Enterprise Architecture Case Study Analysis On GovDept
Question
Task:
GovDept is a mid-size governmental department providing important services of a social nature to the
population of a large territory. From the technology perspective, the organization can be considered
as a late adopter of innovations and characterized by relative underinvestment in IT, which has certain
implications for both its IT landscape and respective management practices. On the one hand,
GovDept’s IT landscape is very heterogeneous and includes many legacy information systems and
technologies some of which have been in use for decades. On the other hand, its IT-related
management practices are also rather archaic. For instance, the relationships between business and
IT leaders in the organization exhibit evident signs of “us and them” mentality, while new investments
in IT are viewed by business mostly as a means to reduce costs of the existing operations.
GovDept has a centralized IT department headed by the CIO and responsible for developing and
supporting information systems for all its business units. The IT department employs around 250
specialists and consists of three main functions: architecture, development and service. The
architecture function includes a few architects focused predominantly on specific IT solutions.
GovDept previously tried to uplift the maturity of its EA practice and extend the scope of architectural
planning beyond separate initiatives, but these attempts did not succeed and respective architects
had been made redundant.
Then, the CIO decided to undertake another deliberate effort to evolve GovDept’s EA practice with
the involvement of external consultants. For this purpose, the organization engaged a rather wellknown boutique EA consultancy to help initiate a full-fledged EA practice. The consultancy formed a
project team consisting of four architects specialized in different subject areas. This consulting team
acted according to a detailed engagement plan agreed with GovDept’s senior IT leadership. The plan
stipulated in which sequence and when exactly various EA artifacts will be produced. In total,
consultants worked for 2-3 months, analyzed the organization, interviewed numerous stakeholders
and developed all the EA artifacts specified in the plan. Specifically, they started from analyzing
GovDept in terms of current and desired maturity of its business capabilities and mapped existing
applications to respective capabilities. Then, they captured all relevant data entities, documented all
technologies used in the organization, depicted current and defined target application portfolios and
created more detailed CRUD (create, read, update and delete) relationship matrices.
1. You are required developed a comprehensive roadmap specifying what projects should be
executed in the next 2-3 years.
2. Discuss 5 key roles that IT will play in the GovDept if implemented.
3. Discuss 5 key EA artifacts that would be delivered in 2-3 months.
4. Explain the taxonomy of documentations that you will implement and why you have
considered it important to GovDept.
5. Discuss the operating model that you will implement and why you have chosen the operating
model.
6. Discuss the roles of standard and landscapes in implementation of GovDept’s EA?
7. Discuss 5 types of IT initiatives that you have considered very important to GovDept’s EA
8. Explain considerations as EA Artifacts that will be delivered in GovDept’s EA
9. Discuss 5 subtypes of visions that you used in EA artifacts implementation.
Answer
1. Introduction:
The concept of Enterprise Architecture (EA) explored in the enterprise architecture case study can be defined as the practice for conducting analysis of an enterprise using a comprehensive approach including collection of special documents or artifacts, designing, planning, implementation and successful development and execution of necessary strategies in order to bridge the communication gap between the IT and Information technology) and business stakeholders with the eventual intention of improving business and IT alignment.
The enterprise architecture case study analysis talks about GovDept, a mid-size department and its ongoing issues with project execution relating to its archaic related management practices, decade old use of technologies and poor communication between the business and IT stake holders. The following critique on enterprise architecture case study would give an in-depth analysis of the ongoing issues and the necessary prospective solutions /strategies that needs to implemented in the organization.
2. In depth analysis and comprehensive roadmap of prospective projects:
Progress and performance monitoring: Progress and performance would be monitored on a weekly basis that would also help in fostering effective communication within the organization: Meetings would be a great way to firm up agreement to discuss various aspects of projects that would be required and for identification of associated risks/issues of the projects. An open line of communication would be maintained throughput the project with necessary review and follow up and communicating ideas and information to IT and business stake holders and team members. There shouldn’t be any concept of I or blame game going within the team which was very evident in GovDept as it is mentioned in the passage that relationships between business and IT leaders in the organization exhibited evident signs of “us and them” mentality, and new investments were mostly viewed by the business stake holders, \
As per the readings of enterprise architecture case study, vision artifacts would require to be developed by the collaborative team effort of the senior business leaders in the making and the IT facilitators. This would help GovDept to achieve the desired alignment between IT investments and business outcomes. Proper use and implementation of vision would lead to improved effectiveness of IT investment of GovDept and would help it deal with the problem of underinvestment. Acknowledgement and credit would be given to the entire team involved in a particular project outlined in the enterprise architecture case study (Alwadain, Fielt, Korthaus, & Rosemann, 2016).
