Elisa Test, Its Development, Uses, Procedure And Types
Question
Task: What is understood by Elisa Test? How did it develop? Procedure to conduct Elisa, its uses and types.
Answer
Introduction
Elisa which is an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is considered as a powerful technique to detect and quantify a particular protein from a specific complex mixture. It is a widely used method to ascertain and detect proteins in a given sample. Antibodies help in detecting the proteins helping the technique to be an immunoassay. The Elisa Test is being used as a diagnostic tool in medicines and plant pathology. One of its uses is quality control in different industries. Elisa Test can be in the form of Indirect Elisa, direct Elisa Test, sandwich Elisa Test and competitive/ inhibition Elisa. It helps to determine the concentrates of serum antibody and is considered as a basic, flexible, quantitative and sensitive test (Vencia, Migone & Vito, 2016). The paper will help in understanding the concept of Elisa, its development along with a discussion on the types of Elisa Test.
What is understood by Elisa Test?
Elisa Test is tool which helps in detecting and measuring the antibodies which are present in the blood. The test is helpful to detect the presence of antibodies in a body when one falls sick or is infected with some disease. Antibodies are nothing but the protein that a body makes when it comes in contact with some harmful substances like antigens. At times Elisa Test is used primarily for screening purposes before any other test is conducted. The term was described by Engvall and Perlmann in 1971 who stated that the tool assists to find out antibodies in a protein sample which is immobilized in micro plate wells (Gandikota, Gandhi & Maisam, 2020). The test also helps in measuring glycoproteins and is helpful in diagnosing the infection of HIV, pregnancy tests, diagnosing virus of chicken pox, zika, rota, etc.
Development of Elisa Test
Before the development of Elisa Test, radioimmunoassy was used on radioactively labeled antigens and antibodies. Through radio activity, the presence of any antigen or antibody was used to be detected. But there were certain risks related to health which some researches could foresee after the usage of radio activity and this led to search for other options. In the year 1960, a process was developed known as enzyme linking by two separate teams headed by Stratis Avrameas and G.B Pierce. Wide and Jerker Porath also published an immunosorbent technique in the same year. There were some independent researches being published by Peter Perlman and Eva Engvall at the University of Stockholm in Sweden and some researches done in Netherland by Anton Schuurs and B. van Weemen, which led to the making of Elisa Test (Gandikota, Gandhi & Maisam, 2020). The traditional Elisa involved the usage of chromogenic reporters along with some substrates which helped in changing of the color and indicated the existence of specific antigen or an analyte. The new technique used fluorogenic, electrochemiluminescent and quantitative PCR reporters in order to create signals. The usage of advanced reporters is an advantage while measuring a number of analytes in a sole or cluster of assays and higher sensitivities. The newer assays in most of the cases utilize reporters which are not enzymes without changing the principles of assays which led the assays to be grouped as Elisas.
Procedure to test Elisa
There are no technicalities involved while testing for Elisa, it is a simple clear procedure. A consent form is to be signed before the test is conducted and the doctor will help in explaining the reason behind conducting the test. Blood samples are collected and in order to do so, the healthcare person will clean the arm using an antiseptic. Thereafter, a band will be tied around the arm to exert a pressure on the veins in order to accumulate the blood at one place (Hoffstetter, Giffin & Brown, 2018). When the veins swell with blood, the blood sample will be taken out with the help of a needle which is placed in the vein. The required amount of blood will be collected and the needle will be replaced with a small band aid in order to stop the flow of blood. The healthcare person will ask you to maintain the pressure at the place where the needle was pierced; this will help in the reduction of blood flow. The process of taking the sample is less painful but there may be a throbbing in the arm.
The collected sample will then be analyzed by a laboratory. The healthcare personal or the technician of the lab will put the blood sample in a petri dish which already contains the specific antigen of the disease or the condition for which the sample was taken.

Source: (Hoffstetter, Giffin & Brown, 2018)
The above image shows sample being put in the plate for the Elisa test. In case the blood already has antibodies to fight the antigen then both will combine. The laboratory person will add an enzyme to the dish to check and observe the reaction between the blood and the antigen. In case there is a change in the color then it signifies the presence of the disease or the condition for which the test was conducted. The amount of change in the color which is caused by the addition of enzyme helps the healthcare personal to quantify the presence of antibodies.
Uses of Elisa Test and risks involved
The test is foremost used to detect proteins in the body and it is also used to test the presence of antigens. Elisa Test can help in the detection of hormones, viruses, allergens, viral fever, bacterial antigens and antibodies present in the body to fight the infection. It can also help in identifying any agent which tries to infect a person.
