Health Care Assignment: Importance of Geriatric Care
Question
Task
This health care assignment consists of following parts:
Part 1: Critical examination
a. Critically examine four holistic factors that predict positive life experiences for an older adult. (approx. 350 words)
b. Evaluate the impact of the selected holistic factors (in a.) on life experiences of the older adult in Aotearoa/ New Zealand. (approx. 350 words)
c. Provide three insightful recommendations to improve positive ageing outcomes in Aotearoa/ New Zealand. (approx. 300 words)
Part 2: Investigation
a. Evaluate physiological changes from three body systems that influence the quality of life of an older adult. (approx. 500 words)
b. Evaluate three psychosocial factors that impact the quality of life for an older adult
Answer
Introduction
The key purpose of this health care assignment is to explore the holistic health of the old aged people from a physiological, psychological, social-economic, spiritual, political, and cultural view under Geriatric Care. The overall report will be based on part 1 and part 2 sections wherein part 1 will provide a critical examination of selected holistic factors, and on the other hand, part 2 will discuss the physiological changes and psychological factors that influence the quality of life for an old aged people.
Part 1: Critical Examination
Four Holistic Factors
Geriatrics is a specialty that is based on recovering health care for elderly people and supports healthy improvement in elderly people by avoiding and treating disability and disease that frequently comes with aging (Besdine, 2019). The below mentioned four holistic factors that predict positive life experiences for older people are important as this makes them fulfilled and satisfied for safety through attaining habitual check-ups from the doctor, a proper and safe place to live, a good facility of transport, and a community to live peacefully.
Hence, under Geriatrics care, the four holistic factors that predict positive life experiences for older people are:
- Health
As per the study, it has been found that it is not enough to just be alive, but a life with good quality is mainly significant for old aged people who are experiencing with several fitness issues and central life transformations. Hence, this factor offer them an affirmative vision of life which can help elderly people to have more energy, better appetite, less anxiety, and avert cognitive demur. The health ageing in New Zealand focuses on promoting people to age well and identified many older people are healthy. - Housing
Siddiqui et al. (2016) state that the senior population is often the most vulnerable to developing severe health issues as the body ages. Its capability to respond to and resist illness, infection, or disease weakens. It generally means that elderly people need special care to make sure they are getting the appropriate preventive care, management of chronic disease, and urgent care or sick as needed or on an on-going basis (DailyCaring.com, 2015). In New Zealand, there are several options for housing when the people get older and the NZ government focuses on the housing choices that elderly people needs and abilities and facilitates them to feel comfortable at their home. Not only that but they need a proper housing facilities that most be focused mostly on their safety. - Transport
As the people ages, they need more reliable and comfortable transport facility within a particular areas where the old aged are mostly resided. Therefore, it can be said that mobility and transport services for old aged people are for important for helping maintain a sense of independence. - Living in the community
For a common framework to the condition of health and well being by living in the community indicates that the quality of life perception and it is essential to measure more specific queries under Geriatrics care, and it is, thus, significant to differentiate health from life satisfaction that includes contentment with the past and present life experiences (RondónGarcía&RamírezNavarrro, 2018). Considering this, it has been identified through researches that a number of gerontologists declare that elderly person who effectively grow old are those who consider satisfied and happy with their present and past and enjoy encouraging social contacts and relationships. For example, a Social support for older people, spiritual perspective, and daily activities to keep them mentally and physically fit.
a. Evaluation on the Impact of Selected Holistic Factors
As per the research, it has been identified that many old age citizens in NZ is rapidly increasing. Most people above 60 years of age are healthy and strong, but a minority are weak or delicate and need maximum degrees of supervision and illness support. Hence, it can be said that the influence of the particular holistic factors on life experiences of the elder adult in New Zealand can have a positive impact because, under NZ’s Ministry of Health, services for older people are provided as they get older and if they need some support to live comfortably and stay healthy(NZ Health System, 2021).
