Identification Of Risks & Stakeholder Analysis Of CardioHealth Project
Question
Task:
In this assignment you will continue working the CardioHealth project. You will need to produce
documents and diagrams related to a few Project Management Knowledge areas.
In this assignment you need to produce the following documents:
• Identify project risks breaking them into categories:
o Market risk: If the IT project will create a new product or service, will it be useful to
the organization or marketable to others? Will users accept and use the product or
service? Will someone else create a better product or service faster, making the
project a waste of time and money?
o Financial risk: Can the organization afford to undertake the project? How confident
are stakeholders in the financial projections? Will the project meet NPV, ROI, and
payback estimates? If not, can the organization afford to continue the project? Is
this project the best way to use the organization’s financial resources?
o Technology risk: Is the project technically feasible? Will it use mature, leading-edge,
or bleeding-edge technologies? When will decisions be made on which technology
to use? Will hardware, software, and networks function properly? Will the
technology be available in time to meet project objectives? Could the technology be
obsolete before a useful product can be created? You can also break down the
technology risk category into hardware, software, and network technology, if
desired.
o People risk: Does the organization have people with appropriate skills to complete
the project successfully? If not, can the organization find such people? Do people
have the proper managerial and technical skills? Do they have enough experience?
Does senior management support the project? Is there a project champion? Is the
organization familiar with the sponsor or customer for the project? How good is the
relationship with the sponsor or customer?
o Structure/process risk: What degree of change will the new project introduce into
user areas and business procedures? How many distinct user groups does the
project need to satisfy? With how many other systems does the new project or
system need to interact? Does the organization have processes in place to complete
the project successfully?
• Stakeholder communication analysis
Answer
1. Risk Identification by Different Categories
1.1 Market Risks considered for CardioHealth project
The global IT market is projected to give over fifteen million management jobs by 2020 to strengthen the technology market. The increasing demand in the technological market makes way for every new product or service related to IT. However, project sustainability will depend on the usage factor of the product. The influential factors behind a particular product make successful innovation of an IT product or service (Velamuri, Schneckenberg, Haller, & Moeslein, 2017). CardioHealth project is an essential tool to check and document the reports related to various 'cardiovascular' disease. The project has a specific target group so that it will survive the market acceptancy risk. The project is mainly designed for the people who need a regular check-up and health update to acquire appropriate treatment.
The management needs to understand the market needs in order to compete with the contemporary market and sustain the product's marketable aspect (Arnett, Sandvik, & Sandvik, 2018). The challenges in front of CardioHealth project is to maintain its operational standard and develop to include more functions as the IT market for healthcare devices is not fully commercial yet, so it would not be difficult for CardioHealth project to grow with the market requirement. Another interesting factor related to market risk is the tendency to be copied by other company based on the concept and divide the market. It can be tackled well if the project management itself engages with its target market to understand their requirements and objections to implement better functions.
The product design for any IT project needs to be adequate to mitigate the chances of having market risks (Grubisic & Ogliari, 2017). The delay in the production process or lack of confidentiality can lead other technical management groups to steal a concept from a company. It allows that other company to make an IT product or service with the same configuration and in a lower budget. It destroys the market of that original product. However, the market of CardioHealth project has lesser competitors in comparison to other markets. The management team can implement effective project planning methods to make the design unique and sustainable. It can also collaborate with various healthcare centers to build trust among the potential consumers to mitigate initial market risks related to product acceptance and increase the competency level.
1.2 Financial Risks
The organization needs to understand the project functions and processes to create a proper budget allocation in the development of CardioHealth project. It has been discussed several times that IT developers frequently increase their budget to implement better technologies during the project process. It led them not to overrun the whole process. "Harvard Business Review" had estimated that the IT developers usually overrun their allocated budget by 27 per cent. One of the highest cost increased project accounted for by the UK's "National Health Service" while developing its IT program. It cost them an additional 26 million dollars back in 2011. It faced financial difficulties in – barriers from various physicians, conflicts among the project managers and developers, and mismanaged project system.
However, the stakeholders related to the CardioHealth project have developed the project design with the help of doctors and technical expertise. They structured the project processes according to the organization's capacity. Various health centres and government funds helped this project to sustain its operational processes. The financial management team measures the ‘Net Present Value’ or ‘NVP’ to sustain the investment flow to not cause any interruption during the project process. It is the parameter to adjust the investment of the project with its process and requirements (Mellichamp, 2019). CardioHealth project has estimated its budget with the help of expert’s advice and government’s help. The investor of this project has also put money according to the project sustainability and market requirement. The project management has implemented 'ROI' to measure the efficiency of the allocated budget and measure an estimated profit after launching this project. The project has estimated its cost after identifying the potential ‘earned value’, ‘planned value’, ‘actual cost’, ‘cost variance’, ‘scheduled variance’, ‘CPI’, and ‘SPI’.