Although it is a simple test but at times a person being tested may be exposed certain risk like contacting an infection, feeling drowsy, flow of blood is continues, etc. In such cases the doctor needs to be contacted and updated about issues. The test is also helping in the detection of Covid 19. It is also necessary to update the doctor in case such cases have happened in near future (Kamarehei, Khabiri & Saidijam, 2018).
Result analysis of Elisa
The result of Elisa test may vary depending upon the analysis conducted by the laboratory which was performing the test. The condition or the disease is another factor on which the result depends. Once the report is available, the doctor will discuss the results and help in understanding what it means. There are times when being tested positive will indicate that the disease or the condition does not exists. There can be occurrence of false positives and false negatives, the former signifies the existence of condition but in reality there is none and the latter indicates non-existence of condition but in reality it exists (Kamarehei, Khabiri & Saidijam, 2018). Due to this confusion, the elisa test may be repeated on a person within weeks or the doctor may ask to conduct some other sensitive tests in order to be sure about the condition.
Types of Elisa Test
The foremost step in Elisa Test is to immobilize the sample antigen in the petri dish. Two methods can be applied to immobilize the antigen, direct absorption on the surface of the dish or with the help of an antibody placed on the plate. The test has four categories named as direct, indirect, sandwich and competitive.
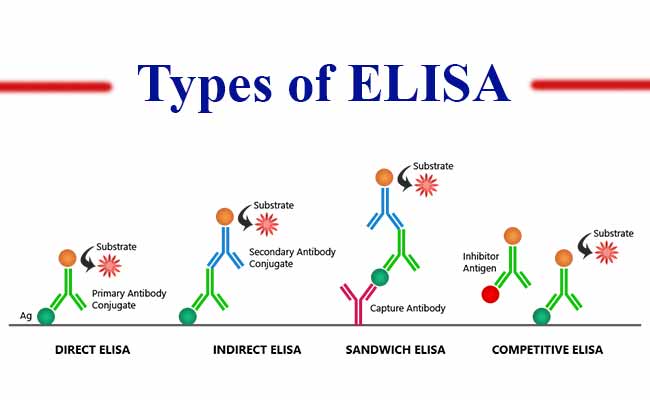
Source: (Lauridsen , Holmetoft & Petersen, 2016)
The image above helps in understanding how different elisa tests work. The categories are divided basis the modifications involved in the procedure. The sandwich elisa test involves higher sensitivity and robustness so it is considered as a powerful elisa assay.
Direct Elisa: It is a faster process to detect the presence of antibodies as compared to other tests as it uses fewer steps. In this technique, the antigen is directly coated to the wells of microtitre plate followed by adding the enzyme which is labeled as the main antibody which detects the complementary antigens. The test has fewer errors as it involves few steps while conducting the same and involves fewer reagents. The technique does not require a second antibody to be tested but there are certain disadvantages as well related to specificity. Due to the low specificity of antigen immobilization, there occurs a greater noise in the background when compared with other elisa tests (Lauridsen , Holmetoft & Petersen, 2016). It is because of no specific interaction between sample proteins and the target protein on the microtitre plate. The direct elisa is less flexible as all the target proteins are joined by enzyme-labeled antibodies. The process to label the primary antibodies is time taking and requires a lot of labor which can affect the immunoreaction. As there is no secondary antibody so it reduces the signal amplification leading to reduction in the assay sensitivity. It can be said that this technique is used for analyzing the response of the immune to a specific antigen.
Indirect Elisa Test: This method shows high sensitivity due to its employment of enzyme-labeled secondary antibody that connects with the primary antibody. It is considered as more economical when compared to direct elisa as it requires labeled antibodies in lesser numbers. The indirect elisa is more flexible due to the bonding character of enzyme-labeled secondary antibody with the other primary antibodies. Secondary antibody is majorly polyclonal in origin having anti-specie reactivity (Lauridsen , Holmetoft & Petersen, 2016). The indirect elisa also has certain limitation which relates to cross reactivity between secondary antibody and a bound antigen which may make a louder noise at the background. The test also involves an extra step to be taken when the secondary antibody is to be incubated. The process is more time consuming. Indirect elisa helps in identifying the total quantity of the concentrated antibody in a given sample.
