Electrical Machines Assignment: Fundamentals of Power Electronics
Question
Task: LO1: Explore the principles of operations and the characteristics of electrical machines and their industrial
Task 1
Discuss the different types of electrical machines and their industrial applications
Task 2
Illustrate the principle of operation of DC machines and induction motors with the aid of
circuit diagrams and waveforms.
Task 3
Investigate the construction, operation and characteristics of synchronous machines.
Task4
Utilise Matlab and Simulink or similar commercially available software for modelling and
simulation of a DC motor.
HNC/HND Engineering 3
Task5
Analyse the characteristics of induction motors and their equivalent circuits.
Task6
Critically evaluate the performance of DC motors using Matlab/Simulink or similar commercially available
software to corroborate its performance or otherwise
LO2 Examine the fundamentals of power electronics converters used in power processing units for electric drives
Task 7
Illustrate, with the aid circuit diagrams and waveforms, the operation of a AC to DC uncontrolled or
controlled converter (half wave/full wave/three phase).
Task 8
Illustrate, with the aid of circuit diagrams and waveforms, the impact of resistive and inductive loads on the
converter’s input and output characteristics.
Task9
Investigate the importance of input and output filters in a AC to DC converter.
Task10
Show how Matlab and Simulink or similar commercially available software may be used for modelling and
simulation of a AC to DC converter.
Task11
Evaluate the key performance characteristics of DC to DC converter.
Task12
Critically evaluate the performance of DC to DC converter using Matlab/Simulink software to corroborate its
performance or otherwise.
LO3 Demonstrate the fundamentals of DC drives and their industrial applications
Task13
Discuss the operating modes of DC drives and control parameters.
Task14
Explain the importance of DC drives in industrial applications.
Task15
Discuss the principle operations of single/three phase choppers with the aid of circuit diagrams and
waveforms.
HNC/HND Engineering 4
Task16
Illustrate, with the aid of circuit diagrams and waveforms, the implementation of closed loop control of DC
drives.
Task17
Develop an open loop block diagram of a DC motor and derive the relationship between the input and the
output of the systems.
Task18
Evaluate how DC drive circuits are used to control the speed of DC motors.
Task19
Analyse the impact of DC drives on the operation and performance of an industrial control system.
LO4 Demonstrate the fundamentals of AC drives and their industrial applications
Task 20
Illustrate the operating modes of AC drives, their control parameters and their importance in industrial
applications.
Task21
Illustrate, with the aid of circuit diagrams and waveforms, the principles of operations of single/threephase AC drives.
Task22
Review, with the aid of circuit diagrams and waveforms, the implementation of closed loop control of AC
drives.
Task 23
Develop an open loop block diagram of an induction motor and derive the relationship between the input
and the output of the systems.
Task 24
Evaluate how AC drive circuits are used to control the speed of induction and synchronous motors.
Task 25
Analyse the impact of AC drives on the operation and performance of an industrial control system
Answer
Task 1
In this electrical machines assignment, we can classify electrical machines two types
1. Static machines – A machine that is used to build up electrical charge or high voltages e.g. Transformers.
2. Dynamic machines –machines associated with movements. E.g. generators and motor.
a. transformers – it is a device in which both input and output feed is electrical power.
Application – It is used for increasing low ac voltage or decreasing high ac voltages as per our requirement.
b. generator- herein electrical machines assignment we give mechanical input and we receive electrical output.
Application – used for power supply, charging battery since it gives constant output voltage etc.
c. motor – it is a device which work reverse of generator. Here mechanical output is produced in terms of motor rotation.
Application – motors are used in pumps, fans, turbines, power tools etc.
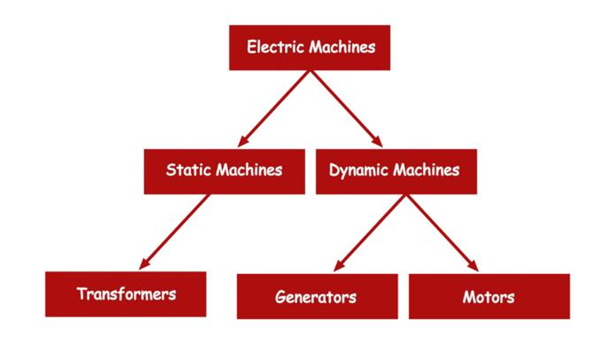
Figure 1-Types of Electrical machine
Task 2 of electrical machines assignment
Principle of operation of DC machine
It is a device that either change electrical to mechanical energy or vice versa.
DC machine are of two types
a. DC motor – it converts DC power to mechanical power.
Principal of DC motor – When current passes a coil which is placed within the magnetic field then on coil a magnetic force will be exerted that will generate a torque and rotates the dc motor.(taufer, 2016)
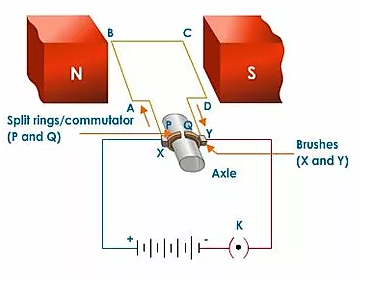
Figure 2-Circuit diagram of DC motor
The force that is produced by this process is given by F =BIL where magnetic flux density is given by B and L denotes the length of conductor that is placed inside magnetic field.
b. DC generator – DC power is obtained from mechanical power.