The initial project operation needs effective help from the healthcare centers and doctors to promote this technology among the patients. It is important to encourage patients who are suffering through various 'cardiovascular’ diseases to experience a convenient check-up. The 'NVP' measurement helps any project to strengthen its financial structure (Hopkinson, 2016). This particular project has developed its mechanisms and project processes with the best deserving expertise to ensure the project’s viability. The investor of CardioHealth project has invested his money after supervising its market demand and credibility. The incorporation of ‘NVP’ and ‘ROI’ will manage the financial sustainability and cost flow during the project process.
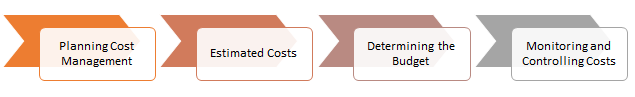
Fig 1: Financial Management Process in an IT Project
1.3 Technological Risks
CardioHealth project needs feasibility in its technical operations to make the project successful and sustainable (Hein, 2016). The internal technological development processes are being done by a software development team appointed by the project management. They have divided a big group that manages the works related to disease measurement, result processing and documentation, and accessible to the patients and doctors. The extended part of CardioHealth project disease is also enabling the 'cloud computing' technique to document the results securely. The project's 'technological feasibility' is depending upon understanding the various function of the operational processes, and implement suitable technology according to its building capacity.
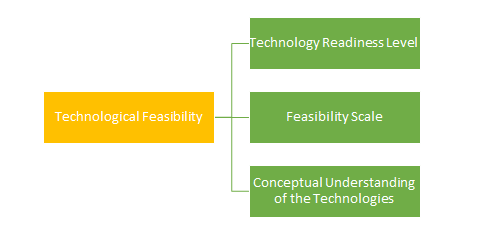
Fig 2: ‘Technological Feasibility’ Area of an IT Project
The management team and the project development team of CardioHealth project have implemented 'leading edge' technology. This technology has enabled the management team to acquire the best-skilled developers and strategies to develop the project according to its design. Various medical instruments need 'leading edge' technology to develop their mechanism (Wulfsberg, Hintze, & Behrens, 2019). It uses most advanced technologies and equipment such as software system, to develop a new IT system. Since the CardioHealth project is engaged in providing health check-up and results, it is essential to implement advanced technologies to make the system sustainable. The project will launch in the market at an appropriate time after meeting its development goals. The initial testing session will be observed in various hospitals to conduct a meaningful operational process.
The technological risks related to the CardioHealth project is related to the following areas,
1.3.1 Hardware: The risk is related to the project design and its user-friendliness. The CardioHealth project device needs to be adequate and straightforward to help the doctors and patients in conducting check-ups. It is also essential to make the device less complicated to access its memory easily to make further treatment decisions.
1.3.2 Software: The software developer team of CardioHealth project has implemented the best functions and software facilities to build the device unique and essential. It is important to develop the software system well to compete with the contemporary market. The software system needs to be capable enough to adopt future improvement updates or bug correction process.
1.3.3 Network: The “CardioHealth project” has developed its online storage system with the help of 'cloud computing' technology to make the documentation process sustainable. It is essential to manage the storage system properly to avoid data misplacement or document leaking risks.
1.4 People Risks
The management team of CardioHealth project has implemented ‘leading edge’ technology to make the process efficient and advanced. It is required to implement skill-based employees to develop the device effectively and decrease resource risks. The management has collaborated with an external technology expert team to conduct the processes related to project design and development processes. Employee's skills and creative function are the main assets in developing a technology device. It is also an integral area of an IT-based organization to make the technological processes efficient with various logical suggestions (Kuhn & Khan, 2019). The assigned contractor has experience in working in other big projects in different fields. The most significant aspect of this project is that it has been designed by the talented doctors who are experts in observing and conducting tests to understand the cardiac issues. The implementation of this technique into a device will enhance the advanced medical technologies for sustainable treatment.
The senior management of CardioHealth project is very supportive towards the technical team to resolve or manage any potential issue during the process. They are engaged in regular contact, weekly meeting about the project progress, and emergency communication process to mitigate any urgent difficulties and risks. The technical team comprises with software developer team, coding management team, an operational supervisor, and 'cloud storage' maintenance team. They are also interlinked in a personal communication channel to conduct the processes jointly. The management team needs to conduct effective communication process with the technician group and their employees to monitor the processes without leaving any gapping area (Sharma & Rani, 2018). It will also help the developers to engage in the work well and decrease the chances of losing interests.
