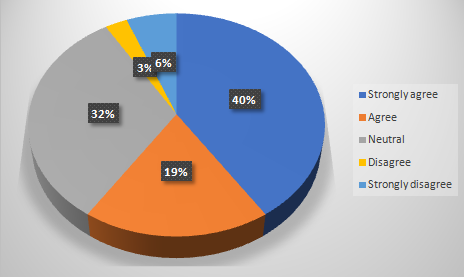
Chart 4.11: Lack of knowledge behind adopting technology readiness among the electronic human resource managementin the UK workforce
Analysis for Question Number 11:
It is one of the obvious questions to ask to the employees from HRM industry in which they have agreed with the fact that it is the problem with lack in knowledge for proper adoption of technology readiness.The analysis of the relevant literature has also provided the same insight of lack of understanding the requirements and possibilities of technology readiness can prevent those industries from adopting advanced technologies soon.
Question Number 12:
12. Do you think the current HRM employees in the UK workforce are capable enough to adopt the technology readiness in a short amount of time
|
Option |
Response percentage |
Responses |
Total respondents |
|
Strongly agree |
47.33 |
71 |
150 |
|
Agree |
20.67 |
31 |
150 |
|
Neutral |
12.00 |
18 |
150 |
|
Disagree |
10.67 |
16 |
150 |
|
Strongly disagree |
9.33 |
14 |
150 |
|
Mean |
Median |
Mode |
SD |
|
30.00 |
18.00 |
#N/A |
23.86 |
Table 4.12: Current HRM employees in the UK workforce are capable enough to adopt the technology readiness in a short amount of time
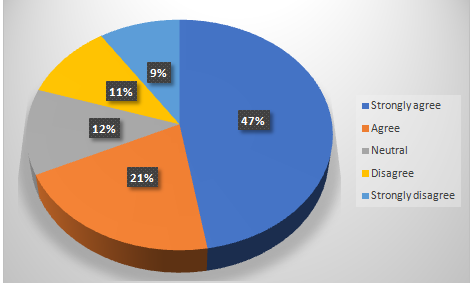
Chart 4.12: current HRM employees in the UK workforce are capable enough to adopt the technology readiness in a short amount of time
Analysis for Question Number 12:
The employees are educated enough to understand that the current HRM practice needs help from the advanced technologies in making the works efficient.Employees from the HRM industry, who are the participant in this survey process, were strongly agreed with the fact they are widely capable of adopting technology readiness within a short amount of time. It explains their understanding and eagerness of implementing something that is the future of current ‘operational’ processes under the electronic human resource managementin the UK workforce.
4.2 Summary
The survey process in the current research paper has been conducted to retrieve the real-world data to strengthen the theoretical argument in the discussion process. It is important to understand the perspective of the current employees under the HRM sector in the UK workforce. The term ‘e-HRM’ has been derived from the requirement for implementing technologies and networking opportunities in the daily activities within an HRM department. Currently, the technology ‘advancement’ makes the electronic human resource managementdevelopment processes more challenging. This is where the technology readiness has become important among the HRM employees. The survey answers have concluded that the current employees are willing to adopt the technology readiness within a short amount of time if the organizations become more flexible in understanding the importance of engaging new technology to achieve sustainability and efficiency.
4.3 Comparison with Literature Review
The current research papers have shown that HRM is one of the main aspects in any business enterprise. Electronic human resource managementcan help to sustain the work of organisation. HR management will be adopting the e-HRM format to evolve the company. It will help to business rationally and analytically. In the line of dividing the consequences into relational, operational, and transformational factors, the e-HRM adoption into the UK organization had a major shift of goals (Musfiqur, Mordi, & Nwagbara, 2018). It involved a shift from effectiveness to the improvement of the service provisions of an HR team along with the strategical reorientation of the departments of the HR. The survey result has expressed the same ideology in acquiring improvement and success from the adoption of the e-HRM tools and techniques in the existing HRM system.
