Economics Assignment: Circular Economy in Adidas
Question
Task:
Develop the economics assignment in terms of circular economy aspects in Adidas considering all the principles, benefits and significance of circular economy.
Answer
Introduction
The economics assignment examines the words of Geissdoerfer et al. (2017) that the circular economy is mainly an industrial system. The basic characteristic of this system is that the design and intention is regenerative as well as restorative. The concept of end of life for products is replaced by restoring them for reuse. The system is inclined towards the use of renewable energy. The use of various toxic chemicals is banned in this circular economy. The chemicals hinder the process of reuse, which eventually prevents the products to return to the biosphere. The design of the materials, systems, products and models in a circular economy is made superior in form so that the generation of waste is reduced.
In this economics assignment, the concept of circular economy is discussed. The principles, benefits and significance of the circular economy have been evaluated under the theoretical perspectives. The circular economy adds value to business, economy, society and environment (Witjes and Lozano, 2016). It creates better job opportunities by implementing the circular supply chain, which has been examined in the report. The practical perspective investigates how Adidas has adopted the principles of a circular economy to increase the economic as well as social efficiency. The circular economy also minimizes the adverse environmental impact, which is clearly analyzed in the report.
Overview of the organization
The company that will be discussed in the economics assignment in terms of circular economy aspects is Adidas that is regarded as a true global economy. The company is rooted in Germany with more than 60000 individuals employed all over the world. Adidas is the German producer of athletic shoes as well as sporting merchandises (Adidas, 2020). It turned out to be the largest producer of sportswear in Europe while being the second largest in the world after Nike. The company is known to trade with goods with a three-stripe trademark. The key customers of Adidas include young adults along with children who are passionate regarding sports as well as fitness. The majority of customers belong between the age group of 15-30 years hailing from upper middle class as well as luxury class.
Theoretical Perspective
Circular Economy
According to Heyes et al. (2018), in any linear economy, the natural resources are utilized and further transformed into various products. These products are later on disposed of. However, the scenario in case of a circular economy is quite different. The aim of a circular economy defined in the economics assignment is to bridge the gap that exists between the cycles of the natural ecosystems and the production made out of it. The humans mainly depend on this raw material transformation and production. A circular economy is pro-environmental. The non-biodegradable wastes are reduced as much as possible, while the rest is recycled and reused. The wastes that are biodegradable are used for composting. The circular economy also tries to reduce the usage of different chemicals so that the natural systems could be regenerated. The renewable forms of energy are used in this economy.
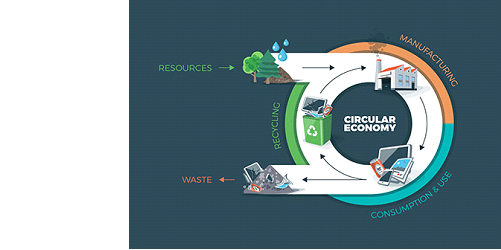
(Source: Jabbour et al., 2019)
Concepts and Characteristics of the Circular Economy
The circular economy is driven by certain principles, which lay the foundation of the system.
Sustainable Use of Energy and Resource: The main objective of the circular economy is to drive out the wastes out of the system. The economy intends to design a way in which the generation of wastes will be minimized (Jabbour et al., 2019). The circular economy even tries to nullify the existence of wastes. The design of the products is made in such a way that they last long. The best quality raw materials or inputs are used for manufacturing the products so that they do not get wasted soon. The economy promotes renewing and reusing what is otherwise considered as a waste. The product cycles in the circular economy are so tight that they minimize the loss of labour and energy by reducing waste generation. The natural capital is conserved and enhanced. The stocks are well maintained under the circular economy and a balance is established in the flow of renewable resources.
Natural Cycle and Design: The natural or biological cycles and the technical cycles run the economy. The consumers are a part of the biological cycle. Various biological or natural products are designed to feed the living system. The biological processes like composting or anaerobic digestion helps in retaining the products back into the system. The natural cycles provide further resources for the living systems. For instance, ocean or soil is renewable resource which supplements the economy. Technical cycles cannot renew the materials. Thus, they are designed in a way which would help in further reuse, recycle, repair or remanufacture (Ünal et al., 2019). Thus, in a circular economy the resources are optimally utilized through circulation of the products, materials or components. The utility of the biological or technical cycles in enhanced in a circular economy.
