Customer Satisfaction Assignment: CS & CL In Travel Retail Of Dubai Duty Free
Question
Task:
Your customer satisfaction assignment task is to prepare a dissertation on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in travel retail of Dubai Duty Free.
Answer
Abstract
The travel retail industry concerned in the present context of customer satisfaction assignment is an emerging industry and it contributes greatly to the economy of a nation. However, the changing patterns of international travels have influenced the level of Customer Satisfaction (CS) and customer loyalty (CL) in this industry. Dubai Duty Free (DDF) is a UAE based travel retailing organization the mainly deals in premium products at a discounted price. The major research question of this research was to identify the extent to which CS and CL are related in the context of DDF and the imminent problems that relates to these variables.
In order to answer the major research question and achieve the research objectives the researcher has conducted a literature review by surveying the existing research articles in the context of CS and CL in travel retail organizations. The literature review has helped in understanding the concept of CS and CL and the interrelationships. Furthermore, a primary research method was designed in which information from 100 international travellers from the airport and 3 business analysts of DDF were collected. The survey and the interview results provided a peep into the views of the customers and the experts into the imminent problems and the suggested strategies that can be adopted by the company, to overcome the imminent issue.
The findings of the research indicate that CL and CS in DDF are highly influenced by the socio-economic factors and status of people. Moreover, the level of CS in the concerned organization is identified to be declining with time that is in turn affecting the level of CL. Owing to the increase in middle-class people travelling by air, it was found that the premium pricing strategy being used by DDF is hindering CS, loyalty and resultantly, the sales of the company.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the organization DDF is required to implement strategies such as development of specific departments with incorporation of products in the range of the middle income groups and applying the theories and models of CS and consumer behaviour in their strategy so that the needs of the customer can be met in a better way.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the organization DDF is required to implement strategies such as development of specific departments with incorporation of products in the range of the middle income groups and applying the theories and models of CS and consumer behaviour in their strategy so that the needs of the customer can be met in a better way.
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.0 Introduction to the topic
Customer Satisfaction (CS) relates to the extent of happiness of the customers with the product and service offerings as well as the capabilities of any business organization (Kim and Kim, 2017, p.41). Customer loyalty (CL) is defined as the outcome of a consistently positive experience both through the emotional and physical attributes of the products and services of any organization. Both of these factors play a role as key performance indicators of a business (Han et al., 2018, p.839). The present research relates to the investigation of CS and CL level in Dubai Duty Free, a travel retail organization based in UAE.
1.1 Background of the research
Dubai Duty Free (DDF) is a company based in the UAE that offers airport retailing services to the passengers and operates its stores in the Dubai International Airport and Al Maktoum International Airport (Dubaidutyfree.com. 2020). The sales and revenue of the organization are therefore highly dependent on the trends of international travels. In recent years, the trends of international travel have encountered significant changes that have driven more people from the middle-income range to travel abroad (Choi et al., 2016, p.99). However, with the enhancement of international travel, the sales and profitability of the travel retail company like DDF have not experienced much change. Therefore, it is important to investigate the CS and CL levels of the organization to understand the possible reasons and mitigating strategies.
1.2 Research aim
The aim of this research project is to investigate the existent problems in ‘CL’ and ‘CS’ in services offered by Dubai Duty Free in the travel retail sector, as well as analyze the strategies that can be taken up by the organization, to improve satisfaction and loyalty among the customers, in the present business scenario.
1.3 Research objectives
- To explore the influence of buying behaviour of customers and allied factors on CS and CL, in the travel retail sector
- To evaluate the ideologies of CS and CL as well as the interrelationship between the two
- To investigate the imminent issues in CL and CS being faced by Dubai Duty Free (DDF) in the travel retail sector
- To analyze the strategies that can be taken up by DDF to enhance CL and satisfaction in the present business scenario
1.4 Research questions
- What is the influence of buying behaviour of customers and allied factors on CS and CL, in the travel retail sector?
- What is CS and CL as well as what is the interrelationship between the two?
- What are the imminent issues in CL and CS being faced by Dubai Duty Free (DDF) in the travel retail sector?
- What are the strategies that can be taken up by DDF to enhance CL and satisfaction in the present business scenario
1.5 The rationale of the research
The travel retail industry or the operators of the duty-free service are facing increasing competition from other similar organizations. The reason behind the rise in the number of players in the industry is the increased number of international travels in recent years. As opined by Thubert et al., (2017, p.536), the growth in the low-cost carriers has contributed significantly to the fact that more middle-class people can now avail the international travel opportunity. It is identified that in the year 2018, the low-cost carriers accounted for 31% of the total scheduled airline traveller across the world (Naletina et al., 2019, p.29). Travel retail operators provide international travellers with the opportunity to shop for international products at a discounted price as well as to spend quality time within the airport after their security check-in.
However, the pricing strategy of some of the travel retail organizations, such as DDF does not allow the middle-class travellers to shop international products with ease. The reason is the inclusion of only premium products. According to Martín et al., (2019, p. 101691), the size of the stores also does not allow the organizations to include a wide range of products for targeting people with different income ranges. As stated by Kim et al., (2019, p.5081) the level of engagement between the staff and the visitors in the duty-free stores which has declined by 5% is another major concern for the reduction of CS and CL in DDF. Therefore, the satisfaction levels of the customers belonging to the middle-income range are very low in relation to DDF. The low level of satisfaction is further reflected as a low CL. For the presence of a number of factors that decline CL and CS, the present research investigates the CL and CS of DDF.
1.6 Significance of the research
The commencement of the research is significant as it can provide valuable information that can be applied by the concerned organization to enhance their performance in the near future. The research outcome would help the existing travel retail companies to identify the ways in which these organizations can enhance the level of CS and Cl. Moreover, the research outcome is likely to provide information regarding the existing relationship between CL, CS and the pricing strategy, customer service and other aspects of the travel retail industry. This piece of research can also serve as an important secondary source in the context of CS and CL in the travel retail and duty-free industry.
1.7 Scope of the research
The research takes into account the CS and CL in the travel retail organization and does not include the perception of the customers in the retail industry. As the research is based on DDF, the researcher has considered information collection from the airport that included a store of DDF within it. The overall perception of the travellers regarding the products offered by DDF and their service is within the scope of this research and therefore, not only the DDF customers but also the non-consumers of DDF were also surveyed in the course of the research.
1.8 Structure of the dissertation
Figure.1: Structure of the Dissertation
(Source: Created by the learner)
1.9 Summary
The present chapter has introduced the topic of research along with a brief explanation of the research background. The research aim, objectives and research questions are formulated and the scope of the research is discussed in the course of the present chapter. The reason behind the commencement of the research is explained as the rationale of the research. The next chapter, literature review includes a critical review of the research articles and journals on a similar topic for the identification of the gap in the literature.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.0 Introduction
According to Seng, (2019, p. 55), the present chapter of this customer satisfaction assignment is considered to be the survey based on scholarly sources associated with a respective study and a research question. This enhances the presentation of critical evaluation for the works related to the study that has been investigated. The respective chapter emphasizes on the discussion about CS and loyalty as well as its relevant issues and trends within the travel retail sector. The information for this chapter highlights the use of secondary sources such as scholarly papers; journals; books, articles; business magazines and similar others. This chapter contributes in understanding the background for answering and responding to the research questions.
2.1 Trends in the travel retail sector, in the present day business scenario
Travel retail has been termed to be a global industry that generally specializes for selling of the products towards the international travellers. The store sales of duty free are known to be tax free along with an exemption through the excise duties within such conditions with which the goods are found to be sold for the travellers who are responsible for transporting them out from the country. As stated by Naletina et al., (2019, p. 100), the bulk based on the respective revenues of the industry generally comes through the airports. Duty-free travel retail outlets have also been available within the border shops, ferrie, onboard cruises within the international waters along with the onboard aircrafts within the international flights as well. However, in some of the areas, travellers are found to have the option for purchasing any goods of duty free after their arrival. The respective trend is known to become the fundamental source related to the airport income. Nevertheless, the travel retail and duty free retail also generates certain necessary revenues based on tourism; travel; maritime along with the aviation industry as well. It has been evidenced that the global travel retail industry is expected to reach $153.7 billion within the year of 2025 while registering a CAGR of 9.6% within the period of forecast.
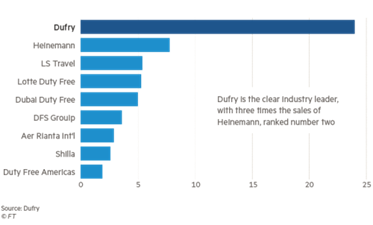
Figure.2 : Recent trends of retail travel industry
Source: (Obeidat et al.,2019, p. 350)
Trends within present business scenario
The global retail market of travel has been segmented relying on the channel; region and products. The segment of product generally involves luxury goods, cosmetics, electronics, catering and similar others. The luxury segment is known to have a higher potential of growth within the emerging markets along with being anticipated towards the witness of a steady growth within the developed regions as per the early adoption for premium lifestyle (Zhang et al., 2019, p. 20). It has been evidenced to have an increase within the living standards of people along with a higher income for developing nations that has popularized for carrying an expensive as well as luxurious products and culture for the customers. The respective culture is considered to be a status symbol for the customers where the luxurious segments of goods within the retail travel industry has been expected for the growth through a fastest rate within the year of 2025. As opined by Genç, (2019, p. 5), in recent years, it has been observed that the duty free market is able to generate value for the economic activity along with developing different opportunities related to employment which can eventually enhance the experience while travelling.