4.4 Discussion
4.4.1 Implementation of electronic human resource managementfor introducing technology readiness on UK workforce
The implementation of the e-HRM for the introduction of technological readiness on the UK workforce constitutes with the globalization, technology, retention of talent and development, management of changes, and support for the transformation of HRM within the UK organizations. Along with the globalization and technological innovation, the strategic changes to be implemented within the organization are to be identified. The HR services constitute all the services to the employees and the managers within an organization through self-service portals of the HR department. In the line of dividing the consequences into relational, operational, and transformational factors, the electronic human resource managementadoption into the UK organization had a major shift of goals in enhancing workforces (Ceric, 2017).
In the early 21st century, the HR was defined as an antithetical to the changes along with the system of HR provided impediments for bringing out changes within the UK organizations. The researcher put forward the increasing responsibilities which presently rest with the consultants in terms of external environment (Mary & Difiva). With various firms delegating the roles to drive the external changes in terms of consulting the UK firms.
However, in today’s organizations, there exists a continuous talk of the outsourcing, downsizing, and redesigning on how the operationalization takes place within the organization for ensuring its competitiveness and efficiency. They are capable of making the most profitable economies in terms of scope and scale. The transformation of the HR needs an analysis along with the recognition of opportunities for the improvement in various areas. They are the HR people and their competencies, implementation of an updated model of delivery, redesigning of the work procedures along with automation, and restructuring of the organization through the HR team (Majeed, Peerzadah, & Mufti). It also includes the impacts on the basis of redefining of the requirements of the HR talents and implementation of the technological support of the HR department.
4.4.2 What is the impact of electronic human resource managementon UK workforce?
The research purpose is concerned with describing the behavioural science theory and the findings of research from the psychology of the organization and the HRM underpinning the development of workforce in terms of implementing the human resource management. The research paper provides a review of the various decades of researching in this area with the aim of providing a summary and an integrated framework as a base for any future researches concerning the topic. Human capital and human resources provide a abase for understanding the diversities in the endowments of resources and the aggregated capabilities distinguishing the organizations those are competing within a specific niche of environment.
For accomplishing the research objectives, the organization should navigate the complicacies, dynamics, and uncertainties of its external environment through counteracting and outperforming the adversaries to become innovative (Kohansal, Sadegh, & Mina, 2016). They must create a unique and capable workforce, then must leverage its specific talents. In the line of dividing the consequences into relational, operational, and transformational factors, the e-HRM adoption into the UK organization had a major shift of goals. The research paper emphasizes on the discussion regarding the shifts along with the implication of changes by the electronic human resource managementinto the organizations of UK for the enhancement of workforce.
The management of human resources became one essential concept for assessing the assets of competitiveness within the organizations of UK. In modern times, with the application of updated and upgraded the technologies of HR, management of the human capital are done by the UK organizations in a mere sophisticated way (Kim, 2018). Consequently, the refined solutions of IT are designed for administering a great variety of the data of human resources allowing the organizations for shifting from the traditional ways of getting delivered the services of HRM to the updated services of HRM that are web-based. The HR services constitute all the services to the employees and the managers within an organization through self-service portals of the HR department. Accordingly, the possibilities of the digital opportunities created ways for functioning of the HR in developing more roles of strategical conquests. For the purpose, the professionals of the HR must develop updated competencies for carrying out the updated and upgraded responsibilities and roles.
The effects include globalization, technology, retention of talent and development, management of changes, and support for the transformation of HRM within the UK organizations (Gaur, 2019). Along with the globalization and technological innovation, the strategic changes to be implemented within the organization are to be identified. Also, through the support of the transformation of traditional to technological HRM innovation, the talent of the employees is identified and undergoes modification and training for further development.
4.4.3 Future Overview of UK Companies
The UK companies integrating the application of electronic human resource managementare mainly multinational corporations who sponsor a student, a project, or an advisory panel. The future overview of the UK companies will include having a project of consultancy undertaken by the company’s management team with specialist knowledge in the functioning of the e-HRM. It will also benefit from their access to the information-based guidance and research in terms of international practices of HRM. It will also raise their awareness regarding the present and upcoming trends in the UK centric e-HRM opportunities (Heikkilä, Rentto, & Feng, 2017). It will become a part of an international as well as globalized technological network of expertise in the UK companies in terms of implementing the e-HRM.
