Health Care Assignment: Research on Start-ups in Kuwait Health Sector
Question
Task: Conduct a critical research on health care assignment and prepare a dissertation on the topic “Start-ups in health care sector of Kuwait”.
Answer
1. Chapter 1: Introduction
1.0 Introduction to the research area
The central theme being healthcare start-ups in Kuwait in this research includes the healthcare industry in Kuwait that has been assisted by increasing the number of cases and in-patients. The developing occurrence of non-communicable illnesses, as well as the aged populace, has further developed the demands of tertiary, primary, and secondary healthcare services (prnewswire.com, 2019).
Various private players understand the development importance of the Kuwait healthcare industry and have capitalized effectively in creating infirmaries around the country. The healthcare market is likely to face an extra of almost fifteen infirmaries in the next 5 years that would add a considerable quantity of beds in both private and municipal hospitals. The private healthcare sector in the country is facing a new demand, where deluxe comforts are one of the main marketing levels for hospital facilities (prnewswire.com, 2019). Private hospitals are advertising higher-end hospitality knowledge and state-of-the-art medical facilities. Increasing concentration on higher revenue intensity streams that involve secondary care, quaternary, and tertiary care with comprehensive health screening policies for developing influence from out-patients added by inspiring occurrence of lifestyle and chronic illnesses would push the country healthcare market income in future. Management aspects of the healthcare industry are also essential as they will concrete the main aspects and achieve the objectives of this industry. Hospital management that will provide many start-ups new business opportunities regarding the establishment of institutes will also be discussed. Same opportunities for start-ups as well as millions of students, practitioners, aspirants will be created.
1.1 A brief overview of the industry
As per WHO, Kuwait has been identified as a higher-income country with one of the developed healthcare systems in the region. Though, with predictable future healthcare needs assume to increase importantly in the phase of a rapidly increasing population (calculated to have reached be 4.2 million in 2017), coupled with budget deficits, as well as a precise insurance-based population, the private industry is assumed to develop their share of the spending burden as Kuwait works effectively to modify, increase and widen their healthcare system over the next years (oxfordbusinessgroup.com, 2020). The MoH’s (Ministry of Health) budget for hospital spending has increased in prior 5 years to almost KD 2 billion ($6.6 billion) in 2016, with the public industry having 80% of the spending as well as functioning fifteen general and expert hospitals; on the top of the primary care system of polyclinic (globenewswire.com, 2020). The hospital industry in the country would likely confront fast development over the future 5 years due to the great investment in Kuwait's healthcare system. The country's healthcare industry is aimed to increase an effective CAGR from 2018-2022 (globenewswire.com, 2020). The income amounted from private industry infirmaries would effort to control the industry as the private contribution is likely to develop and so is the expense of private hospital infrastructure.
1.2 Research problem
- The country suffers from higher levels of obesity, cancer, and diabetes. As per the Global Burden of Disease review, Kuwait is the 4th most obese country around the globe (2016.export.gov, 2019). However, the population is young, the illness burden is a developing problem.
- The country’s healthcare industry includes over 80% of the spending (2016.export.gov, 2019). Recently, the Ministry of Health is the operator, management, authority, and financer of most of the healthcare facilities reduced, medicines buying, and tools acquired in Kuwait. However, the country offers the services of free medical facilities to its people, this fails for offering quality healthcare facilities in many areas. The needed supplies lacking is making people wait for a longer time.
- The country aspires to ensure world-class healthcare providers along with developing quality facilities in treatment facilities like Kuwait Chest Disease Hospital, Ibn-Sina Centre for Ophthalmology, Kuwait Cancer Centre, and others (2016.export.gov, 2019). The healthcare industry needs to develop a collaborative project for replacing or developing 9 operating hospitals (5 general and 4 expert hospitals) within the future 10 years.
- The healthcare industry is facing some reform works. One of the important works involves widening public-private collaboration as well as offering the private industry a large responsibility in the provision of healthcare facilities.
1.3 Aim
This research aims at reviewing the current condition of business start-ups in the healthcare sector of Kuwait.
1.4 Research objectives
- RO1: To elaborate on the issues faced by the start-up companies in the Healthcare sector in Kuwait
- RO2: To understand the growth of start-up companies in Kuwait
- RO3:To implement different strategies to improve the condition of the Healthcare sector in Kuwait
1.5 Research questions
- RQ1: What are the issues faced by start-up companies in the healthcare sector in Kuwait
- RQ2: How do we explain the growth of start-ups in the Healthcare sector in Kuwait
- RQ3: What strategies can be implemented to improve the condition of the healthcare sector in Kuwait
1.6 The rationale of the research
Based on the current healthcare industry infrastructure, operations, and increase of private start-ups, it has been identified that the health industry in Kuwait heavily depends on professionals. The major problems identified above are indicating the lack of professionals and advance technology-based services in this sector also (Salman et al., 2020). The entire nation represents around 6% of total medical practitioners (both female and male) of the country. Therefore, this becomes critical for start-ups to invest majorly in these areas. On the other hand, the country fails to offer an effective number of employees and doctors in various types of medical care operations. This suggests that entrepreneurs in the healthcare industry will need to heavily depend on ex-parts that could be an important matter for various private start-up organizations (Salman et al., 2020). The country still depends on ex-parts for reaching its needs for professionals. It has been reviewed that around 70% of the doctors in Kuwait are from outside. Therefore, lacking in fulfilling the vacancies of the healthcare industry by Kuwaitis remains an issue for private start-ups.
1.7 Structure of the dissertation
The research will include sections such as Introduction, including the main research questions, problem area identification, and others. The literature review section will include secondary information from previous studies for broadening the objectives. The methodology section will elaborate on how the entire research has been done and what tools have been included. The results section will entitle data collected from the survey and other data collection process with a discussion of the results for finding future implications of start-ups in the Kuwait healthcare sector. The conclusion section will brief recommendations, limitations, and practical implications of the study results.
Chapter 2: Literature review
2.1Current Healthcare sector condition in Kuwait
Kuwait’s healthcare industry is in evolution, with increasing signs of private industry involvement despite government control of the provision and investment of care. If the country is to make sure the sustained running of quality health care; this would require a policy to further market the responsibility of the private industry in health care service provision at a reasonable cost to the administration and the economy (Al-Razouki, 2019). The administration funded around 86% of the national medical spending in 2014 as per the World Bank. It is one of the largest levels of inclusion in the GCC in which the basic is almost 79%, against comparison to the G20, in that the basic is around 61% (Awad et al., 2017). The public industry offers more than 80% of beds in hospitals, manages more than thirty hospitals that include some 9000 beds, as well as many clinics. This big public industry responsibility is despite the matter that the core concentration of free administrative medical care is 30% of the country's four million people who are nationals. Kuwait citizens get health care despite charges in public hospitals, and health care overseas if the services are not existing locally (Awad et al., 2017).

Figure 1: Health care report in Kuwait
(Source: Al-Razouki, 2019)
The country has dynamic development in the numbers of healthcare workers and increased the health industry capital cost since the independence, however, this industry development has suffered in the past 20 years (Al-Razouki, 2019). Certainty, in the previous 10 years of preparation and investment in the health care industry in the country, it has been identified that this industry has not developed importantly in terms of access and quality services. The challenge of diseases in the country remains shockingly higher, with some of the high levels of diabetes and obesity rates around the globe. It would have ripple impacts on Kuwait's medical system that provides the New Kuwait Vision 2035, which is only currently starting to reach the population demands in stride.
2.2 Start-up company growth in Kuwait Healthcare sector
Around the medical care industry, infrastructure projects valued over KD1.5bn (around $5bn) are under process in the country. The administrative body is the biggest service providers, recently outlining almost 90% of the entire marketplace in the context of hospital bed numbers as well as medical services with the country is operating as per to the national planning for adopting the WHO's proposal of allotting around 22 beds in hospitals for every 10,000 individuals by 2030, as per to the MoH (Ministry of Health) (oxfordbusinessgroup.com, 2021). This specific process for medical facility development and opportunities for start-up companies in this sector that is concentrated on adding more beds has been the outcome of a large-level construction increase (Darawsheh and Germeni, 2019).
Along with the requirement to offer fundamental care for all people and citizens, focussed works through the administration to offer excellence facilities are also assumed to increase the start-up market demands for specialty treatments and lifestyle medical centers covering the health care customers searching higher quality out-patient and in-patient services (oxfordbusinessgroup.com, 2021).
Among the major player of these private hospitals in Kuwait are New Mowasat, around 100-bed facilities that is publicly accounted on Al Seef Hospital, and Boursa Kuwait; a 120-bed general hospital with the concentration on child care and maternity health facilities that develops part of the local organization UMS (United Medical Services), one of the biggest operators on the Kuwait private health care industry (expat.com, 2020). The United Medical Services has completed work on a global hospital in 2019 with the 140-bed general hospital that offers a wider level of expert treatments. The company and sector planning, as well as regulation for small and medium businesses, are constantly developing in the country. Various important parts for an effective and sustainable eco-system and knowledge are being made. Developing private and public subsidy foundations, incubators, good management and leadership in business, influences and marketplace know-how are also important facts for start-up businesses (expat.com, 2020).
2.3 Issues faced by start-up companies in the Healthcare sector in Kuwait
Coronary ailment and stroke are the top explanations behind death in Kuwait. In both 2007 and 2017, coronary disease and stroke were situated as the first and second most ordinary purposes behind death (ccwa.org, 2016). In 2016, cardiovascular diseases were obligated for 41% of passing, and threatening development was responsible for 15% (ccwa.org, 2016). The country’s residents battle with corpulence. Around 33% of guys and 44% of females beyond 18 years old are fat. A similar report additionally shows that 26% of guys and 20% of females matured 10-19 are large (ccwa.org, 2016).