The trends of the present market has also increased within the recent scenario of business because of the growth within international tourists along with the growth of middle class people and families for international airports that has resulted through the enhanced activities for the lower cost airlines. Hence, this ensures the major benefit that is allowed by the retail organisations is the opportunity to the customers for spending time within temporary spaces after doing the security check-in. It has been evidenced from the early years that the passengers of travel retail tend to make decisions of purchase in a spontaneous way. However, in recent days, travel retail has experienced the change through an impulse purchase within the duty free shops of the airport with the increased demand regarding online shopping, researching travellers and planned purchases as well. With increasing trends observed among the millennial and the baby boomers to buy products online, the percentage of spending over travel retail outlets has decreased dramatically, over the years.
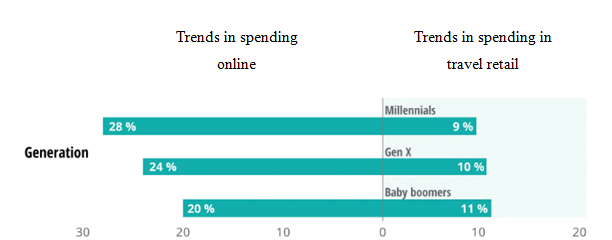
Figure.3: Comparison of spending over online platforms vs in travel retail outlets, in recent years
Source: (Noguti et al., 2019, p. 680)
Nevertheless, as opposed by Kefallonitis and Kalligiannis, (2019, p. 530), the retail industry of travelling must exploit its price advantage that is generally offered through the tax exemption within the core categories. This can allow the industry to compete with the prices that have been found elsewhere such as downtown, online, or rather within the destination of the passengers when the prices might be discovered through a simple search of the web.
On the other hand, airports should also dedicate a separate department regarding travel retail along with a separate pricing as well as strategy of customer acquisition. Owing to the increase in number of Low Cost Carriers, majority of the population travelling by air belongs to budget or middle class families, who are not very interested in purchasing products at premium pricing that has supposedly led to a fall in the sales rate of the travel retails including DDF.
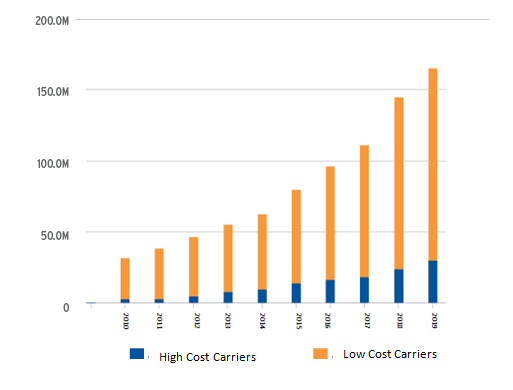
Figure.4: Steady increase in the number of Low Cost carriers, through the years
Source: (Azadian and Vasigh, 2019, p. 20)
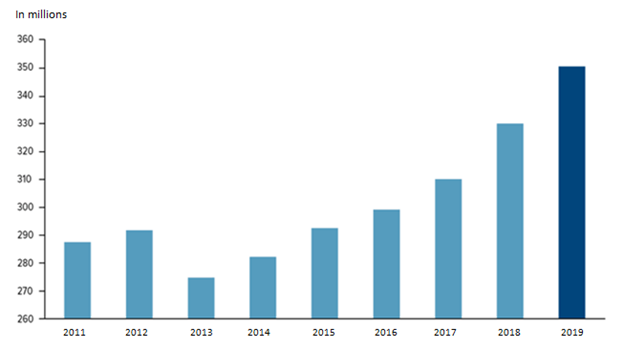
Figure.5: Increase in number of middle-class passengers, travelling through air, on a yearly basis, globally
Source: (Shields, 2019, p. 600)
Innovation for ambience is also required to be brought within the place for succeeding in the setup of an airport. However, as the travel retailers have been consolidated for strengthening its financial performance, they might add much more value for the customers for their shopping experience in a convenient way through the enhancement of loyalty schemes with the vertical integration along with the brands and airport. As considered by Sharma, (2019, p. 85), this considers the satisfaction and loyalty of the customers for the particular industry. The next section discusses the respective concept related to loyalty and satisfaction of the customers.
2.2 Concept of CS and CL
CS is found to provide an understanding for how the services and the products can meet with the expectations within the customers. On the other hand, CL is mainly influenced through the quality of service and product along with similar other factors. This considers the concept of CS to be the measurement for the attitudes of the customers related to the brands; products and the services as well. However, as argued by Cheng, (2019, p. 568), CL comprises that kind of behaviour which is also considered as retention of the customers. This is referred to as the act based on the customers that can make repeat purchases for the current brands as compared with the choice of the competitor brands. Customers are known to be the links regarding the success of the business as businesses cannot afford to lose its customers for the competitive market. Thus, CL and satisfaction is required to implement within the longer term goals of the business. As put forward by Mondragon et al., (2019, p. 3), this can be performed with the creation of the CS planning for feedback as per the overall plan of the business. The plan for surveying all the potential customers along with measuring their satisfaction is referred to as a simple way for maintaining the sense of loyalty for the customers.
The difference in the surveys of CL and satisfaction has been focussed on the customers measuring their current attitudes. The loyalty surveys of the customers are known to focus on prediction of the attitudes and behaviour of the customers. Creation of online software to survey can be beneficial which can involve questions related to loyalty and satisfaction which might lead to the business success. However, CS is also known to lead towards loyalty that can be helpful in the recent business environment which is super competitive within the market. The loyal customers are generally found to be much more likely for the generation of repeat businesses. This can enhance the customers to spend more money for the businesses along with being the brand’s advocate. Thus, as opined by El-Adly, (2019, p. 330), when customers are found to be more satisfied, they can become more loyal to an organisation or rather a brand. It has been evidenced that the satisfied customers generally contribute 2.6 times and double its sales for an organisation. There are many benefits related to CS which generally reduces the spread of negative reputation in the market.
Factors influencing CS and loyalty
There are several factors that majorly affect the satisfaction as well as loyalty of the customers. These are the overall impression for the customers regarding the products and the suppliers that are delivered through the organisations.
Features of services and products are the factors that are influenced through the evaluation of the service and the products. For instance, within travel retail, the comfort of the rooms; privacy; restaurants; price of the room are all evaluated.
As per the views of Kim et al., (2020, p. 101963), the emotions of the customers are also responsible for affecting their perception based on satisfaction with the offered services and products. For instance, positive emotions of the customers such as elation; happiness and pleasure have the tendency to increase the satisfaction of the customers.
Convenience is yet another factor where most of the loyal customers are simple as they can buy the products in their own time being regular customers. This helps the customers to prefer the product along with consisting of other brands within the stock.
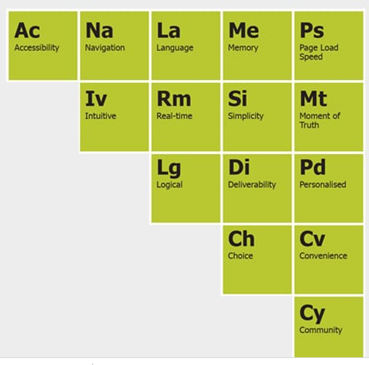
Figure.6: CL and satisfaction factors
Source: (Huang et al., 2019, p. 1450)
These are generally responsible for contributing towards the satisfaction and the loyalty of the customers along with many other factors such as quality of responses that are provided by the suppliers; compatibility and functions that are hassle free along with the operations; capability of the suppliers for committing on the deadlines along with the efficiency that are met. On the other hand, there are several shortcomings for CL and satisfaction. For instance, for the satisfied customers the expected and delivered value is known to be measured which considers CS for not necessarily being the measure for the overall value along with the quality within the organisations and its offerings. As put forward by Budianto, (2019, p. 300), the loyal customers of the particular brands can also enhance the psychological attachment who do not bother for the convenience or rather the price of the products. Nevertheless, this can also create some limitations for the customers such as inconvenience; higher cost of the products along with minimum variety as well as brand tribalism. However, the next section highlights the factors which are responsible for influencing the behaviour of buying for the customers within the retail sector of travelling.
2.3 Influence of buying behaviour and similar such factors, on CS and CL, in the travel retail sector
Buying behaviours of the customers are referred to as the actions that are taken both in an online and offline through the customers before its buying with the service and product. The respective process might involve the consultation of search engines along with engaging into the posts of social media as well as various other actions. It is considered to be valuable for most of the businesses for understanding the respective process as it tends to help the businesses for tailoring better with the initiatives of marketing regarding the marketing efforts which have successfully influenced the customers for buying within the past. As stated by Cha and Borchgrevink, (2019, p. 150), there are different factors that contribute within the process of buyer behaviour and might not result within the purchase. When these factors are found to put together in some of the combinations, the likelihood is known to increase about someone who can connect with the brand along with making a purchase. It has been evidenced that the relationship within the level of CS and service quality within the retail sector along with the buying behaviour of the customer has revealed their higher expectations for their service quality based on the organisations where they can make such decisions while buying any product through the retail stores. According to Mulay-Shah et al., (2019, p. 50), positive intentions of the purchase for the loyal customers can help in obtaining much more customers along with gaining some loyal customers with the provision through the quality of good service.
Customer behaviour in the travel retail industry
According to Chen et al., (2020, p. 20), travel retail has been found to be changed within the past years and has also been undergoing some serious disruptions. For instance, 70% of the impulse buying that has turned 79% of the planned buying. Thus, duty free shopping has been known to not consider cheap rather termed to be a convenience. The rising popularity based on the tourism and travel industry is known to be the primary factors within this global market. These respective services are found to enhance its value and experience for the money that can enable the customers to shop the luxury and premium brands at a discounted price within the global market. The idea based on temporary spaces has offered the end users some extra time after being entertained with the shopping experience and ambience regarding the international products. An increasing focus related to digitalising with the process of retailing can result in maximisation of the profit along with converting more and more customers that can boost the sales within the global market.