GovDept would also need to get rid of their archaic IT related management practices.
Usage of roadmaps e.g technology road maps, investment roadmaps and implementation of Business capability models (BCM) by the IT architects would provide a structured view of the prospective IT investments with their respective timelines, and are to be collaboratively developed by architects and senior business leaders to align IT investments and business plans from both ends and to help in IT projection initiation (Carr, Else, Roth, Graves, & Johnston-Bell, 2017)
Acknowledgement and credit would be given to the entire team involved in a particular project.
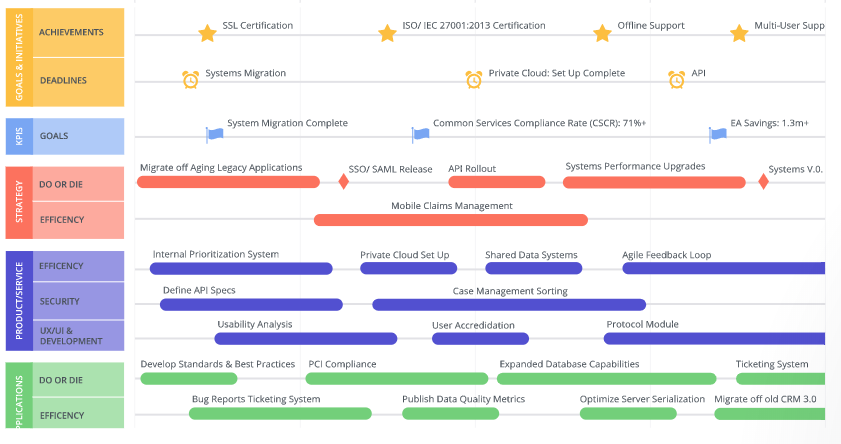
Figure 1: Roadmap for enterprise architecture for GovDept (Dang & Pekkola, 2017)
3. Updating and embracement of technologies would be adopted for enhancing project execution
Project management platforms like Trello and Clarizen as stated in the enterprise architecture case study can be used for instant communication within the team members which could result in fostering decision making and improve overall project execution unlike the decade old email or voicemail options of communications. Project management platforms implementation would also allow team member tracking and would make the job of a project manager easy and help the workers to make quick adjustments. Technology facilated collaboration would make up GovDept much effective in the long run. Data management tools would be implemented which help in analyzing complete project. Work flow automation would also be implemented in order to reduce the need of doing repetitive tasks which would help workers devote more time and efforts in project advancements (Foorthuis, Van Steenbergen, Brinkkemper, & Bruls, 2016).
The flow chart provided in the enterprise architecture case study analysis with the required repositories of the project at Business layer, information layer and application layer is discussed below:
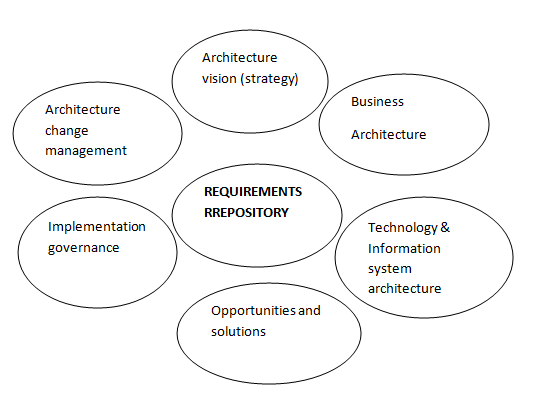
Figure 2: Business layer, information layer and application layer (created by author)
4. Proper use of business focused artifacts and IT focused artifacts needs to be implemented.
Key Roles of IT in the GovDept implementation:
As mentioned in the enterprise architecture case study, the Architecture domain of GovDept includes architects predominantly focused on delivering specific IT solutions. The IT Architects would play a key role in the EA (Enterprise Architecture) practice, as they act as the chief IT planners in the organization.