All Kuwait individuals are qualified with the assumption for free clinical benefits and clinical treatment at government workplaces. Regardless, a couple of organizations, for instance, X-radiates and focused tests, are not free (oxfordbusinessgroup.com, 2019). These organizations commonly come at basic additional cost and many are not offered at government workplaces. Therefore, patients need to go to the private region or, in over-the-top cases, go to North America and Europe (oxfordbusinessgroup.com, 2019). Waiting for the medicines in the medical services associations could be long. The keep it together time is so long for the public territory, which those searching for ensured clinical thought consistently go to the private region.To intensify the circumstance, Kuwaiti crisis facilities are under-accommodating their creating people (apnews.com, 2020). Beginning in 2016, Kuwait had two centre beds for each thousand. The Office of Wellbeing dispatched projects expanding clinical centres and adding essential supplies like beds, working rooms, and offices. The Kuwaiti government expects to meet its destinations by 2030 (apnews.com, 2020).
As of now, the innovative work (Research and Development) use in the territory of Kuwait is far underneath the worldwide guidelines that have been appeared to prompt advancement and the ensuing improvement of an information-based economy (Kelendaret al., 2020). Development of the powerless and unstructured existing R&D mechanical assembly in the State of Kuwait is among the most pressing difficulties confronting the country as these endeavors toward the advancement of an information-based economy (Salman et al., 2020). Creating well-being research limits in Kuwait could fundamentally contribute toward improving general well-being, well-being advancement, sickness avoidance and therapy, and by and large human government assistance.
2.4 Kuwait Hospital eco-system
The Kuwait healthcare industry has projected an effective increase from 2021 to 2017 however, compared to the emerging populace of Kuwait and creating tension on the public clinical offices, the business actually needs to underline the requests (news.kuwaittimes.net, 2021). The utilization of cross-country protection strategy and the inspiration offered by the public authority for privately owned businesses in settings of motivators has delayed help with the incrementation of the medical services area in this country. The medical services industry has been significantly ruled through the privately owned businesses with regards to incomes, then again, in regard of the quantity of individuals, and the quantity of emergency clinics in the business is overwhelmed through the public business (news.kuwaittimes.net, 2021). This sort of inverse condition presents as there is a generous divergence among the fundamental bill size of public and start-up emergency clinics.The government is thinking about concocting a cap on the costs energized through start medical clinics, however, this is far-fetched that such a cap would come nearby as the enrolment just as setting up cost of any medical clinic is itself expensive in Kuwait (gulfbusiness.com, 2021).
Problems in the health delivery process are to minimize the waiting list for people due to higher patient loads and overextension of medical employees. Other problems involve managing a structural evaluation of qualities and services delivered through the primary care services, hospitals, and expert clinics at a regular gap; the referral as well as following-up process that is coupled with the new technology linkages among secondary, tertiary, and primary care levels (gulfbusiness.com, 2021). Development and training of health workers and volunteers with an increase of home-based and society-based interventions are also affecting due to the problems. The drugstores at the primary care level supply all the needed medicines for treating people. This interplay among specific social qualities in Kuwait and the medical system has made a series of inconsistencies that should be underlined if they are to be controlled with, an important step for improving the qualities of medical care in the country (richasharma.atavist.com, 2021).
The major private care centers in Kuwait are Royal Hayat Hospital, Dar Al Shifa, Al Seef Hospital, Al Salam International Hospital, and New Mowasat Hospital (richasharma.atavist.com, 2021). More private medical facilities are likely to be developed in the future. The reformation or development in the fee of medical facilities and care for expatriates in the public sector, launch of the nation-wide medical insurance policies, and the developing involvement of private start-ups in this industry have been the core facts driving the increase in the country's healthcare market (richasharma.atavist.com, 2021).
2.5 Major public healthcare company roles in this sector
The public industry offers around 80 percent of hospital beds capability, managers, more than thirty service centers that include around 9000 beds, and different clinics. This leading public industry responsibility is even though the matter that the key concentration of free administrative medical care is around 30 percent of the county's four million citizens who are nationals (Alsabahet al., 2020). The country nationals accept care despite charges in public centers, and medical care internationally if the services are not existing domestically. Back in 2014, the administration spent around $1.5 billion on international treatments for around 11,000 nationals (AlAli, 2019). Comparing, expatriates, the lasting 70 percent of the people in the country should buy a subsidized medical insurance program from the government for accessing fundamental treatments at public medical centers during main hours of operations. Extra top-up medical insurance is voluntary and generally bought by high-income people or their staff so that they could neglect to wait time for care in public hospitals (Alsabahet al., 2019). The administrate has also developed Dhaman (the country's medical assurance organization), a government and private association, which would cover almost two million of Kuwait's 2.8 million expatriates.
This is an incorporated player and worker company; managing premiums, operating claims, as well as paying for, and offering medical care. This would create 3 secondary health care centers with 700 beds and fifteen primary medical services as reported in 2017. The administrate has already included some of the most significant actions anywhere in the GCC for advancing PPs, a crucial method for getting the private industry more included in the control, deliveries, and inclusion of medical care (ALFadhalah and Elamir, 2019). The challenges with the public industry being the core creator of the medical care system are that this develops the limited and longer time challenge on the investment. The country needs to invest capital and functioning prices and has higher unit expenses as of healthcare inflation. For moving away from the recent status in which the country plays an extreme responsibility is to have an effective duty for the private industry (Alsabahet al., 2020).
2.6 Interprofessional collaboration need in Kuwait health care sector
It has been found out from the healthcare market analysis that a co-operative practice is needed due to the developed chronic illness burden, the swiftly developing expenses of healthcare costs, the aging population, and the spread of urbane therapeutic modalities (Albassamet al., 2020). The provision of secure and efficient people cares requirements have been coupled with healthcare experts for collaborating effectively with clearly identified duties and accountabilities (Katoueet al., 2017). There is agreement that inter-professional co-operation works could increase the healthcare operations and people results. It is specifically significant in the co-operation relationship among doctors and pharmacists in Kuwait. The national pharmacists have been underlined as important parts of this type of co-operation practice modules due to the developing criticality of medical therapies, the expense of medication associated morbidities, and the developing expense of healthcare that underlines the requirement for efficient operating relationships among doctors and pharmacists for developing patient treatment (Albassamet al., 2020). It has been underlined that expert duties and acts of the pharmacist have interestingly modified globally in current times from the fundamental responsibilities of combination and supply of medicines to more patient-oriented care. The pharmaceutical system is a process philosophy in which druggists cooperate directly with other medical care experts and with the people to use medicines usage by recognizing, solving, and protecting medicine-based challenges (Azhar and Ibrahim, 2018). The process of medical pharmacy includes the philosophy of pharmaceutical care.
In the country, over half of the druggists work in the administrative industry involving hospitals, tertiary care, primary medical care, and secondary medical care hospitals and service outlets, medicinal services management, medication directive, medicinal stores management, and academe (Katoueet al., 2020). The application of medical drugstore practice in the administration health care scheme is incomplete to provision and drugstore direction (that is stock supervision, suppository guidelines, and record-keeping) with nominal scientific duties mainly in the infirmaries (Johnson and Carragher, 2018). These medical responsibilities offering medicine data, contributing to the increment of medicine records/ information, including in multidisciplinary people care rounds and managing drug care planning that depends majorly on separate efforts created through some encouraged druggists (Albassamet al., 2020). Developments in medical practice in the private sector drugstores are slower as well as lack far behind the developments to the medical practices in the administrative medical care facilities.
2.7 Approaches and issues impacting hospital bed occupancy and preparation
In the country, hospital bed capability is identified through the MOH. This approach for determining hospital bed capability is not very effective. Indeed, both the domestic level number of beds for around 100,000 people in every kind and the aimed bed occupation is a general process applied for defining hospital bed capabilities (Kelendaret al., 2020). Around 100% bed tenancy level would hardly ever be achieved. Various countries have dissimilar bed residency rates where they have a difference of company settings. This is worth mentioning that the incapacity of the medical care decisional committee to manage hospital functions effectively in a consolidative way would ensure the care more complex outcoming in wasting expensive resources, ineffective bed usage, and ineffective patient flow (Kelendar et al., 2020). It can be demonstrated through an overcrowded emergency unit, people mismanagements, surgery withdraws, and longer waiting time that can directly impact the medical care service qualities (Kelendar and Mohammed, 2019). This variation of bed capability needs is mostly due to the different patient lengths of staying and the unexpected patient demands.
The country’s HCS is recently confronting various unprecedented problems and important change needs (Kelendar and Mohammed, 2019). The government of Kuwait has been continuously vigilant regarding their HCS, trying to develop their service's effectiveness and operation ability. The country's government has created wide investments in the medical care system by creating hospitals and service centers (Kelendar and Mohammed, 2019). The country MOH is recently going through a systematic change in the context of entire bed capability. It has been found out that various big projects valued at around two billion KD are being developed in the country. On the other hand, in contrast to 2013; where the entire bed capability of the administrative industry was around 6663, this number of beds is assumed to develop to around 13474 in 2020 (El Ayyatet al., 2018). It suggests that the bed capability is assumed to be coupled through including 6772 beds. The required bed capability, their physical delivery, and directed rule for a fee are connected to the local or nation-wide tactics, not at an infirmary level (El Ayyatet al., 2018). Thus, before taking any steps, this is important that the public consultant evaluate their present conditions about the prior factors.
2.8 Kuwait healthcare future scope discussion
The future of the medical care sector in Kuwait outlines various opportunities in private and start-up companies, both in the long and medium-term levels. In the medium term, the previous time has shown an important increase in both the private and public cases that have been coupled up through the developing health care requirements of the people at large (Katoue, 2020). The occurrence of chronic illnesses and obesity are on the increase, placing pressure on medical care companies to efficiently and properly treating the developing number of people. Additionally, Kuwait administrative body's developing reliance to offer a developed series of operations in public and private hospitals is a part of its entire policy for making and offering more expert treatments in the nation, through minimizing the number of citizens going overseas for health care (Kelendaret al., 2020). These facts have made the effective combination for the country's medical care sector for flourishing in the previous time and would continue to do so in the times to come.
For instance, Dar Al Shifa Hospital offers an integrated, higher quality of care to its patients. This type of systematic way has effectively positioned the company as one of the medical care leaders in the country market (Salman et al., 2020). This private company is the initial hospital to achieve global accreditation in both the private and public industries, revaluating the aim to treatment quality as well as security. The consistent process in developing new services for helping the increase of chronic and preventive care requirements of the people has evident through over 25 experts recently present (Salman et al., 2020).