As evidenced by Myo et al., (2019, p. 5), easy options for home delivery are also provided by different leading vendors along with some innovative services of the customers which can improve the levels of satisfaction along with contributing towards the growth of revenues for the retail industry of travelling and duty free. There are certain benefits related to service; attractive prices; higher end products; convenience and recognition which can eventually promote with the evaluation associated with the retail industry. On the other hand, as per the enhancement of CL and satisfaction schemes through vertical integration, the retailers can look within innovations with an improvement of the in-terminal formats along with further distinguishing the offerings of the product through traditional mortar and brick stores.
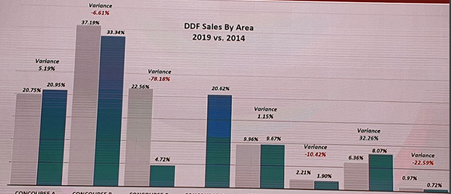
Figure.7: DDF Sales
Source: (Chang et al., 2019, p. 430)
Factors influencing the buying behaviour of the customers
Cultural factors are known to be significant for influencing the buying decision of the customers as each and every person consists of various sets of the habits; principles; belief that is developed from one’s family status as well as the background. Other than one’s nationality, it can also be defined through one's religious beliefs; associations as well as location.
Social factors are considered to be the elements that are possessed in one’s environment that are impacted with the way for seeing the products. It has been evidenced that each and every individual consists of someone across the influence of their decisions of buying. Some of the important social factors have been family; reference groups; status and roles. As opined by Wagner et al., (2019, p. 450), the reference groups generally provide certain points based on comparisons for the customers related to their habits; behaviours and lifestyles as well.
Personal factors are also referred to as the internal influences of the customers which generally arrives through the thinking pattern and lifestyle of the customers. These are generally considered as the personal opinions; attitudes; motivation and similar others. These can also be known as the psychological influences of buying behaviour. However, these factors can also involve marital status; age; personal beliefs and budget for an individual.
Hence, as stated by Choi et al., (2019, p. 200), it has been perceived that positive intention for purchase within the loyal customers can help in acquiring more and more loyal customers with the provision related to good quality of service.
2.4 Imminent issues in the travel retail sector, with focus on DDF, pertaining to CL and CS
According to Lindblom et al., (2020, p. 102055), the organisations for the travel retail industry generally focus on targeting the customers of the elite class through providing luxury products along with the brands of higher class within a higher price. The travel retail and duty free market has been identified for significantly increasing the airports across the globe. Competition has been involved within the expenses of the customers which, in turn, is known to possess several challenges within the travel retail industry and duty free sector as well. Each and every retailer is found to face different types of challenges for maintaining the value point of price along with keeping the customers interested in whatever is sold.
Issues in DDF
The retail industry has been continuously known to face a change with some new challenges within the competitive industry. On the other hand, the Duty Free foundation of Dubai has also been known to organise the initiatives related to corporate social responsibility along with raising its funds regarding some of the worthy causes specially for benefitting the children. As opposed by Bi et al., (2020, p. 104006), the foundation has been known to donate the funds for different charities both within abroad and home along with playing an active role in helping the children and families who were in need.
Through organising the respective foundation, Dubai has recognised and committed for the reduction of environmental impacts along with safety and health risks related to the retailing and storage of goods. This has been considered as the policy of the customers for operating the Integrated Management System related to ISO 14001: 2015 as well as ISO 45001: 2018. The total objective for HSE policy has been considered to be the provision for an environmentally and safer friendly operation based on the neighbours; employees and the customers. Nevertheless, despite these things, there are several challenges that are faced by this travel retail industry and Duty Free of Dubai as well.
Challenges related to CS of retail organisations of travelling
The change within the trends for international travel because of the growth in the low cost airlines has been triggered for most of the middle class individuals in travelling abroad. As argued by Michael et al., (2019, p. 60), on the other hand, there has been a lack of scope for the organisations of travel retailing such as Duty Free of Dubai for offering the products for the middle class families that has impacted the rise within sales. However, because the targeting strategy for the majority of premium customers based on the brands of travel retail have failed in enhancing their sales according to the increase within international travels. Nevertheless, DDF has also suffered within the categories like tobacco due to the difficulties consisting of the excise regime that is imposed for excise duty within the arrivals along with an implementation of the digital stamps of tax upon cigarettes through the year of 2019. Customer service within the airports has also been the key priority regarding the airport operators related to a higher degree of the competition. However, the inclusion within the premium products affects the concept of CL and satisfaction within the retail organisations of travelling such as DDF. Thus, it has been evidenced that through the increase in the competition within the airports, a continuous improvement has also gained a priority within the service quality. Thus, as stated by Genç, (2019, p. 5), the next section highlights several strategies through which the CL and satisfaction can be improved in the present context or rather the industry.
2.5 Strategies, backed by theories and models, which likely can solve the stated issues
The organizations for being within the leading providers of the services might need to understand both the expectations of the customers along with its assessment before providing the services that are made after providing them with the services. However, higher satisfaction of the customers can also be achieved when each of the employees within an organisation is found to be aware of the particular expectations based on the customers along with consisting of the ability for fulfilling them as well. For instance, proactive organisations are known to emphasize prevention based on the failure of service out-performing the organisations that can focus within the reactive approach for recovering the service level after any damage which is done. As opined by Murphy, (2019, p. 950), being a part of the corporate social responsibility, Dubai Duty Free has been known to take a part within the green initiatives which involved the environmental program of the United Nation which is the campaign of Clean up the World. In recent days, the organisation has also launched its own plastic recycling drive for helping in combating the issue of global environment for landfill and waste. As the Duty Free of Dubai consists of the safety and environmental issues to be its core value of business, the organisation has been committed for a continual improvement along with the uses of Integrated Management System. Nevertheless, the airports should also be noticed as a separate channel of sales through the retailers and must not be clubbed with the existing offerings of other stores. They should enhance a separate department for the travel retail along with comprising a separate pricing as well as strategy of customer acquisition.
Theories related to the improvement of issues in retail industry of travelling
However, as argued by Brochado et al., (2019, p. 500), it has been evidenced that the retail industry of travelling such as DDF comprises several shortcomings within its strategies of marketing. For instance, it consists of a demographic segmentation within the market and also targets the people with a higher level of income. This requires the organisations for maintaining the products within the range of middle class families along with changing within the strategies of segmentation targeting and positioning of the brands and the organisation. Thus, these strategies might be supported through highlighting disconfirmation theory. According to the respective theory, satisfaction has been related with the direction as well as size of the disconfirmation experience which generally occurs being the result for comparing the service performance over the expectations and Meta analysis for making the paradigm of disconfirmation to be the best predictor for satisfaction of the customers. Owing to the fact of the particular theory, the feature of a service or rather a product needs to provide a pleasurable consumption level that is related to the fulfilment involving the level of over and under fulfilment.
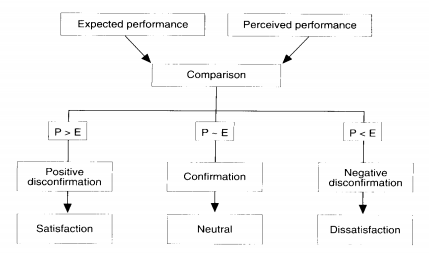
Figure.8: Disconfirmation Theory
Source: (Abushaikha et al., 2020, p. 40)
The present theory of satisfaction is mainly concerned with the comparison of the service performance over the expectations. However, the implementation of assimilation contrast theory can also help in maintaining the performance of a service or a product when it tends to fall beyond the range of acceptance for the customers. According to the concerned theory, it can be applied for satisfaction of the customers which can hypothesize the variables as compared with the magnitude based on discrepancy for observing the level of assimilation and contrast in such a situation when the performance of a product is difficult for judging. As per the views of Abushaikha et al., (2019, p. 40), the expectations can also result in leading towards the higher involvement for the circumstances. The strengths related to these expectations can also affect whether the effects of contrast or the assimilation are observed.
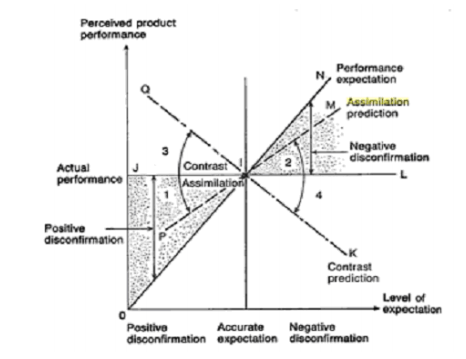
Figure.9: Assimilation-contrast theory
Source: (Camilleri, 2019, p. 20)
Thus, according to this theory, when the performance has been within the latitude of customer’s acceptance, the assimilation can be operated allowing the performance to be acceptable. However, when the performance falls below the latitude, contrast can be prevailed along with exaggerating the difference where the product is considered to be unacceptable. Nevertheless, as opposed by Michael et al., (2019, p. 60), this theory is found to have mixed results which is one of the limitations of this theory and is also known to be flawed methodologically. This results in perpetual differences within the satisfaction or the disconfirmation of the customers.