- They would have an imperative role in fostering good communication and relationship between the diverse business and IT stake holders in order to bridge the gap between them.
- They would have a key role in facilitating dialogs and conversations amongst the different stake holders at different levels of the organization
- They would be the ones who would help in connecting business and IT by finding optimal IT strategies and solutions basis the scenario of enterprise architecture case study that would satiate business needs and strategies. The architects must be more innovative in approach and need to have good critical thinking and knowledge of both Business and IT (Guzman, Monsalves, Grandon, Ramirez-Correa, & Alfaro-Perez, 2018).
- Their major responsibility would include finding, proposing and discussing optimal planning decisions and to satisfy the concerns of diverse IT and business stakeholders.
- Their role would also be to develop and update EA artifacts on a regular basis and to establish and maintain a proper repository (Central place or location for maintaining multiple databases and files that would be accessible to the users of the organization) with the eventual intention to run an optimized EA process.
5. Key EA artifacts to be delivered:
Business Focused artifacts outlined in the enterprise architecture case study:
ProperConsiderations/business focused rules: which would include principles, policies, strategies (with strategy papers), conceptual data models, governance papers with description of global conceptual and consideration for the overall business and IT development of GovDept and would necessitate a collaborative team effort of the business stakeholders and IT architects of the organization. This would help GovDept to achieve a mutual agreement based on principles, values, aims etc.
Proper use of vision: would include usage of capability and activity business modes, business context diagrams, enterprise process maps and all sorts of road maps. Such Artifacts would have a high level of conceptual description of the organization as whole. Vision artifacts would require to be developed by the collaborative team effort of the senior business leaders in the making and the IT facilitators. This would help GovDept examined in the enterprise architecture case study to achieve the desired alignment between IT investments and business outcomes. Proper use and implementation of vision would lead to improved effectiveness of IT investment of GovDept and would help it deal with the problem of underinvestment (Hansen & Hacks, 2017).
IT focused artifacts:
Proper use of Standardsrules: would include proper guidelines, standards, IT principles, data models, technology applications, enlistments of all the global technical rules, standards and patterns developed by individual architects and required subject matter experts of the organization. This would be helpful for GovDept to achieve an overall technical consistency and help them to reduce, the overall cost risk and complexity.
Proper use of Landscapes: would include platform architecture application portfolio, relational diagram, IT system value maps and all sorts of landscapes, with high level of technical description of organization and landscapes would require to be developed by the IT architects solely. It is discussed in the enterprise architecture case study analysis that proper usage of landscape would leads to increased flexibility and reduced legacy of the organization (Shanks, Gloet, Someh, Frampton, & Tamm, 2018).
Proper use of Designs: would include detailed designs (both physical and technical designs), full solution definitions with detailed technical description ad would require the collaborative effort of the architecture business representatives and different project teams. This would be key to improvement of the overall quality of project delivery of GovDept as mentioned in the context of enterprise architecture case study (Hinkelmann, et al., 2016).