2.9 Dynamic performance management for Kuwait health care
While private and public collaborations are well developed in different countries and have been included in the planning of others, a question increases as to their efficiency level in developing access, as well as in maximizing qualities and efficacies (Alsabahet al., 2020). Some of these information and knowledge gaps are underlined in this context through outlying performance results attained as well as the comparative advantages of constricting out, community-oriented medical insurance, country health insurance and vouchers in Kuwait (Witter et al., 2020). A developing number of private-public collaborations have been applied in other countries. Although, there is a lack of collated pieces of evidence on this type of collaboration performance to assist selection among competing private and public partnership modules in Kuwait. Notwithstanding, various global instances on this type of partnership have documented the fact that there is a requirement for higher quality instances on which to base suggestions as well as it is offered by a strategic review of the evidence (Witter et al., 2020).
Because of the rising interest in and developing intricacy of medical services and because of the expanding utilization of innovations, the range of abilities needed by wellbeing laborers has changed (Alsabahet al., 2020). There is an increment in the requirement for "cross-over abilities"— relational abilities, for example, correspondence, cooperation, and receptiveness to consistent learning. A few endeavors exist to attempt to normalize performance estimation in other countries (Alsabahet al., 2020). Kuwait had figured out how to create medical care foundations and offices yet the capacity to support the great level is unsure. Indeed, grumblings in practically all emergency clinics in Kuwait are ascending because of long holding up occasions and absence of order (particularly in open medical clinics).
2.10 Human resource management in Kuwait health care sector
This has been found out that the application and usage of non-country employees would go on for many future years. There has been a "Kuwaitization" program that has been developed, which accounts for more than several years effective nation-wide doctors, pharmacists, and dentists would be provided with training for declining the dependence on international expert healthcare employees (Darawsheh and Germeni, 2019). Although, for the nursing area, the forecasts of training are accounted the fact that enough domestic nurses are not favorable. From this information, it could be said that human resource requirement evaluations, as well as needed proper training, have been undertaken in every unit and main medical facilities (Salman et al., 2020). The human resource system and department operations are irregular, as well as have not collaborated. There is a requirement for developing a systematically considered strategy, program, and planning for human resources for medical care. An inclusive HR process must also be planned for helping in the evaluation of HR needs, control processes, and production policies (Zaim et al., 2018). The planning, program, and HR activities for the medical system must be flexible as well as permit the entire involvement and active participation of various units to plan the training requirements of departments, health facilities with permitting for effective collaboration, and more price-efficient processes for increasing capabilities of the health employees.
Employee management training providers in the healthcare industry must be active partners in the HR for the medical system and must be able to synchronize their courses for benefiting the medical sector in Kuwait (Ahmed et al., 2019). The government and non-nationals have other ways and planning, which help the most disadvantaged expatriate employees, however, a non-governmental company, the Patient Support Fund in collaboration with the Ministry of Health. This is necessary for all the non-Kuwaitis to have medical coverage planning by the public or even private industry. Though and deliberation must be provided on evaluating the recent medical investment management in Kuwait for making sure the sustainability matter (Darawsheh and Germeni, 2019). The importance must be to fund more in the public medical surveillance process, creating a better public medical workforce, which could efficiently assist in redeveloping the medical system for addressing emerging medical safety threats, involving antimicrobial resistance as well as infections control in the current medical care system (Darawsheh and Germeni, 2019). An effective and development channel of public medical laboratories will be another step, which Kuwait can consider as significant for longer-term finds for medical infrastructure development.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
3.1 Introduction
The Research methodology is considered as one of the main processes of a research work where it concentrates on selection, identification, and processing of the information required for the research. This particular process is important because of its explanatory as well as constructive nature and these are one of the major helping hand for the researcher in order to control the entire research work. For this case, after analyzing the topic and different articles, it can be said that the Positivism philosophy, deductive approach, primary and secondary data collection could be beneficial for the research in order to extract the accurate result.
3.2 Research Philosophy
It can be said that research philosophy is the most important part of the entire research process and it solely involves conducting the research. The main function of the process is to engage in the various ways by which the data regarding the research can be gathered in a proper way. It also concentrates on the data interpretation, usage, and analysis of the collected data (Dougherty et al., 2019). Research philosophy happens in different ways such as positivism, pragmatism, realism, and interpretivism. From the analysis of the project and observing the entire research field and processes, it comes to conclude that the Positivism approach can be beneficial for the completion of the entire research work.
Positivism research philosophy is connected to the phenomenon of different natural processes and is also associated with the logical formulation of the data along with the functions of every taken approach. Moreover, it also follows the concept of factual data which has been deducted from reliable sources and practical observations. This philosophy made the research process more fluent as it helps the researchers to remain limited and these particular characteristics further assist the researchers to stick to the objectives and research questions formulated (Moon et al., 2019). This approach is also beneficial for the study as it follows the hypothesis and deduction according to the progress of the research, which has resulted from the statistical impacts of the startups of the healthcare sector of Kuwait.
On the other hand, the realism research process is another section of the research brunch where it concentrates on the science-based disclosure of reality. Interpretivism is related to common factors and in-depth research. Whereas, Pragmatism is related to the approaches of practical and logical responses. The main reason for choosing positivism for the research is because of the capability to gather quantitative data along with the freedom of values (Ryan, 2018). As it is concentrated on the ever-growing sector that is the healthcare sector, it is necessary for the researcher to stay flexible with the data in the time of conducting the research.
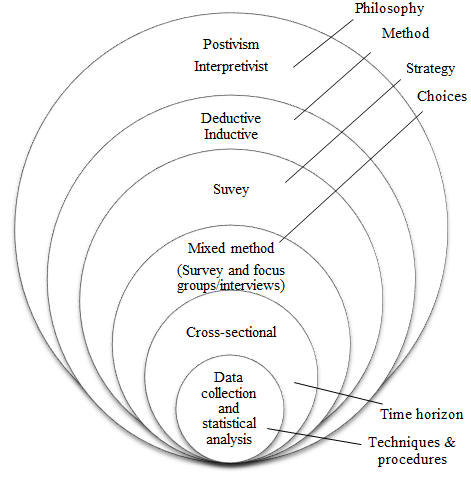
Figure: Research Philosophy
(Source: Nguyen et al., 2021)
3.3 Research Approach
The research approach is concentric on the construction of the plans and programs essential for the conduction of the research. It has a vast field of interest ranging from the huge assumption procedure to the specific techniques of the data gathering and analysis. It has been seen that research approaches can be categorized into three different segments and those are the Abductive approach, Inductive approach, and Deductive approach. The main differences among the three approaches are based on the presentation of the plans entirely. In the case of the deductive approach, the entire process of the plan is arranged from the generalized pattern to the specific way. On the other hand, the Inductive approach concentrates on the testing approach where the result has been generated through the conclusions (Alase, 2017). However, the remaining approach is the Abductive approach connected to the conclusions but it has been deducted from the interaction among the notions of generalized methods and particular dictums. With the help of the research approach, the researcher is capable of creating a proper hypothesis and in accordance with the research, it can facilitate the collection of information regarding this.
After analyzing the research aims and objectives, it has been seen that the deductive mode of approach is appropriate for the study and further it is also associated with the theories and practices used for the study. As it has the capability to identify the areas from generalized to a specific way, it can be highly beneficial for gathering the information related to the Kuwait Healthcare sectors. It is also useful in order to identify the appropriate theories that can be helpful for the startup businesses related to healthcare in Kuwait and its effects on the other industries and operation strategies (Van den Berg and Struwig, 2017). As it is specified to the specific data it is more effective in this kind of flexible case as the other two can work only after generating the conclusion. The deductive approach analyzes the entire data on the process and based on the result it concludes the accurate outcome. Whereas the other two processes have started their works after taking the conclusion.

Figure: Research Approach
(Source: Mohr et al., 2018)
3.4 Research Design
The proper methodological section of research lies in the construction of the research design. In this particular part, it has been seen that the framework is directly engaging with various variables so that the measurement of the field can be accurate. It is considered one of the most significant parts of the entire methodology section. The main and foremost function of research design is to identify the applicability of the research questions and find out the proper answer to the question with respect to the research topic. The research design concept can be classified into various types and some of the significant ones are Experiments, Descriptions, Meta-analysis, correlation, and reviews. Furthermore, integration of the independent variables along with research issues and experiments are also included in this section. In order to choose the exact design for a particular study, an understanding of the entire process along with the suitability is required (Abutabenjeh and Jaradat, 2018).
It has been seen that descriptive and experimental designs are popular among the researchers, however, in this case, the highlight is focused on the experimental research design. In the process of research, it can be seen that there are many advantages as well as disadvantages have come for selecting the design. The explanation characteristics can be the key for the researcher to tackle the issues that have been arisen in the process of research. As it has the capability of explaining the causes and effects of any condition, it further helps the researcher to fulfill the objectives by solving the issues at the same time. In addition to these factors, it is also seen that in the case of a broader process, the explanation side of the design helps the researchers to stick on track and manage the drawbacks that are part of the entire process (Rahi, 2017).
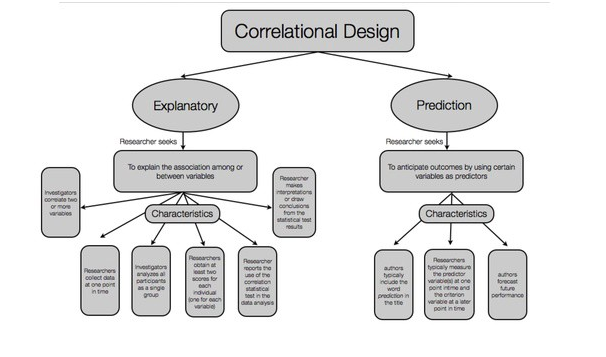
Figure: Research Design
(Source: Flynn et al., 2018)
3.5 Data Sources
In this section, the sources of the collected data have been discussed. As the process is containing both the primary and secondary processes, it is important to highlight the different sources so that they can be cleared to the audience. For the section of primary research, a survey has been conducted among the employees of the healthcare sector in Kuwait. The survey questions were related to demographic, occupational, and knowledge so that the answers can be calculated in a numeric way. On the other hand, the interview process has been conducted among the managers of the healthcare startups in Kuwait. The questions were open-ended so that data can be gathered in a descriptive way. Moreover, the secondary data have been collected through the already published journals and articles. These secondary resources and information will be used in the literature review, data interpretation as well as the development of the hypotheses (McNichols and Stubben, 2018).