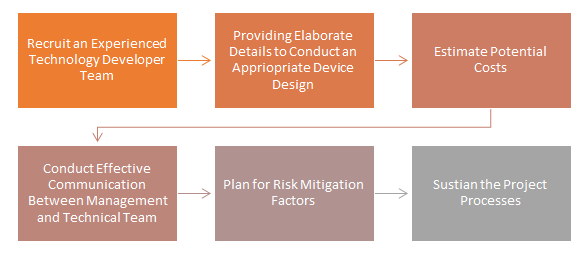
Fig 3: What are the management processes to sustain the operations of CardioHealth project?
However, the relationship between the sponsor and the technician team is not regular enough. The investor only communicates with the project owners and management head to observe the process and possible completion time. It is because the investors is focused on sustaining the financial flow throughout the project process and cover any cost related issue efficiently. On the other hand, the technology development team is determined to conducting the processes to complete the works within the deadline. The management and technical team are well skilled and experienced to complete the CardioHealth project effectively. The hierarchal authority and the investor need to engage with the technician team to understand any difficulties to solve risks related to the project people.
1.5 Project Structure and Process Risks
Before planning the creation of “CardioHealth project" – a mobile technical device to detect and measure various 'cardiovascular' diseases, there were no such technical devices available to the market. Heart specialist doctors developed the main conception of this project. They implemented 'machine learning' techniques to conduct 'ECG' procedures with a mobile device. This device is capable of conducting 'ECGs', produce results, and store it to the cloud to access at any moment. It is designed as the cloud storage can be accessible by patients and their assigned doctors. The product has introduced an excellent way to develop healthcare systems.
The CardioHealth project has a specific distinct group to provide its features and facilities. People who are suffering from various 'cardiovascular' diseases are the main target group for this project. The healthcare centers that are specializing in treating heart diseases can also acquire the device. The CardioHealth project only needs to interact with medical systems and people related to the healthcare sector. The structure of the project needs to maintain the government's guidelines related to ‘health policy’ and ‘health IT policy’ to sustain its engagement with the patients and doctors without having any risks (Lawrence, et al., 2019). The project manager needs to implement a 'quality management' system to monitor and observe the processes to avoid any structural risks. Every IT project has several control factors to avoid any risk situation – ‘functionality’, ‘features’, ‘system outputs’, ‘performance’, ‘reliability’, and ‘maintainability’.
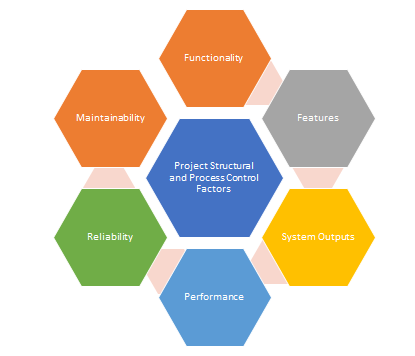
Fig 4: ‘Project Structural and Process Control’ Factors
The ‘quality management’ factors of CardioHealth project is related to planning, performance, and process control areas. The management team has placed appropriate strategies in every step of the project processes to start and conduct the whole operation effectively. The appointed technical development group has already organized planning and testing sessions to understand the appropriate method to implement. The project needs to prepare some internal policies to control the developers to not attempt any techniques from outside the planning. It is essential to control the mechanisms to conduct the project operations according to the plan and mitigate any risks related to the project process.
