Cross cultural leadership assignment on leadership traits required to manage MNCs
Question
Task: How can managers improve their leadership skills using cross cultural leadership assignment research methodologies?
Answer
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Background of research
This cross cultural leadership assignment has observed in the current era, globalization has been forming modern society, wherein it has become an interesting field of study which has open up various topics of relevance for research. With the advent of globalization, the distinction of nation borders has dramatically decreased, while progressively creating a new opportunities for the organizations in terms of entering into new markets and expanding in size and resources. Along with this, the internationalization process has developed an intercultural workplace environment, while opening a new field of research, which is of increasing relevance to the study of how to meet the new requirements created by the various cultures for competence. In addition to this, there has been an increase in the awareness of how the international leaders adapt to the regional culture, wherein many firms are curious about the knowledge in relation to the advantages of localization. Thus the concept of cross culture derive, which is generally the interaction of numerous different cultures and the character of such context (Song and Yap, 2014).
With rapid globalization and industry cross-border consolidation, as experienced by the business in the current era, cultural difference has seemingly becoming one of the significant foreign activities. There has been notable increase in international joint venture, acquisition, and pother various global corporations such as mergers. It is therefore, understanding the insinuation of cultural factors on the effectiveness of leadership has become imperative, while emphasizing on the extent of culturally driven leadership adjustment at the period of cross border activities, its potential impact on leadership and business performance, and its critical determinants. (Nicholson, Carr and Smith, 2020)
As mentioned earlier on this cross cultural leadership assignment, the workforce of the organization are becoming more diverse, and multi cultural, while have a major impact on the leadership decision of the MNC. In any organization, culture plays a vital role because it reflects one’s behavior, mindset, and perception of the individual. Since MNCs have their original root in one country wherein they have to operate in another countries, while coping up with diverse culture, the leadership decision become quite a challenge both for the leaders as well as the organization (Kinkhabwala, 2019).
Thiscross cultural leadership assignment research paper aims towards understanding the impact of cross culture factor on the leadership decision of MNC, using various models and theories. The organization that has been chosen for the research is Unilever, which is one of the largest and renowned MNC in the global economy, wherein the progress of the company is related with its organizational culture, cross cultural activities, and policies implemented by the leaders over the time. It is an integrated international firm, where the leadership, organizational culture, and human resources are all interrelated (Gregory, 2015). During the procer4ss of internationalization, the firm faced various challenges and issues linked with the leadership decision and managing employees from diverse cultural background.
1.2 Scope of research
The MNCs are often not clear with the concept that whether the firm must adapt a new leadership style in order to match with the regional expectation or it will be better to continue with the same leadership style and practices, previously established by the management. Though the practical relevance of impact of cross cultural factors on the leadership decision has been growing dramatically, along with the cultural leadership adjustment, the expatriate research is still underdeveloped and fragmented (Nicholson, Carr and Smith, 2020). The relationship between the cross cultural factors and its impact on the leadership decision of MNC still lack empirical evidence, wherein the research on such given topic has still not reached maturity. The majority of theoretical debated surrounding such topic has been accompanied by relatively few data driven studies. The cross cultural factors has a major contribution towards the need of leaders in terms of adapting and adjusting to the culture of other nations, wherein the increased in competition has forced the organizational leaders to understand the limitations of the organizational culture, and leadership practices (Alapo, 2017).
In concern to the chosen topic, the scope of this cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch is to engage in the study of impact of cross cultural factors on the leadership decision of MNC. Since it is not possible to include all the MNCs from across the globe, the study has chosen Unilever; a leading UK based multinational consumer goods company, the firm primarily focuses on its diverse workforce. Using Hofstede’s cultural dimension model and cross cultural and leadership theories the cross cultural factors and its impact on the leadership practices has been examined as these models and theories directly relate with the given topic. In addition to this, it will provide information and data for the research of the similar topic
1.3 Aim
The primary aim of this cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch is to fill the gap in the study of impact of cross cultural factors on the leadership decision of Unilever. It seeks to identify and observe the leadership adjustment, along with the identification of the challenges that the firm face while managing the cross cultural factors. With the use of various theories and model, this paper aims towards analyzing what cross cultural leadership are likely to be deployed in order to enhance the organizational performance both within the national and international borders. Hence, the common cross cultural challenge will be identified by this research while aiming to provide recommendations in order to mitigate those challenges, primarily in reference to Unilever. The aim and motivation of this cross cultural leadership assignmentpaper is to explore the volatility linkages between the cross cultural factor and the leadership of the organization in the existing era.
