Global Marketing Assignment Discussing Organizational Profile of Sun Pharma
Question
Task: Write a global marketing assignment analyzing a global marketing and online business of an organization of your choice based on a specific host country.
Answer
Background of Global Marketing Assignment
In today’s fast changing and competitive global market, it is important for the companies to establish a strong global presence so that they can reach out to more people at different parts of the world. With the help of online presence the businesses are able to grow in the global market, expand their customer base and increase their revenues (Iheanachor, David-West and Umukoro, 2021). Sun Pharma is a company in India, which operates in the pharmaceuticals industry. Since its establishment in the year 1983, the company has been adapting to the changes in the micro and macro environment. The company today has expanded into other countries across the world. In this report, the organizational profile of Sun Pharma will be discussed with reference to the pharmaceutical industry. The micro as well as macro environment of the organization will be analyzed using the SWOT and PESTEL methods respectively. Further the report will highlight the different theories and models on internalization. The marketing activities including segmentation, targeting, brand positioning and current customer trends will be evaluated for Sun Pharma. The significance and effectiveness of online activities will be emphasized in the report with some strategic recommendations that would enable Sun Pharma to develop their business further.
Organizational Profile
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Limited popularly known as Sun Pharma is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. In the global pharmaceutical industry Sun Pharma ranks 4th and in India they are the biggest multinational company in the industry (Sun Pharma, 2021). The company has its headquarters in Maharashtra at Mumbai. The operations of the company comprise manufacturing and sale of pharmaceutical formulations. In India and U.S, Sun Pharma also manufactures and sells active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). There are various therapeutic areas like psychiatry, cardiology, diabetology, gastroenterology and neurology, in which Sun Pharma produces formulation. The common APIs, which Sun Pharma provides include warfarin, etodolac, carbamazepine and clorazepate. The company also produces and sells APIs for anti-cancers, peptides, controlled substances, sex hormones and steroids. The company has been successfully running and flourishing since 1983.
The company has expanded from two persons’ team of marketing and five products in psychiatry in 1983 during its establishment to a strong network for sales across 24 nations around the globe in1996 (Sun Pharma, 2021). The company has entered into some alliances and made few acquisitions. In the year 2013, Sun Pharma was catapulted by Ranbaxy acquisition to the fifth largest pharmaceutical company in the world in specialty generic.
Industry Analysis
Sun Pharma operates in the pharmaceutical industry in India and has also expanded its business across various other nations of the world. To analyze its position in the pharmaceutical industry in India, the Porter’s five factors have been used.
Threat of new entry:There are several new entrants in Indian market who enter the pharmaceutical industry finding it profitable and a sustainable business. Sun Pharma has reached a position where it rules the pharmaceutical market in India and also has a significant position at the global market (Sun Pharma, 2021). Though the company does not need to feel threatened by the new entrants, it has to ensure that the new companies do not overpower the company with their latest research and developments. Thus, the company has to constantly research for betterment in pharmaceuticals.
Bargaining power of consumers:Thepharmaceutical products have an inelastic demand from the consumers (Beladi and Mukherjee, 2017). The final consumers do not have much bargaining power in case of pharmaceutical products of Sun Pharma. However, the healthcare professionals and pharmacists are quite price-sensitive. Bargaining power of suppliers: The suppliers of Sun Pharma include the raw material suppliers, the suppliers of labour, suppliers of other essential components of pharmaceuticals and suppliers of expertise or services related to pharmaceuticals. As Sun Pharma cannot operate without its suppliers, they definitely have a bargaining power over the company. Moreover, Sun Pharma prefers working with the same set of suppliers to maintain consistency in supply chain across India. Therefore, the company tries to hear the voices and demands of its suppliers. However, considering the fact that every supplier wants to work with a reputed brand like Sun Pharma, the company strikes a favorable bargain with its suppliers.
Rivalry among competitors: As pharmaceutical is an essential industry, the government regulates the level of competition in the industry in India. There are quite a few existing competitors of Sun Pharma among which Cipla Ltd., Ranbaxy, Dr. Reddy’s, Glenmark, Cadila Pharmaceuticals, Lupin and Aurobindo are some of the significant ones (Poddar and Machado, 2019).
Threat of substitutes: In few areas, Sun Pharma has its monopoly in producing medicines, APIs and formulations in India. In such areas like in specialty generics Sun Pharma faces no threats from substitutes (Sun Pharma, 2021). However, for the general medicines there are substitutes produced by other pharmaceutical companies in India and outside. Threat of substitutes is quite low for Sun Pharma considering its vast range of products, good reputation among customers and excellence in quality in Indian pharmaceutical market.