3.6 Data Collection Methods
This section represents the various methods of the data collection process for establishing the results from the research. It has been seen that there are two broad categories of the data collection methods as Primary data collection and Secondary data collection method. The choice of the data collection pattern is highly dependent on the type of the research and the situation of the environment (Al-Qurabat and Idrees, 2018). Primary data represent the real-time data where the team of researchers has engaged directly with the population to gather the real-time data. On the other hand, the secondary data analysis represents the analysis of the already published data and creates and co-relation with the present one.
In this case, after reviewing the entire literature review part, it has been concluded that both the primary and secondary data can be essential for the study. In the primary section, the researcher has conducted the real-time interaction with the population so that the experience and thoughts of the people can be collected in an accurate way. On the other hand, the addition of secondary research can have additional benefits as it can help the researcher to gather the data from the different published journals and articles and helps in comparing the data with the qualitative managerial interviews as well (Iwata et al., 2018). It has various benefits as the comparison of the data can assist the research to stays on track and also helps in understanding the changes that have been seen with the time in the healthcare sector of Kuwait.
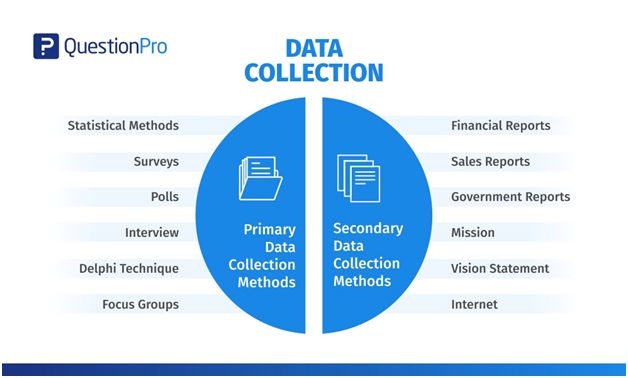
Figure: Data Collection Methods
(Source: Jentoft and Olsen, 2019)
3.7 Data Analysis Methods
Data analysis is the next stage of the data collection process. It can be different according to the type of data collection. In the case of primary data collection, it can further analyzed through the quantitative and qualitative way. In case of quantitative data analysis, some closed-ended question has been asked to a group of people and on the basis of their answer result can be created in numeric format. On the other hand, in qualitative data analysis, some set of open-ended questions have been asked to some people so that quality information can be gathered (Johnston, 2017). In this case, SPSS has been used in order to carry out the data analysis for generating precise and reliable quantitative resultsalongside qualitative interviews are also conducted to gather a broader viewpoint of the topic.
For this study, it has been seen that both quantitative and qualitative studies can be applied for better results. For the section of the self-administered survey process, the questionnaires have been formulated depending upon the hypothesis and research questions. The responses of the candidates were then calculated and measured for finding the connection between theory and hypotheses in this study.On the other hand, the qualitative interview process has been conducted among the few candidates who are in the top position of the sector for better information. In this case, the questions are related to the open-ended so that the candidates can express their thoughts without hesitations. The questions were related to the startup section of the company like job availability, different public-private sectors, operations, and customer demands (Mansoret al., 2017).
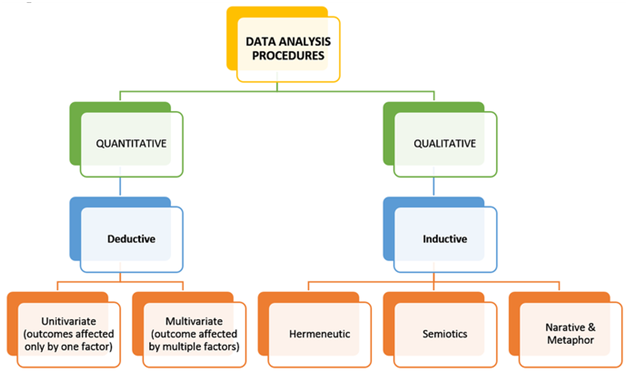
Figure: Data Analysis Method
(Source: Peredericet al., 2018)
3.8 Data Interpretation
Data interpretation is a process where the collected data are reviewed and process according to the need of the result to conclude the result. It is not only assigned the information rather determines the significance of the data towards research and implications. In case of qualitative data interpretation, observation, documentation, and interviews are taken in charge. Observations identify the quality of the information by the body language and speaking pattern of the candidate.
Documentations are important to save the pattern of the information that has been collected through the observations. Lastly, the interview is the best way to interpret the data. With this process, the data interpretation can be smoothened as it contains everything that is required for the interpretation (Battelinoet al., 2019).
On the other hand, quantitative analysis can be interpreted with the help of different processes like calculating mean, standard deviation, and frequency distribution. Mean can help in identifying the average of the data that has been collected. Lastly, frequency distribution can help in gauging the rate of responses in the collected data set. The survey identifies the specific ordinal scale responses that appeared (Peters et al., 2019).
3.9 Sampling Technique
Sampling is a crucial tool in a research process that has helped the researchers to identify the population so that it can extract accurate data from it. The application of the probability sampling method has been used in this particular research process. In this process, the researcher has selected the samples from the vast population through the application of the probability theory (Ijaz et al., 2018). The selection of the members is restricted to the fixed procedure. In this process, it has been seen that 500 members have been identified from the entire population for the survey process, whereas, 100 members have been selected from the population for the survey and 5 managers for the interview process.
Figure: Sampling Technique
(Source: Sharma, 2017)
3.10 Sample Size
The sample size is the key by which the research can get the informatics and numerical data. In the process of sampling, the research has selected some of the members from the population. For the purpose of the quantitative approach that is surveyed, 50 employees from the 500 members of the identified population have been selected. These 50 people have been participating in the survey process only in order to gather the mass numerical data. On the other hand, for the sake of the interview process, 5 managers have been selected among the 15 identified members from the population. The main reason for the selection of the people among the population is for extracting the accurate result.
3.11 Research Limitation
During the management of the entire study, it has been seen that there are several loopholes in the entire process. The first thing that has been seen in the process is the lack of proper engagement of the primary research process. As the pandemic has taken control all over the world, the research process has faced different obstacles during arranging the process. In the case of an interview, the face-to-face interview session cannot be organized which makes the process of observing critical for the researcher. Furthermore, in the case of the survey process, a similar reason created many gaps in maintaining the process. On the other hand, the secondary research process showed much more complications. As it is less valuable than the primary research, due to the pandemic situation, the research had to be concentric on the secondary process. In that case, the researcher has faced different complications. As the healthcare start-ups in Kuwait are ever-changing and ever-growing, the collected secondary values were not accurate as expected. Moreover, it has been seen that the research process has used the explanatory type of research design and this design has been performing well. However, the application of the experimental research design can have opened many more dimensions to the research as the entire topic of healthcare start-ups in Kuwait is ever-growing. The use of both research designs could generate a more accurate result with future probable information.
3.12 Ethical Consideration
Ethical considerations are one of the crucial parts of performing the research process. In order to maintain the entire research process, the researcher has to be looked upon the ethics related to the research topic. The ethical considerations in context to the present research were prevention of harm to the respondents in any form and respecting the dignity of the participants. Additionally, emphasis has been given to obtain full consent from the respondents as well as ensuring the protection of privacy. The main ethical considerations that have been followed by the researcher are no data violation as well as maintaining the confidential data. When the research follows the path of secondary research, it is important to focus on the interpretation of the data as the violation of the data can be destructive for the study as well as for the researcher (Arifin, 2018). On the other hand, managing confidentiality is important for the primary research process and it has been seen that this particular step has been maintained properly.
It has also been seen that the taken sources are also being credited through the entire research process and management of the data has been formulated properly. Every journal and article that has been used was authentic and was published on reputed sites. Extraction of the information is also taken a good glance so that the quality of the research can be maintained. In the primary research process, every particular data has been taken as confidential where the personal information of the participants is not exposed out. The collected data from the primary research has been taken accurately and did not entertain any kinds of manipulations. The main objective of the primary research was to make the intact information for the research.
Chapter 4: Data Analysis
4.1 Quantitative data analysis
Q1
|
What_is_your_gender |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Male |
26 |
52.0 |
52.0 |
52.0 |
|
Female |
24 |
48.0 |
48.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
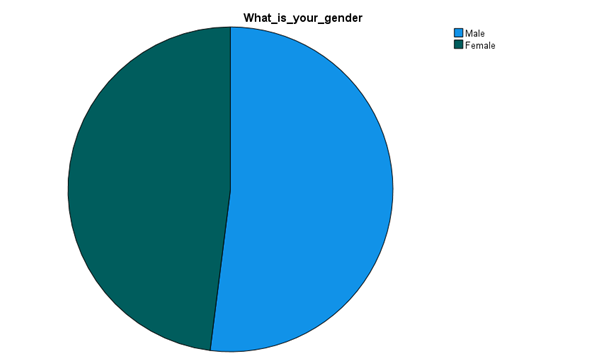
Analysis:
From the above data collection, it has been understood that in the Kuwait health care sector; major employees are male. It has been identified that around 52.0 percent of people are male and 48.0 percent of respondents are female. From the above data collection, it can be understood that the health care sector employability gap between female and male workers is not huge. This indicates and proves the fact that the government of Kuwait is thus considering alternative processes to motivate employees, reduce costs and develop diversity. This type of result has a link with the huge demand for private health care workers also.