1.4 Objectives
• To analyzee the impact of cross cultural factors on leadership decision using Hofstede’s cultural dimension model
• To analyzee the impact of cross cultural factors on leadership decision in Unilever
• To provide recommendation to manage cross-cultural factors in Unilever
1.5 Research questions
• What is the impact of cross cultural factors on leadership decision of Unilever?
• What challenges are posed by the cross cultural factors in the MNC?
• What remedies can be applied by the firm to mitigate the challenges posed by cross cultural factors on leadership decision?
1.6 Importance of cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch
The importance of this research is that it will develop understanding of the cross cultural factors and its impact on the leadership decision. Since the given topic lack empirical evidence, this research builds knowledge, while facilitating efficient learning about the chosen topic, and helps to understand both the advantages and challenges of having diverse culture within the organization, and how it influence the leadership style and practices of the organization. In addition to this, this cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch is likely to help the entities in terms of identifying the market opportunity in the diverse work environment, along with the way to tackle with the hardship faced by the organization within the context of leadership decision. It uncovers and identifies potential problems and opportunities, along with the data and information for further research. In reference to Unilever, this paper has explored various aspects of MNCs, while dealing with the cross cultural factors and its influence on the leadership practices of organization.
1.7 Summary of chapters
This paper has been divided in various chapters, such as introduction, literature review, methodology, finding, analysis, discussion, conclusion and recommendations. As seen above, the introduction chapter has provided the background, significance, aim, and objectives of the research. In the second chapter, the existing literature has been reviewed while focusing on the investigation of how the cross culture actually impact the leadership decision of the MNC, in relation to Unilever. In methodology chapters, the methods that has been used for the completion of this research has been elucidated in detailed form including the cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch techniques, design, sampling, approaches etc. the next chapter has analyzed the finding of the research, while evaluating and discussing the relationship and major impact of cross cultural factors on Unilever, its leadership practices, and the challenges of diverse cultural factor faced by the organization. Hence, the chapter culminates with the brief conclusion of the overall research, while providing potential recommendations to efficiently mitigate the identified challenges.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
The main objective of the literature review is simple as it helps to accumulate and gather information about the literature based on a specific topic before shaping the justification or an argument. A literature review in simple terms is a classification, compilation and evaluation of a topic written by a particular researcher. The Literature review has been conducted by reviewing previous articles, journal articles and valid sources about the information based on the particular topic. The literature review will help to identify the cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch area, the interrelationship between key ideas, dynamics and variables as well as current trends and theories. The literature review is based on the impact of cross-cultural factors on leadership decisions of MNC: reflection on the leadership of Unilever. The literature review also includes Hofstede’s cultural dimension theory to understand its impact on people from different geographic and cultural backgrounds. The review includes articles and journals of different authors to collect the relevant information for the research topic.
2.2Hofstede’s cultural dimensional model
According to (Ao, 2016), the complex characteristics of cultural value and rapport between the leadership and cultural difference, Hofstede’s cultural dimension theory have become a really important framework. The cultural dimension theory includes six different dimensions the first being the power distances which gradually deal with inequality which exists among the people with power or without it. A high score of PDI specifies that society has accepted a classified distribution of power and inequality exists. The lower PDI normally indicates the power is broadly dispersed and shared. For example, in the power distance index in a country where the PDI is generally high, the team member doesn't determine any action for the tasks and if no individual takes leadership for the task it fails to be completed. The dimensional theory is utilized in quantifying the variances among different cultures and is widely used in the field of cross-cultural communication, international business and cultural psychology.
As stated by (Agodzo, 2015), the next cultural dimension according to Hofstede is Individualism. The concept of Individualism can often be described as the social mentality which emphasises an individual, recognising and valuing the individual's achievement. Individualism also can be referred to as the encouragement of independent actions and thoughts. The self-concept is highly emphasized in these societies as opposed to the cultures rooted in collectivism is an overriding consideration. The higher score of IDV indicates a feeble interpersonal connection between those who are not a part of the core family. In this scenario, the person or an individual takes lesser accountability for other outcomes and actions. For example, the United States has a relatively high score on IDV than the UK, so necessary in this context; the residents of both countries view the prominence on those matters as family compulsions and individual choices from different perspectives.