Principal of DC generator –it operates on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. It says when conductor is placed in an unstable magnetic field than an electromagnetic force is started getting induced in it.
This induced emf is given by equation mentioned below in the electrical machines assignment
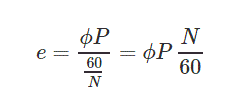
Here
N = Speed of armature conductor
Total flux = P
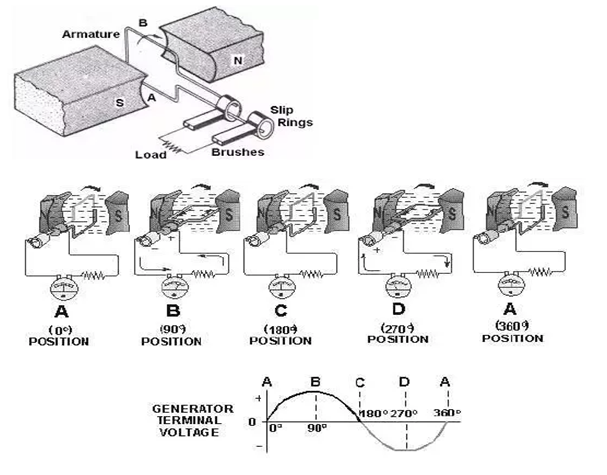
Figure 3-DC generator operation and working
The above figure provided in the electrical machines assignment shows how terminal voltage is generated in generator.
Task 3
Construction of synchronous machines
Synchronous machines consist of alternator which consists of stator and rotor.
It is clear on this electrical machines assignmentthat the static part of the machine is stator which consists of parts winding, stator core, stator frame etc(E, 2004).Armature winding is carried by stator and here we get the generated voltage.At terminal box the output is taken.
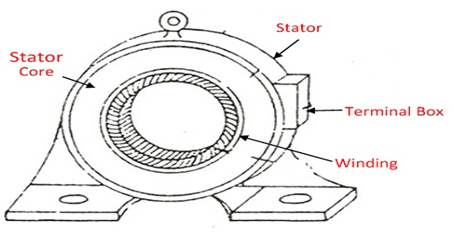
Figure 4-Construction of Stator
The rotating part of machine is called Rotor. it helps in producing the field flux. Rotor is generally of two types
a. salient pole rotor
It is evident in the electrical machines assignmentthat poles in this type of rotor project out form the rotor core surface. It has non uniform air gap. It is mechanically strong because it is part of rotor.
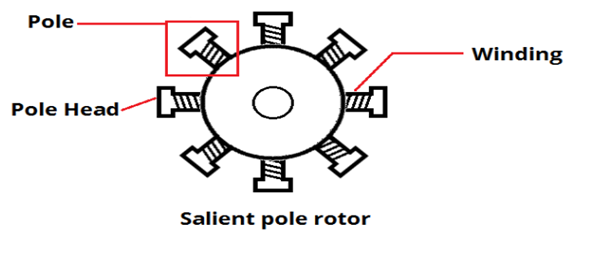
Figure 5-Construction of salient pole rotor
b. cylindrical rotor type.
There are no projecting poles in this type and there is uniform air gap between stator and rotor. It is not a part of rotor since it is fixed with bolts so it is not mechanically strong.
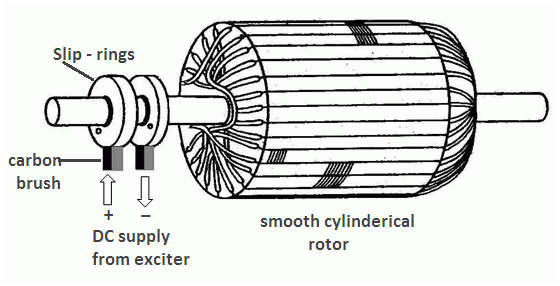
Figure 6-Cylindrical rotor
Principle of synchronous machine
Synchronous machine mentioned in the electrical machines assignment work on the principle of law of electromagnetic induction According to law of electromagnetic induction which is also called Faradays first law it states that a rotating current carrying conductor in field is induced by emf.
Working
Once direct current passes through winding of rotor a magnetic field is produced in the machine. This filed is rotating in nature. Due to this a 3phase voltage is produced at Stator winding.
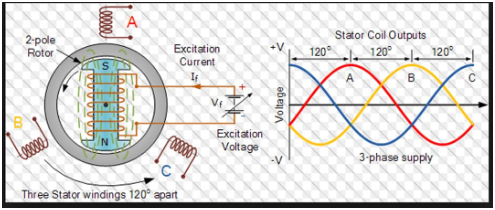
Figure 7- Working of Synchronous machine
The generated three phase voltage is given by

As mentioned in the electrical machines assignment, Synchronous machines are used in various equipments like coolers, refrigerator, fans, air conditioner etc.
Characteristic of synchronous machine are discussed below within this electrical machines assignment
a. synchronous motor run with synchronous speed which is given by
Synchronous RPM = 120*frequency/number of poles
b. it starts as induction motor.
c. it operates at a wide range of power factor.
d. speed controlling can be done by varying frequency.