Q2
|
Period_of_working_in_the_industry |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Less than 2 years |
16 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
32.0 |
|
2-5 years |
25 |
50.0 |
50.0 |
82.0 |
|
|
Above 5 years |
9 |
18.0 |
18.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
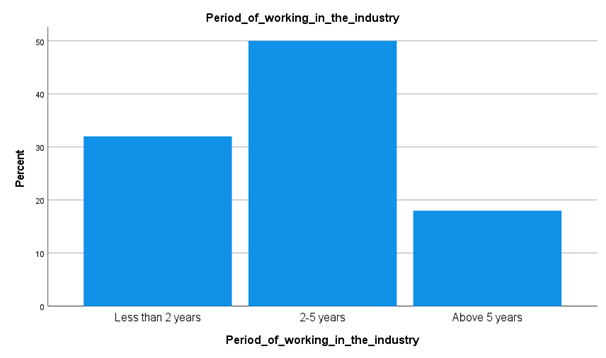
Analysis
From the above data collection, it has been understood that most of the respondents working in this industry for between two to five years. From the total number of respondents surveyed; it has been understood that 50 percent of the workers are employed for 2 or more than 2 years but less than 6 years. On the other hand, the next major category of workers covering around 32 percent of the total number surveyed. This category of workers has been employed in this sector for less than 2 years. The more experienced workers responded accounted for 18 percent, which is triggering the fact that highly experienced workers are low in this industry.
Q3
|
Increment_in_competition_of_Kuwait_health_sector |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
44 |
88.0 |
88.0 |
88.0 |
|
No |
1 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
90.0 |
|
|
Neutral |
5 |
10.0 |
10.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
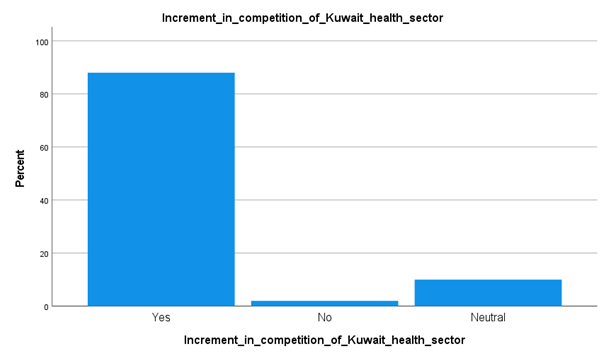
Analysis
From the above data collection results, it has been understood that around the total number of the respondents, around 44 percent of the candidates have stated that the competition of private start-ups in Kuwait has been increased before. It can be stated that the country’s healthcare industry is in transition, with developing signs of private industry involvement despite administration dominance related to the matters such as funds and provision of care. If the country is to make sure the continuous provision of quality care this will require a policy to further advertise the responsibility of the private industry in this sector provision at a reasonable cost to the economy and administration.
Q4
|
Company_performing_mini_audits_on_recent_channels |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
29 |
58.0 |
58.0 |
58.0 |
|
No |
3 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
64.0 |
|
|
Maybe |
18 |
36.0 |
36.0 |
10.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
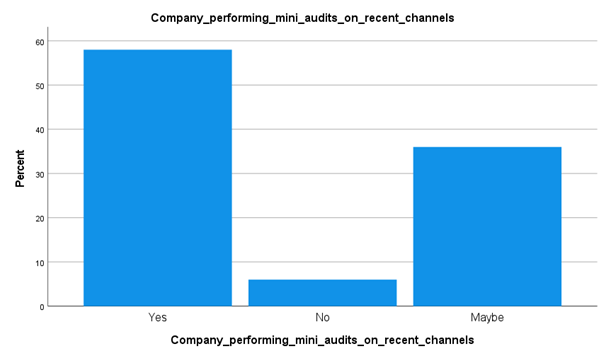
Analysis
The above-collected data and graph, have pointed out that many companies are focusing on doing mini audits on the healthcare delivery process. Around 58% of the respondents have stated yes and 36% have stayed in-between positions while answering this question. This type of data has outlined the fact that While internal and mini audits operations at the Kuwait healthcare providers are focusing on a future generation functioning process, more development is still required to attain an optimal level. The public and private healthcare providers in Kuwait are developing-both in the way of care they offer and their functions to their consumers.
Q5
|
High_competition_between_public_healthcare_organizations |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
40 |
80.0 |
80.0 |
80.0 |
|
No |
3 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
86.0 |
|
|
Maybe |
7 |
14.0 |
14.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
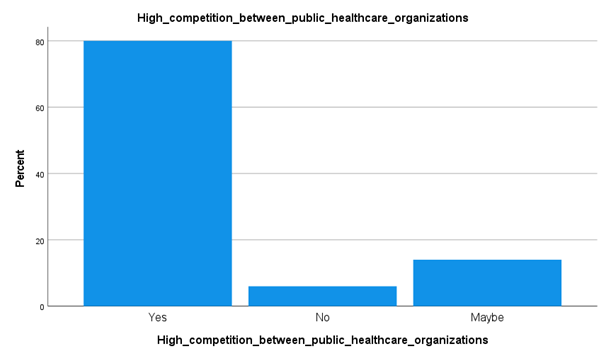
Analysis
The collected data listed in the graph above, outlining the fact that high competition among private healthcare organizations exists in Kuwait. Around 80% of the total number of respondents have stated the fact. It can be said that most of the hospitals in this country are controlled by MoH. Although, currently, in the context of revenue the private industry has been dominating the market in the country, owing to the excessive price of private health care in Kuwait. This is one of the prime reasons that the public sector is thriving to develop their operations and facilities delivered. Thus, developing the competition level.
Q6
|
Possible_reasons_for_startup_health_centres_in_Kuwait |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
People are demanding more advanced care |
23 |
46.0 |
46.0 |
46.0 |
|
Lack of public infrastructure |
11 |
22.0 |
22.0 |
68.0 |
|
|
Swift treatments of patients |
9 |
18.0 |
18.0 |
86.0 |
|
|
Technical development |
7 |
14.0 |
14.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
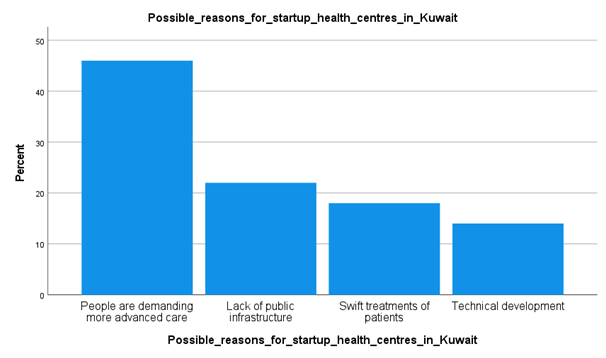
Analysis
From the above survey data, it has been identified that around 46 percent of the respondents have addressed that patients' demands for more advanced care are one of the major reasons for the increase of private health care organizations in Kuwait. On the other hand, it has been understood that the lack of proper infrastructure in the public healthcare sector is the second-highest reason for start-up development in this industry. Around 11 percent of the candidates have pointed to this option. These are focusing on the fact that the public sector of hospitals needs to develop their healthcare qualities and reduce patient waiting time with a limited number of patients return to their facilities. Additionally, the government should focus on developing investment in case of developing technological compatibilities, skillful workers, and others in public hospitals.
Q7
|
Governmental_help_in_growth_of_public_healthcare_organizations |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
33 |
66.0 |
66.0 |
66.0 |
|
No |
3 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
72.0 |
|
|
Maybe |
14 |
28.0 |
28.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
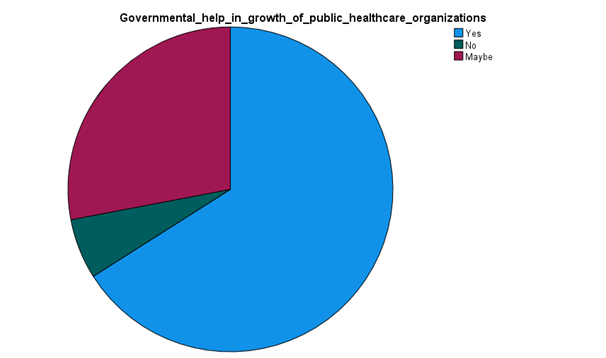
Analysis
From the above-collected data and development graph based on the respondents, it has been understood that the government in Kuwait is concentrating on developing public healthcare infrastructure. Around 66% of the total number of respondents surveyed have stated this fact. It can be said that MoH is concentrating on developing private and public participation for better medical facilities and hospital infrastructure in this country. It could be said that bed density level is still low compared to the developed countries around the world, however, developing. The demand and supply imbalance should be minimized by the government to reduce healthcare cost levels.
Q8
|
Possible_causes_for_people_visiting_private_hospitals |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
More advanced treatments |
19 |
38.0 |
38.0 |
38.0 |
|
Customized care units |
19 |
38.0 |
38.0 |
76.0 |
|
|
Low time for waiting |
12 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
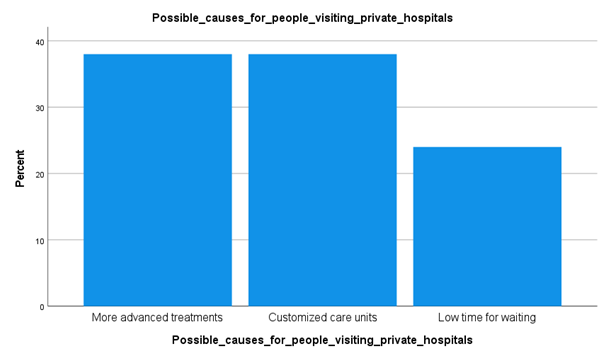
Analysis
From the results and data collected in the survey, it has been understood that more advanced treatments and customized care units are one of the two main reasons that are influencing patients to cue in the private hospitals. Around 38% of the total number of candidates surveyed have pointed to these facts. From this type of data collection, it can be understood that the private sector hospitals are running low or lack hospital services and healthcare professionals.
