How should Lyft collect relating Ubers global operations and expansion using global Strategic Management assignment research techniques?
Question
Task: How can lyft expand its operations globally by critically analysing Uber operations using global Strategic Management assignment research techniques?
Answer
Introduction
This global Strategic Management assignment will analsyzercompetitior strategies to identify and advice the client on suitable global expansion stratopgies.As per the global Strategic Management assignmentresearch findings, Lyft is one of the fastest-growing transport companies in the US. The company was founded in 2012 and one of its biggest rivals is Uber. The assignment helps to understand the external factors, such as the car rental industry of Vietnam as well as aims to understand the best international strategy that Lyft can implement to expand its business in Vietnam after the pandemic.
PESTLE Analysis of Vietnam
Political Factors
Vietnam follows a policy of forging and maintaining good relations with all countries. As stated by Phan (2021), “The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the World Trade Organization (WTO)”, and the “United Nations” are just a few of the significant organisations it is a member of (UN). The past 20 years have seen a major improvement in US-Vietnam ties despite a tumultuous background (how and what. net,2020).
Vietnam, however, has an extremely bad track record when it comes to upholding human rights. Conversely, Diep (2019), the rights to free speech, association, and peaceful assembly are severely curtailed, while the imprisonment of dissidents is quite common. Since the “Communist Party of Vietnam” controls the nation's media, journalists and media outlets frequently run the risk of punishment for covering sensitive subjects and criticising the administration. Similar issues exist with corruption, despite Vietnam's extensive attempts since 2016 to remove it (how and what. net,2020). Thus, the political impact is moderate for Lyft for expanding its business in Vietnam.
global Strategic Management assignment -Economic Factors
Vietnam is the 46th-largest economy in the world. Its “nominal GDP” was $245 in 2018 and is expected to reach $265 billion by the end of 2020. According to Manh Cuong & Hung (2020), the country made great progress in eradicating poverty between 2002 and 2018, assisting 45 million people in doing so. The economic outlook for the nation is positive and stable for the future years. The fact that Vietnam has benefited greatly from the trade dispute between China and the USA is interesting to note (how and what. net,2020). Furthermore, it should be remembered that Vietnam has a history of experiencing high price increases.
The usual “corporate income tax (CIT)” rate in Vietnam is 20%. Likewise, Mai (2022) stated that the tax rate for companies operating in the oil and gas industry ranges from 32% to 50%. On the other hand, the “personal income tax (PIT)” rate can be anything between 5% and 35% (how and what. net,2020). The economic impact for the company to expanding its business after the pandemic is positive.
Social Factor
As per the global Strategic Management assignment research, on February 2020, 97 million people are living in Vietnam. The principal language in the country is Vietnamese, and Buddhism is the most popular religion. Men typically live 93 years, compared to women's 81 years.
As suggested by Dan (2020), by 2026, the country's rapidly growing middle class is projected to comprise 26% of the population. 2020. Vietnamese folks are generally friendly. Many tourists have written online about their special and memorable encounters with locals. Many tourists have, however, also voiced their displeasure at being hassled, overcharged, and abused by locals. However, Tran (2020) stated that “Wealth distribution” is a matter of growing concern notwithstanding Vietnam's impressive economic progress. Between the wealthy and the poor, there is a huge and growing wealth disparity. Another social problem in the nation is the ageing population (how and what. net,2020). The social impact for the company to expand its business in Vietnam is moderate.
Technological factors
A strong start-up culture, international investments, low costs, government initiatives, and an educated workforce are “long-term drivers of the IT revolution in Vietnam”. As commented by Phan (2021), there are several tech parks in the country, most notably Da Nang Hi-Tech Park and Saigon Hi-Tech Park, which are home to more than 700 businesses, including 220 international companies that specialise in “infrastructure development, hardware production”, IT and software engineering, and which also house their offices and factories (how and what. net,2020).
Vietnamese IT service companies are now ranked eighth worldwide. The top five IT industries at the moment are finance technology, “artificial intelligence, e-commerce, software outsourcing, and educational technology”. However, Diep (2019) stated that as more companies move their “industrial operations to Vietnam”, fierce rivalry in the labour market is escalating an already severe shortage of qualified personnel. As per the global Strategic Management assignment findings, the technological impact for the company to expand its business in Vietnam is positive (how and what. net,2020).
global Strategic Management assignment - Legal Factors
Foreign businesses are allowed to operate in Vietnam, and the government frequently encourages them to make direct or indirect investments. According to Manh Cuong & Hung (2020), there has been noticeable ease in the corporation law in recent years. Limited liability firms can now be quickly incorporated by foreign investors. “The Vietnamese National Assembly” approved a new labour code in November 2019, and it will go into effect on January 1, 2021. This new code updates and adds to several provisions included in all “chapters” of the current labour legislation (how and what. net,2020). The legal impact for the company to expand its business in Vietnam is positive.