Task 4 of electrical machines assignment
Using Simulink software, we can draw DC motor circuit as follows with following parameters
Equations used for DC model simulation
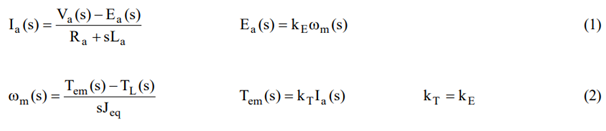
These equations noted in the electrical machines assignment can be easily implemented in Simulink using standard blocks as shown below
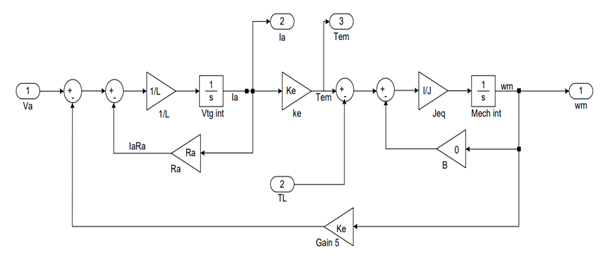
Figure 8-Circuit diagram of simulation of DC motor
Task 5
Induction motor
It is a device which works on the principle of transformer. Electromagnetic induction produces a voltage in rotor when an EMF is supplied to stator. (Rashid, 2004)
Slip = synchronous speed – actual speed / synchronous speed
The synchronous speed is given by = 120*frequency/Poles
Equivalent circuit of induction motor is shown below
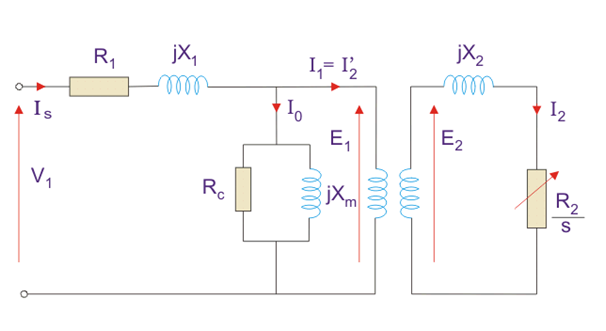
Figure 9-circuit of induction motor
Analysing the characteristics of induction motors
The curve between torque and slip give us information about characteristic of induction motor by giving information about torque with the slip. (Warachart Sae-kok, 2003)
Mode of operation can be described in three modes as discussed in the next section of electrical machines assignment
a. breaking region
In this region motor start rotating in reverse direction due to change in polarity. So, rotating in reverse direction makes the motor to stop in short time.
b. motoring region
It is the mode in which motor rotates below synchronous speed. When slip varies from 0 to 1 torque in motor varies accordingly. Generally, torques varies directly with slip.
c. generating region
In this motor rotation is done above synchronous speed. Due to negative torque and slip motor receive mechanical energy and provide electrical energy. That is why it called generating region.
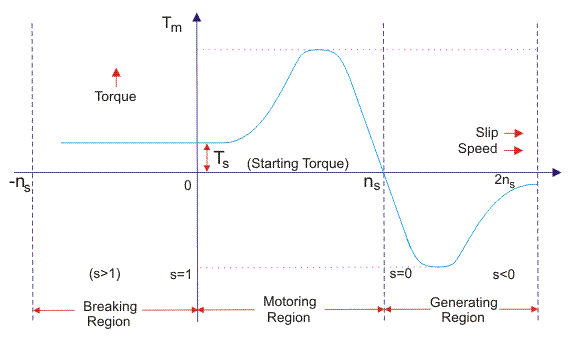
Figure 10-Torque slip curve for three phase induction motor
Task 6
Simulation output of the DC motor modelling that is done in Task 4 of electrical machines assignment.
a. waveform for wm
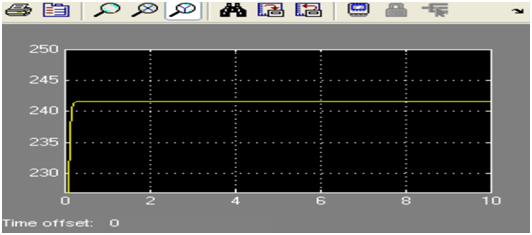
b. Waveform for Ia
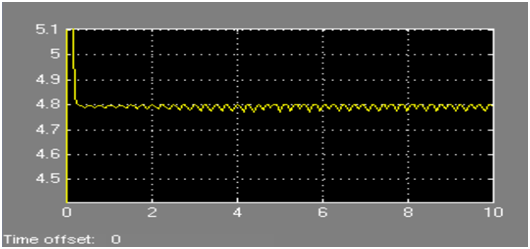
c. Waveform for Tem
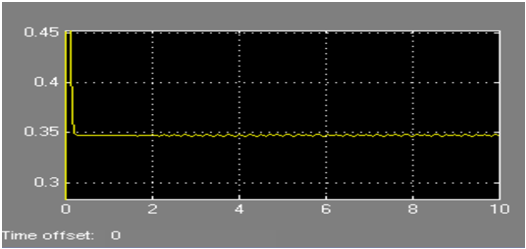
Task 7of electrical machines assignment
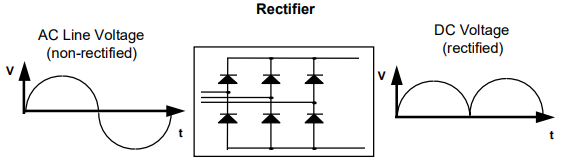
Rectifiers are the converters that are used for AC to DC conversion. That rectifier circuit that uses diode for conversion process is called uncontrolled rectifier and those rectifier circuits that usethyristor for conversion is called controlled rectification.(Lung-Sheng Yang, 2012)
Let us discuss uncontrolled rectification
Herein electrical machines assignment, uncontrolled rectification can be done for following types of circuit
a. half wave rectifier
In the diagram below a half wave rectifier is shown with resistive load. Only one diode is connected that is used for rectification process. This diode as we can see in the circuit is fed with secondary transformer that will give ac signal as an input to diode.