6. Taxonomy of the key artifacts and their importance
|
Considerations |
Visions |
Outlines |
|
|
BUSINESS |
Identified Artifacts Purpose or Aim of the company explored in the enterprise architecture case study: Importance and Expected Benefits: Improvement of the overall conceptual consistency of Govdept. |
Identified Artifacts Purpose or Aim: Benefits: |
Identified Artifacts Purpose or Aim: Estimation of the overall value of the business of the IT projects can be made. Benefits: |
|
Standards |
Landscapes |
Designs |
|
|
IT |
Identified Artifacts: proper guidelines, standards, IT principles, data models, technology applications, enlistments of all the global technical rules, standards and patterns Purpose or aim: to achieve an overall technical consistency Benefits: help GovDept in reduction, of the overall cost risk and complexity. |
Identified Artifacts: platform architecture application port folio, relational diagram, IT system value maps and all sorts of landscapes, with high level of technical description of organization and landscapes (Vargas, Cuenca, Boza, Sacala, & Moisescu, 2016) Purpose or aim: Benefits:Proper usage of landscape would leads to increased flexibility and reduced legacy of the organization |
Identified Artifacts: detailed designs (both physical and technical designs), full solution definitions with detailed technical description Purpose or aim Benefits: Key to improvement of the overall quality of project delivery of GovDept. |
7. The operating model for Govdept enterprise architecture
There are four distinctive operating models in practice in the scenario of enterprise architecture case study for implementing enterprise architecture in Govdept infrastructure. The four operating model namely coordination model, unification model, diversification model and replication model. In the current context, unification model needs to be chosen (Korhonen & Halén, 2017).
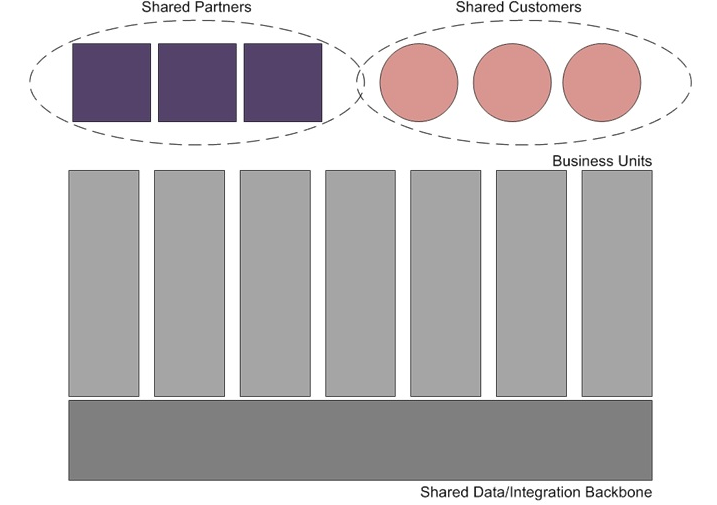
Figure 3: unification model ()
Unification model: The set of integrated models shared in global perspective where suppliers and customers are distributed within a vast geographic location. A centralized data processing needs to be done in case of unification model. The business units are controlled and monitor by matrix approach.
The choice of unification model in case of Govdept infrastructure illustrated in the enterprise architecture case study based on various factors such as dynamic data configuration, high level business process and unified sharing of global customer and suppliers. Choosing unification model helps to develop a standardize business process methodology in GovDept platform.
8. Roles of Standards and Landscapes in implementation of GovDept EA:
Considering the enterprise architecture case study, Standards (Principles also known as maxims) would have significant impact on both the business and the IT of GovDept. The principle needs to be reviewed in a collaborative fashion by by the senior business leaders as well as IT architects of all the projects (e.g review of architecture of IT project by architectures to achieve an overall technological homogeneity and consistency. in order to achieve a mutatual agreement based on values, rules and aims. There is no denying the fact that principles would be the most classic artifacts if we take generic consideration of business focused rules. Implementation of technology standards using reference models would help provide the use of standardized setoff technologies to be used in all IT projects pertaining to their domain. Usage of proper guidelines/standards or IT specific prescriptions to be used in all IT projects would provide prescriptions on how to use TRM technologies (Technology reference models) (Korhonen & Halén, 2017).
Landscapes: landscape diagrams, , interactive diagram, one page diagrams, platform architectures would give a brief description of the connections between different sort of applications, databases systems and as well as certain business processes forming the major part of IT , usually would be dealt by IT architects. Landscape diagrams would be helpful to GovDept in optimizing IT landscape. Usage of roadmaps e.g technology road maps, investment roadmaps would provide a structured view of the prospective IT investments with their respective timelines, and are to be collaboratively developed by architects and senior business leaders to align IT investments and business plans from both ends and to help in IT projection initiation. Implementation of business capability models (BCM) would be key to identify the best investment opportunities and To ensure alignment between IT investment and business outcome. BCM would be complementary to road maps as BCM would help decide where the future investments would go and what would it led to where as road maps would decide when such IT investments would be made come into play. BCM and road maps hence would be an imperative part of long-term goals to business and IT of GovDept (Lange, Mendling, & Recker, 2016).