2.6 Conceptual framework
Figure.10: Conceptual Framework
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
2.7 Literature Gap
As stated above, the discussion has been conducted with the use of secondary sources which has possessed certain gaps within its information. For instance, travel retail viewing as an omnichannel ecosystem offers atmosphere and customer service within the market of Duty Free; solutions for overcoming the core challenges of the retail industry in travelling along with the plan of DDF for its development and its improvement has not been considered in the present discussion. Not covering these points within the information has created a loophole within the particular literature of the study. However, these gaps have led to the future scope of the respective study where all these information can be covered.
2.8 Summary
To summarize, the present discussion has provided with the knowledge related to the concept of CL and satisfaction within the retail industry of travelling such as Duty Free of Dubai. However, the trends within the retail travel sector; influence within the buying behaviour of the customers related to their loyalty and satisfaction within the respective industry has been emphasized in the present chapter. On the other hand, several issues within the retail travel sector focusing on the DDF have also been highlighted pertaining towards the satisfaction and loyalty of the customers followed by exploring theories; strategies and models to mitigate these issues. Nevertheless, the gap within the literature has also been considered in the discussion which has increased the scope of future research for the study.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.0 Introduction
The study regarding the systematic techniques or procedures that are used by the researchers for the recognition of the research problems, selection of the appropriate process to the collection, analysis and interpretation of data in research relates to the research methodology (Fletcher, 2017, p.182). The present chapter includes the different methodological choices made in the course of the present research along with proper justifications. The chapter also incorporates quotes from the research participants along with a brief overview of the significant findings.
3.1 Research onion
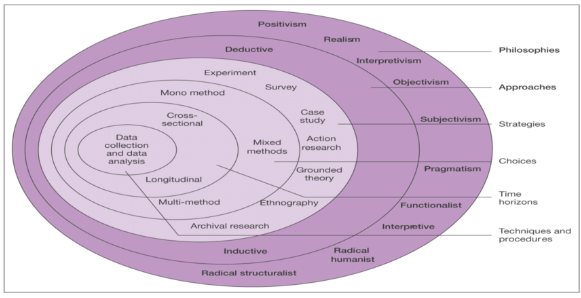
Figure.11: Research Onion
(Source: Saunders et al., 2009)
3.2 Research Philosophy
According to Mohajan, (2018, p.25) philosophy in research is the system of thoughts that can help in reaching the generation of new and reliable knowledge of a particular research object or phenomenon. In the case of business research generally, three types of research philosophies are utilised, interpretivism, realism, and positivism. The present study has utilised positivism research philosophy. Positivism is defined as the philosophy that adheres to the viewpoint that trustworthy factual knowledge can be gained only when a proper observation is made along with the appropriate measurement. As the positivism philosophy allows the researcher to utilise an objective way and make the findings observable and quantifiable it is justified for the present research. Moreover, as opined by (), positivism research philosophy is based upon the idea that states the science to be the only way for learning about the truth along with having the atomistic and ontological view within the world that comprising the observable and discrete element and events which interacts in the determined and regular manner.
3.3 Research paradigm
Attia and Edge, (2017, p.37) has explained research paradigms as a theoretical framework and a basic belief system VIT exam sun regarding ontology, epistemology, methodology, and methods. Ontology relates to the nature of the beliefs of the researchers regarding reality. Epistemology relates to the branch of philosophy wherein the process as well as the nature of knowledge through which knowledge can be validated and acquired is studied. Methodology, on the other hand, relates to the critical analysis and study of the techniques of data production. Methods are specifically the means for collecting and analysing data through interviews and questions.
3.4 Research Approach
Choosing an appropriate research approach can ensure the success of the research project. The research approach has been defined as the procedure or plan that involves the major assumptions regarding the procedure of collecting, assessing, and integrating data (Page et al., 2017, p.467). There are three different types of research approaches that are generally used, abductive, inductive, and deductive research approaches. To conduct the present research, the use of the deductive approach has been done. The inductive research approach refers to the development of a hypothesis on the basis of the theories that are already present and designing an appropriate strategy of research so that the hypothesis can be tested. As, in the present case, there is an abundance of sources or literature, the application of deductive research approach is more suitable. The approach has helped in completing the study in a short time with the avoidance of risks. It is involved in the beginning with the theory that develops the hypotheses from the theory and then it collects and analyzes the data for testing those hypotheses. Thus, as stated by (), it helps in explaining the causal relationship among the variables and concepts, measuring the quantitative concept along generalizing the research findings.
3.5 Research Strategy and tools; Time Horizons of study
According to Cuervo?Cazurra et al., (2017, p.236), different types of research strategies that are utilised in business research are case studies, observations, experiments, action research, focus groups, interview, and survey strategy. In the present research, the researcher has utilised an interview strategy for the collection of data. These two strategies are most suitable for the present research as these strategies are helpful in the collection of data in a short time and in a cost-effective way. For the survey method, one-to-one survey technique has been utilised however, in the case of the interview the Skype software has been utilised as a data collection tool. In the present case, regarding time horizon, the researcher has utilised a cross-sectional approach in which data has been collected from the population at a single point of time for examination of the relationship between the variables included in the research question. Resorting to this time horizon ensured that the research was completed within a short time, so that the deadlines could be effectively met, after proper analysis and interpretation of the collected data. Thus, the present study involves the explanatory research strategy that is conducted for the problem that is not at all well researched before, and demands priorities along with generating the operational definition that provides the better model for research. Hence, as opined by (), this research strategy mainly focuses upon the explanation of the aspects of the study within the detailed manners.
3.6 Sampling technique/ Population
Research population refers to the large group of objects, items, or individuals that are the area of interest of particular research while sample relates to a small number of objects, items, or individuals taken from the population for including in research (Ulmer, 2017, p.837). In the present case, the consumers of international products from the travel retail companies as well as the business and of DDF are the research. In order to select the consumers for the survey, the researcher has utilised a random sampling technique. 100 respondents from the airport who were both customers and non-customers of DDF recruited in the survey. On the other hand, for conducting the interview, 3 business analysts of DDF were chosen with the help of the non-random sampling technique.
3.7 Data Collection techniques
Basias and Pollalis, (2018, p.97) stated that there are two types of data collection methods that are primary data collection and secondary data collection. In the present research, the primary data collection method has been selected for collecting data from the consumers of the travel retail industry and the business analyst of DDF. The primary data collection includes two types of data that are quantitative or numerical data and qualitative or non-numerical data. In the present research, both quantitative and qualitative data has been collected. For the collection of qualitative data, the interview method was applied and a survey method was applied to collect quantitative data. Moreover, secondary sources like research articles, industry reports and peer-reviewed journals have been utilized for the development of the literature review.
Furthermore, the data analysis tools help in detecting and correcting the errors from the data sets with the help of the data cleansing. It assists in improving the quality of the data along with the benefits to both the customer and the institution as well as delivering relevant outcomes.
3.8 Reliability and validity of research
Research reliability and validity are two major aspects of research that indicates the overall quality of the research as well as the research outcome. As explained by Ndlovu-Gatsheni, (2017, p.187), the higher research reliability and validity can reflect that the research methods are applied in a proper way and are helpful in addressing the research questions. For increasing the research reliability the researcher had used a well planned and structured questionnaire in the primary research method. Moreover, a consistent environment of the survey and interview has also helped in validating the research.
3.9 Ethical consideration
This is the most significant part of the research methodology where the participants should never be the subject to any harm and their dignity and respect needs to be prioritised. moreover, full consents need to be obtained from the participants and protection needs to be given to them regarding the information and facts that they have provided. Adequate confidentiality level needs to be ensured and thus, exaggeration of the objective and aims of the research needs to be avoided.
3.10 Limitations of the research
The limited-time for the completion of the research is identified as one of the limitations of this research. Due to limited time the researcher was not able to interview more business analysts in DDF. The limited financial resource was one of the limitations of this research. In this research, the researcher has focused on primary data collection methods and avoided data collection through the secondary research method. As a secondary source helps in gaining relevant data from already existing research outcomes from other research, it could have increased the reliability of the present research.
3.11 Transcripts of qualitative interview
1st interviewee
Response to Q1: “CS is related to positive purchase intention and it also drives CL. The socio-economic condition of the travellers is critical in the purchase decision and has a direct impact on CS and CL in DDF”
Response to Q2: “Individual characteristics and perceived values results in behavioural intentions of the customers regarding the brands of DDF”
Response to Q3: “The application of CL and CS models and theories can help in meeting the needs of the customers.”
2nd interviewee
Response to Q1: “CS directly influences the purchase behaviour and customers become loyal when they are satisfied with the quality of the brand. DDF’s brand image is able to promote purchase intention among customers”
Response to Q2: “The loyalty and satisfaction of the customer has impacted with the changing demography of travellers and the emergence of low-cost carriers”
Response to Q3: “Customer acquisition strategies along with systematic and sustainable objectives can help the company to bring more customers from the airport inside the stores”
3rd interviewee
Response to Q1: “Social factors impact greatly on consumer behaviour as well as CS and Cl. The self-image of the consumers is related to social factors as well as consumer behaviour.”