In positive cycle of signal diode conducts since it is forward bias and in negative cycle of signal diode conducts will not conduct since it is reverse bias. The output mentioned in the electrical machines assignment that is received during each cycle is shown in waveform diagram.
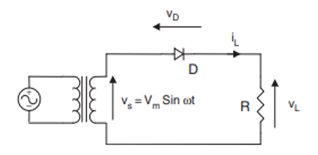
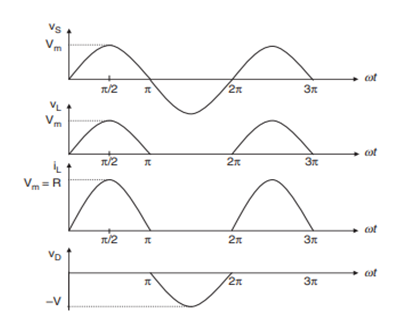
Figure 11-circuit and waveform of half wave rectifier
b. Full wave rectifier
In the diagram presented in the electrical machines assignment a full wave rectifier is shown whose input is given by centre tapped transformer. There are two diodes in this circuit and each work as half wave rectifier which together in output makes it full wave rectifier. (Hughes, 2013)
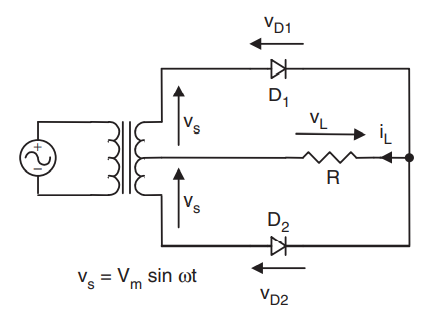
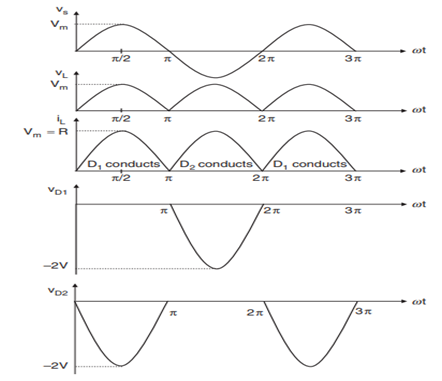
Figure 12-Circuit and waveform of full wave rectifier uncontrolled
c. bridge rectifier
If we have to make bridge rectifier than we have to use four diodes to complete the circuit. In case of bridge rectifier, we can avoid use of center tapped transformer(Hughes, 2013). At positive cycle diode D1 and D2 conduct and at negative half cycle diode D3 and D4 conducts. This bridge rectifier has the best efficiency among other circuits.
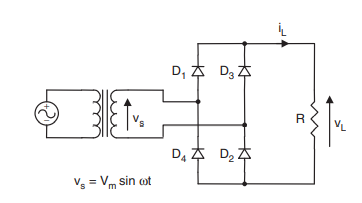
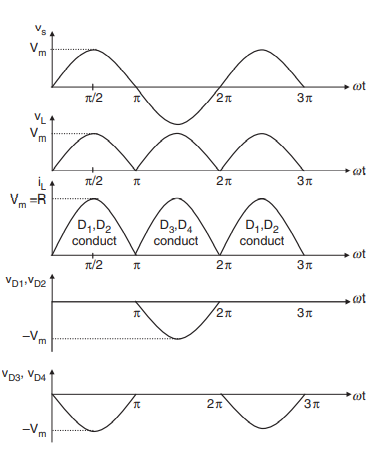
Figure 13-Bridge rectifier
Three phase diode rectifiers
A three phase rectifiers is required when we need power output higher than 15kW. It is of two types one is star rectifier and other is bridge rectifiers.(Rashid, 2004)
Talking about star rectifier in the electrical machines assignment
In start rectifier conduction will only happen when voltage at one phase is higher than other two phases.
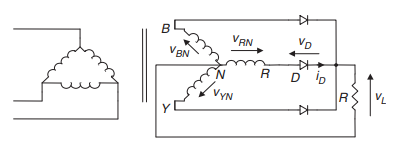
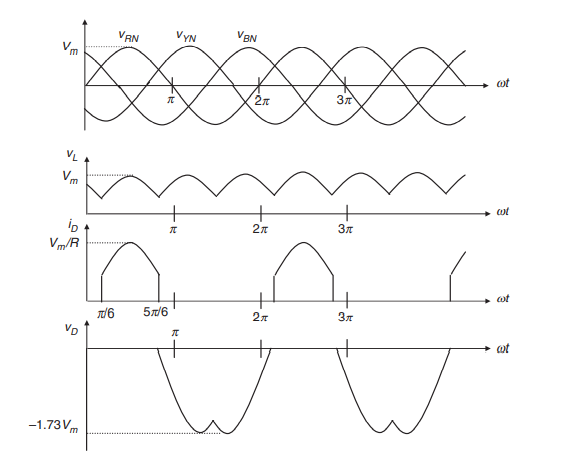
Figure 14-three phase rectifier
Controlled rectifier
We know that for controlled rectification we use thyristor instead of diode. The simplest phase-controlled rectifier is single – pulse rectifier.