Situation Analysis
Micro environmental analysis: SWOT
|
Strengths: · Strong global presence in 100+ nations (Sun Pharma, 2021) · Developing the business in emerging markets · Good brand reputation across India and U.S · Faces low or no competition in U.S in Eloxatin and Pantoprazole · Sales and marketing workforce comprises 12,000 staff · Brand’s position is consolidated across markets in India after the successful acquisition of Taro Pharma |
Weaknesses: · Faces intense competition in the pharmaceutical industry from the global as well as Indian Pharma brands · Presence of many companies in the industries implies a limited market share · Presence in Europe and emerging markets is limited |
|
Opportunities: · Using the acquisitions for growing the business further · Exploring contract manufacturing and increasing global presence · Enhancing healthcare awareness across India |
Threats: · Increasing competition in the generic segment (Sun Pharma, 2021) · Constricted patent regulations · Highly price sensitive consumers |
Macro environmental analysis: PESTEL
The various elements in the external environment affect a business. The political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental factors affect the business of Sun Pharma. The PESTEL analysis will provide a better understanding of its external environment.
Political factors: The politics of a country or region affects any business that intends to thrive in that area. The business of the pharmaceutical company, Sun Pharma is affected by various political factors like:
- The political stability in the markets in which the company is already operating
- The political situation of the markets the company is aiming to enter (Yayla e al, 2018)
- The regulations imposed by the local governments across India
- With every change that comes with the change in the party forming the government, the company has to adjust its operations
- Governance system and policies regarding Pharma industry in India
Economic factors: To operate in an economy, the companies need to plan their business keeping the economic conditions in mind. For Sun Pharma to operate in a country like India, they need to consider the ups and downs in the economic cycles, the poverty and economic condition of the mass (Kizildag and Ozdemir, 2017). Accordingly, they can decide upon the pricing for the medicines. Some of the important economic factors include:
- Economic state of India
- Infrastructural availability in India
- Inflation rate of India
- Skill and knowledge of the workforce in India
- Financial markets’ efficiency in India
Social factors: The society affects business, as the people in the society will be using the products or services that are being produced and offered for sale. The social factors that affect the business of Sun Pharma include:
- Power structure in India
- Level of education in India
- Interests in healthcare and hygiene (Richards, 2020)
- Norms in the society and hierarchy in India
- Access and availability of essential services
Technological factors: The level of technology available in a country impacts the businesses that exist in that country. The technology available in India influences the business of Sun Pharma. The online business of Sun Pharma will also be affected by the technological factors. The significant technological factors that affect the business and marketing of Sun Pharma include:
- Availability of latest technology in India
- Technology induced production cost reduction (Wang et al, 2017)
- Research and development for new technology
- Protection of intellectual property rights in India
Environmental factors: The businesses have to think of the ecology which planning their operations. Today the consumers are so environment conscious that they choose the companies that are eco-friendly or green in their approach (Kumar, Prakash and Kumar, 2021). Besides, the general environment like weather, climate, etc. of India also affects the business of Sun Pharma. The business is affected by the following environmental factors:
- Consumer activism in India
- Renewable technology
- Environmental norms in India
- Extreme weather conditions prevailing in India
Legal factors: The legal factors are very important for any business as no business can operate outside the legal boundaries in a place (Ruggie, 2018). The legal norms present in India impact the business of Sun Pharma. These legal factors include:
- Health and safety norms in India
- Data protection laws
- Legal protection
- Environment laws
Models and Theories
According to Uppsala model, organizations mainly start their business in a nearby market to have adequate resources available, in-depth knowledge about the market. After the company gains experience in the domestic market starts to expand into a more distanced market. Distance market can be characteristically considered as geographically, politically and culturally different from where gathering market information would one of the most difficult part of expanding into a distanced market (VahlneandJohanson, 2017). Therefore, a firm that is planning to enter into an international market needs to obtain and use adequate market data from different sources abroad. The model suggests that “series of incremental decisions” would help mitigating the risk of hurrying up and clutter the process. Cultural factors that might impact on the successful internationalization of the company where language differences, differences in perspectives, beliefs and values can create significant barrier and can hinder the effectiveness of the workforce. Therefore, diversity and inclusion workshops and trainings along with guidance would help mitigating this challenge.