Environmental Factors
Vietnam is “one of the most” beautiful countries in Asia. In 2019, 18 million foreign visitors visited its eight UNESCO World Heritage Sites. As stated by Mai (2020), due in great part to tourism, Vietnam's once-agrarian economy has been converted into one based on services. It is crucial to keep in mind that concerns over the coronavirus have put the tourism industry and public health at risk.
Unsustainable resource exploitation brought on by rapid economic growth may have an impact on “future growth prospects”. However, Dan (2020) stated that Vietnam experiences severe air pollution problems. Water pollution is a severe problem that harms people's health, just like air pollution. “Typhoons, earthquakes, floods, droughts, and volcanic eruptions” are extremely dangerous for Vietnam (how and what. net,2020). The environmental impact of the company expanding its business in Vietnam is moderate. Thus with the help ofglobal Strategic Management assignment PESTLE analysis of Vietnam, it can be seen that for Lyft to expand its business might have some face some challenges.
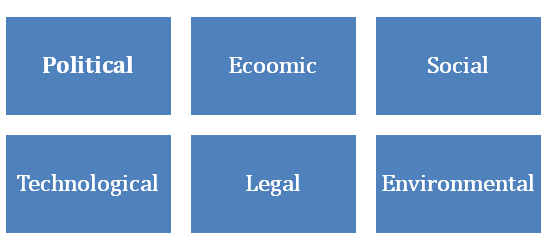
Figure 1: PESTLE of Vietnam
(Source: Self Made)
Porter’s five-factor model of Vietnam’s car rental industry
High threat from new competitors
As stated by Verma et al. (2018), the danger of new entrance may be viewed as significant because Vietnam had fully opened the transport sector to foreign businesses in 2015 as a form of “Foreign Direct Investment”. Competition with foreign businesses that have greater resources and higher competitiveness presents a big challenge for Vietnamese car rental companies (Li et al. 2021).
The medium threat of substitutes
The “effectiveness and efficiency” of the car rental and distribution networks will be crucial factors in determining the success of the participating enterprises. Likewise, Kövesdi et al. (2021) stated that this implies that for manufacturing firms, and specifically car rental firms, to compete in the market, they must identify and create effective car rental solutions.
Medium-sized suppliers' negotiating power
The development of effective car rental methods in the nation is being hampered by the “inefficiencies of the transportation system” and a lack of supporting infrastructure. On the contrary, Wijaya et al. (2018), stated that the car rental environment in Vietnam is anticipated to improve thanks to government attempts to upgrade the country's car rental infrastructure and a rise in the number of foreign operators.
Buyers' negotiating power: Medium/High
Vietnamese businesses have not yet completely realised the car rental industry's great potential for growth. Similarly, Kieseker et al. (2022) stated that currently, just 18% of all import-export activity is handled by domestic companies; “the remaining 80% is handled” by foreign car rental companies. Inadequate car rental infrastructure, such as bad “road connections connecting airports, warehouses, and seaports”, has increased the cost of car rental. It is also observed on this global Strategic Management assignment, the development of the “Vietnamese car rental sector” has been hampered by this disadvantage (Adelakun, 2020).
The rivalry between current businesses: High
“More than 600 mostly small-scale car rental businesses” operate in Vietnam, but they have a limited supply of “personnel, cash, and technological resources”. Likewise, Vermaet al. (2018) stated that additional obstacles to the growth of car rental in Vietnam include a dearth of infrastructure and several legal limitations.
This is projected that major international car rental companies will grow their presence in Vietnam through joint ventures and direct investment. However, Li et al. (2021) stated that the operating environment for service providers is anticipated to improve as decision-makers and end users become more aware of the benefits of an integrated car rental system. Thus, with the help of Porter's five-factor model, it can be seen that the car rental industry of Vietnam is competitive which would force Lyft to make proper policies to successfully expand its car-rental business in Vietnam.
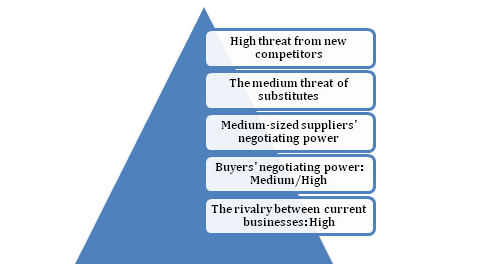
Figure 2: Porter’ five forces model
(Source: global Strategic Management assignmentSelf Made)
Integration–Responsiveness Grid for Lyft
Global strategy
As stated by Tan (2021), this strategy can help Lyft to focus as much as possible on consistency, including colours, messaging, commodities, and operations, to build repeatable, “scalable procedures regardless of the foreign market they operate in”.
