Health Promotion Assignment: Analysis of Behaviour Change of Community
Question
Task
Find three scholarly journal articles in order to develop this health promotion assignment that:
- Describe a health promotion intervention. Note: they do not need to be the same health behaviour or same type of intervention. Please note, in this instance an intervention is when the researcher/s (authors) conduct a study where they focus on some type of health behaviour. (Note: a systematic review is NOT an intervention – however systematic reviews examine interventions, so they may contain appropriate journal articles within them that you could find and use).
- USE the SAME health behaviour change theory For example: you may decide to focus on organisational health promotion interventions and then use Goodman’s four stage model as the theory you choose to focus on.
You would find 3 journal articles that include an organisational health promotion intervention that uses Goodman’s 4 stage model. Critically review the three interventions (in the journal articles) reflecting on the following:
- Describe how the chosen theory or model was used in each of the three interventions.
- Compare and contrast how effectively the theory was used in each of the interventions.
- Finally: provide an argument which either supports or negates the use of theory in health promotion interventions. Your thoughts and ideas MUST be supported by appropriate scholarly references
- Correct referencing using the UOW Harvard method and appropriate structure and presentation.
Answer
Introduction
Health promotion intervention mechanisms discussed in the present context of health promotion assignment need to be adopted often transforming behavior change within the community (Nutbeam et al., 2010). One of the most prominent health behavior change theory is the behavior change wheel (BCW) where nineteen frameworks encompassing nine intervention functions along with seven policy categories that could not provide effective interventions, this model could lead to behavior change. This proposed framework for transforming behavior could easily be encompassed with three crucial conditions which include opportunity, capacity as well as motivation. These conditions formed the focus of behavior change in an effective manner. This system comprises of 'behavior system' encompassed by intervention functions as well as by policy categories. The current scope of discussion identified three articles and connects them to the application of the behavior change wheel theory in the three interventions undertaken in the article.
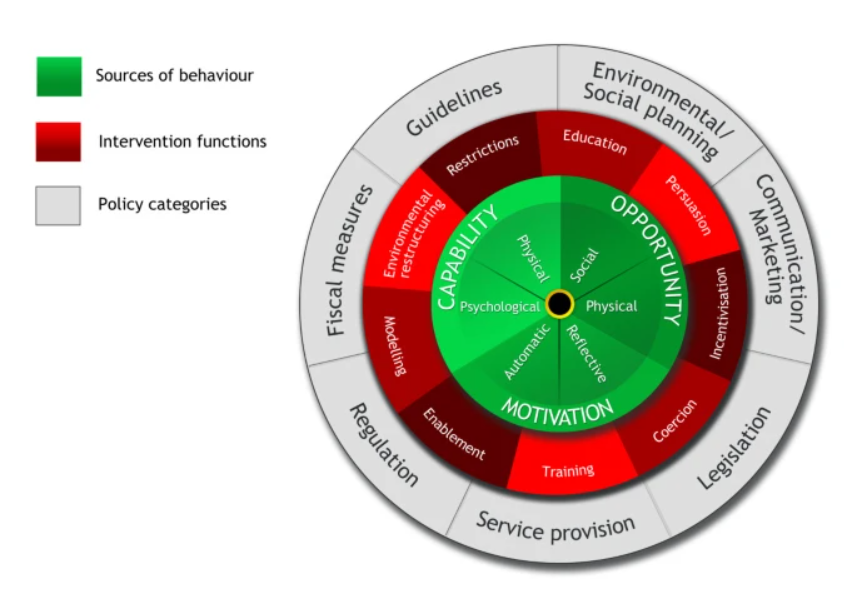
Figure 1: Behaviour Change Wheel
Source: (Michie et al., 2011)
Analysis
The current discussion includes three prominent articles of behavior change that have been undertaken effectively within the scope of the model. In the first article by Barker et al. (2016) the behavior change wheel has been applied for improving hearing aid use in adult auditory rehabilitation. The article makes use of the complex intervention mechanism as advocated by the Medical Research Council (MRC) framework to implement research. The MRC framework is suitable in audiology as audiologists interact with individuals with hearing loss with self-management support (SMS). The BCW model was used in a step-by-step manner in the study as discussed in the article with an understanding of each element to arrive at results regarding the same. This theory linking to intervention design is consistent according to the advice received by the MRC on complex interventions. All the behaviors such as usage of hearing aids take place within a system that depicts competing behaviors. While applying the BCW process has selected the target group for attaining to the behavioral problem. While applying hearing-aid use patients, changing behavior of the patient is seen to be dependent upon on other individual's behaviors, encompassing healthcare professional's behaviors. The article appropriately applies the relevant criteria to the behaviors in the system identifying four prominent behaviors that are targets for the development of intervention mechanisms.