Renewable Energy: The energy that is used in the circular economy is renewable in nature. This increases the resilience of the system and reduces the dependency on resources (Stahel, 2016). The effectiveness of the economy is improved by designing the system in such a way that the negative externalities are wiped out. The energy is derived from renewable sources so it is repeatedly circulated and reused.
What are the benefits of Circular Economy discussed in the economics assignment?
Unlike the linear model, the circular economy adds value to the economy, business, society and environment. The goods are not produced, used and wasted like the linear economy. The goods are designed to improve the performance of the resources.
Business: The businesses benefit greatly from the circular economy. The input costs are quite low in this model. There are new streams opened from which profit can be earned in business. There are new opportunities that are generated for market operations which businesses can utilize. The wastes are reduced and the energy consumption is also less in the circular economy. Thus, the costs are curtailed. The raw materials used are lesser in quantity. Most of the products are recycled and reused. This makes the business organizations less dependent on the volatile market prices. The cost of labour is also minimized. The supplies are continuous and the organizations’ business is protected from any crisis, like geopolitical or socio-economic. As per Nußholz (2020), it is stated in this economics assignment that the businesses gain more resilience under circular economy as they depend least on the climatic changes. The circular economy creates higher demand for various new services. The businesses like reverse logistics that aim at reintroducing the products after their end of life have higher demand in the circular system. The marketers or sellers who promote longer life and greater utilization of resources and products make good business. The businesses associated with refurbishment or remanufacturing earn good profits in circular economy as their goods are in high demand (Rizos et al., 2016). The businesses are able to know their clients better through the circular economy. The products are all meant to serve the customers for a longer time. Therefore, the consumer-producer relationships improve due to this long term bond. This helps the businesses to foster and develop their products by understanding the customers’ needs.
Society: The society benefits greatly as the circular economy preservation of the natural environment. The negative externalities are minimized and a pure and safer environment is available for the society. The circular economy contributes towards a social enterprise of making a better and sustainable society with least wasteful behaviour (Manninen et al., 2018). Thus, this system has high social value. The employment growth takes place, which reduces the misery of the people in the society. People have job and income flow. The social problems like poverty, hunger, deprivation, discrimination, high death rate, high infant mortality rate, etc. are resolved to some extent under circular economy. The economic growth is fostered as more resources are preserved and put to optimum use.
Environment: The circular economy aims at protecting the ecosystems across the planet. The natural resources are optimally utilized following the sustainable nature of consumption. The emission of greenhouse gases is reduced. The productivity of the economy and its various sectors is enhanced through minimization of waste generation. The negative externalities are reduced. According to Lieder, Asif and Rashid (2017), the circular model aims at restoring the natural ecosystems. The soil quality is retained through composting and anaerobic processes. The biodiversity is conserved and the soil degradation is controlled. The economy prohibits the increased use of chemicals as it harms the natural systems. The climate is protected as toxic substances are banned and pollution is controlled.
Role of Circular Supply Chain:
The circular supply chain comprises the entire process of production, consumption and disposal (Lewandowski, 2016). The raw materials or inputs are first taken through the manufacturing process. Once the inputs are transformed into finished products, they enter the market. These products are consumed by the consumers. At the end of life of these products, they are discarded by the consumers. Thus, these products are transitioned into wastes. The aim of the circular economy is to optimize this process. The readings developed in the economics assignment signifies that the performance of the circular supply chain has to be enhanced so that the economy retains the natural resources in their original form, the resources are put to optimal use and wastes are minimal. The reverse logistics process is embraced to make the discarded or disposed products or materials reusable. The processes and products are gifted a new life even after their end of life through remanufacturing and reusing. The waste is reduced in a circular supply chain and the wasted products are renewed for further use.