Response to Q2: “Changes in the demography and the increasing number of low-cost carriers in airlines have decreased CL and CS level in DDF due to the premium-priced products of the company”
Response to Q3: “Maintenance of the price range of products can be effective for increasing the access of the middle-class families in DDF”
3.11 Significant findings from survey
Age of respondents
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
18-25 |
35 |
100 |
35 |
|
26-32 |
30 |
100 |
30 |
|
33-50 |
20 |
100 |
20 |
|
51 and above |
15 |
100 |
15 |
Table 1: Criteria of age
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
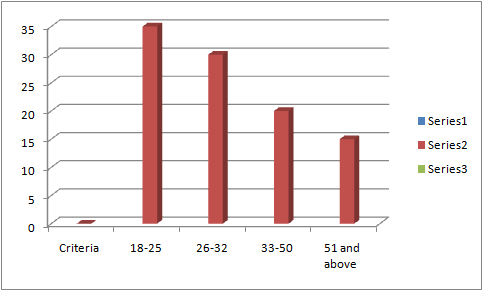
Figure 1: Criteria of age
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
Frequency of visit at DDF
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
Very often |
25 |
100 |
25 |
|
Often |
40 |
100 |
40 |
|
Not always |
20 |
100 |
20 |
|
Never |
15 |
100 |
15 |
Table 2: Criteria of visit
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
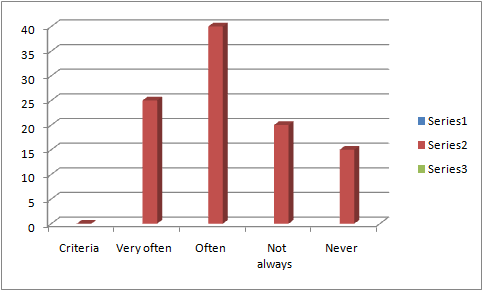
Figure 2: Criteria of visit
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
Unsuccessful meeting of customer needs
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
Highly agree |
20 |
100 |
20 |
|
Agree |
30 |
100 |
30 |
|
Neutral |
35 |
100 |
35 |
|
Disagree |
10 |
100 |
10 |
|
Highly disagree |
5 |
100 |
5 |
Table 3: Criteria of not meeting the needs of the customers
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
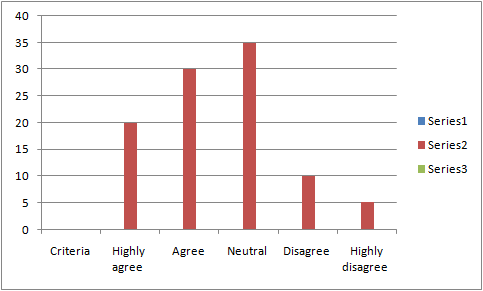
Figure 3: Criteria of not meeting the needs of the customers
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
Not providing as high value as pricing
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
Highly agree |
25 |
100 |
25 |
|
Agree |
30 |
100 |
30 |
|
Neutral |
32 |
100 |
32 |
|
Disagree |
7 |
100 |
7 |
|
Highly disagree |
6 |
100 |
6 |
Table 4: Criteria of DDF not providing value for premium pricing
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
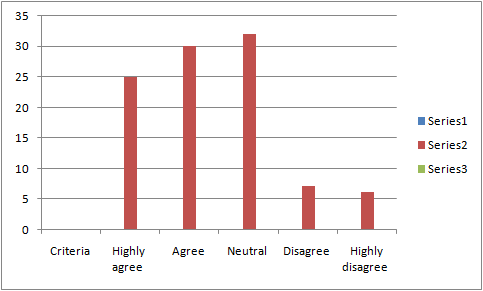
Figure 4: Criteria of DDF providing value for premium pricing
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
Recommending against visiting DDF
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
Very likely |
22 |
100 |
22 |
|
Likely |
30 |
100 |
30 |
|
Neutral |
33 |
100 |
33 |
|
Not that likely |
10 |
100 |
10 |
|
Not at all likely |
5 |
100 |
5 |
Table 5: Criteria of recommending for not visiting DDF
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
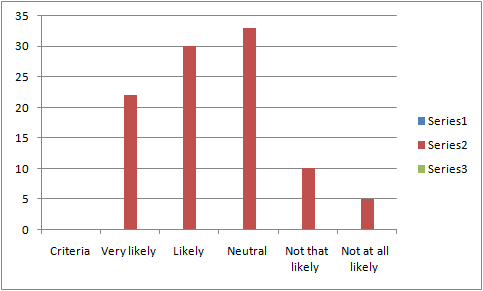
Figure 5: Criteria of recommending for not visiting DDF
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
Repeat purchase at DDF
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
Very likely |
17 |
100 |
17 |
|
Likely |
25 |
100 |
25 |
|
Neutral |
5 |
100 |
5 |
|
Not that likely |
34 |
100 |
34 |
|
Not at all likely |
19 |
100 |
19 |
Table 6: Criteria of repeat purchase
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
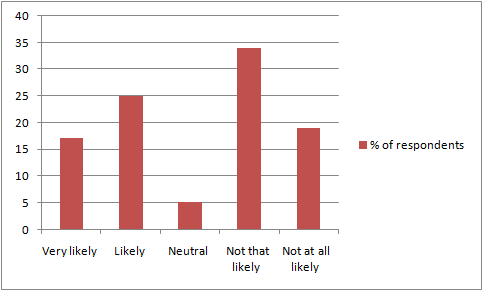
Figure 6: Criteria of repeat purchase
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
Strategies for improvement
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
Maintaining the range of the products for the middle class families |
25 |
100 |
25 |
|
A separate travel retail department along with separate pricing needs to be considered |
25 |
100 |
25 |
|
Considering the strategies related to customer acquisition |
20 |
100 |
20 |
|
Implementation of theories and models related to CS such as disconfirmation theory and assimilation-contrast theory |
30 |
100 |
30 |
Table 7: Criteria of strategies
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
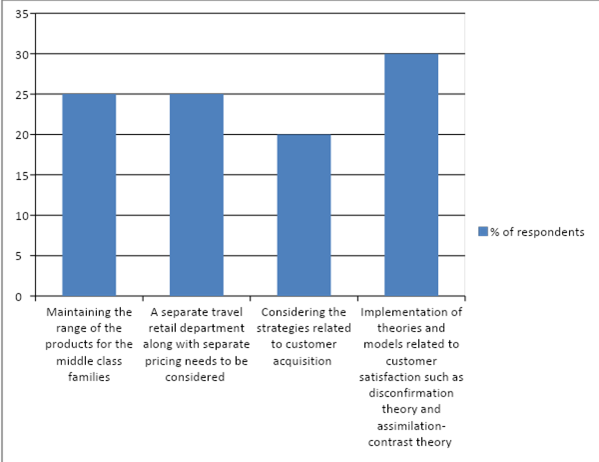
Figure 7: Criteria of strategies
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
Need for changing the strategies
|
Criteria |
No. of respondents |
Total no. of participants |
% of respondents |
|
Highly agree |
20 |
100 |
20 |
|
Agree |
25 |
100 |
25 |
|
Neutral |
30 |
100 |
30 |
|
Disagree |
15 |
100 |
15 |
|
Highly disagree |
10 |
100 |
10 |
Table 8: Criteria of changing strategies
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
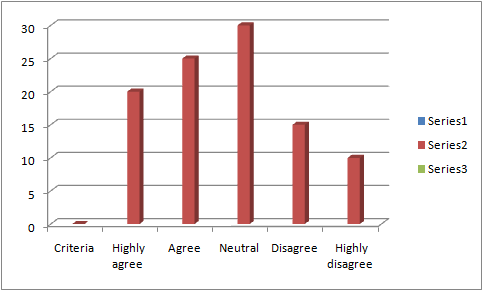
Figure 8: Criteria of changing strategies
Source: (Developed by the Learner)
3.12 Summary
The present chapter has highlighted the ideology of research philosophy, research approach, data collection and analysis methods, sampling techniques along with the justification of the choice made against these methods. The research strategy chosen by the researcher has been explained and justified with proper reason. The chapter also includes major research limitations. Moreover, the transcripts of the interview commenced on the three business analysts have been provided in this chapter along with the brief explanation of the major findings.
Chapter 4: Data analysis
4.0 Introduction
The chapter of data findings and analysis is known to be the most significant part for the research, which emphasizes on the principle outcomes related to a research project. Data analysis tends to summarize about the gathered data. This includes the interpretation based on the collected data while making use of logical and analytical reasoning for determination of the patterns; trends and relationships. The present chapter highlights the process of analysis through visual representation of statistical methods along with graphs and charts of the results. Thus, the respective section generally contains about a detailed description based on the outcomes, which were deducted after conducting the research.
4.1 Quantitative analysis
On investigating the age of the respondents, it was observed that most of the respondents that are 35 customers of DDF have been aged within 18-25 years. On the other hand, the lowest no. of participants have been aged within the 51 years and above. Accordingly, the percentages of these customers have been 35% and 15% respectively. However, the mean value for the respective criteria has been 2.25, which is greater than the SD value, which is 0.99873658 followed by the median that is 2. This indicates that the criteria of age are highly significant with the shopping experience of DDF. Thus, it can be analysed that the young participants are much more likely to be the customers of Dubai Duty Free. This was an attempt to gauge the shifting demographics of the travellers at the airport, which was found to be one of the most significant issues afflicting the sales of the travel retail sector. In order to understand the buyer behaviour and the trends of low CS and CL, it is essential to check the age of the sample population used for the research, so that the findings can be validated
On investigating about the frequency of visit of the customers, to DDF, it has been evidenced that most of the participants that are 40, often visit DDF whereas, the least number of participants that are 15, never visit DDF. Thus, the percentages came out to be 40% and 15% respectively. It can be considered that there has been a great difference within Dubai Duty Free shopping as well as the regular shopping which might not be charged for the sales taxes and import duties. The stores of DDF are generally found within the international areas based on the seaports and airports or rather some of the overland border crossings. When customers generally look for a higher-end product, it is known to be worth checking within the duty free shops of the airport. However, on the other hand, it has also been evidenced by Seng, (2019, p. 60), that shopping within the duty free shops can result in free savings of big tax and can also be left disappointed along with spending much more money as compared to spending online or rather at home. The options of online shopping and the trend observed among the international visitors, to shop from the local shops when visiting attraction sites, as a measure for responsible tourism, has also notably minimised the visits to DDF outlets. This finding is significant for establishing the reliability and validity of the research objective undertaken to explore the influence of buying behaviour and allied factors on the CS and CL of the travel retail sector. Putting up this question was necessary in order to gauge the number of tourists from the representative sample that prefer visiting the DDF outlets as per their will.