With the application of the appropriate methodology for the intervention mechanism, each element of the theory has been appropriately evaluated such as capability – where audiologists evaluated that the physical capability not being an issue for developing a behavioral plan for patients. The psychological capability was also evaluated where it was analyzed whether the patients were able to understand benefits arising for them as being an essential motivating aspect. The participants in the study depicted the capability to make plans in a quick and easy manner with psychological skills of adaptability for planning. Mental stamina such as tiredness at the end of the long clinic was identified as a potential barrier for the planning of behavior. While evaluating an opportunity, the article appropriately evaluated social and physical opportunity as being essential in planning for behavior. There have been significant areas discussed that were of concern were analyzed. The study was undertaken in the article also allowed participants to access an onscreen template connected to EHR which could impact access to information as well as later appointments that could analyze the benefits. When understanding motivation, the article evaluated undertaking reflective along with automatic motivation having a role in the determination of carrying out behavioral planning in likelihood. The participants in the study depicted making use of a plan for the inclusion of behavioral plans in their appointment. The article also evaluated automatic motivation that includes desires, emotional reactions, reflex responses, impulses, as well as habits to motivate desires for positive outcomes for themselves which provides benefits. Thus, this article provides a systematic manner for moving from behavior analysis towards the identification of potential intervention functions as well as policy categories for bringing about transformation.
In another article Sinnott et al., (2015) an intervention for improvisation of managing medication in multimorbidity has been undertaken to apply the BCW model. Prevalence of multimorbidity with the presence of two or greater than two chronic conditions has been seen across patients in almost 60% of primary care. With BCW receiving tremendous academic interests, there is seen a large number of studies that are applying its intervention mechanism as healthcare professionals. This article is novel in its scope as it provides intervention targeted at the complex domain of multimorbidity. The scope of this article discusses applying the MRC framework, intervention for improvising management of medication in multimorbidity by GPs with the BCW model for transparent implementation. This article effectively identifies and applies stages as well as steps of the BCW initiating with defining the problem in terms of behavioral patterns. Hence the model was applied to understand ways to undertake behavior change for adopting better management of medication. While identifying the problem, the article undertook a qualitative review from varied published articles which in turn included quantitative aspects along with the systematic review. Then in the next step selected targeted behavior was identified which will need transformation as per the BCW guide to specify targeted behavior. The model for targeted behavior is then applied for understanding the choice of intervention functions. Reflective as well as automatic motivations, GP's physical and psychological capabilities, and social with physical opportunities were identified. Then using 19 frameworks of behavioral-intervention strategies, intervention functions impacting behavioral change were analyzed. Matrices of BCW for the broad policy-level intervention of behavioral change were also analyzed. This article effectively describes in a structured, systematic manner the development of an intervention for improving the management of medication for multimorbid patients by GPs in primary care. The problem identified in the article included GP's sense of isolation in managing such multimorbid patients, and their lack of efforts as well as certainty for sharing the onus of responsibility, hence intervention mechanism primarily aimed at professional support. In this research, BCW has been used as a lens for understanding the shift in intervention designs and for facilitating approach in the complex clinical area.
In the third article by Fulton et al., (2016), BCW was applied for the development of an App such that there is an increase in uptake as well as attendance at NHS Stop Smoking Services. The scope of this article identifies intervention of behavioral change mechanism of stop smoking, as smoking is identified to be the major cause of mortality as well as morbidities worldwide. In this profound intervention by the NHS to undertake stop smoking in the UK, there were identified tremendous challenges, hence a cost-effective intervention was planned such that smokers would stop smoking. This article also clearly identified all the steps of the model for understanding the changing of behaviors which led to the outcome of devising the StopApp intervention mechanism for increasing motivation amongst participants. Thus, the intervention mechanism was effective as it effectively identified all the elements as well as aspects included in the BCW model for transforming behaviors.