Q9
|
Companies_effectiveness_in_emergency_care_unit_operations |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
45 |
90.0 |
90.0 |
90.0 |
|
No |
1 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
92.0 |
|
|
Maybe |
4 |
8.0 |
8.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
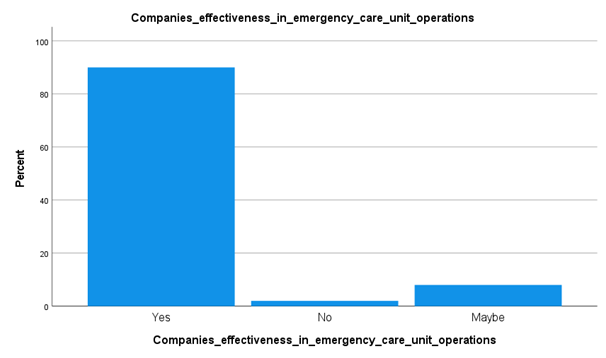
Analysis
From the above data collected, it has been understood that around 90 percent of the candidates surveyed have stated that their companies are good in the emergency care unit. From this type of data, it has been understood that the government in Kuwait is concerned with patients and employees, medical experts working in the emergency unit care satisfaction level. This is significant in Kuwait's healthcare sector and applied as an indicator in evaluating the quality of facilities and care delivery in the ER unit. On the other hand, from the data collected, it has also been understood that a lower level of patient satisfaction can be associated with waiting time and time involved with the experts along with the waiting area in the public sector.
Q10
|
Companies_in_providing_efficient_patient_care_promotions |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
26 |
52.0 |
52.0 |
52.0 |
|
No |
24 |
48.0 |
48.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
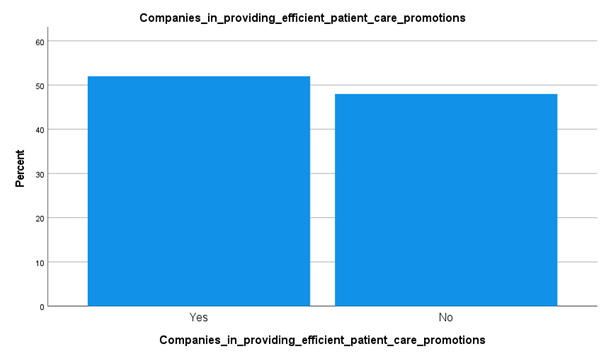
Analysis
From the above data collected and graph representation, it has been understood that in Kuwait the health care promotions for patients have been increased from the past. This is as around 52% of the total respondents have pointed to this fact. Around 48% of the total respondents have stated that their companies are well organized or govern for providing patient care promotions. This type of data collection is pointing to the fact that the government is planning to develop participation of SEM as a planning model for building sustainable health care promotions in the country. The Socio-Ecological Model is effective in developing studies in health-related promotions for various concerning health-related factors in the Kuwait population.
Q11
|
Companies_effectiveness_in_employee_management |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
22 |
44.0 |
44.0 |
44.0 |
|
No |
28 |
56.0 |
56.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
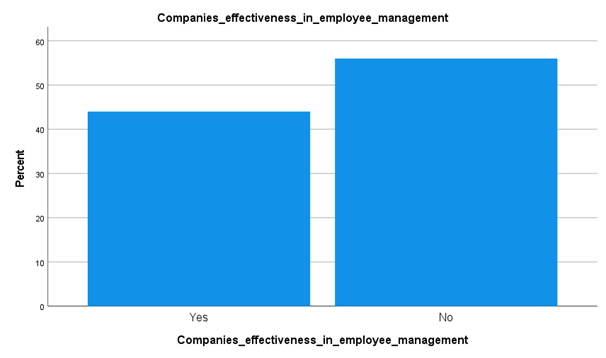
Analysis
From the above data collection and results achieved from the survey, it has been understood that around 56% of the candidates have stated that their companies are not effective in employee management. This is outlined that employee turnover levels are higher around medical staff and nurses working in Kuwait hospitals. This is one of the main challenges, expensive and this is assumed to influence the quality of medical and nursing care provided in this sector. This is triggering the fact that government and private healthcare companies are incompetent in providing good employee management results and staff sustaining results in the hospitals around the country.
Q12
|
Company_providing_updated_innovative_treatments |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
41 |
82.0 |
82.0 |
82.0 |
|
Maybe |
9 |
18.0 |
18.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
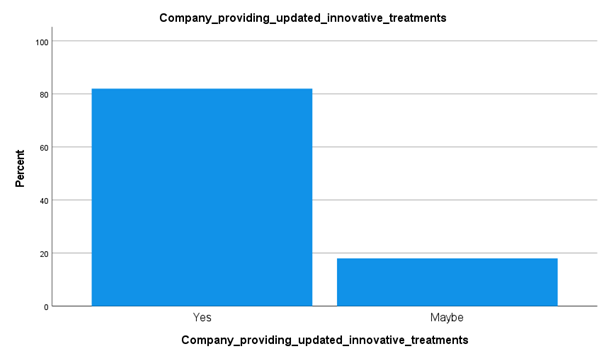
Analysis
The collected data from the survey has pointed out the fact that modified innovative treatments in their hospitals are continued to be stable. Around 82% of the staff has pointed to this fact. This result is pointing to the fact that the government currently ensuring effectiveness on the "triple target" of developing the quality of patient care, developing population medical results, and curtailing health expenses needs. These are connected with the optimal development of the private care sector.
Q13.
|
Current_organization_efficacy_in_managing_rush_hours |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Yes |
25 |
50.0 |
50.0 |
50.0 |
|
No |
25 |
50.0 |
50.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
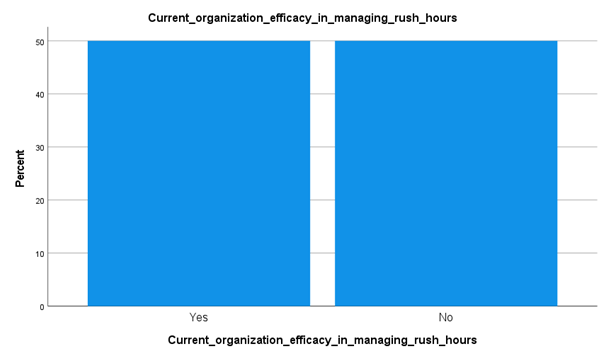
Analysis
From the above data collected and graph developed, it has been understood that managing rush hours in the hospitals are gradually developing. Around 50 percent of the candidates have stated yes and half of the candidates have said No. This is targeting the fact that public healthcare organizations are not good at managing the rush hours. It is underlying the fact that hospitals are not good at managing the patient waiting time and time of treatment delivery time. This is also suggesting the fact that private hospitals are lacking in managing internal medical and developed treatment facilities.
Q14
|
Effcicacy_of_patient_waiting_outdoor_treatment_services |
|||||
|
|
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
|
Valid |
Satisfactory |
32 |
64.0 |
64.0 |
64.0 |
|
Not satisfactory |
3 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
70.0 |
|
|
Extremely long |
12 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
94.0 |
|
|
Mismanaged outdoor treatment |
3 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
|
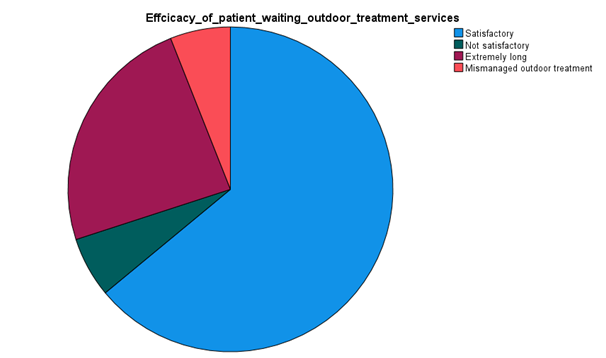
Analysis
From the above data collection and graph represented, it has been understood that outdoor treatment services were satisfied in the hospitals. Around 32 percent of the total candidates surveyed have pointed to this level. It is pointing to the fact that there is the scope of developing the outdoor patient service quality in the private hospitals in the Kuwait healthcare sector. This is also pointing to the fact that there is a need for proper resource management, technology inclusion in medical care providing and effective hospital administration works in the public sector industry.
4.2 Qualitative analysis
From the interview results including five managers in the health care industry of Kuwait, responses and their discussions are listed below;
1. What are the current governmental interventions for private and public collaboration efforts in the healthcare sector
According to the first manager, the government is trying to develop the public care facilities gradually instead of fully collaborating with the private sector health care in the country. Kuwait government and the Ministry of Health shifted the economic risks and care provision duties of more than 100,000 Kuwait retirees away from the plan. This attained this through putting the people in a country-funded private health insurance planning, which permits them to get fundamental healthcare operations in private hospitals. The government will pay the premia as well as the private insurer will bear all the challenges. Corresponding to this response, the second manager has outlined that the government is trying to offer extra capability in the context of hospital beds by increasing the current number to 18000. The country requires doubled up the bed count as its population is increasing and aging. The trouble with the public area being the principal manufacturer of medical care foundation is that it builds the short-and long-haul trouble on the financial plan. The state needs to finance the capital and working expenses and has high unit costs due to clinical expansion.
As per the third manager’s response, it has been outlined that for moving away from the recent challenges in the public healthcare sector in which the country acts an excessive responsibility is to have an effective duty for the private industry. It is the most ideal approach to manage rising interest, financial requirements, and the need to control medical services costs. There are 3 ways and 3 empowering influences that the administration ought to remember for its wellbeing area designs that could diminish the expense to the state and improve quality.
As per the fourth manager, the Kuwait administration should ensure public healthcare organizations more effective as well as have them effective for more private industry inclusion through turning them into state-owned organizations. It includes dividing public hospitals from the Ministry of Health. The public authority should then change over these emergency clinics into state-claimed companies with autonomous administration and accountabilities. It would develop their functional effectiveness and root the seeds for future private industry involvement. It has already proceeded in the UAE with the SEHA (Abu Dhabi Health Services Company).
The fifth manager’s responses have pointed that the government could evaluate how effectively the private industry is performing in specific test results, for instance, the longer-term acute care, home care, and rehabilitation. Private healthcare can be allowed the chance to show that it can serve the interest in a savvier way than the public area and that it can step in with administrations that the public authority would not like to manage. Carried out effectively, expanded private area investment can encourage more prominent admittance to medical care, improve its quality, and cut expense, for example, by diminishing the requirement for outbound clinical the travel industry. The outcome could be more competitive around healthcare organizations (whether private or public), processing to more effectiveness, developed control, and so low functional expenses. The application of investment could become more effective as well as the private industry could finances development, saving the administration costs. By ensuring the funding of medical services more moderate, Kuwait will want to follow through on its social obligation to give widespread medical services.