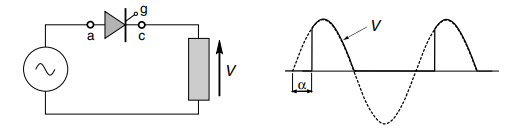
Figure 15-Single pulse-controlled rectifier
During the positive supply thyristor will block the current until the gate pulse arrives till then voltage is 0 across the resistive load(Hughes, 2013). And when firing pulse is triggered device is turned on. Waveform of his circuit is shown in diagram.
Controlled full wave rectifier
This circuit is formed using four thyristors as shown. Same circuit can be drawn in two ways.
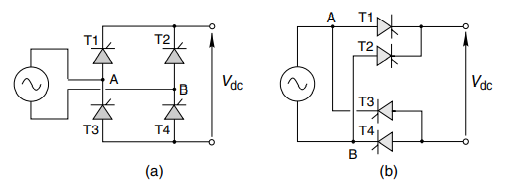
Figure 16-Controlled full wave rectifier
The output voltage in this circuit depends on the nature of load that we apply like resistive or inductive load.
Task 8 of electrical machines assignment
As we have seen in case of controlled full wave rectifier, type of load decides the output of rectifier.
Impact of resistive load
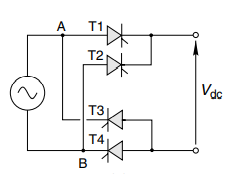
In the above diagram provided in the electrical machines assignment, when the supply at terminal A is positive than diode T1 and T4 are active. And on the other half cycle terminal B becomes positive and it will make diode T2 and T3 active. The output of this is shown in the diagram
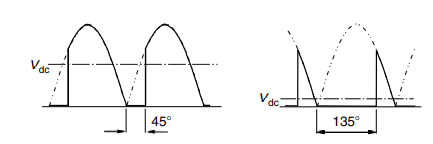
Figure 17-waveform
There are two pulses in the output waveform. One is fired with firing angle of 45 degree and other one is fired with angle of 135 degree.
The maximum output voltage that we can obtain is
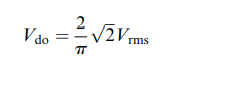
And Vdc is the mean voltage obtain with firing angle it is given by
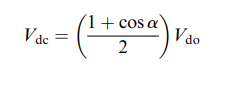
So, we can see herein electrical machines assignment that at resistive load dc voltage can be varied with firing angle alpha and maximum at Vdo.
Impact of Inductive load
In inductive load current cannot change instantaneously. So, it is not possible to give general formula for mean voltage in terms of firing angle alpha. If we want to get output voltage waveform for given alpha then there is a need to give sufficient inductance that will prevent the load current from falling to zero. (Singh, 2011)
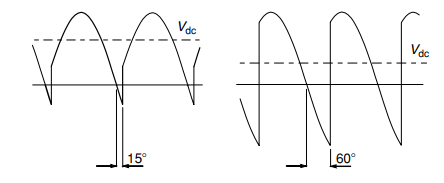
Figure 18-waveform on inductive load
Waveform output at different firing angle is shown in figure above. With resistive load output voltage is never negative but with inductive load output voltage becomes negative at some time the reason behind is due to the smoothing out of the current due to inductor.
Circuit diagram with inductive load
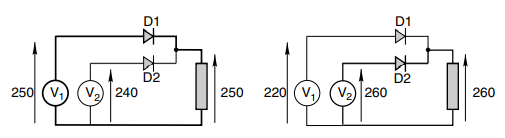
Figure 19-inductive load circuit
From the above circuit diagram noted in the electrical machines assignment, we can conclude that diode with highest anode potential will conduct. In case of inductive load equation for mean dc voltage is given by
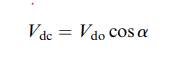
So, when alpha becomes greater than 90 degree it will give negative output voltage.
Task 9 of electrical machines assignment
Importance of input filter in AC to DC converters
a. Input filter helps in reducing noise that is produced in the power supply switching element. The filter that is used passes 50 to 60 Hz mains frequency and it will attenuate higher frequency noise and harmonics.(K. Arora, 2016)
b. in other parts of the circuit reactive element like capacitor and inductor play very important role. As we know that capacitor cannot pass DC and it can be used in series as a high pass filter and in parallel to shunt high frequency to ground since it will prevent from getting through the converter.
c. input filter sometime also has varistor it will help in preventing high voltage spike. Importance of output filter in AC to DC converters
a. at output in-line chokes are used to reduce the differential noise by increasing the rise time of voltage pulse.
b. Output filters are required to minimise EMI and to provide reliable operation to power converter and load.
c. filtering for DC output usually comprises of LC networks since it will help in providing energy storage and reducing differential noise.
Task 10
Model made using MATLAB for simulation of AC to DC converter.