The future overview of the UK companies in implementing electronic human resource managementfor increasing work efficiency constitutes the exploration on how the national background influences the utilization of the e-HRM utilizing data from almost 13 countries of Europe. The findings suggest that the e-HRM adoption is specified to the regions and are influenced by various factors. They tend to support the existence of two unique sets of technological systems of HRM from top-down and bottom-up view (Kazeroony, 2019). The transformation of the HR needs an analysis along with the recognition of opportunities for the improvement in various areas. They are the HR people and their competencies, implementation of an updated model of delivery, redesigning of the work procedures along with automation, and restructuring of the organization through the HR team.
5. Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1 Linking the research objectives with Research Findings
The research objectives have been thoroughly analysed based on the research findings taken from primary data. The primary data is mainly consisting of responses collected from the questionnaire in the form of the numeric value. The numeric value helps proper authentication of data based on the real scenario. The research findings have mainly focussed on the research questions for analysing the research objectives and fulfil the needs of this research. Findings suggest that electronic human resource managementcan develop new technological methods on the system. The reason for lagging is the lack of proper knowledge among the HR managers. Thus, HR managers must be given proper training on e-HRM methods. It helps them to adopt methods effectively on the system.
On the other hand, the research has also collected secondary data from the existing pieces of literature for analysing the consistency of primary data on the research. It has helped the researchers in authenticating the primary data and it suggests that the work structure of the Company plays an essential role in implementing new methods on the system. Moreover, e-HRM can implement new technological methods on the system effectively.
5.2 New Contributions
The research will provide many new contributions for future research. They have been listed below: -
- Implementing new technological tools for expanding the area of e-HRM for defining the HRM roles in the company.
- Managing HRM roles through an updated method of electronic human resource managementand thus, engaging employee satisfaction related to the company (Al Shobaki M. , Naser, El Talla, & Amuna, 2017). It will help the company or a particular industry to improve its growth and reach a high rank in the international market.
- Upgrading the work structure of the industry and monitoring employee performance and their role in improving firm performance. It will help to engage potential investors as well as customers on the company or industry.
- The challenges related to technology readiness can be mitigated by providing proper knowledge on electronic human resource managementto the HR managers. It will help to mitigate the flaws that occur on the system (Bondarouk, Harms, & Lepak, Does e-HRM lead to better HRM service?, 2017). Problems occurring on the system can be instantly mitigated by the HR managers by implementing proper HRM goals on the Company.
- Upgrading the e-HRM system helps in motivating both the HR managers and employees as they can interact effectively under one roof (Bondarouk, Harms, & Lepak, Does e-HRM lead to better HRM service?, 2017). The activities can be monitored effectively through web-based technologies and the chances of mistake also get decreased.
- Sustainability can be achieved and the electronic human resource managementcan adopt new technologies for improving the industry growth. The industry can expect consistent growth in the international market. Thus, helps in engaging new investors in the industry.
5.3 Significant Factors for future researches
After reviewing the existing pieces of literature, it can be concluded that the significant factors are very useful for future researches. The significant factors are mainly “role of e-HRM in technology readiness”, “capability of e-HRM in implementing new methods”, “sustainable goals for adopting new technologies” and “mitigating the challenges in e-HRM for being technology readiness”. These factors will help future researchers to make an effective study on specific fields and implement the results of this research. The researchers will get the authentic data as it has been collected through primary research. The questionnaire can be also used in the future researches for retrieving the data. However, all the copyright factors must be maintained while using the same questionnaire.
The factors will help to derive the themes related to the research and it suggests that e-HRM is an effective tool for monitoring all the activities of the HRM. The employee performance can be easily measured through performance in build within the electronic human resource managementtool of the particular industry. The research will help to adopt new practices at the UK workforce and thus, improving the quality of the UK works culture for various communities of diverse culture.