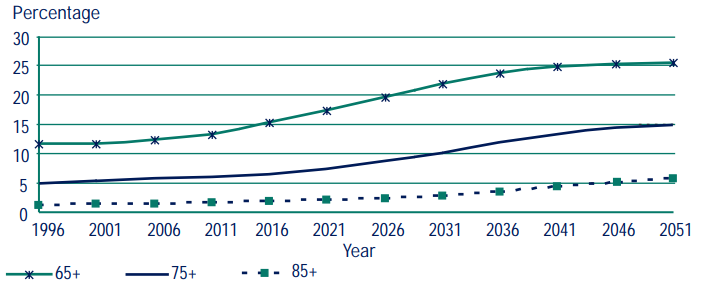
Fig 1- Estimated NZ Population above 65+ to 2051
Sources- (Ministry of Health, 2016)
However, an evaluation has been done below on the outcome of the certain factors on life experiences of the elder people in New Zealand has been discussed on the following grounds:
- Housing
Treat depression- As per the study, it has been found that more than 6 million old aged people above 65 are mostly affected by depression. This can be due to the hectic events of life like retirement or losing a spouse. Thus, it is important to identify the depression signs to improve the life quality of those people by helping them from counselor, doctor, psychologist. - Health
Keep them active mentally- Having an active and sharp mind improves overall well-being; therefore, great activities must be offered for mental encouragement which helps to stay active and healthy. - Transport
Accessibility- The transport facilities for the elderly people needs to be accessible as there are many ways of looking at an ideal public transport system for old aged people. Thus, in order to make transport a smart option for elderly people, all factors of the public transport chain has to be considered. - Living in the Community
Help them remain connected with community, family, and friends- Old-aged people who are lonely and isolated are said to have minimum existence and are at high hazard for dementia. Thus, living in a community encourages and helps them stay connected with friends and family, which will eventually free them from several diseases like dementia.
b. Three Insightful Recommendations to Improve Positive Ageing Outcomes in NZ
The three insightful recommendations to improve positive aging outcomes in NZ have been discussed on the following grounds accordingly.
- Housing
High-quality care closer to home- Generally, primary health care services are the old aged people’s initial interaction with the health system when they are not well. Thus, in order to improve positive aging outcomes in NZ, the health department needs to work with housing providers to develop the superiority and level of aged-friendly housing for elder individuals. Hence, it involves a focus on the stock of rental housing wherein elderly people are growingly likely to live in and encouraged living housing options for better health facilities (BassemElsawy& Higgins, 2011). Thus, the NZ government should also need to understand the needs for housing for the aging population. - Health
Improving the environmental and social factors influencing health- Mutually working with administration and communities can be helpful for the health system to work for the improvement within the social, economic, and physical aspects for healthy aging and acquire equity, eradicating barriers to participation. Thus, the NZ government needs to coordinate and form a system-wide approach to prevent, recognize and eliminate elder abuse and neglect that includes delivering accessible as well as well-tailored and effective services to the old aged people. - Transport
Need of proper mobility and transport policy- The old aged citizens needs a proper mobility and transport policy in NZ. Though this has a negative impact on old aged people as they feel they are not independent enough to take a transport by themselves but this will help the old aged people from several factors like accidents. - Living in a Community
Building Age-friendly communities- As per the study, it has been found that age-friendly communities are easily reached and wide-ranging. Thus, the administration needs to value the old aged people and improve opportunities for healthy aging that includes the areas of security, dignity, involvement, and quality life. Thus, the communities of age-friendly make sure that older people have a voice involving those with dementia and disabilities and neglected old aged people. This will ultimately help to figure out old people's extensive skills and resources and assure that these communities can protect those who are weak.
Part 2: Investigation
a. Evaluation of Three Physiological Changes
The physiological changes from the three-body systems that influence the old aged people's quality of life have been listed and discussed below:
- Integumentary system- This system is the biggest organ of the body that builds a physical barrier within the internal and external environment that it helps to maintain and protect. The Integumentary system consists of skim (dermis, epidermis), hairs, nails connected to glands, hypodermis (Physio-pedia.com, 2021). Aging and the Integumentary system show all systems in the body accrue delicate and certain non-delicate changes when a person ages. Among these changes are decreasing in metabolic activity, cell division, hormonal levels, blood circulation, and muscle strength (Biology of Aging, 2021).
