Healthy Cities Essay: Challenge faced and the Planning Required
Question
Task: My topic is "HEALTHY CITIES" Please write an essay on Healthy Cities directly related to Urban & Regional Planning and please i am saying again, context should be directly related to Urban and Regional Planning.
Answer
Introduction
Healthy Cities are considered arguably one of the best largest and known setting approaches. The program relates to long-term international development drives that aim for placing health high on the agenda of the decision makers as well as promoting comprehensive local planning for sustainable development and health protection. The basic traits include community empowerment and participants, participant’s equity and intersect oral partnership.
The major aim to promote Healthy Cities are creating healthy as well as supportive environment, providing basic hygiene and sanitation needs, supplying access to the health care and achieving good quality of life. Being a Healthy City do not only encompass recent health infrastructure, rather than relates to the commitment that are built in order to enhance cities willingness and environs to frame all the necessary connection in aspects of social arenas, economic and political. The present healthy cities essay aims to investigate the different aspects of a healthy city and the urban and regional planning involved in the same, in details.
Discussion
Concept of Healthy Cities: The first program of Healthy city had been established in Australia, European, Canada, United Nations and similar such developed countries. The developing countries applied specific implications strategies and resources irrespective to gain success from the established programmes. The concept of Healthy Cities is widely followed in the urban areas, implementing effective infrastructural facilities. Furthermore, Health is the term that states completion overall mental, social and physical well being as well as do not based on mere absence of infirmity and disease. According to Huan et al., (2015), meeting new challenges of urban health depends on reuniting urban planning and public health in the academic world, professional arena in government and community development. The present healthy cities essay focuses on establishing and exploring the links between urban planning and public health. The context, therefore, enables the practitioners to generate more adequate policies decisions that enables universities to provide appropriate educational. In addition, it also leads to provide conceptual frameworks for guidance, integrating healthy considerations while practicing urban planning.
There are certain challenges on health policies, implementing crucial matter towards healthcare professionals. On the contrary, concern for the well-being and health are becoming central focus to several aspects of local and national policies. In a similar manner, the link between planning and health across the range of non-communicational diseases are multi-dimensional. Based on the view of de Roo, (2017), it compresses environmental, social and economical purposes of urban planning.
The World Health Organization introduced the concept of the Healthy City, in the year 1986. According to Ramaswami et al., (2016), from the data analysis of WHO, 112 cities has been profounder with a population of more than 1 million, implementing various issues in aspects of ecological, environmental and hygienic, that are rapidly increasing with increasing populations and industries. However, WHO is the organization that enacts certain activities in order to promote the concept of Healthy City. According to the statement of Guidotti, (2015), it expects that the densely populated city must not only consist of negative impacts that lead to environmental pollutions, but also implement positive aspects including Lifestyle of Health and Sustainability (LOHAS). The Healthy City concept must include social affairs as well as medical affairs, health must be served to prior responsibilities to all the urban sectors, and expert must evaluate the specialized field that includes social studies, environmental studies, natural science and aesthetics. In addition, health must be manifestations of all community participants as well as cooperation of private and public sectors. According to the view point of Berendsen et al., (2015) the concept of Healthy City considers all the macro factors as well as medical and health of overall developing country.
Urban Planning as a determinant of health
The environment and surroundings of the place highly affects the policies and conceptualizations development. However, the environment has been recognised as key determinants for health. Promoting the health social programmes in aspects of changing behaviours does not deemed to be effective, implementing only a small proportion of populations while maintaining the long term seldom. According to Bennett, (2017), fundamentals are mandatory for environmental, social and economical impacts, while shaping the spatial planning and implementing on physical development. On the contrary, there are growing recognitions among the health professionals that promote essential facts on health, in aspects of different programmes are not very effective. The programmes are necessary to be spread within huge proportions of population, which seldom leads to maintenance of benefits of local publics in long term.
Urban planning, as mechanism of the environmental control, implements health in number of authentic manner. The below diagram set and explains various spheres of economic and social life with the wider environmental factors that are affected by the planning.