2. What are the reasons for customers visiting more individual or private hospitals despite more costs
The first manager has communicated certain triggering or challenging matters that the public healthcare sector in Kuwait is facing and that is directly influencing the patients' perception of the care facilities the public organizations are capable of. These matters are of the hospital is to offer effective care as well as treatment of its consumers. This principal item is medical facilities, surgical and nursing operations to the consumers and its core concern is the life and health of the consumers. This has been seen that public hospitals are facing challenges in lack of medical experts and nursing voluntary turnover rates. Stressing to these points, the second manager has pointed out that incapability in managing the rush hours is also one of the reasons why patients are truing to the private hospitals despite more costs. On the other hand, the third manager has corresponded that lack of custom care units and lack of technological modifications in the Kuwait public health care sector is also a major point of poor patient incoming and bed occupancy rates.
According to the fourth manager, it has been pointed out that in Kuwait currently, the majority of the patients have the thought that private hospitals will offer higher quality treatments compared to the public hospitals. It has been found out that medical practitioners, doctors have the faith that this is the developed equipment applied, which sets them separated from the public hospitals. Additionally, the market is projecting that low mortality could be one of the factors, though, doctors trust consumers’ care is the differentiating factor. As per the 5th manager, it has been understood that Private care also offers more facilities and space for consumers, with lower restrictions compared to public care centers in Kuwait, depending on clinical requirements. To assist in making the stay as comfortable as possible, various private care centers also offer additional operations like laundry facilities, beauty treatment, and others.
3. How the current start-ups in the Kuwait health sector are impacting the facilities and services of public hospitals
According to the 1st manager, it has been pointed out that the Private sector healthcare industry is contributing more than the public healthcare hospitals. It has been found out that the private sector is owning to the exorbitant expense in Kuwait. On the other hand, the second manager has communicated that the sluggish-paced development of the blossoming private medical care area is driven by new clinical focuses, each hoping to solidify their own corrective or outpatient specialty. According to the third manager, Clinical centers in Kuwait focuses are in accordance with patient longings and a couple even present quality and accreditation not found in the public area.
On the other side, the 4th manager has stated that private patient health facts outline a deeply required technical modification in the country, as out-dated paper filing processes are still in process in public hospitals. Additionally, the 5th manager expressed that the hybrid medical care processes will help in curbing administrative expenses in near future. Hybrid medical care frameworks empower patients to look for medical care however pay an expense for quicker, better help. If Kuwait is to understand the 2035 New Kuwait Vision, half-breed medical services and digitized frameworks should turn into the new typical.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1 Conclusion
In the above conversation on Kuwait's medical care framework and start-up in the current medical services industry, it has been perceived that the Kuwait emergency clinic market is accepted to increment at a powerful speed and a place of CAGR from 2018-2022. The nation is considered as a higher-pay class country just as the requests for a better-quality agreeable stay at clinics are additionally creating among the nation's citizens. The country's public area market is probably going to confront extra of different emergency clinics later on 5 years, with a blend of openly and exclusive consideration communities. Then again, it has been illustrated that strength care homes for Paediatrics and Maternity, consistent irresistible cases, and related drugs including school wellbeing activities and dentistry are likely to begin later on. The quantity of existed medical clinic beds in open clinics is likewise presumably to increment critically with the expansion in the quantity of medical clinics.
This examination has cantered that income gathered from the private business medical clinics would keep on expanding the market in the country as private contribution is accepted to create as is the cost of private medical care. This is accepted that later on 5 years, a progression of normal clinics would come put in the nation.Albeit, attributable to the expanding cases and necessity for master tertiary just as quaternary clinics, the arrangement of master medical clinics would be more rather than public general consideration habitats. This is normal that by 2022, the income gathered from outpatients would be more than the income from the inpatients because of the normal expansion in the quantity of outpatients looking for private consideration.
This paper has pointed that as per the Ministry of Health, the private area will be instrumental in the general advancement of the clinical area. The private medical services market is assessed to develop by 15-20% in the coming years. Right now, a sum of 12 private clinics (adding up to 1,038 emergency clinic beds) offers private clinical types of assistance in Kuwait. A few new private emergency clinics are relied upon to open in the following not many years, adding 1,800 emergency clinic beds. Albeit the public authority offers free medical care administrations, patients will pay a charge for private therapy to lessen holding up occasions and therapy plans. Discussions have pointed that the medical services area is seeing some change activities. One of the changes incorporates expanding public-private associations and giving the private area a bigger job in the arrangement of medical care administrations.
The analysis also says that the Kuwait health care start-ups have facilitated the management aspects of the industry directly or indirectly. Management has become mandatory for the hospitals for tackling peculiar issues regarding resource management, HR management for tackling peculiar issues regarding resource management, HR management, wealth management, pathological waste management, patient guidance, specialized management of specific illnesses, etc. Recently the government of Kuwait has invested a lot of wealth in establishing institutes to educate millions of students with the necessary management skill. These management aspects have provided a significant amount of business opportunities to the private players too. The discussion above also says that the health care industry is now running at its peak potential and most of the aspects are either already optimized or being optimized. Kuwait's health care industry now experiencing the need for advanced technologies, software solutions, and devices. The government as well as other private players have made some serious investments in the research and development departments of the health care industry. Beneficial partnerships among different organizations of the market that provides the tech, software solutions have made many development projects cost-effective and achievable. The health care industry is experiencing a huge need for medicines and chemicals too.
5.2 Recommendations
Through the analysis of the Kuwait health-care industry, it can be said that there are a lot of ways that can optimize the system. Though this system is progressing like never before, still many aspects are being ignored. The health care system of Kuwait should invest more in high-end as well as treatment for common people. The government, banks, hospitals should introduce affordable life insurances and medical claims for the person in need. Private players as well as small start-ups should come up with creative ideas to tackle this discrimination among people of different financial capabilities.
Government, as well as private hospitals, should be equipped with advanced devices as the rate of peculiar diseases has increased and diagnosis of them has become difficult. Despite the difficulties, there is a lack of several competent devices that can support the rapid diagnosis of the diseases. The management aspects of the health-care industry should be reviewed as it is essential and a great business opportunity for any start-up. An increment in managerial skills in various phases is expected. Management will not only make the industry strong and capable of handling any kind of risk but also it will create opportunities for practitioners, students, medical aspirants too. Hybrid medical processes should be considered for cutting a significant amount of investment regarding administrative actions. Government, as well as private players, can invest in establishing management institutions and as the demand, it will make more profits. The chemical and medicine production industry should not be ignored as health-care and medicine acts parallelly. Private players and government should invest in medicine production.
5.3 Limitation of this study
This study has investigated the current private healthcare sector upsurge in the Kuwait healthcare sector. The possible reasons for the development of start-ups and private sector participation in Kuwait healthcare sector have been documented. Though, this study has not included sufficient evaluation of what challenges private sector doctors, nurses and patients are facing and how that is affecting the overall healthcare system in the country. The quantitative study should have included both the negative and positive effects of increase of start-ups in Kuwait healthcare sector. This way, assessment of government interventions and condition of public healthcare centres would be more cleared.
5.4 Future scope of this study
Government Kuwait, as well as private firms, should give importance to the research and development department of the health-care. Research on the potential threats upon mankind should be praised. Research on cancer, the future potential of another pandemic, genetic disorders, etc, should be conducted. These research works are expensive and long-term processes but these projects have more prospects than any other business opportunities. Hence government, private players, start-ups should consider these investments carefully, they should be more open to new ideas of business. As cost-effective treatment of cancer and other genetic disorders will develop it will attract more domestic as well as international customers in Kuwait which will increase the opportunity to attract more foreign currencies. Government and private health-care providers should work as a team by forgetting all taxation and compensation for the good fare of Kuwait people.
References
2016.export.gov. 2019. Healthcare Resource Guide: Kuwait. [online] Available at:
Abutabenjeh, S. and Jaradat, R., 2018. Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36(3), pp.237-258.
Ahmed, Z., Saada, M., Jones, A.M. and Al-Hamid, A.M., 2019. Medical errors: Healthcare professionals’ perspective at a tertiary hospital in Kuwait. PloS one, 14(5), p.e0217023.
AlAli, M.S., 2019. Examining the Effect of Altman¡¯ s Zeta Model Score on the Share Price of Healthcare Companies Listed at Kuwait Stock Exchange. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 11(4), pp.25-29.
Alase, A., 2017. The interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA): A guide to a good qualitative research approach. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 5(2), pp.9-19.
Albassam, A., Almohammed, H., Alhujaili, M., Koshy, S. and Awad, A., 2020. Perspectives of primary care physicians and pharmacists on interprofessional collaboration in Kuwait: A quantitative study. PloS one, 15(7), p.e0236114.
ALFadhalah, T. and Elamir, H., 2019.Exploring leadership styles in government hospitals in Kuwait. Leadership in Health Services. Vol. 32 No. 3, pp. 458-476. https://doi.org/10.1108/LHS-11-2018-0059
Al-Qurabat, A.K.M. and Idrees, A.K., 2018. Energy-efficient adaptive distributed data collection method for periodic sensor networks. International Journal of Internet Technology and Secured Transactions, 8(3), pp.297-335.
Al-Razouki, D., 2019. Kuwait 2020 Health Report. [online] Medium. Available at:
Alsabah, A., Haghparast-Bidgoli, H. and Skordis, J., 2019.Measuring the Efficiency of Public Hospitals in Kuwait: A Two-Stage Data Envelopment Analysis and a Qualitative Survey Study. Available at SSRN 3416095.
Alsabah, A., Haghparast-Bidgoli, H. and Skordis, J., 2020. Comparing Public and Provider Preferences for Setting Healthcare Priorities: Evidence From Kuwait. Available at SSRN 3685721.
Alsabah, A.M., Haghparast-Bidgoli, H. and Skordis-Worrall, J., 2020.Hospital Managers’ Perceptions Regarding Setting Healthcare Priorities in Kuwait. Global Journal of Health Science, 12(10), pp.1-79.