When collecting the views of the respondents regarding the extent to which DDF presumably failed in meeting the needs of diverse groups of customers, in an efficient manner, it was observed that most of the respondents, as high as 35, chose to remain neutral with the criteria. On the other hand, the lowest number of respondents that are 5, highly disagreed with the concerned criteria. Accordingly, the percentages came out to be 35% and 5% respectively. Nevertheless, the mean value has been considered as 2.5 which is greater than the SD, which is 1.077782984 followed by the median value that is 2.5. This resembles that meeting the needs of the customers has a positive correlation with the success of DDF. Thus, it can be said that for meeting with the needs of a diverse market, the customer service team should consist of enough insight for being capable of empathizing with customers that they have been trying to help. Owing to factors like limited stocks, premium price ranges of the products and availability of cheaper options like online shopping, DDF fails to meet the expectations of most of the present-day customers (Mohasses, 2019, p. 400). This question was an attempt to investigate one of the various challenges that DDF is facing in current times that is attributing to lower CS and CL for the organization. The diverse demographics and the increase in the number of middle-class customers is something that DDF has not coped up with yet, which is contributing to the rise of such challenges.
A question was posed to check for the views of the respondents regarding the extent to which DDF failed to meet the expected high values of products, keeping in mind the high price the customers have to pay to buy them. It has been observed that most of the participants that are 32 have been neutral with the criteria that DDF does not provide value for its customers in comparison with the premium pricing. On the other hand, the lowest numbers of participants that are 6, have highly disagreed with the particular criteria. However, the percentages for both the values came out to be 32% and 6% respectively. Accordingly, the mean value has been considered as 2.39 and the median value is 2 which are greater than the SD which is 1.118214667. This shows that meeting with the expected values is highly significant with the premium pricing of the products.
It can be said that Dubai is more popular due to its higher end designer stores and while shopping within the duty free shops, the customers generally do not get any bargain. However, a premium pricing is used by the DDF, which at times is known to be worth it as it provides quality products along with many other factors (Obeidat et al., 2019, p. 350). This fact is established through the response of the people who responded in negation to the posed question. Few respondents felt that DDF provides value for pricing; for them shopping at DDF often provides them with an opportunity to get rid of their leftover coins for the local currencies as DDF generally accepts many currencies, which also make this a good place for spending. DDF is termed to be a larger mall where people can get anything and everything along with the best quality. Thus, all these factors make the higher class people shop within Dubai Duty Free. Quite many respondents chose to stay neutral while responding to this question, which exhibits the fact that they have either not visited the outlets or have not analysed the strategies or experiences in such depth. This question was also a part for investigation of the challenges for DDF and was thus, essential for retrieving an answer to the third research question posed in this project.
33 respondents to be exact have been neutral with the criteria that they would recommend DDF to their relatives and friends while travelling. However, the lowest numbers of respondents that are 5, were found not to be likely at all with the concerned criteria. Similarly, the percentages came out to be 33% and 5% respectively. Nevertheless, the mean value has been 2.46 along with the median that is 2 which are greater than the SD value that is 1.095629518. This resembles that not recommending any one for visiting DDF has a higher significance for the customers while travelling. Thus, DDF generally spreads over the airport comprising many things that are generally required by the customers while travelling. There has been no tax while purchasing anything in DDF.
However, DDF is not that advantageous in offering its prices except several commodities such as perfumes; alcohol and similar others, though there is not that much difference within the perfumes. These factors have made the business of DDF to slow down as DDF majorly provides luxury products for the customers consisting of high class brands (Mehrotra, 2019, p. 340). On the other hand, change within the trends have also been considered for international travel as it has been evidenced that the lower cost airlines have been increased for the middle class families who travel abroad. This section of people were found to be not very interested in exploring the outlets of DDF, either owing to the high price tags or owing to the availability of other options for timepass in the airport, such as free wifi. People not visiting the stores were less likely to respond to the question of recommending the shop to others, which justifies the high number of respondents who chose to stay neutral while responding. The finding stresses the fact that CS and loyalty quotients of DDF are running at a low level and some strategies for improving the scenario is the need of the hour, for the organization.
Upon investigating the likeability of the respondents to repeat-purchase from DDF, it was observed that most of the participants that are 34 are not that likely with the criteria to repeat their purchase at DDF. However, the lower numbers of participants that are 5, have been neutral with the concerned criteria. Accordingly, the percentages came out to be 35% and 5% respectively. Hence, this has been due to its majority of premium pricing. The mean and median came out to be 3.13 and 4 that are greater than the SD value, which is 1.425985394. This shows that the criteria of repeat purchase of the customers have a higher correlation with the DFF. However, as stated by Alnuaimi and Yaakub, (2020, p. 12), products that are purchased from DDF, are found to be covered through the local warranty over the defects of manufacturing within a one year period of purchase. Damages that are caused due to misuse, accident or rather improper repair are generally not covered within the respective warranty. It has also been known that the supply purchases of the respective organisation have been made within the US dollars that make the things to become much more expensive. Owing to the evolution of trends in online shopping, responsible tourism and availability of free, high speed wifi for enjoying games in smartphones or do some other work, people are choosing to spend their times at the airport doing something other than shopping, which accounts for less number of respondents choosing to repeat-purchase at DDF. This was an attempt to investigate the extent of CS and CL for DDF as well as to study the interrelationship of the same with the customer behaviour.
While investigating for the likely strategies, it was found that a higher number of respondents that are 30 customers have supported the strategy of implementing models and theories associated with CS such as disconfirmation and assimilation contrast theories for the criteria to solve the challenges that are faced by DDF. On the contrary, the lowest numbers of respondents that are 20 have considered making use of customer acquisition strategies as per the concerned criteria. Thus, the percentages were known to be 30% and 20%. Implementation of these models and theories can help the organisation in achieving customer retention that can make the customers to be within the website for a longer duration of time. As evidenced by Brochado et al., (2020, p. 500), the theories can help in analysing the wants and needs of the customers and the way it can be perceived. This can, in turn, offer DDF in meeting with the expectations of the customers. On the other hand, it can also emphasize on the failure of its service out performance for the organisation, which can rely on the reactive approach to recover the level of service after the damage. This question was essential for meeting the fourth research objective and question posed in this project.
While investigating the response of the customers to the necessity of changing the strategies for maintaining CL and CS within DDF considering the changing demographics, it was observed that 30 respondents remained neutral with the criteria. On the other hand, the lower numbers of respondents that are 10, have highly disagreed with the specific criteria. Nevertheless, the percentages came out to be 30% and 10% respectively. However, the mean and median that are 2.7 and 3 are known to be greater than the SD value, which came out to be 1.23501114. This indicates the change of strategies and satisfaction of the customers positively correlates with each other. It has been noticed that DDF comprises environmental and safety issues for being its core business value, which made the respective organisation for being committed to a constant improvement and making use of Integrated Management System (Yasmeen et al., 2019, p. 35). Nevertheless, the strategies related with customer acquisition generally encompass each and every effort for bringing the customers within the final stage for making purchases. This response too, contributed to the realization of the fourth objective and research question posed.
4.2 Qualitative analysis
The major findings from the interview are that the emergence of the low-cost carriers in international travel has contributed greatly to the enhancement of middle-class customers in DDF. However, the premium-priced products and the ineffective services of the company have resulted in a low level of satisfaction among middle-class customers. Application of CS and CL theory along with customer acquisition strategies can help the company to elevate the level of CL and CS.
When questioned about the impact of purchase intentions of travellers on the CL and CS of DDF, according to the first analyst, it has been evidenced that CS consists of a positive impact upon the purchase intention of the customers as satisfied customers are mainly found to display satisfaction along with coming back for repurchasing the product as well. Satisfied customers also tend to recommend the services of the shop to others as well, thus ensuring positive word-of-mouth promotions for the company. Two of the factors generally play a major role for determining the purchase decision of the travellers within DDF such as the socio-economic condition along with the social influence. Social class is known to have a profound effect within the spending habits of the customers and is considered to be the level of disposable income for each of the social class. The second analysts stated that CS comprises a direct impact within the purchase intention as customers are found to make their purchases when they are loyal or satisfied with the brand quality. However, for the present context, the brand image of DDF consists of a favourable impact upon the purchase intention. This makes the dimensions of satisfaction; loyalty and purchase for being linked with one another and tends to affect each other (Genç, 2019, p. 5). However, the third analysts have been found to support the views of first business analysts and suggest that social factors generally affect the behaviour of the customers in a significant way where the reference group majorly influences the self-image of the customers along with their behaviour.
When asked about their views on the impact of changing demographics of travellers as well as evolution of Low Cost Carriers, the second business analyst stated that the change within the demographics of the travellers along with the evolution based on lower cost carriers have impacted the loyalty and satisfaction of the customers within DDF. It has been evidenced that connecting the demographic characteristics of the customers along with their tourism behaviour is known to remain scarce. For the present case, the middle class families are not that familiar with the higher end brands of DDF along with the strategy of premium pricing which has been reducing the satisfaction of the customers along with their loyalty and eventually impacting the business at DDF. This view is in continuity with the problem statement derived for the research and validates the finding from the quantitative survey, which exhibits imminent dissatisfaction among the customers.