5.4 Recommendations The current study can be improved by the following recommendations. They are listed below: -
- The research can also adopt a qualitative analysis method for studying the research. It will help the readers to get an idea on the use of both the research method on the respective topic.
- The research must include data from other countries that have already implemented the methods of electronic human resource managementon their companies. It will help in the deep understanding of the real scenario of e-HRM on the international market. The use of e-HRM in other countries is also not known to the researchers. Thus, researching on other countries will help the researchers to get an idea on the use of e-HRM all over the world.
- The sustainability rate has not been calculated based on the real scenario. The responses are not also sufficient for calculating the sustainability rate of e-HRM. Thus, creating a flaw in the research. The readers will not get a proper idea on the sustainability rate of the electronic human resource managementon a particular industry.
- The research must use some data from the big companies where the e-HRM have been applied and discussed in the particular section. It will help in a deep understanding of the problem and purpose of the research on the practical scenario.
- The research must use more practical data to give a deep and useful message to future researchers. Electronic human resource managementis a vast area of research and thus, many researchers can be done in future based on specific fields.
6. Reflective Statement
It was a very challenging task for me to conduct a whole dissertation process comprising of the survey process and discussion on the research topic elaborately. I have gained a significant amount of knowledge from the HRM field in different industries in the UK. The current research paper has done extensive research on the electronic human resource management factor and its different approach in adopting electronic human resource managementto improve and sustain the HRM works. The current research paper has implemented the ‘Gibbs Model,’ which encourages the researchers in analysing a specific situation with the help of a systematic approach. The ‘Gibbs Model’ is consisting of different steps, where the first step is related to the description of the research background and its reflective area. The next step is related to my feelings in that research area which helps me proceed to the next stage that is evaluation.
The next step is about the analysis of the evaluation areas of the research paper. The analysis process is also related to the engagement of the external theories that helped me in developing and understanding the discussion process. The next two steps are the conclusion and action plan. The conclusion is related to the results generated from the analysis section and the action plan is related to the future research possibilities and learning outcome from the current research paper. All of these steps helped me in understanding, developing, discussing, analysing, and concluding the research process related to the technical readiness among the workforce in the UK for adopting the e-HRM for further improvement and sustainability at the HRM process. ?
7. Bibliography
Schoonenboom, J., & Johnson, R. (2017). How to construct a mixed methods research design. KZfSS Kölner Zeitschrift für Soziologie und Sozialpsychologie, 69(2), 107-131.
Meyers, L., Gamst, G., & Guarino, A. (2016). Applied multivariate research: Design and interpretation. Sage publications.
Wildemuth, B. (2016). Applications of social research methods to questions in information and library science. ABC-CLIO.
Beins, B. (2017). Research method: A tool for life. Cambridge University Press. Stieglitz, S., Mirbabaie, M., Ross, B., & Neuberger, C. (2018). Social media analytics–Challenges in topic discovery, data collection, and data preparation. International journal of information management, 39, 156-168.
Moser, A., & Korstjens, I. (2018). Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 3: Sampling, data collection and analysis. European Journal of General Practice, 24(1), 9-18.
Heeringa, S., West, B., & Berglund, P. (2017). Applied survey data analysis. CRC press.
Agresti, A. (2018). An introduction to categorical data analysis. John Wiley & Sons.
Bondarouk, T., Harms, R., & Lepak, D. (2017). Does e-HRM lead to better HRM service? The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28(9), 1332-1362.
Al Shobaki, M., Naser, S., El Talla, S., & Amuna, Y. (2017). HRM University Systems and Their Impact on e-HRM.
Thite, M. (2018). e-HRM: digital approaches, directions & applications. Routledge.
Njoku, E., Ruël, H., Rowlands, H., Evans, L., & Murdoch, M. (2019). An analysis of the contribution of e-HRM to sustaining business performance. In E. Njoku, H. Ruël, H. Rowlands, L.
Evans, & M. Murdoch, HRM 4.0 For Human-Centered Organizations. Emerald Publishing Limited.