All three articles appropriately apply the theoretical model BCW for transforming change in behavior. All three articles carefully plan their intervention mechanism in a step-by-step manner accommodating each element of the BCW model. However, the discussion in the second and third article are more detailed in the various stages as against the first article. The first article though clearly identifies the components of change that need to be adopted yet it is not as effective when compared against the second and third articles. The first article is rather detailed on the intervention approach of improving the use of hearing-aid in adult auditory rehabilitation. With the application of the BCW model, the studies have identified the intervention mechanism in a systematic and transparent manner for implementing change. With the selection of policy categories, the intervention functions were selected for bringing about transformation. Transforming behaviors will lead to an impact on the behavior of patients with implementation to be appropriate to calculate. The third step of the BCW has been applied for the development of appropriate specifications to depict persons who will be performing the targeted behaviors for transforming. Hence it can be safely stated that the identified behaviors in each case were arrived at by examining through varied aspects of the BCW model, especially in the third article. Though in the second and first articles the BCW has been applied for examining the effectiveness of the application of BCW in transforming behavioral change. The theory of BCW was applied in an effective manner in all the articles where three different intervention mechanisms have been identified.
However, it is crucial to understand that while theory enables a planned approach towards undertaking health interventions, it is always nearly impossible to identify and apply the same. Healthcare professionals in practice might often find it to be impossible to identify all the components of the BCW model for impacting a behavioral change in the community that is of public importance such as the use of hearing -aid, medication management or stop smoking approaches. Though the theories can serve as suitable guides that can be adopted by professionals and integrated into day-to-day lives for bringing about change. Health behavior promotion interventions are crucial for the benefit of the community as well as to the society as a whole but might not be facilitated with ease, as there remain varied macro-environmental constraints linked to them. It might always not be feasible to undertake systematic frameworks for interventions. Most importantly, judgment is crucial when conceptualizing any intervention function across policy categories. There is no mechanism that can depict optimal arriving at the behavior change. Different frameworks might be more or less useful in varied circumstances. Even if the proposed framework might appear to be comprehensive and can be applied in reliably characterizing intervention approaches, broader health interventions might appear difficult to implement and use. The core importance of this model lies in its systematic approach with which the model provides a robust nature for developing an improvised framework that can enable health interventions possible.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it has been observed that with effective intervention undertaken with the usage of the behavior change model, it has been possible to arrive at behavior change in each of the three articles. This proposed framework for transforming behavior could easily be encompassed with three crucial conditions which include opportunity, capacity as well as motivation. The theory of BCW was applied in an effective manner in all the articles where three different intervention mechanisms have been identified. All three articles carefully plan their intervention mechanism in a step-by-step manner accommodating each element of the BCW model. Even if the proposed framework might appear to be comprehensive and can be applied in reliably characterizing intervention approaches, broader health interventions might appear difficult to implement and use. Judgment is important in conceptualizing any intervention function across policy categories. There is no mechanism that can depict optimal arriving at the behavior change. Health professionals hence need to make use of this model as a guiding practice for undertaking interventions in health for impacting the broader community and translating in practice.
References
Barker, F., Atkins, L. and de Lusignan, S., 2016. Applying the COM-B behaviour model and behaviour change wheel to develop an intervention to improve hearing-aid use in adult auditory rehabilitation. International journal of audiology, 55(sup3), pp.S90-S98.
Fulton, E.A., Brown, K.E., Kwah, K.L. and Wild, S., 2016, June. StopApp: using the behaviour change wheel to develop an app to increase uptake and attendance at NHS Stop Smoking Services. In Healthcare (Vol. 4, No. 2, p. 31). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
Michie, S., Van Stralen, M.M. and West, R., 2011. The behaviour change wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implementation science, 6(1), p.42.
Nutbeam, D, Harris, E, & Wise, M 2010, Theory in nutshell: A practical guide to health promotion strategies, 3rd Ed, McGawHill, Australia (page xiii).
Sinnott, C., Mercer, S.W., Payne, R.A., Duerden, M., Bradley, C.P. and Byrne, M., 2015. Improving medication management in multimorbidity: development of the MultimorbiditY COllaborative Medication Review And DEcision making (MY COMRADE) intervention using the Behaviour Change Wheel. Implementation Science, 10(1), pp.1-11.