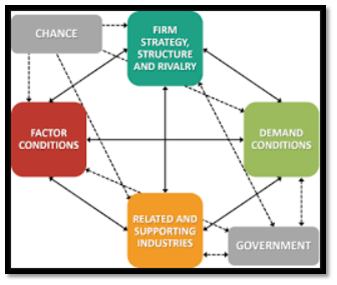
(Source: Fanget al., 2018)
The application of the Porter’s Diamond model in the Indian context suggest that in relation to the firm structure, strategy and rivalry, India has an advantageous position due to the continuous growth of economy of scale. Indian companies are enjoying bilateral trade relation since 1991 due which a variety of product and innovation is important. Government allows FDI in approved single and multi-bands under some rules and regulations. In India, the availability of cluster specific supportive industries is high, therefore, the power of the suppliers would be moderate or low which can be advantageous for Sun Pharma. Therefore, there is a high demand for generic drugs as identified in the context of demand conditions. This can significantly influence the production decision taken by Sun Pharma in future.
Marketing Activities
Among the marketing activities, segmentation, targeting and positioning are the most significant aspects.
Segmentation: As per Zhao and Zhou (2017), segmentation refers to the process of forming smaller homogenous target market within the large heterogeneous market on the basis of certain characteristics like demographic, geographic, psychographic or behaviour. The segmentation of Sun Pharma includes psychiatry, diabetology, cardiology, neurology and gastroenterology.
Targeting: As stated by Camilleri (2018), targeting enables a company to break the larger market into smaller target market and address the needs of a specific segment. The target market of Sun Pharma comprises the professionals in healthcare sector and the pharmacists in and outside India.
Positioning: As opined by Iyer et al (2019), positioning is very important for a brand. It helps the company to create an image in the mind of the consumers based on which one brand is differentiated from its competitors. In the generics market, Sun Pharma has a strong global presence. They are one of the biggest specialty pharmaceuticals company in generics, operating internationally. This is the positioning for the brand, Sun Pharma.
Branding: The branding of Sun Pharma is effectively done with the implementation of its vision. They strive to reach the people internationally and touch their lives as a leading and most preferred valued medicines’ provider. The humility, integrity, innovation and passion have increased its brand value. The brand reputation or perception of the consumers about the Sun Pharma is highly influenced by the trust, reliability, quality and consistency in the products of the company (Sun Pharma, 2021).
Consumer Trends: The company, mainly targets the pharmacists and healthcare professionals, through whom the medicines reach the mass. The recent decade shows rising consumer trends for Sun Pharma. The charts given below show a continuous rise in the total income and net profits of the company between 2004 to 2014.
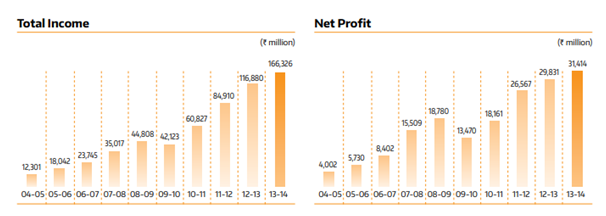
(Source: Sun Pharma, 2021)
Sun Pharma has expanded its customer base and is now present in more than 100 nations outside India. The company is present in healthcare business as well as in prescriptions. In the host country, India, Sun Pharma is the leading pharma company in chronic prescription in India.
Online Activities
As opined by Krizanova et al (2019), online activities related to marketing are very significant for companies these days if they want to consistently maintain their global presence. Sun Pharma should engage more aggressively in online activities as they can have a global access 24X7, operate at lower costs, make marketing cost saving and enhance client services by operating with flexibility. Sun Pharma is already present in 100+ countries and the online business will get them more consumers. The technology these days is highly improved and they save a lot of money, which was earlier invested in traditional marketing activities. Moreover, through online marketing many customers can be reached out to in no time. The customers increase, revenue increases and market share grows through online presence. As stated by Kumar et al (2019), the entire world will become a market for the company, as the online presence will facilitate breaking all geopolitical barriers. The online activities will make Sun Pharma a remembered name in the minds of the customers. The brand name and credibility enhances through online activities. Instead of collaborating with companies outside India, through online platform Sun Pharma can directly enter many global markets.