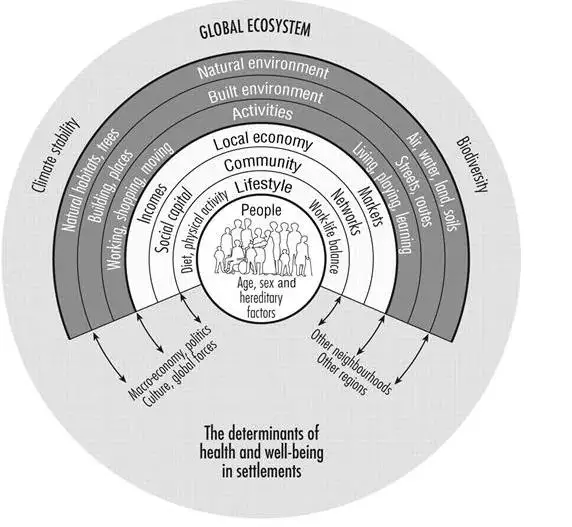
Figure 1: Human Ecology model of a Statement
(Source: Bennett, 2017)
From the above figure, it has been observed that health is considered casual. The decline in the regular daily cycling and walking is implemented in raised risk and obesity of cardiovascular and diabetes diseases. Henceforth, the social polarisation of the opportunity that are exacerbated has been accentuated in the given healthy cities essay. All factors reduce the opportunities for supportive social contacts vital for the mental well-being. Thus, the health issues are storing for future betterment that will lead to present the health issues while delivering health services that are looked trivial by comparison. Thus, from the specific article transporting planning has been fully integrated with use of urban land planning. Transport is widely recognized as the essential determinant of health.
Modern day regional and urban health challenges
The new challenges to urban health depend on reuniting urban planning and public health in the academic world, community development, and government as well as in professional arena. Henceforth, challenges to urban health facing the industrialization across the world are relatively multifaceted and complex. Mass immigration and industrialization placed great pressure on medical and social services along with the rising demands of jobs and housing in urban areas. Such influx within people demands sensitive planning in aspects of culture. Urban planner and health professionals needs to understand the field for which they are required to plan and focus on plans accordingly. However, this bottom-up approach is inherently different from standard approach and terms to be one of the challenges today in aspects of urban health. In addition, of leading causes of death along with health changes in developing nations that are shifted from the infectious diseases to the chronic condition are challenges in today's era in urban areas.
Multi-Sectoral prevention has been established by the new sets of challenges for public health. Thus, the field of the urban planning must enact beyond traditional manners while approaching to health issues. However, such policies are not considered in aspects of changing nature of the health. The modern era’s industrialized nations are responsible for generating new and deadly disease producing agents. Firearms, tobacco, motor vehicles, toxins are some of the leading causing agents that considered as killers generated from industrialization world. Furthermore, from the public research it has been observed that diseases are caused more often by those who are having fewer social relationships, lower in hierarchical positions and from those who are disconnected from cultural and biological heritages. Both the statistical and literature trends exhibit the interconnected and complex nature of current bills as well as calls for a wide perspective. As opined by Huang et al., (2015) one that are separated from traditional health concepts of the urban planning into comprehensive realms that are the links to functions of the urban planning and creation of vibrant, healthy and strong neighbourhoods, cities and towns. On the contrary, European experiences growing pains implemented from inhabitants, that is absorbing huge number of immigrants.
The aspects of urban and regional planning that needs to be considered for planning of healthy cities
Crucial and effective regional and urban planning is required to be evaluated in aspects of planning healthy cities to ensure the overall health of the citizens.
Controlling diseases and preventing illness: The foremost consideration by public health issues for urban planning encircles aspects to control disease. The basic services like safety and housing were nonexistent in some of the urban areas that implements several challenges to general people. Industrial workers are forced to live in overcrowded conditions without any exporter to ventilation and daylight in many of the urban areas where the concept of Healthy Cities were neglected. Under such conditions, the workers are exposed to several diseases like tuberculosis, cholera, yellow fever and typhus, implementing several losses in terms of economic and human lives.
Thus, with the advancement of technologies, several methods have been invented to prevent the illness. Living quarters with adequate ventilations and light, minimizing the exposures towards toxins for example lead and asbestos are some of the facts that are focused while urban planning.
Safety for reducing accidents: Urban planners are very much concerned in aspects of specific measures that enables them to reduce injuries and fatalities due to accidents. Based on the De Leeuw and Simos, (2017) thus, traffic planning and control, adequate fire station planning and standard playground equipment and pavement standards are traditionally aligned. On the other hand, the increasing crimes raised the fear of safety among the people, implementing different challenges to be imposed on urban planner. One way to reduce the climate deserting and fear in public areas are enhanced by planning, management and design effective safety measures that are accessible. According to Sallis et al., (2016) three basic principles initiatives that are strived to be communicated while development and planning into public spaces are maintaining physically cleaned environment, creating mixed-use environment while generating varieties of activities and ensuring public areas visible to longer distance with adequate uniform lighting.
On the contrary, the urban planner is required to focus in aspects to reduce pollution, violence and other similar factors in addition to the above points. Healthy City is a term that consists of community outcome valued highly at the regional level. On the other hand, the outcome of community reflects the priority and wishes of overall populations served by regional and city councils. It has been observed that with these outcomes, the health is enhanced while perceiving local government’s contributions.