Sandwich elisa: This method uses pairs of antibodies namely capture and detection antibody. The antibody can be either monoclonal or polyclonal. Every antibody has high specificity towards antigen epitome and it has been found that this assay is suited for antigens with two epitomes. The antibody pairs must have a matched specificity so that it binds with different epitomes and provide an accurate result. The antibody which is captured mixes with an antigen leading to the detection of elisa via direct and indirect technique. As the quantification of antigens takes place in the upper and lower layer of antibody so the entire process is known as sandwich elisa test (Pereira, Cunha & Fernandes, 2020). In case a sandwich elisa is applied then it requires to be validated more often due to its characteristic of providing positive results which may be false. At times the test can take a considerable time due to its requirement of matching pairs of antibodies. The foremost step of sandwich assay requires elisa plate to be coated with a captured antibody. The second step is to add a sample antigen to the plate which is followed by detection of antibody. The antibody that is detected can be enzyme-labeled or enzyme-unlabeled and based upon the same it will be identified as direct sandwich elisa or indirect sandwich elisa. The indirect sandwich elisa involves secondary enzyme-labeled antibody which is detected and introduced to bind the primary unlabeled antibody detected. The technique of sandwich elisa is more sensitive compared to direct and indirect elisa (Pereira, Cunha & Fernandes, 2020). The technique is more flexible while using it for detection purposes as it implements both methods, direct and indirect. The test helps in analyzing complex samples which are highly specific and sensitive as it does not involve purification of antigen in advance. But this technique also has some disadvantages which need to be considered like, the elisa kit needs to be tested beforehand for reaction and detection and this may be time consuming.
Competitive/ inhibition Elisa: Another name of this test is blocking elisa and it is based on plate/surface assay. It is known to be one of the toughest assays to be performed among all other elisa techniques but the other tests can be modified to meet the standards of competitive elisa. This method helps in quantifying the concentration of antibodies or the antigens in a provided sample which is based on a signal output by the resulting interference (Sahli, Mouelhi & Tlig, 2018). It showcases the competitive interaction of the given antigen or the antibody with a labeled antigen or the antibody which has a limited concentration. The signal which is obtained from the output has an inverse proportion to the concentrated antigen in a given sample which has a weaker output signaling at higher antigen concentration. The test demonstrates the coating of antigen over a microtitre plate. Once the optimal blocking and washing process is completed sample of antigens which are not known are added. It is dragged by adding labeled detection antibody with the use of substrates like 3,3’,5,5’-Tetramethylbenzidine or TMB. One of the important steps in this test is the competitive reaction which is caused due to the sample and the antigen which bounds the multiwall plates with main antibody (Sahli, Mouelhi & Tlig, 2018). If the concentration of antigen is high then the signal of the output will be low whereas if the concentration of antigen is low then the resultant output will be high. It is best to apply on situations when the available antibody is one for the sample antigen. It helps in detecting all types of antigens whether big or small as compared to sandwich technique. The process involves incubation of the sample with another component before proceeding to the reaction.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that Elisa test is helpful in the detection of antigen or an antibody in a given sample. It helps in confirming whether a person is suffering from a condition or not and if yes then whether he has an antibody to fight the condition or not. The Elisa test kits are available in the market which contains an already coated plate, detection antibody along with other chemicals which is required to perform the test. There are different types of Elisa tests and sandwich elisa test is considered to be an appropriate method.
References
Gandikota, C., Gandhi, L & Maisam, G. (2020) A novel anti?NS2BNS3pro antibody?based indirect ELISA test for the diagnosis of dengue virus infections. Journal of Medical Virology.
Hoffstetter, A., Giffin, D & Brown, L. (2018) An ELISA based method for quantifying arabinoxylan in wheat flour. Journal of Science, 79.
Kamarehei, F., Khabiri, A & Saidijam, M. (2018) Designing a novel ELISA method based on CagA, NapA recombinant antigens to increase sensitivity and specificity of Helicobacter pylori whole cell antigen detection.
Lauridsen H., Holmetoft, U & Petersen, A. (2016) Comparison of three commercial fecal calprotectin ELISA test kits used in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 51(2).
Pereira, C.S., Cunha, S.C. & Fernandes, J.O. (2020) Validation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Test Kit for Determination of Aflatoxin B1 in Corn Feed and Comparison with Liquid-Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Method. Food Anal. Methods.
Sahli, H., Mouelhi, A & Tlig, L. (2018) An advanced intelligent ELISA test for bovine tuberculosis diagnosis. Biomedical Signal Processing and control, 46.
Vencia, W., Migone, L & Vito, G. (2016) Validation of an Elisa method. XVII Congresso Nazionale S.I.Di.L.V., Pacengo di Lazise (VR), Italia, 28-30 settembre 2016 2016 pp.322-326 ref.4