This has the advantage of giving Lyft a globally recognisable brand and a step-by-step strategy for breaking into new areas. However, Krueger & Cruden (2020) stated that the biggest problem with a global strategy that can impact the business of Lyft in Vietnam is deciding how much standardisation to pursue. Even the most well-known international brands continue to make some investments in localization and market adaptation, simply not enough to compromise their “scale and efficiency” (Smartling. com,2022).
International Strategy
As commented by Zhou & Feng (2020), an international strategy is typically the first one that can be used by Lyft “when they enter secondary markets” because of its accessibility. It is merely an extension of the domestic strategy of Lyft to conduct business with a “head office in San Francisco” while providing its services to Vietnam (Smartling. com,2022).
The key advantage of this approach observed on this global Strategic Management assignmentis that it provides a quick way to ascertain whether the services can be sold internationally without requiring significant investments in the infrastructure or human resources of other countries. However, Khan et al. (2022) stated, that an international strategy does have some drawbacks even if the company is just experimenting in a global market, translation is always the responsibility of Lyft. Regardless of the level of global integration the company seeks, its customers must be able to understand what the company have to offer and how to pay for it (Smartling. com,2022).
Transnational Strategy
“In addition to having a central office or head office” in a single country, multinational corporations like Lyft can also employ local subsidiaries in foreign markets. According to Kohlhepp et al.(2019), this allows them to combine the best of both worlds: a “single umbrella brand” that provides a uniform structure and efficient centre of operations while appropriately adjusting to the local market inclinations and tastes. The most variety is found in transnational (Smartling. com,2022). Some companies give their local branches a greater degree of autonomy than others. Conversely, Charqaouy et al. (2020) stated that one of the major issues for multinational corporations like Lyft is to strike a balance between corporate and local decisions, which has an impact on all business decisions, from hiring to marketing (Smartling. com,2022).
Multi domestic Strategy
As stated by Tan (2021), the "local-first" method among the four is a multi-domestic strategy since it performs well in terms of local responsiveness but poorly in terms of global integration. Businesses that employ a multi-domestic strategy modify their products, “messaging, go-to-market strategy, and customer support” depending on the country they enter (Smartling. com,2022). The biggest benefit of this is a highly specialised, locally produced good that precisely matches client likes and preferences, with local staff who are aware of local customs. However, Krueger & Cruden (2020) stated that the drawback of this is that the changing environment of both the foreign as well as domestic markets can impact the business of a company. Thus, with the help of the grid, it can be understood that for Lyft to successfully expand its business in Vietnam, the company should implement a “Transnational strategy”.
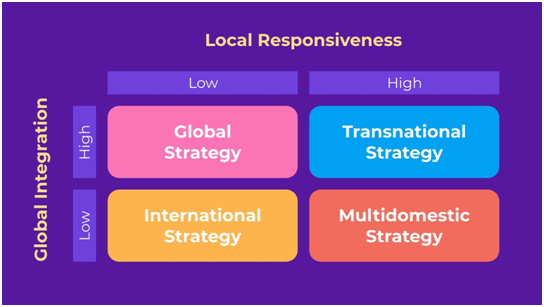
Figure 3: Integration responsiveness strategy
(Source: Smartling. com,2022)
Conclusion
With the help of the global Strategic Management assignmentreport, it can be seen that Vietnam might provide some challenges for Lyft to conduct its business in the country. The car-rental industry of Vietnam is competitive and policies should be implemented to allow Lyft to expand its business properly. The global Strategic Management assignment findings show, in order to successfully start its car rental business in Vietnam, the company should implement a “Transnational strategy”.