On the other hand, as per the views of the first manager, the perceived values and individual characteristics tend to produce various results within their future behavioural intention for the integrated brands of DDF. Personal satisfaction has been known to be highly influential within the customers with lower income, which requires the organisation for the growth of micro-marketing strategies. As stated by the third analyst, in regards to the views of the second manager, the analyst has stated that the demographic changes, which have happened within DDF due to the lower cost airlines, have been known to be likely for impacting the CL and satisfaction. This has been due to the offering of premium pricing of brands for the middle class customers at DDF (Dupuis, 2019, p. 342). This resembles that the perceived value of the attitude of travellers as well as satisfaction can impact the repurchase decisions of the customers.
When requested to give their valuable inputs towards the likely strategies that needs ot be adopted by DDF, the first analyst stated that, to resolve the challenges that are faced by DDF, implementation of models and theories related to CS, for restructuring the services and the products as per the needs of the customers would be beneficial. Application of these theories and models can help in measuring the ways services and products need to be supplied within an organisation for meeting or rather surpassing the expectations of the customers. However, the third business analyst opposed the views of the first analyst, as maintaining a range of prices that can be accessible for the middle class families might result in being effective. This can help DDF with the metrics, which can be used for improving and managing the businesses (Simon and Fassnacht, 2019, p. 50). Nevertheless, the second manager has supported the views of the first manager while considering the use of customer acquisition strategies, which can help DDF in bringing new clients and customers for its business. The main purpose of this process has been for creating sustainable; systematic objectives which can be changed and might evolve with the recent trends.
4.3 Summary
To summarize, the present chapter has evaluated the data that was gathered from the participants through visual representation of graphs and charts along with considering the interpretation for the same. Logical and analytical reasoning has been emphasized for analysing the data in the present discussion. Thus, the outcomes and recommendations for challenges has been highlighted in the present chapter which can be considered by the travel retail organisations.
Chapter 5: Conclusion
5.0 Conclusion
The present research was aimed at the investigation on the imminent issues in relation to CL and CS in the travel retail service offered by the UAE based organization Dubai Duty Free (DDF). In order to answer the research questions and reach the aim, primary research was designed in the course of this research along with a strong literature review. The literature review process has helped in identifying that CL and CS is a very closely related concept in the travel retail industry. The existing literature has also helped to identify that the existing travel retail business focuses on selling premium products at a discounted price to the travellers. However, the changing trends in international travel have created numerous challenges for these organizations. However, the literature review did not help in fully understanding the extent to which the buying behaviour and the CL and CS in DDF are related and the existing problems among these variables.
The results of the research indicate that the extent of visit DDF is very high among travellers at the international airport. However, a significant number of travellers have been identified who do not prefer to visit the stores of the DDF while travelling abroad. This indicates the presence of certain factors that have prevented them from visiting the stores of DDF. It has already been observed from the existing literature that the premium pricing strategy of travel retail organizations like DDF prevents them from acquiring customers from diverse groups. The incorporation of people from the middle class due to the emergence of low-cost carriers has greatly changed the demography of international travels in recent years. In relation to this particular perspective, the current research has found that the majority of the travellers in the airports with DDF stores perceive that the organization is not much efficient in meeting the needs of the people from diverse groups. Therefore, there is a similarity in the existing literature and the results of this particular research which in turn contributes to the validation of the outcomes.
From the literature, the two CS and customer behaviour theory that are the Disconfirmation theory and Assimilation contrast theory has been identified. Moreover, in relation to the statement of these theories, the present research has identified that among the travellers there is a tendency to compare the value provided by DDF with their own expectations. However, it is identified that in the view of the majority of the travellers the premium pricing of the products and the incorporation of only premium products has resulted in the dissatisfaction of the customers. Moreover, the resulting customer dissatisfaction also leads to a decline in sales of the organization with the sharing of information regarding the products and services of DDF among travellers. The result has depicted that the incidents of repeat purchases have also declined in DDF that indicates a low CL in DDF.
It has been identified from the outcome of the research that incorporation of marketing and sales strategies followed by the theories and models of CS like disconfirmation can help DDF in attracting more customers. On the other hand, the incorporation of products in the range of the middle-class people can also help the company to elevate the level of CS as well as CL. The strategy of a separate travel retail department within the airport can be another important strategy of the DDF in which the company can target specifically the middle-class people. On the other hand, Customer acquisition strategy can also be implemented for the elevation of the CL and CS levels in DDF.
5.1 Recommendations
Based on the results of the research, the organization DDF is already facing trouble due to the changing demography in international travel. However, the problems pertaining to the organization can be strengthened more in the future and can hamper the financial performance of the organization. In this situation, the organization is required to adopt strong strategies that can help it to enhance the level of CS and CL. In the process of the research, both in the literature review and the data analysis, a number of strategies are identified that can help the company to enhance the CS levels. Firstly the organization has to understand and appreciate the existing relationship between the level of CL and CS and the socio-economic status of the customers. Moreover, the organization is also required to interpret the purchase behaviour of the middle-income groups who avail the international travelling opportunity through low-cost carriers. In this aspect, the implementation of the theories and models that relate to CS, CL and consumer behaviour such as the Assimilation-contrast theory, Disconfirmation theory are needed to be explored for the incorporation of the knowledge in the business strategies.
The organization is recommended to develop a separate DDF department within its store in the airport that would include products in the medium price range and thereby can attract more people from the middle class. In this particular approach, the company can also focus on providing greater discounts of the premium products so that more people from the middle class can avail the service. On the other hand, the level of engagement between the employees and the customers must be enhanced in DDF so that the needs of the customers from the middle-class groups can be better identified in the near future. Apart from focusing on maintaining medium-priced products, the company can also arrange loyalty programs for the customer for enhancing the extent of CL among the customers. This particular strategy can also help in positive information sharing about the organization among the international travellers and elevate the level of sales of the organization.
In future, it is necessary to improve the process of research through more reliable and valid research methods. In the present research, the researcher has utilized the Skype interview method due to the lack of time for arranging personal interview sessions. In future, a face-to-face interview can be arranged as it is more helpful in understanding non-verbal communication. Furthermore, the numerical data can be analysed in future research with the help of statistical software like SPSS which is able to provide a more accurate interpretation of statistical data. Along with literature review, a separate secondary research method can be applied in future studies in which data can be analysed with thematic analysis technique.
5.2 Linking with objectives
Objective 1: This objective has been achieved in the section of the literature review as well as in the data analysis chapter. The qualitative analysis, analysis of data collected against Q1 and in quantitative analysis, Q3 has helped in addressing this particular objective.
Objective 2: This specific objective is partly achieved in the literature review chapter wearing the interrelationship between cs and CL is identified from the existing literature. The analysis of data collected against qualitative Q2 and quantitative Q6, Q5, and Q4 has significantly contributed to the achievement of this objective.
Objective 3: The third objective of the research that related to the eminent issues regarding CS and CL in DDF is achieved in the data analysis chapter in quantitative analysis of Q3, Q4, and Q5 and qualitative analysis of Q2.
Objective 4: The literature review chapter has identified a number of strategies to eliminate the level of CS and CL in the travel retail industry. Moreover, the quantitative analysis of Q8 and Q9 and qualitative analysis of Q3 has helped in addressing this objective.
5.3 Reflection on the research process
Along the course of the research, I have learnt regarding the concepts of CS and CL in the airport retailing industry or duty-free industry. I have identified that the duty-free industry has an immense impact on the economy of a nation and therefore it is important to maintain a stable CS level in the organisations in this industry. While conducting the research I have faced numerous challenges in relation to the collection of data. However, extensive research on the existing methods of data collection has greatly helped in identifying appropriate methods that can be used in this particular research. The knowledge gained from the overall research process can be utilized in future research.
5.4 Future scope of the research
In the future, the results of this research can be used in order to analyse the impact of CS and CL on the organisational performance of the major travel retail company, DDF. In future research, the researcher can utilise both the primary and secondary research methods to improve the strength of the research outcome. The impacts of the other external business factors on the CS and CL aspects of DDF can also be studied in future course of research.
References
Abushaikha, I., Al-Weshah, G. and Alsharairi, M., 2020. How do retail firms benefit from co-locating in logistics-intensive clusters? A focus on the inbound supply function. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 30(1), pp.27-45.
Alnuaimi, A.S.A. and Yaakub, K.B., 2020. The Impact of Leadership Practices on Total Quality Management and Organizational Performance in the UAE Interior Ministry. European Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 5(2), pp.10-15.
Attia, M. and Edge, J., 2017. Be (com) ing a reflexive researcher: a developmental approach to research methodology. Open Review of Educational Research, 4(1), pp.33-45.
Azadian, F. and Vasigh, B., 2019. The blaring lines between full-service network carriers and low-cost carriers: A financial perspective on business model convergence. Transport Policy, 75, pp.19-26.
Basias, N. and Pollalis, Y., 2018. Quantitative and qualitative research in business & technology: Justifying a suitable research methodology. Customer satisfaction assignment Review of Integrative Business and Economics Research, 7, pp.91-105.
Bi, J.W., Liu, Y., Fan, Z.P. and Zhang, J., 2020. Exploring asymmetric effects of attribute performance on CS in the hotel industry. Tourism Management, 77, p.104006.