9. IT initiatives to GovDept :
IT Architects would play a key role in the EA (Enterprise Architecture) practice of GovDept, being the chief IT planners of the organization.
- They would have an imperative role in fostering good communication and relationship between the diverse business and IT stake holders in order to bridge the gap between them by facilitating dialogs and conversations amongst the different stake holders at different levels of the organization
- They would be the ones who would help in connecting business and IT by finding optimal IT strategies and solutions that would satiate business needs and strategies. The architects must be more innovative in approach and need to have good critical thinking and knowledge of both Business and IT. Their major responsibility would include finding, proposing and discussing optimal planning decisions and to satisfy the concerns of diverse IT and business stakeholders & to develop and update EA artifacts on a regular basis and to establish and maintain a proper repository (Lapalme, et al., 2016).
- Usage of roadmaps e.g technology road maps, investment roadmaps and implementation of Business capability models (BCM) by the IT architects would provide a structured view of the prospective IT investments with their respective timelines, and are to be collaboratively developed by architects and senior business leaders to align IT investments and business plans from both ends and to help in IT projection initiation (Niemi & Pekkola, 2017).
- Business process re-engineering is a significant IT initiative in case of GovDept. it investigates the process associated with GovDept in order to incorporate methodologies to reduce operation cost and to increase productivity.
- Service oriented architecture method is adopted by GovDept which is associated with various application components that provides services to each software component. The service-oriented architecture is a significant initiative devoid of technological and vendor support.
10. Importance of consideration as EA artifact: Proper Considerations/business focused rules:
would include principles, policies, strategies (with strategy papers), conceptual data models, governance papers with description of global conceptual and consideration for the overall business and IT development of GovDept and would require a collaborative team effort of the business stakeholders and IT architects at different levels of the organization. This would help GovDept to achieve a mutual agreement based on principles, values, aims etc. These principles needs to be reviewed in a collaborative fashion by the senior business leaders as well as IT architects of all the projects. Review of architecture of IT project by architectures would help GovDept achieve an overall technological homogeneity and consistency (Niemi & Pekkola, 2017).
11. Considerations as EA Artifacts that will be delivered in GovDept’s EA
Usage of capability and activity business models, like TRM models ( Technology Reference models , BCM( Business Capability models) e.g (BCM would be complementary to road maps as BCM would help decide where the future investments would go and what would it led to whereas road maps would decide when such IT investments would be made come into play) BCM and road maps along with Business context diagrams, enterprise process maps would be an imperative part of long term goals to business and IT of GovDept. To achieve the desired alignment between IT investments and business outcomes which would be key in Improvement in effectiveness of IT investments of GovDept (Lapalme, et al., 2016).
12. Visions in EA artifact implementation
There are 5 sub-types of visions associated with EA artifact implementation as mentioned in below section of enterprise architecture case study analysis:
Architecture vision: it the primary vision to provide first cut, primary architecture consisting of data, business application and technology etcetera.
Business architecture: the aim of the business architecture outlined in the enterprise architecture case study is to incorporate hierarchical structure, governance structure, information flow management process and business process methods etcetera.
Information system architecture: the role of information system architecture is to stream line the data associated with information technology system.
Technology architecture: the role of technology architecture is to design the vestural, physical and logical architecture of the system.
Migration planning: the role of migration planning is to implement the matrix of change in the enterprise architecture methodology. The objective of the migration planning is to incorporate change management process.