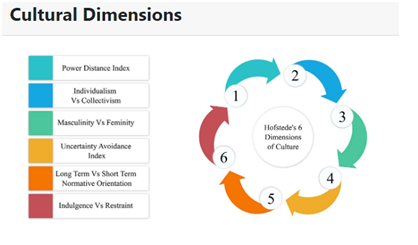
Figure 1:Hofstede’s cultural dimensional model
Source:(Nickerson, 2022)
According to (Zamanabadi, 2015), the next Hofstede’s cultural dimension also includes uncertainty avoidance. Uncertainty avoidance can be referred to as the extent to which various people feel the danger of ambiguity and uncertainties. Therefore people are more likely to try and avoid these circumstances. The dimension in simple terms means how well an individual can cope and handle anxiety. A higher score in uncertainty avoidance means that individuals tend to make their life more controllable and predictable as possible. However, if an individual identifies that they are unable to control their lives they may be curious about trying to stop it. A particular country with a relatively low score in uncertainty avoidance is more inclusive, open and relaxed as compared to a high score. The higher score in UAI consists of characteristics like rigid, structured and conservative as well as many societal conventions present there.
According to (Milosevic, 2018), the next cultural dimensions of Hofstede include Masculinity-Femininity. This particular dimension deals with the dispersal of roles between males and females. In context with masculine societies, the male is ultimately expected to be behaving in an assertive manner and the roles of women and men overlap less. The steadfast, strong and successive factors are often seen as the triumph and positive characteristics. In femininity societies, it is believed that both men and women should be caring and modest in nature. Therefore a good outcome and greater importance are determined by good relationships with the people who are cooperative with one another or directly with the supervisors. For example, if Japan has a high score on the MAS index, the operations in japan will be more deferential, hierarchical and patriarchal society traditionally. This can become difficult for the female members of a team to gain advancement in a relevant field owed to family commitments. As stated by (Beugelsdijk and Welzel, 2018), the next cultural dimension was often referred to as the PRA (Pragmatic versus Normative). Later on, Hofstede changed its name to long-term versus short-term orientation; this particular dimension refers to a society display where the time horizon people exist. The long-term orientation can be defined as more thrifty, realistic and modest. It is also considered to be more future-oriented and accept the overdue gratification for an individual's effort. The short-term orientations are generalized by now and here temperament programs them to take an additional advantage and benefit whenever the time desires. The short-term oriented region also laid more emphasis on consistency, truth and principles which are nationalistic and religious. The short-term orientation characteristics can include strong convictions; people often thrive to know the "why?" The last cultural dimension in Hofstede’s cultural dimensional theory is indulgence versus restraint. In the context of this dimension, happiness is regarded as the measure and indulgence can be defined as the need to live a free and enjoy the basic needs a human perceives from entertainment and social life. However, indulgence and restraint are relatively new dimensions and extensive data is not available. However, the countries with a high score of IVR encourage or allows free gratification of people's emotion and own drives that including having fun and enjoying themselves. The characteristics of higher indulgence include personal happiness, freedom of speech and being more optimistic about life. The countries relatively with low IVR scores suppress gratification of people, social norms are stricter and regulations on people's conduct and behaviour. The higher restraint characteristics include rigid and controlled behaviour and an inclination towards pessimism. This concludes the cultural dimension of Hofstede.
According to (Ogunremi and Adebola Boka, 2019) there are different factors that influence the behaviour of workers in a multicultural business environment. The first factor is the different cultural backgrounds of people andindividuals they come from and it is equally important for the co-workers to understand each other culture, ethnicity and values. The importance of understanding and interpreting the different behaviour of individuals from the top management to an employee level will enhance a better relationships and good cooperation among them. In the case of Unilever, there is a huge number of stakeholders, employees, managers and other team members that influence the decision-making process of leadership. The main component for an organization to achieve the desired goal and effectiveness is human capital and it was necessary for the Unilever employees, subordinates and management team to consider an effective rapport between them rather than avoiding the unnecessary circumstances that hamper the overall growth for the company.
According to (Rao Nicholson, Carr and Smith, 2020), there is different cross cultural leadership assignment research and has suggested that cultural background plays an important role in impacting leadership. All over the globe, the main threat every other corporate is witnessing is how they can turn a cultural differences threat into valuable resources. In context with Unilever, the impact of cross-culture in several instances has made a good impact on their management style and communication. There are multiple levels of management functioning in Unilever with different people, race culture and religious beliefs. In some cases, the company had a positive outcome such as high context communication among the subordinates and leaders who specifically deal with the same motive, objectives and vision for the company even though they come from different backgrounds. The successive factor for Unilever's different leaders in their multicultural work environment has also been its avoidance of ethnocentrism (Over evaluation of others' cultural backgrounds).