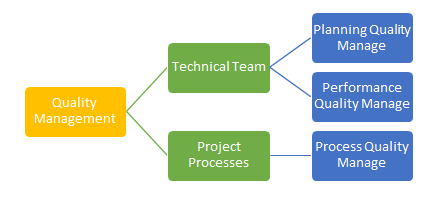
Fig 5: ‘Quality Management’ Areas in “CardioHealth” Project
2. Communication Analysis of Stakeholders
|
Stakeholder Team |
Document Name |
Document Format |
Contact Person |
Due Date |
|
‘Technical Development Team’ |
Monthly project status report |
Soft copy and group presentation |
COO of ‘Technical Development Team’ |
During the first week of every month |
|
‘Software Development Team’ |
Implementation of new function |
Soft copy and machine test report |
Team Leader of ‘Software Development Team’ |
Twice in a month or during implementing a new function |
|
‘Cloud Storage Management Team’ |
Monthly development status |
Soft copy and group meeting |
Team Leader of ‘Cloud Storage Management Team’ |
During the first week of every month from the second month |
|
‘Project Management Team’ |
Monthly project status report |
Soft copy, email and group meeting |
Project Manager |
Every week |
|
‘Project Owner’ |
Additional development planning |
Soft copy, email and group meeting |
‘Project Owner’ |
After planning a new development function |
|
Comments: |
||||
3. Project Progress: Gantt chart
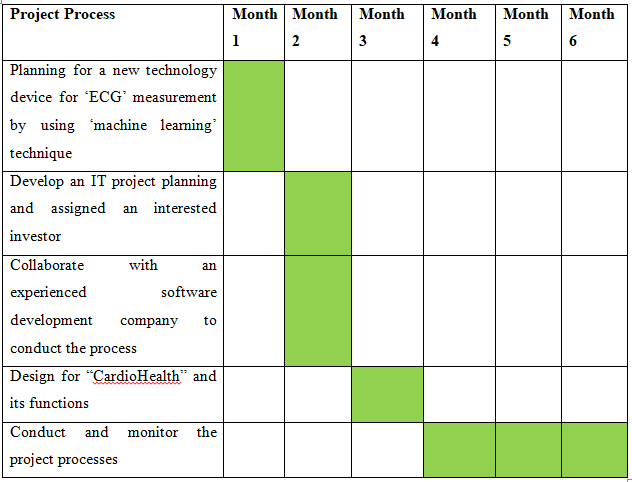
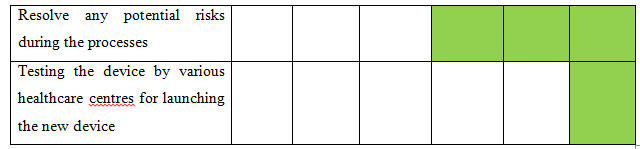
4. Cost Analysis Details
4.1 System Life Cost Profile
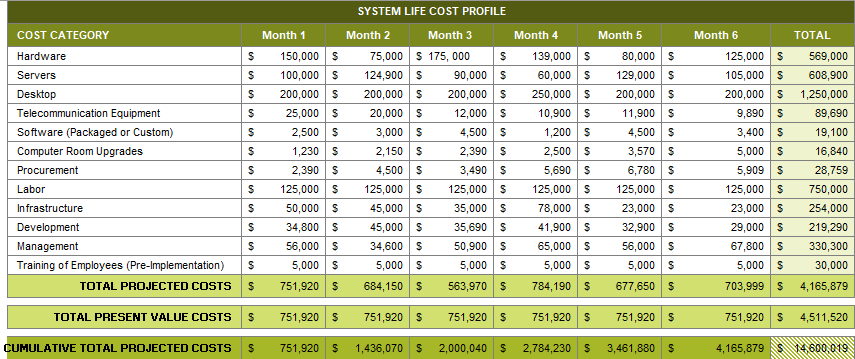
4.2 System Benefits Profile
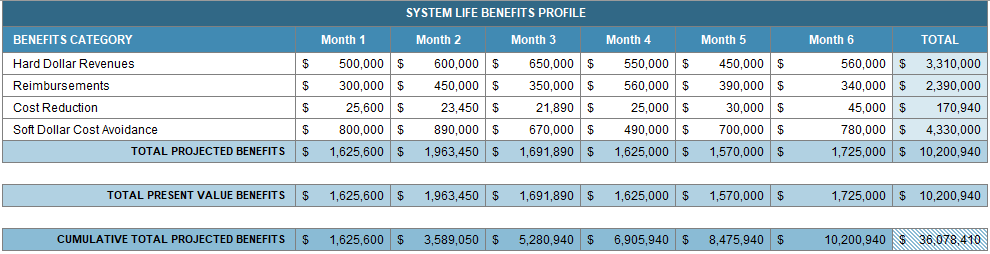
4.3 Cost Benefit Analysis
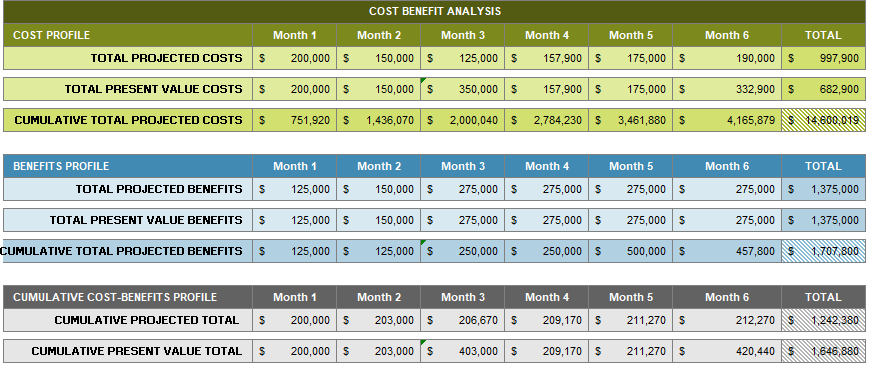
5. Progress Report – Monthly
|
Project Process |
Previous Month’s Progress (%) |
This Month’s Progress (%) |
Total Progress to Date (%) |
Scheduled Progress (%) |
Due Schedule |
|
Developing functional planning for “CardioHealth." |
26 |
12 |
38 |
37 |
Month 3 |
|
Testing the device once a week to sustain the project process |
21 |
8 |
29 |
25 |
Month 6 |
|
Software and effective ‘cloud storage’ mechanism development |
15 |
4 |
19 |
24 |
Month 6 |
|
The technical factors development process |
28 |
16 |
44 |
45 |
Month 5 |
|
Financial estimation for sustaining the project process |
29 |
13 |
42 |
50 |
Month 5 |
|
Implementation of planned configurations |
30 |
21 |
51 |
53 |
Month 6 |
6. Project Quality Management Plan for CardioHealth project
|
Project Process |
Measurement Unit |
Likelihood |
Target |
Measurement Technique |
Data Source |
|
‘Defect Resolving Process’ |
% |
After completing a project process |
95% |
Observing the project processes and testing the device after completing each step to detect any error |
(Declined defects ÷ defects found) × 100 |
|
‘Implementing Effective Software Functions’ |
Project report |
Twice a monthly, or before implementation |
Secure the functional goals |
Analyzing the project test reports and understand the requirements of implementing an additional function to make the operation efficient |
Monthly/ weekly project report and Group meetings |
|
‘Cost Variance’ |
$ |
Twice a month |
0% (10% exception) |
Analyzing the project cost report |