Here we can see that 4-thyristor circuit is connected with input pulse generator and a NOT logical operator is used to give negative cycle input to thyristor 3. (Chen, 1993)
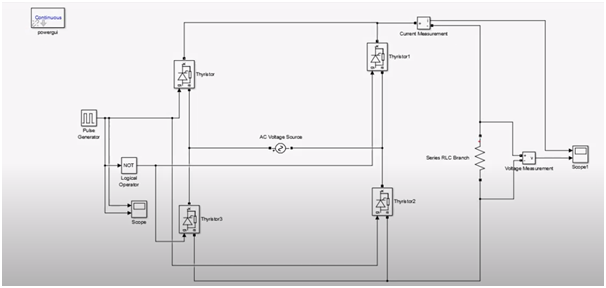
Output of simulation model
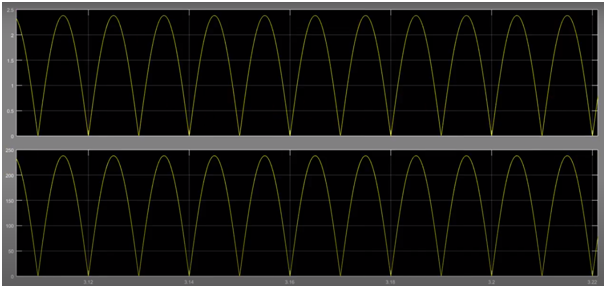
Task 11 of electrical machines assignment
Performance characteristics of DC to DC converter(Hughes, 2013)
DC to DC converts are mainly used to regulate voltage. These converters circuit are high frequency power circuit that uses capacitor, inductor, and transformer to smooth out the noise to get regulated DC voltages. Some important performance characteristics of DC to DC converters are discussed below within this electrical machines assignment:
a. Current rating tells us the maximum amount of current that can be provided by DC -DC converter to load.
b. temperature rating tells us the maximum temperature that can allow DC -DC converter to work under full load condition. If it exceeds this temperature rating than it can be shut down.
c. transient response is provided in DC to DC converter since this converter uses closed loops feedback so for any change in load current and input voltage converter will make changes accordingly.
d. Voltage rating – DC to DC converter have mentioned limit of the voltage level that can be transformed.
Task 12
DC -DC converter model using MATLAB<
In this mode 4 ideal switch is used which are connected with DC voltage source of 100 V. After that transformer is connected to the output of the converter and setting up nominal power, frequency, and peak voltage rms. Now diodes are required and output of transformer is connected to diodes. Finally, diode is connected with RLC and one terminal of RLC to mid-point of transformer.
After that we Simulink the sources by giving pulse and connecting with switches by providing correct delay. At both input and output voltage measurement device is added and connected both voltage measurement devices to one scope.
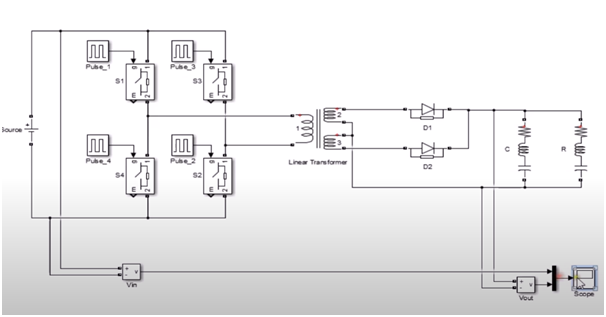
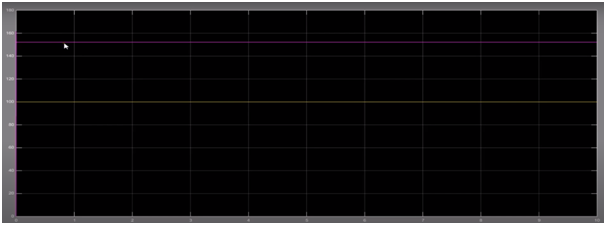
As we can see from the simulation that our input voltage is 100V and Output voltage we are getting is 150V.
Task 13 of electrical machines assignment
DC motor drive has four operating modes these are discussed with controlled parameter like armature voltage, speed, torque and power.(Hughes, 2013)
a. forward motoring
In forward motoring armature current is flown since back emf is less than terminal voltage. Here speed, torque, power is positive hence motor rotates in positive direction.
b. forward braking
in this mode of electrical machines assignment there is no terminal voltage and motor work as generator. Here speed is positive and torque and power is negative. This mode is also called regenerative motoring.
c. reverse motoring
in this mode terminal voltage direction is interchanged so direction of motor is also reversed. Here speed and torque are negative and power is positive.
d. reverse braking
This mode is also called regenerative braking. Here torque is positive.
Diagram showing controlled with current and speed feedback control loop
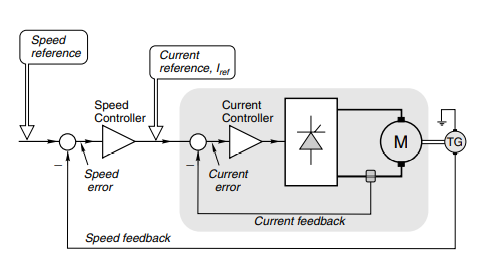
Figure 20-control loop diagram with feedback
Task 14
DC drives are nothing but a speed control system for DC motor. DC motor drives is very necessary for smooth operation of motors. It helps in speed regulation, starting motor, braking and reversing. DC drive technology is efficient and reliable and can be operated easily. DC drives are used in various industrial applications like controlling speed of DC motors generally thyristor-based technique is used. Programmable logic control used in automation industry makes use of DC drives.
Task 15 of electrical machines assignment
Chopper type converter is generally used when source supply is DC. In chopper type motor current only flows from supply terminals for parts of each cycle.