As stated by (Jayasundera and George, 2017), the cross-cultural issues at certain times have also hampered the leadership functioning its decision making and team performance for Unilever PLC. There are numerous projects by Unilever that defines innovation, leadership style, team management and efficient product placement in the market forum. The collective team member of Unilever authorized to handle the project formulation and strategize its successive measures in the market depending upon their action plan and procedures. However the lack of communication among different team members for the allocated project might perceive different ideas and cultural values in the product, this can ultimately lead to disagreements, and conflict among the leaders involved in the project and hampers the final decision binding. Therefore a majority of performance management enterprise and performance problems transpire in the organizational context which is deemed to affect the leadership decision.
According to cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch done by (Maity, 2018) the cross-cultural issues in the workplace or in any organization can hamper the leadership and influence the decision-making process. Some of the issues faced in the cross-culture environment and creates the differences in the workplace include cultural behaviour, generation gap, religion and ethnicity. The cross-culture environment and its factors in certain instances had a varied impact on its leadership decision. The issues like teamwork, feedback, employee commitment and working behaviour and communication were some of the cross-cultural problems identified in context with Unilever PLC. However to deal with the issues of a multicultural workforce Unilever can play a definite role to deal with those problems. For example, the communication gap among the subordinates and managers at MNCs from different cultural roots fails to validate each other’s points due to a lack of communication or language barrier. Unilever or many other MNCs tend to follow the rigid and strict management style this has led to a cultural shock for most of the employees if they are posted or relocated to any other locations. If the companies follow a dynamic style of cross-cultural management there is a possibility of shared knowledge between each other for better teamwork and learning process.
2.3 Impact of cross cultural factors on leadership decision in Unilever
According to (Kapur, 2020) leadership refers to the fundamental ability of individuals to formulate and alter the perspectives of their subordinates by effective decision-making and exercising necessary commands. Leadership is a significant aspect of an organization since effective leaders contribute to achieving the objectives and long-term goals of the organization. Leaders are aware of the varied techniques and approaches that will drive them to attain organizational goals in an efficient manner. The primary objective of leaders is to provide knowledge and support to the employees of the organization. They ensure that the performance levels and productivity of the subordinates are directed towards the organizational goals. Leaders are required to carry out varied functions and responsibilities and possess a certain set of skills to put the functions into operation. Some vital functions of leaders are: a leader is the representative of the subordinates; he or she is an appropriate counsellor; leaders are expected to manage time and organization’s resources in an efficient manner; provide provision of security to the employees; develop a working environment that is conducive to work; enable co-operation amongst the workforce and communicate the company’s policies to the workforce (Abdussamad, 2017). Leaders must possess effective problem-solving and critical-thinking skills in order to resolve any underlying issue in the organization.
As stated by (Li, 2018) the general principle for organisational culture in Unilever is its responsibility, integrity, performance, efficiency and quality on the global forefront for their business and operations. Effective leadership has been a fundamental role in the company's to approach better policies and functioning among different people that comes from different race and cultural background. It is very important to understand cultural value because it has a general impact on the implementation of the foreign manager's leadership. The cross-cultural situation can have an adverse impact on leadership and its effectiveness so for better illustration, it is important to approach with a theoretical model. The cross-cultural model indicates that a substantial performance by the leader which primarily does not focus on the harmony and interest of the group can be subjected to an ineffective and negative collectivist nature.
As per (Shyanka, Abeysekera and L.S., 2014) leadership plays a significant role in the proper functioning of business operations in a Multinational Company (MNC). Leaders tend to attract the right employees for attaining sustainable performance. Inspirational motivation is the main component of leadership since good leaders motivate their subordinates and inspire them to achieve organizational objectives by setting examples for them. Every organization must focus on leadership development to improve the overall profitability and productivity of the organization. Leadership development refers to the procedure of improving the skills and capabilities of an individual which will enable him to perform better and direct the organization toward its long-term goals. It enables the leaders to develop the required set of skills which will be beneficial in enhancing the productivity of the workforce.