- Cardiovascular system- Ageing can be the reason for changes in the blood vessels and heart. For e.g., as people get older, their hearts cannot beat as fast while doing physical activity. Hence, the heartbeats number per minute at rest normally does not change considerably with normal aging. Changes that occur with age might increase the risk of a person's heart disease. While aging does not bring changes in the cardiovascular system but it does lower the verge for the manifestation of disease. As most populations from the developed nations continue to become older, on average, the significance of aging as a risk aspect for all cardiovascular disease increases in kind, and these changes within the body systems can influence the quality of life of an older adult (Strait & Lakatta, 2012).
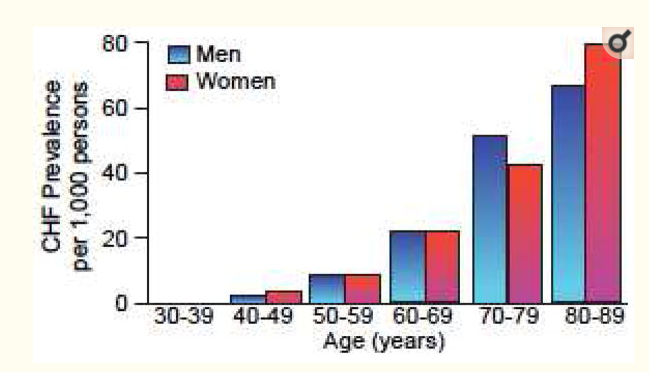
Fig 2- Average prevalence of heart failure as per the age and sex
Sources- (Strait & Lakatta, 2012)
Moreover, it can be said that adults over the age of more than 65 are more probable than young citizens to suffer from cardiovascular infection, which is the issues with the blood vessels, heart, or both (Nia.nih.gov, 2021). - Musculoskeletal system- When people are aged, their joints are influenced by changes in connective tissue and in cartilage. As per the study, it has been found that muscles deliver the strength and force to move the whole body, and hence, coordination is led by the bran. However, it is influenced by changes in the joints and muscles (Siddiqui et al., 2016). Thus, changes in the muscles, bones, and joints affect the walk and posture and lead to slowed movement and weakness. In addition to this, it can be said that aging changes the strength and force of the body, wherein people lose bone density or mass as they age, mainly women after menopause. The bones drop other minerals and calcium. However, the effect of aging changes generally shows the strength and stamina change as well as muscle mass decreases strength.
b. Evaluation of Three Psychological Factors
The three psychological factors that can influence the class of life for an elder adult has been listed and discussed on the following grounds:
- Relocation- Relocation is said to be a stressful life event for old-aged people. The ratio of relocation in people more than 50 years of age has been reported to be between 30 to 50%. Relocation to care facility based on long-term incline to be a chief transform of life for most old-aged people with resulting in transformation in relations with their friends and family (Wu et al., 2015). Several old-aged individuals face problems in accepting transformations to their physical living environment along with transformations to their daily living activities and social networks ensuing transfer. Experts have emerged with diverse terminologies such as syndrome of repositioning stress, transfer trauma, and rearrangement syndrome to point out the harmful psychological influence of relocation (Wu & Rong, 2020).
- Loneliness- As per the study, loneliness has a negative impact on health in old age. Hence, loneliness, coupled with other mental and physical issues, gives rise to depression feelings in old aged persons. Thus, it can be said that loneliness, as well as social isolation, resulting in many negative health conditions (Lim & Kua, 2011). Hence, the effects of loneliness show a higher risk for different mental and physical conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, anxiety, a weak immune system, Alzheimer's disease, cognitive decline, and even death (National Institute on Aging, 2019). However, old-aged individuals who locate themselves unpredictably alone due to the demise of their colleague, friends and family separation, mobility loss, and be short of of transportation are at a certain risk.