The mode of operation of chopper fed dc motor is in first quadrant. Here speed, torque, power is positive hence motor rotates in positive direction. (Rashid, 2004)
During the time period T when the chopper is on the load voltage is equal to source voltage. During off time of chopper load current flows through the diode. The load voltage is 0 during the time chopper is off since load terminal is short circuited by diode.
Average load voltage = V0 = Ton/ (Ton +Toff) * Vs
Waveform of the output is shown in figure
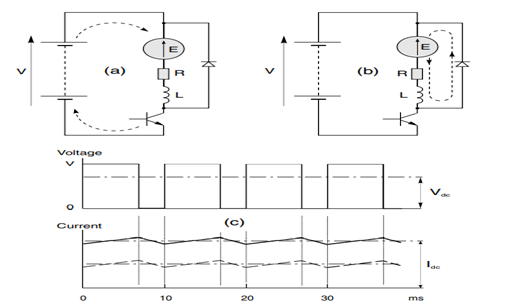
Figure 21-diagram and waveform for chopper type
Task 16
Closed loop control of DC drives can be obtained using angle feedback from a servo type potentiometer and controlling angular position(Hughes, 2013). The set up for this is shown in the diagram.
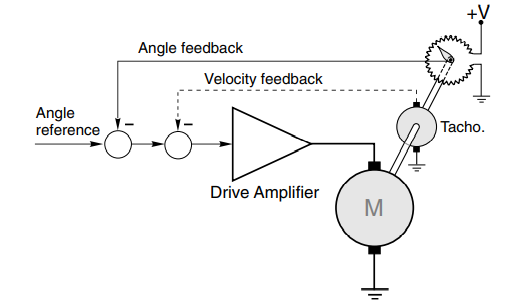
Figure 22-closed loop control ac drives
The angular position follows the reference voltage. Potentiometer is mounted on output shaft will help in providing feedback voltage which is proportional to the actual position of the output shaft.
This feedback voltage is subtracted from the reference voltage to get the resulting positional error signal.
This positional error is amplified finally and used to drive the motor.
Waveform of this closed loop position-controlled system is shown below
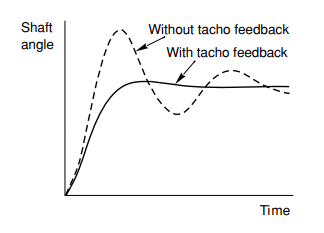
Here we can clearly see variation with and without feedback.
Task 17
Open loop control of DC motor
In open loop speed of motor only depend upon the supply voltage. If the potentiometer sends less resistance voltage is high and the speed of motor is also high.
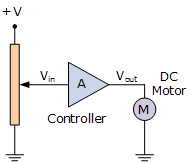
Figure 23-open loop dc motor
Open loop model is cheap and very easy to implement. This relationship between input and output is not disturbed by any external factor. But variation in the system make impact on motor speed.
Task 18of electrical machines assignment
DC drive is one of the important components. It helps in converting ac to dc current that will run the motor. Speed in DC drive is proportional to armature voltage.
A DC drive circuit consist of
a. operator controller
b. drive controller
c. DC motor
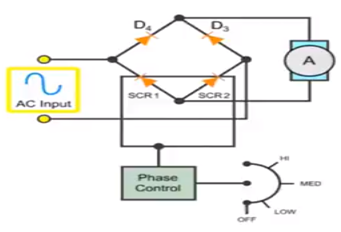
Figure 24-Role of DC drives
Task 19
DC drives helps in saving the power in industry and it is industry workhorse for decades. It has various advantages like it gives precise torque and speed control without any complex electronic circuits.(Hughes, 2013)
These DC drives are used in many industries since nowadays dc drive include all components like how to operate, maintain and trouble shoot the system which makes them one of the important. It includes fuse, SCR converter, field exciter, heat sinks etc all included in one terminal unit. This make DC drive more reliable and important from industry point of view. A diagram showing the package of DC drive design.

Figure 25-modern dc drives
Task 20
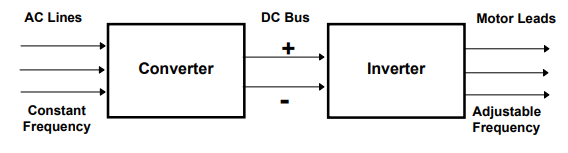
An AC drive is a device for controlling the speed of motor by controlling the frequency of the voltage that is supplied to motor.
This can be done by
a. by first converting 3 phase 60Hz frequency AC power to DC power.
b. then by using switching mechanism it inverts DC power into sine wave ac with adjustable frequency. This ac is connected to motor.(Jarc, 1983)
For AC drive there are two controls available for frequency control
1. Six step
2. Pulse width modulated
Converter will convert AC to DC.
Once DC voltage is received it is smooth out with the use of filter and then fed to inverter to get AC voltage.
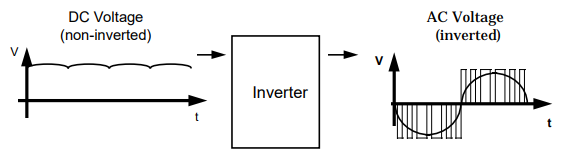
Industrial importance of AC drives
AC drives are used in industries like automation, food and beverages, chemical, textile, paper, wood and metallurgy.
Task 21
AC drives operation can be explained in three sections. It consists of a rectifier unit, a dc bus unit and an inverter unit.