The objective of the circular supply chain is aligned with the circular economy. The circular supply chain plays a very important role in encouraging the producers and sellers to collect the discarded products or materials and put them to reuse (Kirchherr, Reike and Hekkert, 2017). The manufacturers gather the discarded or disposed items, remanufacture them and resale them in the form of refurbished items. The manufacturers, who are a part of the circular supply chain, are encouraged to produce goods that have a long life. The products should have more than one time use so that they are not easily discarded as wastes. The operational process, through which the used or discarded items are melted, moulded and remanufactured or refurbished, helps in turning the waste products back into the supply chain. The circular supply chain reduces the generation of wastes, minimizes pollution and maintains a sustainable approach. The production becomes self-sustained as the raw materials are kept in circulation and they return back to the production cycle. The circular supply chain is very effective in making the economy pro-environmental and sustainable.
Role of the Circular Economy in Promoting Job Creation
The circular economy helps in job creation. As per Jain (2017), the reverse logistics, refurbishment and remanufacture based jobs would be created in the market. The jobs that were based on repairing, recycling and reusing of products had fallen out of demand. However, it is also clear on this economics assignment that these jobs would be recreated and be in high demand in a circular economy. The skills of remanufacturing can be put to economically beneficial use again. Thus, many people who had lost their jobs would regain their professional positions and many new job aspirants would find jobs. Thus, the circular economy opens up new job opportunities.
Application of Concepts
Business model in terms of circular economy
The business model is defined as a strategy that is used by a company to initiate profit. In other words, it is regarded as a high-level policy that is used to carry out a business in a profitable way. The business model has been illustrated with regards to operations as well as supply chains in terms of circular economy aspects. Adidas is known to provide major focus on innovation in order to create sustainability. According to Storbeck (2018), it has been reported that approximately 65 to 75 percent individuals belonging to the age group of 35 years prefers brand that are sustainable. With regards to the concept of circular economy explored in the economics assignment, Adidas intends towards sustainability. In other words, Adidas sustainability ingenuities have reflected on will of the company towards generating a more circular economy. As a part of operations, to bring about more sustainability the company started fighting for plastic-free oceans. As a result, the company teamed up with Parley and started manufacturing Adidas Parley shoes that are made out of plastic garbage found in the ocean. Adidas was successful in selling almost 1 million plastic made shoes in the year 2017. The eagerness to manufacture recycled shoes turned out to be a part of Adidas sustainability initiatives that aimed to help the company shift to completely recycled polyester by 2024 (Segran, 2020). The Futurecraft Loop has been regarded as a 100 percent recyclable shoe that intended to unlock a circular future for the sports sector. The sustainability initiatives taken by Adidas implemented an additional stride that involved introducing a voucher system in the UK. This system intends to make it easier for the individuals return their worn-out shoes. In return the individuals will be able to make an earning of almost $25 in credit that will be used to initiate a future purchase. In order to initiate a circular economy, Adidas will recycle the worn-out shoes that will create an inherent value in the shoes.
The supply chain of Adidas has provided supported to the business operations that helped to initiate a sustainability program. The supply chain approach has helped the company to improve the working circumstances as well as well-being to establish Workplace Standards. The supply chain is regarded as a channel that exists between a company as well as the suppliers to manufacture as well as distribute a particular commodity to the end user. In this scenario of economics assignment, Parley collaborated with Adidas in order to raise consciousness regarding the damages done to the oceans thus ending the destruction. Adidas started its partnership with Parley under the Ocean Plastic Program with the aim to transform the ocean trash to recyclable shoes. Parley acted as the supplier that helped Adidas to make this idea successful. In this scenario, Parley along with its partners gathers trashes from oceans such as Maldives. They then sort the waste and sent the recovered plastic to Adidas manufacturing plant (Segran, 2020). The waste is then used by the company that comprises of PET. The waste that are sent to Adidas are crushed, washed as well as dehydrated that leaves nothing behind rather than small plastic flakes. These flakes are then heated as well as dried that is segmented into small resin pellets. The Ocean Plastic is used by Adidas to create the upper portion of shoes as well as clothing that includes jerseys. The goal of the company is to transform all virgin polyester to recycled polyester by the year 2024.