- Bereavement- It is the elderly is an apprehension to chief care physician as this can result to psychological infection such as depression. A number of individuals are able to handle the terms with their sorrow without any intervention, but some individuals are not. Hence, it is the state of having suffered a loss, and wherein sorrow is a natural call to loss. The impact of bereavement on old-aged people includes yearning, searching, preoccupation with perceptions of the deceased, disbelief, crying, and feeling shocked by the death. This creates somatic symptoms such as chest pain; headache or palpitations might also be features of complicated sorrow. Thus, it can be said that bereavement in old aged people can lead to isolation as well as loneliness and an increased possibility of depression, and it is awful that older bereaved people are not being offered access to services and support that can make a huge difference to their well-being (Hashim et al., 2013).
Conclusion
To conclude, it can be said that the report critically examines the four holistic factors Health, Housing, Transport and Living in the community that predicts the positive life experience for an older person. Each holistic factor has a significant impact on the life experience of older people. They keep them mentally stable by treating their depression and helps them to stay connected with their families and friends. After these analyses, a recommendation was given to improve the positive life experience of older people in a community.
References
Bassem Elsawy, & Higgins, K. E. (2011). The Geriatric Assessment. American Family Physician, 83(1), 48–56. https://www.aafp.org/afp/2011/0101/p48.html
Besdine, R. W. (2019). Introduction to Geriatrics - Geriatrics. MSD Manual Professional Edition. https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-in/professional/geriatrics/approach-to-the-geriatric-patient/introduction-to-geriatrics
Biology of Aging. (2021). Age Related Changes to the Integumentary System | Biology of Aging. Courses.lumenlearning.com. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/atd-herkimer-biologyofaging/chapter/age-related-changes-to-the-integumentary-system/
DailyCaring.com. (2015). 5 Ways to Improve Quality of Life for Seniors – DailyCaring. DailyCaring. https://dailycaring.com/5-ways-to-improve-quality-of-life-for-seniors/
Hashim, S. M., Eng, T. C., Tohit, N., & Wahab, S. (2013). Bereavement in the elderly: the role of primary care. Mental Health in Family Medicine, 10(3), 159–162. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3822663/
Lim, L. L., & Kua, E.-H. (2011). Living Alone, Loneliness, and Psychological Well-Being of Older Persons in Singapore. Current Gerontology and Geriatrics Research. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cggr/2011/673181/
Ministry of Health. (2016). Healthy Ageing Strategy. https://www.health.govt.nz/system/files/documents/publications/healthy-ageing-strategy_june_2017.pdf
National Institute on Aging. (2019, April 23). Social isolation, loneliness in older people pose health risks. National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/social-isolation-loneliness-older-people-pose-health-risks
Nia.nih.gov. (2021). Heart Health and Aging. National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/heart-health-and-aging#:~:text=Adults%20age%2065%20and%20older
NZ Health System. (2021). Older Persons’ Health | Community & Public Health. Www.cph.co.nz. https://www.cph.co.nz/your-health/older-persons-health/
Physio-pedia.com. (2021). Integumentary System. Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Integumentary_System
Rondón García, L. M., & Ramírez Navarrro, J. M. (2018). The Impact of Quality of Life on the Health of Older People from a Multidimensional Perspective. Journal of Aging Research, 2018, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4086294
Siddiqui, M. I., Iliyas, M., & Manzoor, S. (2016). Health of Elderly. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308021555_Health_of_Elderly
Strait, J. B., & Lakatta, E. G. (2012). Aging-associated cardiovascular changes and their relationship to heart failure. Heart Failure Clinics, 8(1), 143–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hfc.2011.08.011
Wu, C.-S., & Rong, J.-R. (2020). Relocation experiences of the elderly to a long-term care facility in Taiwan: a qualitative study. BMC Geriatrics, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01679-5
Wu, Y.-T., Prina, A. M., Barnes, L. E., Matthews, F. E., & Brayne, C. (2015). Relocation at older age: results from the Cognitive Function and Ageing Study. Journal of Public Health, 37(3), 480–487. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdv050