A figure with three phase supply with ac drive working is shown below in the electrical machines assignment
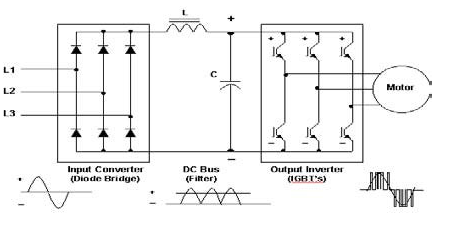
Figure 26- 3 phase ac drives working
Rectifier unit help in converting supply ac voltage to dc. The DC bus section consists of filter circuit that willhelp in filtering of DC wave that we have got. After the unwanted harmonic is removed it is fed to inverter section which consists of six IGBT. The dc signal that is filtered out is supplied to feed to an ac motor to make it operate.
In the whole process frequency is varied from input to output and that is how ac motor is controlled by varying the frequency.
Speed (rpm) = Frequency (Hertz) x 120 / No. of poles
One important thing to be noted that the ratio of output voltage and frequency always remains constant for all AC drives.
Task 22
In the circuit below provided in the electrical machines assignment we have closed loop flux vector with ac drive. In this circuit torque is indirectly controlled by the frequency and voltage value that is determined by the feedback circuit.
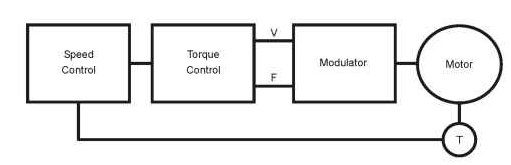
Figure 27-closed loop ac drive circuit
Herein electrical machines assignment, there are several advantages of this type of drive
a. it gives good torque response.
b. full torque at 0 speed or at 0.5 Hz output.
c. accurate speed control is possible with the help of feedback.
Waveform showing torque speed curve
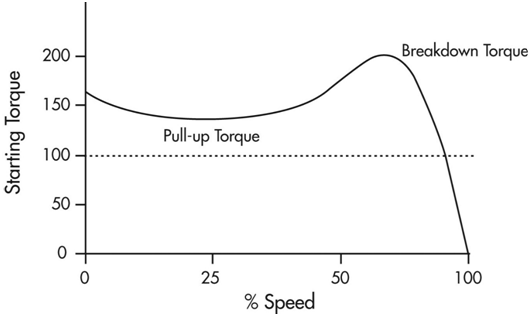
Task 23
The open loop method is most common method to control speed. In the block diagram we can see that PWM is merged with inverter block.
Some disadvantages of open loop drive are discussed below within this electrical machines assignment:
a. preciseness is reduced in controlling speed.
b. synchronous speed remains only control variable.
c. the operation can sometime operate in unstable region.
d. due to unstable region stator current exceed rated current and can destroy circuitry.
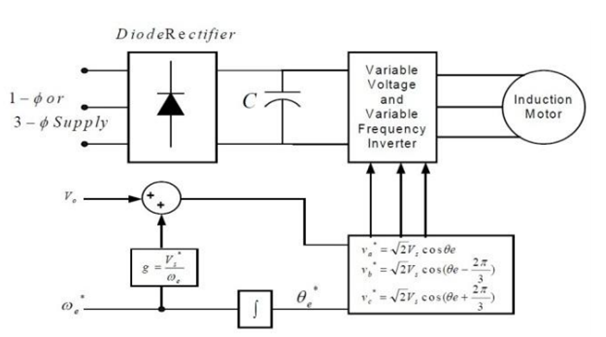
Figure 28-open loop ac drives
To avoid the above condition PI controller is used. It will help in avoiding error.
Task 24
As we know at the output of PWM VFD’s a pulse is produced is of varying width these are merge to form the sinusoidal ac signal that can start the motor. It is stated herein electrical machines assignmentthat to reduce unwanted harmonics converters uses
diode to remove it.(B. T. Ooi, 1988)
A switching frequency is produced from the speed of power device that remain either ON or OFF. This frequency ranges between 3Kz to 4Khz as compare to SCR based carrier frequency that is only 200 to 300 per second thus, we get higher resolution of output waveform.
So, the main phenomena in controlling speed of induction motor are by controlling V/F ratio which is easily obtained in ac drives.
Similarly, in this electrical machines assignment, in synchronous motorspeed is control by changing the supply frequency.
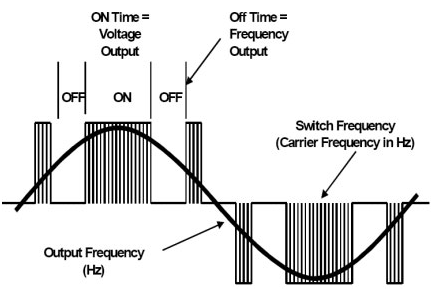
Figure 29-output waveform of ac drives that drives motor
Task 25
Impact of AC drives on industrial system mentioned in the electrical machines assignment:
a. when it operates at lower speed it saves lots of energy.
b. Also due to lower rotating speed life of the rotating component is increased.
c. it helps in reducing noise, thermal and mechanical stress.
d. it provides lower KVA rating and has higher power factor.
e. it provides controlled starting current.
f. it helps in reducing power line distribution.
g. it provides controlled acceleration.
h. adjustable torque limit and operating speed.
i. it eliminates the need of mechanical drive component.