Berber, N., ?or?evi?, B., & Milanovi?, S. (2018). Electronic human resource management (e-HRM): A new concept for digital age. Strategic Management, 23(2), 22-32.
Sobo?an, A., Bertotti, T., & Strom-Gottfried, K. (2019). Ethical considerations in social work research. European Journal of Social Work, 22(5), 805-818.
Brittain, S., Ibbett, H., de Lange, E., Dorward, L., Hoyte, S., Marino, A., . . . Veríssimo, D. (2020). Ethical considerations when conservation research involves people. Conservation Biology.
Clark-Kazak, C. (2019). Developing ethical guidelines for research. Forced Migration Review(61), 12-13.
Kunisch, S., Bartunek, J., Mueller, J., & Huy, Q. (2017). Time in strategic change research. Academy of Management Annals, 11(2), 1005-1064.
Zangirolami-Raimundo, J., Echeimberg, J., & Leone, C. (2018). Research methodology topics: Cross-sectional studies. Journal of Human Growth and Development, 28(3), 356-360.
Heikkilä, J.-P., Rentto, O., & Feng, Y. (2017). Aiming for Strategic e-HRM: Motives and Consequences of e-HRM Implementation in an MNC. Electronic HRM in the Smart Era, 173-199.
Kazeroony, H. (2019). The role of electronic human resource management in diverse workforce efficiency.
Ceric, A. (2017). E-HRM challenges: An Australian perspective. Electronic HRM in the Smart Era, 201-220.
Mary, A., & Difiva, E. (n.d.). A Study on Employees Perception on E-HRM.
Majeed, S., Peerzadah, S., & Mufti, S. (n.d.). Electronic Human Resource Management: Need of the Hour.
Kohansal, M., Sadegh, T., & Mina, H. (2016). E-HRM: From acceptance to value creation. Journal of Information Technology Management, 27(1), 18.
Kim, M. (2018). The Role of ICT Enabling Diversity Management in Organization through e-HRM. , 22(9), 1185-1190.
Gaur, A. (2019). A Paradigm Shift from Human Resource Management (HRM) to Electronic Human Resource Management (E-HRM)-A Review. Journal of the Gujarat Research Society, 21(11), 80-88.
Al Haziazi, M. (2019). Implementing e-Human Resource Management for Improving Organizational Performance: A Conceptual Framework in the Oman Context. European Conference on Management, Leadership & Governance (pp. 11-16). Academic Conferences International Limited.
Al Shobaki, M., Naser, S., Amuna, Y., & El Talla, S. (2017). The Efficiency of Information Technology and its Role of e-HRM in the Palestinian Universities.
Al-kasasbeh, A., Halim, M., & Omar, K. (2016). E-HRM, workforce agility and organizational performance: A review paper toward theoretical framework. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 14(15), 10671-10685.
Blom, T., Du Plessis, Y., & Kazeroony, H. (2019). The role of electronic human resource management in diverse workforce efficiency.
Bondarouk, T., Parry, E., & Furtmueller, E. (2017). Electronic HRM: four decades of research on adoption and consequences. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28(1), 98-131.
Bos-Nehles, A., Bondarouk, T., & Smit-Methorst, H. (2019). A Sociomateriality Perspective of Sustainable E-HRM Implementation. STUDI ORGANIZZATIVI(2), 29.
Škudien?, V., Vezeliene, G., & Stangej, O. (2020). Transforming human resource management: innovative e-HRM value creation for multinational companies. In V. Škudien?, G. Vezeliene, & O. Stangej, Innovation Management. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Ziebell, R.-C., Albors-Garrigos, J., Schoeneberg, K.-P., & Perello-Martin, R. (2019). e-HRM in a Cloud Environment: Implementation and its Adoption: A Literature Review. International Journal of Human Capital and Information Technology Professionals (IJHCITP), 10(4), 16-40.
Ziebell, R.-C., Albors-Garrigos, J., Schoeneberg, K.-P., & Marin, M. (2019). Adoption and success of e-HRM in a cloud computing environment: a field study. International Journal of Cloud Applications and Computing (IJCAC), 9(2), 1-27.