Finance report of the project |
|
‘Monitoring the Project Process’ |
Project report |
Weekly |
Competing for the project steps within the deadline |
Observing ana analyzing project processes effectively to match with the planned operation |
Monthly/ weekly project report |
|
‘Effective Communication Process’ |
Project meeting frequency |
Multiple times in a week |
Conduct group meets twice a week |
Conduct group meeting with the project stakeholders and employees to discuss project progress, new functions, requirements, and estimate completion schedule |
A survey among the project stakeholders and employees |
|
‘Design Revision and Change if Needed’ |
Project report |
Once a month |
Constant observation to identify better functions |
Analyzing the defective areas to figure out better function for implementation |
Group meetings |
|
‘Schedule Variance’ |
Days |
Once a week |
0% (5% exception) |
Analyzing the project process schedule |
Project schedule and completion time |
7. Bibliography
Arnett, D., Sandvik, I., & Sandvik, K. (2018). Two paths to organizational effectiveness–Product advantage and life-cycle flexibility. Journal of Business Research, 84, 285-292.
Grubisic, V., & Ogliari, A. (2017). Methodology for the integrated management of technical and managerial risks related to the product design process. CardioHealth project Product: Management & Development, 7(2), 149-160.
Hein, A. (2016). TECHNOLOGICAL FEASIBILITY AND MATURITY-ASSESSMENT METHODS. Presented at the International Space University.
Hopkinson, M. (2016). The Case for Project Net Present Value (NPV) and NPV Risk Models. PM World Journal.
Kuhn, R., & Khan, S. (2019). Leading-Edge Technologies. IT Professional, 21(6), 4-5.
Lawrence, T., Douglas, M., Rollins, L., Willock, R., Cooper, D., Gooden, R., . . . Mack, D. (2019). Health Policy Engagement Strategy for the Health Information Technology Policy Project of the Transdisciplinary Collaborative Center for Health Disparities Research. Ethnicity & disease, 29(Suppl 2), 377.
Mellichamp, D. (2019). Profitability, risk, and investment in conceptual plant design: Optimizing key financial parameters rigorously using NPV%. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 128, 450-467.
Sharma, P., & Rani, A. (2018). ROLE OF EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION BETWEEN MENTORING AND EMPLOYEE SATISFACTION: PLS APPROACH. Prestige International Journal of Management & IT-Sanchayan, 7(1), 33-43.
Velamuri, V., Schneckenberg, D., Haller, J., & Moeslein, K. (2017). Open evaluation of new product concepts at the front end of innovation: objectives and contingency factors. CardioHealth project R&d Management, 47(4), 501-521.
Wulfsberg, J., Hintze, W., & Behrens, B.-A. (2019). Correction to: Production at the leading edge of technology. In J. Wulfsberg, W. Hintze, & B.-A. Behrens, Production at the leading edge of technology (pp. C1-C3). Springer.