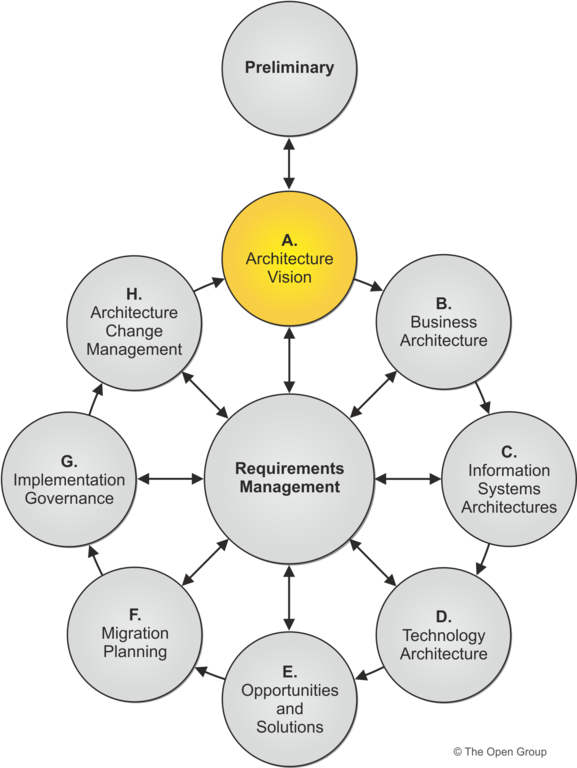
Figure 4: visions in EA artifact implementation
13. Conclusion:
If the afore mentioned strategies illustrated within the enterprise architecture case study (Monitoring performance and progress and updation of technologies) are implemented and the discussed business focused and IT focused artifacts are taken into consideration, it would enable GovDept to refrain from the current technological complexities and achieve a technological consistency.
14. Bibliography
Alwadain, A., Fielt, E., Korthaus, A., & Rosemann, M. (2016). Empirical insights into the development of a service-oriented enterprise architecture. Enterprise architecture case study Data & Knowledge Engineering, 105, 39-52.
Carr, D., Else, S., Roth, J., Graves, T., & Johnston-Bell, D. (2017). ENTERPRISE ARCHITECTURE PROFESSIONAL JOURNAL.
Dang, D., & Pekkola, S. (2017). Systematic Literature Review on Enterprise Architecture in the Public Sector. Electronic Journal of e-Government, 15(2).
Foorthuis, R., Van Steenbergen, M., Brinkkemper, S., & Bruls, W. (2016). A theory building study of enterprise architecture practices and benefits. Information Systems Frontiers, 18(3), 541-564.
Guzman, S., Monsalves, L., Grandon, E., Ramirez-Correa, P., & Alfaro-Perez, J. (2018). Exploring an enterprise architecture for higher education institutions: A proposal for the area of undergraduate teaching. 2018 13th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Hansen, P., & Hacks, S. (2017). Continuous delivery for enterprise architecture maintenance. Full-scale Software Engineering/The Art of Software Testing, 56.
Hinkelmann, K., Gerber, A., Karagiannis, D., Thoenssen, B., Van der Merwe, A., & Woitsch, R. (2016). A new paradigm for the continuous alignment of business and IT: Combining enterprise architecture modelling and enterprise ontology. Computers in Industry, 79, 77-86.
Korhonen, J., & Halén, M. (2017). Enterprise architecture for digital transformation. 2017 IEEE 19th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI).1, pp. 349-358. IEEE.
Lange, M., Mendling, J., & Recker, J. (2016). An empirical analysis of the factors and measures of Enterprise Architecture Management success. European Journal of Information Systems, 25(5), 411-431.
Lapalme, J., Gerber, A., Van der Merwe, A., Zachman, J., De Vries, M., & Hinkelmann, K. (2016). Exploring the future of enterprise architecture: A Zachman perspective. Enterprise architecture case study Computers in Industry, 79, 103-113.
Niemi, E., & Pekkola, S. (2017). Using enterprise architecture artefacts in an organisation. Enterprise Information Systems, 11(3), 313-338.
Shanks, G., Gloet, M., Someh, I., Frampton, K., & Tamm, T. (2018). Achieving benefits with enterprise architecture. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 27(2), 139-156.
Vargas, A., Cuenca, L., Boza, A., Sacala, I., & Moisescu, M. (2016). Towards the development of the framework for inter sensing enterprise architecture. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 27(1), 55-72.