Strategic Recommendations
For every business, there is always room for improvement. When a company continuously tries to find out the problems in their business including the analysis of its weaknesses and threats and tries to overcome them by implementing some strategic actions, they continue growing. The strategic action plan should incorporate the measures that would enhance the strengths and explore the opportunities. Besides, the limitations and advantages of the external environment should also be considered while planning the actions.
For gaining a stronger market position, it can be recommended for Sun Pharma that:
- The company should maintain a strong leadership position in the pharmaceutical industries of India and other existing markets.
- The company needs to concentrate more on innovation, research and development to continue being No.1 pharmaceutical company in India.
- They should focus on developing products that are complex and make them available across various dosage forms.
- The company should continuously strive for improvement of the processes, systems and human capabilities in the company so that they are able to meet the compliance norms and regulatory standards in India and at the global pharmaceutical market.
- They should emphasize on enhancing ROCE.
- The company should try to reduce employee turnover and retain their employees as this brings about continuous growth for the company.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be stated that the organization SunPharma’sinternal and external business environmental situations shows different long term impact possibilities on the organization. The technological factors or infrastructure could be identified to have a role in enhancing the online presence of the company. In order to successfully enter the international markets Sun Pharma would need to analyze the business environment first and utilize the experience is has gathered from doing business in India as proposed by the Uppsala model of internationalization. Moreover, market research on the host country would help making better decisions about business internationalization.
References
Beladi, H. and Mukherjee, A., 2017. Union bargaining power, subcontracting and innovation. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 137, pp.90-104.
Camilleri, M.A., 2018. Market segmentation, targeting and positioning.In Travel marketing, tourism economics and the airline product (pp. 69-83).Springer, Cham.
Fang, K., Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Ye, R. and Guo, S., 2018. Assessing national renewable energy competitiveness of the G20: A revised Porter's Diamond Model. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 93, pp.719-731. Iheanachor, N., David-West, Y. and Umukoro, I.O., 2021.Business model innovation at the bottom of the pyramid–A case of mobile money agents. Journal of Business Research, 127, pp.96-107.
Iyer, P., Davari, A., Zolfagharian, M. and Paswan, A., 2019.Market orientation, positioning strategy and brand performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 81, pp.16-29.
Kizildag, M. and Ozdemir, O., 2017.Underlying factors of ups and downs in financial leverage overtime. Tourism Economics, 23(6), pp.1321-1342.
Krizanova, A., L?z?roiu, G., Gajanova, L., Kliestikova, J., Nadanyiova, M. and Moravcikova, D., 2019.The effectiveness of marketing communication and importance of its evaluation in an online environment. Sustainability, 11(24), p.7016.
Kumar, A., Prakash, G. and Kumar, G., 2021. Does environmentally responsible purchase intention matter for consumers? A predictive sustainable model developed through an empirical study. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 58, p.102270.
Kumar, P., Kumar, A., Palvia, S. and Verma, S., 2019. Online business education research: Systematic analysis and a conceptual model. The International Journal of Management Education, 17(1), pp.26-35.
Poddar, N. and Machado, A., 2019. A Study on Performance Analysis of Top Pharma Companies in India. SFIMAR Research Review, 14(2), pp.24-34.
Richards, B., 2020. Balancing interests in healthcare: What happens when commercial interests outweigh patient welfare and a brief overview of the swinging pendulum of informed consent in Singapore. Journal of bioethical inquiry, 17, pp.15-20.
Ruggie, J.G., 2018. Multinationals as global institution: Power, authority and relative autonomy. Regulation & Governance, 12(3), pp.317-333. Sun Pharma2021.,About Us. Available at https://www.sunpharma.com/. [Accessed 23rd March 2021]
Vahlne, J.E. and Johanson, J., 2017. From internationalization to evolution: The Uppsala model at 40 years. Journal of International Business Studies, 48(9), pp.1087-1102.
Wang, Q., Wei, W., Gong, Y., Yu, Q., Li, Q., Sun, J. and Yuan, Z., 2017. Technologies for reducing sludge production in wastewater treatment plants: state of the art. Science of the Total Environment, 587, pp.510-521.
Yayla, S., Yeniyurt, S., Uslay, C. and Cavusgil, E., 2018.The role of market orientation, relational capital, and internationalization speed in foreign market exit and re-entry decisions under turbulent conditions. International Business Review, 27(6), pp.1105-1115.
Zhao, W. and Zhou, X., 2017. From institutional segmentation to market fragmentation: Institutional transformation and the shifting stratification order in urban China. Social science research, 63, pp.19-35.