Winarto, W. (2018). Electronic Human Resources Management (E-HRM) adoption studies: past and future research. DeReMa (Development Research of Management): Jurnal Manajemen, 13(1), 100-120.
Waheed, A., Xiaoming, M., Waheed, S., Ahmad, N., & Tian-tian, S. (2020). E-HRM implementation, adoption and its predictors: a case of small and medium enterprises of Pakistan.
International Journal of Information Technology and Management, 19(2-3), 162-180.
Waheed, A., Waheed, S., Karamat, J., Ahmad, N., & Majeed, A. (2017). Implementation and Adoption of E-HRM in Small and Medium Enterprises of Pakistan. ITITS, (pp. 573-582).
Umar, T., Yammama, B., & Shaibu, R. (2020). The Implications of Adopting and Implementing Electronic Human Resource Management Practices on Job Performance. Journal of Human Resource Management, 8(2), 96-108.
Iqbal, N., Ahmad, M., Raziq, M., & Borini, F. (2019). Linking e-hrm practices and organizational outcomes: empirical analysis of line manager’s perception. Revista Brasileira de Gestão de Negócios, 21(1), 48-69.
Rahman, M., Mordi, C., & Nwagbara, U. (2018). Factors influencing E-HRM implementation in government organisations. Journal of Enterprise Information Management.
PrabaDevi, M. (n.d.). ROLE OF E-HRM AND VIRTUAL INTELLIGENCE IN EFFECTIVE ORGANISATIONAL BRHAVIOUR.
Iqbal, N., Ahmad, M., Allen, M., & Raziq, M. (2018). Does e-HRM improve labour productivity? A study of commercial bank workplaces in Pakistan. Employee Relations. Panos, S., & Bellou, V. (2016). Maximizing e-HRM outcomes: a moderated mediation path. Management Decision.
Omran, K., & Anan, N. (2018). Studying the impact of using E-HRM on the effectiveness of HRM practices: An exploratory study for the internet service providers (ISP) in Egypt. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(4), 458-492.
Iqbal, N., Ahmad, M., & Allen, M. (2019). Unveiling the relationship between e-HRM, impersonal trust and employee productivity. Management Research Review.
Obeidat, S. (2016). The link between e-HRM use and HRM effectiveness: an empirical study. Personnel Review.
NAGESWARI, R. (n.d.). E-HRM AND ITS TRENDS IN INDUSTRY 4.0.
Musfiqur, R., Mordi, C., & Nwagbara, U. (2018). Factors influencing e-HRM implementation in government organisations: Case studies from Bangladesh.
8. Appendices
8.1 Survey Questionnaire
Survey Questionnaire
Topic: A quantitative analysis of the role technology readiness plays with e-HRM adoption in a UK workforce
1. Do you think the industry is aware of technology readiness among the e-HRM from the UK workforce?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
2. Do you think technology readiness can sustain the work processes among the UK workforce?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
3. Do you think the UK workforce has already adopted technology readiness?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
4. Do you think that the UK workforce is facing challenges while adopting technology readiness?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
5. Do you think technology readiness is the future of e-HRM of the UK workforce?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
6. Do you think technology readiness is important for sustaining the current HRM works?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
7. Do you think the industry is aware of current best practices in the e-HRM for sustaining a business process?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
8. Do you think the future is going to be fully digitalized in the HRM sector with the help technology readiness?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
9. Do you think technology readiness is essential to implement in the e-HRM of the UK workforce?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
10. Do you think the acceptability of technology readiness among the e-HRM is valid among the UK workforce?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
11. Do you think there is lack of knowledge behind adopting technology readiness among the e-HRM in the UK workforce?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree
12. Do you think the current HRM employees in the UK workforce are capable enough to adopt the technology readiness in a short amount of time?
a. Strongly agree
b. Agree
c. Neutral
d. Disagree
e. Strongly Disagree