Success stories and dynamic change in health conditions of the citizens
The final study provides evaluation of real example of healthy planning urban project, both in small as well as large scale. The illusion of the success stories provides both the informal and formal theoretical that are underpinnings in this healthy cities essay.
On the contrary of De Leeuw et al., (2015) European cities have served benefits from provisions of the open space. In Italy, piazzas and France places are propounded as a place where people convene multiple purposes. Individuals having extraordinary understanding and vision of art behind the catalytic leadership thus, turned European tradition into a reality for American city of Portland, Oregon.
As stated by Frumkin, (2016), during the time the city was losing its vitality just like American city, the Governor Tom McCall announced for new Portland, implementing vital heart where both residents as well as visitors can feel different and special qualities of Pacific Northwest. As per the statement of Giles-Corti et al., (2016) from the work and visions of many people, additionally, Portland city reinvested in downtown while purchasing and razing the parking garage in aspects to build Pioneers Courthouse Square, in order to provide the citizens access to open spaces for convening different gatherings and functions. The plaza was located at the centre of Portland downtown, serving as transferring points for both regional of light rail and local bus lines. Henceforth, the residents of downtown Portland refers to the area of “Portland’s Living Room”. The courthouse Square of Portland has huge open space that hold summer concerns as well as other community celebrations. According to statement of Freestone and Wheeler, (2015), Tom McCall, the plaza is considered as true heart of city.
Conclusion
The given healthy cities essay deals with the importance of Healthy Cities. All the factors that are responsible in aspects of negative impact of the environment in the urban areas are evaluated in the given study. Specific challenges that are faced by the urban planning at the time of development are determined in the current healthy cities essay. Thus, from the context it has been accentuated that the cities that are termed as healthy enjoy all the positives in aspects of environmental, social as well as economic factors. Furthermore, all the key principles are discussed that influences urban planning. A success story of Portland's downtown that has attended dynamic changes in aspects of the effective and adequate urban planning has also evaluated in the healthy cities essay. A Human Ecology model of a Statement has been discussed in order to accentuate health conditions that implements declination of daily working of human are also exhibited in the following healthy cities essay.
Reference List
Bennett, J.W., 2017. Human Ecology as Human Behavior: Essays in Environmental and Developmental Anthropology. Routledge.
Berendsen, B.A., Kremers, S.P., Savelberg, H.H., Schaper, N.C. and Hendriks, M.R., 2015. The implementation and sustainability of a combined lifestyle intervention in primary care: mixed method process evaluation. BMC family practice, 16(1), p.37.
De Leeuw, E. and Simos, J. eds., 2017. Healthy cities: the theory, policy, and practice of value-based urban planning. Springer.
De Leeuw, E., Kickbusch, I., Palmer, N. and Spanswick, L., 2015. European Healthy Cities come to terms with health network governance. Health promotion international, 30(suppl_1), pp.i32-i44.
de Roo, G., 2017. Integrating city planning and environmental improvement: Practicable strategies for sustainable urban development. Routledge.
Freestone, R. and Wheeler, A., 2015. Integrating Health Into Town Planning. The Routledge handbook of planning for health and well-being: Shaping a sustainable and healthy future.
Frumkin, H., 2016. Urban sprawl and public health. Public health reports.
Giles-Corti, B., Vernez-Moudon, A., Reis, R., Turrell, G., Dannenberg, A.L., Badland, H., Foster, S., Lowe, M., Sallis, J.F., Stevenson, M. and Owen, N., 2016. City planning and population health: a global challenge. The lancet, 388(10062), pp.2912-2924.
Guidotti, T.L., 2015. Health and sustainability: an introduction. Oxford University Press. Haaland, C. and van den Bosch, C.K., 2015. Challenges and strategies for urban green-space planning in cities undergoing densification: A review. Urban forestry & urban greening, 14(4), pp.760-771.
Huang, L., Wu, J. and Yan, L., 2015. Defining and measuring urban sustainability: A review of indicators. Landscape Ecology, 30(7), pp.1175-1193.
Ramaswami, A., Russell, A.G., Culligan, P.J., Sharma, K.R. and Kumar, E., 2016. Meta-principles for developing smart, sustainable, and healthy cities. Science, 352(6288), pp.940-943.
Sallis, J.F., Bull, F., Burdett, R., Frank, L.D., Griffiths, P., Giles-Corti, B. and Stevenson, M., 2016. Use of science to guide city planning policy and practice: how to achieve healthy and sustainable future cities. The lancet, 388(10062), pp.2936-2947.