Brochado, A., Oliveira, C., Rita, P. and Oliveira, F., 2019. Shopping centres beyond purchasing of luxury goods: a tourism perspective. Annals of Leisure Research, 22(4), pp.484-505.
Budianto, A., 2019. Customer loyalty: quality of service. Journal of management review, 3(1), pp.299-305.
Camilleri, M.A., 2019. The business of tourism: An introduction. In Strategic perspectives in destination marketing (pp. 1-27). IGI Global.
Cha, J. and Borchgrevink, C.P., 2019. Customers’ perceptions in value and food safety on CS and loyalty in restaurant environments: moderating roles of gender and restaurant types. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 20(2), pp.143-161.
Chang, K.C., Hsu, C.L., Chen, M.C. and Kuo, N.T., 2019. How a branded website creates customer purchase intentions. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 30(3-4), pp.422-446.
Chen, Y., Wu, C.L., Koo, T.T. and Douglas, I., 2020. Determinants of airport retail revenue: a review of literature. Transport Reviews, pp.1-27.
Cheng, K.T., 2019. Factors Affecting Information System Satisfaction from a Two-Dimensional Perspective. Open Journal of Business and Management, 7(02), p.568.
Choi, E.A., Lee, S.S. and Lee, D., 2016. Improvement of Service Encounter in Duty Free Shop Using Service Blueprinting. Journal of the Korea Industrial Information Systems Research, 21(4), pp.95-110.
Choi, I.Y., Moon, H.S. and Kim, J.K., 2019. Assessing Personalized Recommendation Services Using Expectancy Disconfirmation Theory. Asia Pacific Journal of Information Systems, 29(2), pp.203-216.
Cuervo?Cazurra, A., Mudambi, R., Pedersen, T. and Piscitello, L., 2017. Research methodology in global strategy research. Global Strategy Journal, 7(3), pp.233-240.
Dubaidutyfree.com. 2020. Available at: https://www.dubaidutyfree.com/ [Accessed 30 Apr. 2020].
Dupuis, D., 2019. Ex-dividend day price behavior and liquidity in a tax-free emerging market. Emerging Markets Review, 38, pp.239-250.
El-Adly, M.I., 2019. Modelling the relationship between hotel perceived value, CS, and customer loyalty. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 50, pp.322-332.
Fletcher, A.J., 2017. Applying critical realism in qualitative research: methodology meets method. International journal of social research methodology, 20(2), pp.181-194.
Genç, R., 2019. Luxury Shopping as a New Opportunity for Tourism Market Development. Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Education, 9, pp.1-8.
Han, H., Yu, J. and Kim, W., 2018. Airport shopping–an emerging non-aviation business: triggers of traveler loyalty. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 35(7), pp.835-845.
Huang, P.L., Lee, B.C. and Chen, C.C., 2019. The influence of service quality on CS and loyalty in B2B technology service industry. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 30(13-14), pp.1449-1465.
Kefallonitis, E. and Kalligiannis, K., 2019. The Effect of Airport Branding to Air Traffic and Passenger Movement: An Overview. In Strategic Innovative Marketing and Tourism (pp. 523-531). Springer, Cham.
Kim, H., Kim, J.J. and Asif, M., 2019. The Antecedents and Consequences of Travelers’ Well-Being Perceptions: Focusing on Chinese Tourist Shopping at a Duty Free. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(24), p.5081.
Kim, P.J. and Kim, H.K., 2017. The Effect of Loyalty Factors Perceived by Consumers on General Super Market. Journal of Industrial Distribution & Business:: Vol, 8(4), pp.37-46.
Kim, W., Kim, H. and Hwang, J., 2020. Sustainable growth for the self-employed in the retail industry based on customer equity, CS, and loyalty. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 53, p.101963.
Lindblom, A., Lindblom, T. and Wechtler, H., 2020. Retail entrepreneurs’ exit intentions: Influence and mediations of personality and job-related factors. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 54, p.102055.
Martín, J.C., Martín-Domingo, L., Lohmann, G. and Spasojevic, B., 2019. The role of travel patterns in airport duty-free shopping satisfaction: A case study from an Australian regional airport. Journal of Air Transport Management, 80, p.101691.
Mehrotra, A., 2019, April. Artificial Intelligence in Financial Services–Need to Blend Automation with Human Touch. In 2019 International Conference on Automation, Computational and Technology Management (ICACTM) (pp. 342-347). IEEE.
Michael, N., Reisinger, Y. and Hayes, J.P., 2019. The UAE's tourism competitiveness: A business perspective. Tourism Management Perspectives, 30, pp.53-64.
Mohajan, H.K., 2018. Qualitative research methodology in social sciences and related subjects. Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People, 7(1), pp.23-48.
Mohasses, M., 2019, February. How AI-chatbots can make Dubai smarter?. In 2019 Amity International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AICAI) (pp. 439-446). IEEE.
Mondragon, G., Méndez, K., Mauricio, D. and Díaz, E., 2019, August. Evaluation model of the digital experience in the retail sector using customer journey. In 2019 IEEE XXVI International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computing (INTERCON) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
Mulay-Shah, A., Lambert, L., Younis, Y. and Wood, B.P., 2019. Commercial life: The private sector’s contribution to wellbeing. In Positive Psychology in the Middle East/North Africa (pp. 37-70). Springer, Cham.
Murphy, J.T., 2019. Global production network dis/articulations in Zanzibar: practices and conjunctures of exclusionary development in the tourism industry. Journal of Economic Geography, 19(4), pp.943-971.
Myo, Y.N., Khalifa, G.S. and Aye, T.T., 2019. The Impact of Service Quality on Customer Loyalty of Myanmar Hospitality Industry: The Mediating Role of CS. International Journal Of Management And Human Science, 3(3), pp.1-11.
Naletina, D., Dami?, M. and Bebek Gori?ki, A., 2019. Passenger Retail at Airports: The Case Study of the Republic of Croatia. InterEU law east: journal for the international and european law, economics and market integrations, 6(1), pp.21-41.
Naletina, D., Petljak, K. and Sremac, M., 2019. Empirical research on user satisfaction with the transport and the supporting services at Croatian airports. Pomorstvo, 33(1), pp.92-101.
Ndlovu-Gatsheni, S., 2017. Decolonising research methodology must include undoing its dirty history. Journal of Public Administration, 52(Special Issue 1), pp.186-188.
Noguti, V., Singh, S. and Waller, D.S., 2019. Gender differences in motivations to use social networking sites. In Gender economics: Breakthroughs in research and practice (pp. 676-691). IGI Global.
Obeidat, B., Tawalbeh, H.F. and Akour, M.A., 2019. Reviewing the Literature among Human Resource Management (HRM) Practices, Total Quality Management (TQM) Practices and Competitive Advantages. Journal of Social Sciences (COES&RJ-JSS), 8(2), pp.327-358.
Page, D., Gilroy, M., Hurrion, E., Clark, L. and Wilkinson, S., 2017. Optimising early neonatal nutrition using translational research methodology. Nutrition & Dietetics, 74(5), pp.460-470.
Saunders, M., Lewis, P. and Thornhill, A., 2009. Research onion. Research methods for business students, pp.136-162.
Seng, W.M., 2019. Design Science Approach to Build a CS Theoretical Framework to Evaluate E-Government Services. Electronic Journal of Information Systems Evaluation, 22(1), pp.54-64.
Sharma, P., 2019. Research Directions and Implications. In Intercultural Service Encounters (pp. 75-95). Palgrave Pivot, Cham.
Shields, R., 2019. The sustainability of international higher education: Student mobility and global climate change. Journal of cleaner production, 217, pp.594-602.
Simon, H. and Fassnacht, M., 2019. Price Strategy. In Price Management (pp. 29-84). Springer, Cham.
Thubert, S., Francoulon, L., Weber, L., Maniere, I.C. and Boyaval, F., 2017. Duty-free shops: Are luxury brands being democratized?. Procedia computer science, 122, pp.533-540.
Ulmer, J.B., 2017. Posthumanism as research methodology: Inquiry in the Anthropocene. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, 30(9), pp.832-848.
Wagner Mainardes, E., de Almeida, C.M. and de-Oliveira, M., 2019. e-Commerce: an analysis of the factors that antecede purchase intentions in an emerging market. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 31(5), pp.447-468.
Yasmeen, H., Wang, Y., Zameer, H. and Waheed, A., 2019. Service-innovation capability founded on knowledge from customers. Human Systems Management, 38(1), pp.29-41.
Zhang, X., Xie, H., Zhao, J. and Lui, J.C., 2019. Understanding assimilation-contrast effects in online rating systems: modelling, debiasing, and applications. ACM Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS), 38(1), pp.1-25.
Appendix: Questionnaire for survey and interview
Quantitative survey questions
- What is your age?
- How often do you shop at / visit DDF?
- How far do you agree that DDF does not successfully meet the needs of diverse groups of customers efficiently?
- How far do you agree that DDF does not provide the expected high values as compared to its premium pricing?
- How likely are you to advise your friends and relatives to avoid visiting DDF, during their travel?
- How likely are you to repeat-purchase at DDF?
- According to you, what strategies need to be considered for solving the challenges faced by DDF?
- How far do you agree to the fact that DDF is in dire need of changing their CS and customer loyalty strategies, to satisfy the shifting demographics of travellers?
Qualitative Interview Questions
- According to you, how purchase intentions of travellers are impacting the CL and CS within DDF?
- What are your views on the fact that the changing demographics of the travellers and the evolution of Low Cost Carriers are impacting the CS and customer loyalty at DDF?
- According to you, what strategies can be implemented for resolving the imminent challenges of DDF?