Reference List
Adelakun, A. (2020). Should Porters Five Forces have value in Businesses today. Computing for Business (BSC) Aston University Birmingham. global Strategic Management assignmentRetrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Andrew-Adelakun/publication/340771629_Should_Porters_Five_Forces_have_value_in_Businesses_today/links/
5e9c998ca6fdcca78928352e/Should-Porters-Five-Forces-have-value-in-Businesses-today.pdf
Charqaouy, S. S. E., Saifaoui, D., Benzohra, O., & Lebsir, A. (2020). Integration of Decentralized Generations into the Distribution Network-Smart Grid Downstream of the Meter. International Journal of Smart Grid, 4(1). Retrieved from: https://www.academia.edu/download/79794719/pdf.pdf
Dan, T. (2020). Market Study for Functional Food and Oat Products in Vietnam. Retrieved from: https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/344307/Tran_Dan.pdf?sequence=3
Diep, T. H. (2019). Live streaming as a business model for teaching English in Vietnam. Retrieved from: https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/163643/Thesis%20-%20HaoDiep%20%28final%2020190401%29.pdf?sequence=2
Khan, B., Guerrero, J. M., Chaudhary, S., Vasquez, J. C., Frederiksen, K. H., & Wu, Y. (2022). A Review of Grid Code Requirements for the Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in Ethiopia. Energies, 15(14), 5197. Retrieved from: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/14/5197/pdf
Kieseker, G. A., Anderson, D. J., Porter?Steele, J., & McCarthy, A. L. (2022). A psychometric evaluation of the Female Sexual Function Index in women treated for breast cancer. Cancer Medicine, global Strategic Management
assignment11(6), 1511-1523. Retrieved from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/cam4.4516
Kohlhepp, P., Harb, H., Wolisz, H., Waczowicz, S., Müller, D., & Hagenmeyer, V. (2019). Large-scale grid integration of residential thermal energy storages as demand-side flexibility resource: A review of international field studies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 101, 527-547. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364032118306944
Kövesdi, G., Orosz, S., & Fogarassy, C. (2021). Strategy Analysis of International Forage Laboratory Networks. HUNGARIAN AGRICULTURAL ENGINEERING: PERIODICAL OF THE COMMITTEE OF AGRICULTURAL AND BIOSYSTEM ENGINEERING OF THE HUNGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES, (40), 91-95. Retrieved from: http://real.mtak.hu/143009/1/40-2021-09-HAEDOI10.17676HAE.2021.40.91.pdf
Krueger, H., & Cruden, A. (2020). Integration of electric vehicle user charging preferences into Vehicle-to-Grid aggregator controls. Energy Reports, global Strategic Management assignment6, 86-95. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352484720301992
Li, Y., Teng, Y., Shi, W., & Sun, L. (2021). Is the Long Memory Factor Important for Extending the Fama and French Five-Factor Model: Evidence from China. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021. Retrieved from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/mpe/2021/2133255/
Mai, N. C. (2022). Analysis of the Vietnamese commercial real estate market-Strategic investment implications for Evergreen Properties of Michigan, Inc. Retrieved from: https://osf.io/3cya7/download
Manh Cuong, N., & Hung, P. V. (2020). Sea navigation-based Thai Canal implication: an analysis of its effect on the Vietnamese maritime industry. Australian Journal of Maritime & Ocean Affairs, 12(2), 83-94. Retrieved from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/18366503.2020.1764174
Phan, S. (2021). The effect of pestle factors on development of e-commerce. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 5(1), 37-42. Retrieved from: http://m.growingscience.com/ijds/Vol5/ijdns_2020_28.pdf
Tan, T. K. (2021). The impact of digitalization on international expansion: A study on market entry strategy based on< the Integration-Responsiveness Framework. global Strategic Management assignmentRetrieved from: https://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1370&context=etd_coll
Tran, H. (2020). Entering the Vietnamese textile and apparel consumer market: Case: Marimekko. Retrieved from: https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/341450/Tran_Hanh.pdf
Verma, P., Kumar, V., Muthukumaar, V., & Gajbhiye, R. (2018). Implementation of Horizontal Strategy for Conglomerate firms: The Role of Five-Factor Model. Retrieved from: http://ieomsociety.org/ieom2018/papers/531.pdf
Wijaya, L. I., Irawan, R. K., & Mahadwartha, P. A. (2018). Test of Fama & French five factor-model on Indonesian stock market. Retrieved from: http://repository.ubaya.ac.id/34731/1/Liliana%20Inggrit_Test%20of%20Fama%20%26%20French%20five%2
0factor-model%20on%20Indonesian%20stock%20market_2018.pdf
Zhou, M., & Feng, D. (2020). A New Modeling Approach for Power Grid Online Analysis. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 53(2), 13131-13136. Retrieved from: http://ifatwww.et.uni-magdeburg.de/ifac2020/media/pdfs/1235.pdf
howandwhat.net, (2020), pestel-analysis-Vietnam. Retrieved on: 16 August 2022 from: https://howandwhat.net/pestel-analysis-vietnam/
Smartling. com,(2022), the-4-most-common-international-business-strategies-pros-and-cons.global Strategic Management assignmentRetrieved on: 16 August 2022 from: https://www.smartling.com/resources/101/the-4-most-common-international-business-strategies-pros-and-cons/