Economic, social and environmental benefits
The circular economy approach by Adidas will help the economy keep away plastic trash from oceans that will save the environment. On the other hand, upcycling the waste will generate high-performance shoes as well as apparel. It will be advantageous for the environment as it will help to reduce the overall carbon footprint. It will also act as a social benefit as millions of shoes will be manufactured through recycled plastic waste. Adidas has been simply depending on compensating measures and encouraging sustainable substitutions. The overall environmental performance will be improved through the aspects that have been followed by Adidas to initiate a circular economy.
Conclusion
The economics assignment concludes that following a circular economy model would facilitate optimum utilization of resources, reduction of wastes and create a sustainable production-consumption cycle. The circular economy is beneficial for business, society and environment. There are new jobs created and the economy grows. The company analysis of Adidas shows how they have utilized the opportunity to increase their supply chain and operational efficiency, turning them into a profitable outcome. The company has reduced its carbon footprints and made their operations eco-friendly. They have also contributed to the betterment of the society and environment through adoption of the 3 R’s: reduce wastes, recycle products and reuse them.
References
Adidas, 2020. About Us. Available at: https://www.adidas-group.com/en/. [Accessed 2nd September 2020].
Geissdoerfer, M., Savaget, P., Bocken, N.M. and Hultink, E.J., 2017. The Circular Economy–A new sustainability paradigm?. Economics assignment Journal of cleaner production, 143, pp.757-768.
Heyes, G., Sharmina, M., Mendoza, J.M.F., Gallego-Schmid, A. and Azapagic, A., 2018. Developing and implementing circular economy business models in service-oriented technology companies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 177, pp.621-632.
Jabbour, C.J.C., de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L., Sarkis, J. and Godinho Filho, M., 2019. Unlocking the circular economy through new business models based on large-scale data: an integrative framework and research agenda. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 144, pp.546-552.
Jain, R., 2017. The Value Circle: Assessing Value Creation in Circular Business Models. IIIEE Theses.
Kirchherr, J., Reike, D. and Hekkert, M., 2017. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resources, conservation and recycling, 127, pp.221-232.
Lewandowski, M., 2016. Designing the business models for circular economy—Towards the conceptual framework. Sustainability, 8(1), p.43.
Lieder, M., Asif, F.M. and Rashid, A., 2017. Towards Circular Economy implementation: an agent-based simulation approach for business model changes. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 31(6), pp.1377-1402.
Manninen, K., Koskela, S., Antikainen, R., Bocken, N., Dahlbo, H. and Aminoff, A., 2018. Do circular economy business models capture intended environmental value propositions?. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, pp.413-422.
Nußholz, J.L., 2020. Circular Business Model Design: Business Opportunities from Retaining Value of Products and Materials (Doctoral dissertation, Lund University).
Rizos, V., Behrens, A., Van der Gaast, W., Hofman, E., Ioannou, A., Kafyeke, T., Flamos, A., Rinaldi, R., Papadelis, S., Hirschnitz-Garbers, M. and Topi, C., 2016. Implementation of circular economy business models by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): Barriers and enablers. Sustainability, 8(11), p.1212.
Segran, E., 2020. Inside Adidas’s ambitious plan to end plastic waste by 2030. [online] Fast Company. Available at:
Stahel, W.R., 2016. The circular economy. Nature, 531(7595), pp.435-438.
Storbeck, O., 2018. Adidas vows to use only recycled plastics by 2024. [online] Financial Times. Available at:
Ünal, E., Urbinati, A., Chiaroni, D. and Manzini, R., 2019. Value Creation in Circular Business Models: The case of a US small medium enterprise in the building sector. Economics assignment Resources, conservation and recycling, 146, pp.291-307.
Witjes, S. and Lozano, R., 2016. Towards a more Circular Economy: Proposing a framework linking sustainable public procurement and sustainable business models. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 112, pp.37-44.