AP NEWS. 2020. Kuwaiti Healthcare Sector Examination 2013-2020: Healthcare Indicators, Infrastructure & Productivity, Across Time, Ownership, Country's Borders, Healthcare Needs, Government Initiatives, Challenges - Researchandmarkets.Com. [online] Available at:
Atavist. 2021. GCC Healthcare Industry, Kuwait Hospital Ecosystem, Kuwait Healthcare Key Metrics, Introduction Kuwait Hospital- Ken Research. [online] Available at:
Awad, A.I., Al-Rasheedi, A. and Lemay, J., 2017. Public perceptions, expectations, and views of community pharmacy practice in Kuwait. Medical Principles and Practice, 26(5), pp.438-446.
Azhar, S. and Ibrahim, M.I.M., 2018.Quality of Pharmacy Health Services.In Social and Administrative Aspects of Pharmacy in Low-and Middle-Income Countries (pp. 281-294).Academic Press.
Battelino, T., Danne, T., Bergenstal, R.M., Amiel, S.A., Beck, R., Biester, T., Bosi, E., Buckingham, B.A., Cefalu, W.T., Close, K.L. and Cobelli, C., 2019. Clinical targets for continuous glucose monitoring data interpretation: recommendations from the international consensus on time in range. Diabetes care, 42(8), pp.1593-1603.
Ccwa.org. 2016. Health Challenges: Kuwaitcleveland Council On World Affairs. [online] Available at:
Darawsheh, B. and Germeni, E., 2019. Implementing health technology assessment in Kuwait: a qualitative study of perceived barriers and facilitators. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care, 35(6), pp.422-426.
Darawsheh, B. and Germeni, E., 2019. Implementing health technology assessment in Kuwait: a qualitative study of perceived barriers and facilitators. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care, 35(6), pp.422-426.
Dougherty, M.R., Slevc, L.R. and Grand, J.A., 2019. Making research evaluation more transparent: Aligning research philosophy, institutional values, and reporting. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 14(3), pp.361-375.
El Ayyat, A., Sayed, H.A., Helmy, A.H. and Esmat, M.E., 2018. Improvement of surgery department performance after implementing hospital quality standards’ policies: two decades experience. The Egyptian Journal of Surgery, 37(3), p.405.
Flynn, B., Pagell, M. and Fugate, B., 2018. Survey research design in supply chain management: the need for evolution in our expectations.
Gulf Business. 2021. GCC Start-Ups Set To Drive Healthcare Innovation - Gulf Business. [online] Available at:
Ijaz, M.F., Alfian, G., Syafrudin, M. and Rhee, J., 2018. Hybrid prediction model for type 2 diabetes and hypertension using DBSCAN-based outlier detection, synthetic minority over sampling technique (SMOTE), and random forest. Applied Sciences, 8(8), p.1325.
Iwata, M., Tang, S. and Obana, S., 2018. Energy-efficient data collection method for sensor networks by integrating asymmetric communication and wake-up radio. Sensors, 18(4), p.1121.
Jentoft, N. and Olsen, T.S., 2019. Against the flow in data collection: How data triangulation combined with a ‘slow’interview technique enriches data. Qualitative Social Work, 18(2), pp.179-193.
Johnson, J.M. and Carragher, R., 2018. Interprofessional collaboration and the care and management of type 2 diabetic patients in the Middle East: a systematic review. Journal of interprofessional care, 32(5), pp.621-628.
Johnston, M.P., 2017. Secondary data analysis: A method of which the time has come. Qualitative and quantitative methods in libraries, 3(3), pp.619-626.
Katoue, M.G., 2020. Enablers and challenges to pharmacy practice change in Kuwait hospitals: a qualitative exploration of pharmacists’ perceptions. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice.
Katoue, M.G., Awad, A.I., Al-Jarallah, A., Al-Ozairi, E. and Schwinghammer, T.L., 2017.Medical and pharmacy students’ attitudes towards physician-pharmacist collaboration in Kuwait. Pharmacy Practice (Granada), 15(3).
Katoue, M.G., Awad, A.I., Dow, A.W. and Schwinghammer, T.L., 2020. Interprofessional education and collaborative practice in Kuwait: attitudes and barriers from faculty. Journal of Interprofessional Care, pp.1-9.
Kelendar, H. and Mohammed, M., 2019. Hospital Bed Occupancy and Utilisation: Is Kuwait on the Right Track. Journal of Hospital & Medical Management, [online] Vol.5 No.2:3(ISSN 2471-9781), pp.1-11. Available at:
Kelendar, H., Faisal, M. and Mohammed, M.A., 2020. Lean processes mapping of diabetic patient flow in primary healthcare centres in Kuwait highlights opportunities for fewer patient visits. Middle East Journal of Family Medicine, 7(10).
Kelendar, H., Faisal, M. and Mohammed, M.A., 2020.The Need for Lean Thinking in the Kuwaiti Healthcare System. Health Science Journal, 14(2), pp.1-6.
Kelendar, H., Faisal, M. and Mohammed, M.A., 2020.The Need for Lean Thinking in the Kuwaiti Healthcare System. Health Science Journal, 14(2), pp.1-6.
Kuwait Times. 2021. Healthcare In Kuwait - Kuwait Times. [online] Available at:
Mansor, S., Pfaehler, E., Heijtel, D., Lodge, M.A., Boellaard, R. and Yaqub, M., 2017. Impact of PET/CT system, reconstruction protocol, data analysis method, and repositioning on PET/CT precision: An experimental evaluation using an oncology and brain phantom. Medical physics, 44(12), pp.6413-6424.
Markets, R., 2020. Kuwait Hospital Market Outlook To 2022: Public & Private Hospitals, Inpatients & Outpatients, General & Specialty. [online] GlobeNewswire News Room. Available at:
McNichols, M.F. and Stubben, S.R., 2018. Research design issues in studies using discretionary accruals. Abacus, 54(2), pp.227-246.
Mohr, D.C., Riper, H. and Schueller, S.M., 2018.A solution-focused research approach to achieve an implementable revolution in digital mental health. JAMA psychiatry, 75(2), pp.113-114.
Moon, K., Blackman, D.A., Adams, V.M., Colvin, R.M., Davila, F., Evans, M.C., JanuchowskiHartley, S.R., Bennett, N.J., Dickinson, H., Sandbrook, C. and Sherren, K., 2019. Expanding the role of social science in conservation through an engagement with philosophy, methodology, and methods. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10(3), pp.294-302.
Nguyen, M.N., Pandey, S.R., Thar, K., Tran, N.H., Chen, M., Bradley, W.S. and Hong, C.S., 2021. Distributed and democratized learning: Philosophy and research challenges. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 16(1), pp.49-62.
Oxford Business Group. 2019. Private Sector Participation To Meet Rising Health Care Demand In Kuwait. [online] Available at:
Oxford Business Group. 2021. Large-Scale Projects To Cater To Growing Demand In Kuwait's Health Care Sector. [online] Available at:
Perederic, O.A., Cunico, L.P., Kalakul, S., Sarup, B., Woodley, J.M., Kontogeorgis, G.M. and Gani, R., 2018. Systematic identification method for data analysis and phase equilibria modelling for lipids systems. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 121, pp.153-169. Peters, B., Haber, E. and Granek, J., 2019. Neural networks for geophysicists and their application to seismic data interpretation. The Leading Edge, 38(7), pp.534-540.
Rahi, S., 2017. Research design and methods: A systematic review of research paradigms, sampling issues and instruments development. International Journal of Economics & Management Sciences, 6(2), pp.1-5.
Research, K., 2019. Kuwait Hospital Industry Driven By Rise In Population And Increase In Number Of Hospitals Beds: Ken Research. [online] Prnewswire.com. Available at:
Salman, A., Fakhraldeen, S.A., Chun, S., Jamil, K., Gasana, J. and Al-Hunayan, A., 2020, September. Enhancing Research and Development in the Health Sciences as a Strategy to Establish a Knowledge-Based Economy in the State of Kuwait: A Call for Action. In Healthcare (Vol. 8, No. 3, p. 264).Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute. Sharma, G., 2017. Pros and cons of different sampling techniques. International journal of applied research, 3(7), pp.749-752.
Van den Berg, A. and Struwig, M., 2017.Guidelines for Researchers Using an Adapted Consensual Qualitative Research Approach in Management Research. Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods, 15(2).
Witter, S., Hamza, M.M., Alazemi, N., Alluhidan, M., Alghaith, T. and Herbst, C.H., 2020. Human resources for health interventions in high-and middle-income countries: findings of an evidence review. Human Resources for Health, 18(1), pp.1-17. Zaim, H., Keceli, Y., Jaradat, A. and Kastrati, S., 2018. The effects of knowledge management processes on human resource management. Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management.
Appendix
Questions for the survey
Quantitative survey questions for the employees
1. What is your Gender
• Male
• Female
2. How long have you been working in the industry
• Less than 2 years
• 2-5 years
• Above 5 years
3. Do you think the private start-up competition in Kuwait health care increased
• Yes
• No
• Neutral
4. Have your company performing mini audits on the recent channels
• Yes
• Neutral
• No
5. Do you think the competition between public healthcare organizations is high
• Yes
• No
• Neutral
6. What are the possible reasons for private start-up health centres’ development in Kuwait
• Technical development
• Swift treatments of patients
• People are demanding more advanced care
• Lack of public infrastructure
7. Do you think government is helping public hospitals for growth
• Yes
• No
• Neutral
8. What do you think the possible causes for people visiting more private hospitals
• More advanced treatments
• Customized care units
• Low time for waiting
9. Is your company effective in emergency care unit operations
• Yes
• No
• Neutral
10. Is your company being effective in providing patient-care promotions
• Yes
• No
11. Is your company being effective in employee management
• Yes
• No
12. Is your company providing up-to-date innovative treatments to their patients
• Yes
• Neutral
• No
13. Is your current organization being effective in managing the rush hours
• Yes
• No
14. How effective do you think the patient waiting and outdoor treatment services in your company
• Satisfactory
• Not satisfactory
• Extremely long
• Mismanaged outdoor treatment
Qualitative questions for managers
1. What are the current governmental interventions for private and public collaboration efforts in the healthcare sector
2. What are reasons for customers visiting more individual or private hospitals despite more costs
3. How the current start-ups in Kuwait health sectorare impacting the facilities and services of public hospitals