According to (Kinkhabwala, 2019), the corporate culture is comprised of different patterns values and behaviours, the artefacts of an organization, narratives and accounts that reinforce those values. Over the years there are multiple companies expanding around the globe and a range of people from different backgrounds and ethnicity has made the idea of culture a complexity. Cross-cultural differences are the interactions among people from different classes, races, ages and backgrounds. Unilever a multinational company operating in more than 190 countries has a varied workforce that comes from different cultural backgrounds, languages and origins. Therefore it is equally important for the company to have better cross-cultural leadership skills in diversifying its workforce and gaining an economic advantage. However cross-cultural factors can also affect leadership styles and communication that can have a negative impact on an individual working style, motivation and directions.
According to (Simiyu, 2015) it is significant to understand the role of effective leaders within an organization since leadership patterns dictate the personal outcomes of the workforce. Organizational development is dependent on the efficiency of leaders to direct the company toward its long-term goals. Organizational development refers to the practice of engaging in organizational culture modification which will ensure the overall profitability and enhance the productivity of the employees (Kapur, 2018). This will facilitate learning and enable the personal as well as professional growth of the workforce. Leadership plays a significant role in creating and cultivating organizational culture within the workplace. Leaders must be committed to motivating their subordinates and assisting them to face challenges that may arise in an organization. Leaders must acknowledge the significance of the employees and formulate strategic plans that will align the workforce and empower them to perform efficiently. Leaders must be visionary individuals who will communicate the vision to their followers with the intent of supporting change within the organization.
As per (Das, 2015) the impact of rampant globalization and international integration of businesses has led to individuals from varied cultural and ethnic backgrounds being a part of the workforce. Therefore, it is significant for leaders of organizations to understand the cultural differences and similarities that arise due to the presence of multicultural aspects in the workplace. By appointing individuals belonging to various cultural backgrounds, an environment of cultural diversity and identity is formed in the organization. Cultural diversity refers to the coexistence of various cultures, practices, values, customs, morals, beliefs, languages, ethnicities, religions, races and nationalities (Lin, 2020). Therefore it is important for organizations to develop a cross-cultural style of leadership pattern that will create a diverse workforce and lead the entire team towards achieving organizational goals. Leaders will be able to extract resources and enhance their capabilities which will garner effective outcomes for the organization. Leaders of a culturally diversified team will ensure coordination, reduce linguistic barriers, resolve communication problems and sort out any form of misunderstanding between team members.
According to (Vailati, 2014) culture is a significant factor that impacts the decision-making of leaders in an organization. Cross-cultural factors such as language, social background, communication, historical background, cultural identity and gender tend to have a significant impact on the leadership pattern within an organization. Leadership patterns must be designed and implemented in accordance with the specific cultural characteristics of the workforce.
According to (Smith and Peterson, 2017) leadership is a vital element in determining the success of multinational businesses. Cultural differences within an organization contribute to improving the job performance of the employees. A multicultural workforce will require the leaders to create benchmarks of functions and norms that will be beneficial for the team to work efficiently. Leaders need to develop the ability to manage individuals with varied cultures and must be able to adapt themselves to the changing environment. The interaction of cultural values and norms affects the style of leadership and enables the leaders to be more understanding towards understanding their subordinates. The leaders are culturally aware and intercultural sensitivity is visible in their decision-making process. This will enable the leaders to effectively deal with the varied complex challenges that arise in a cross-cultural and diverse workforce.
As per (Gantasala and Omar, 2016) leadership functions are significant to organizations that operate in cross-sectional market economies. The cultural diversity of varied geographical locations and the interconnectedness of the workforce will be able to determine the success of the organization. Cross-cultural leadership enables leaders to understand individuals from varied cultural backgrounds and interact with them in an effective fashion. Leaders who focus only on getting the tasks accomplished do not yield positive outcomes for the organization. A leader must be culturally sensitive and lead the organization with an open mind. He should be mindful of the cultural differences within the workforce while making significant decisions. This will lead to enhancement of the job satisfaction level amongst employees and improve the profitability and productivity of the workforce.
Chapter 3: cross cultural leadership assignmentResearch Methodology
Research methodology refers to the process used by the researcher to conduct their research. The research methodology is the systematic, logical plan to resolve research queries. While designing a research methodology a researcher is posed with different queries regarding the choice between various data methodology types. Methodology denotes the entire understanding of the research process including its philosophical assumptions, ethical principles, social organisational context and the political effect of new information from the research enterprise (Adedoyin, 2020).
3.1 Research Philosophy
Research philosophy denotes the set of beliefs about the nature of the reality that is being investigated (Chege and Otieno, 2020). Research philosophy is considered to be a crucial part of research methodology and is classified as epistemology, ontology and axiology. The research philosophical approach enables the decision regarding the approach which must be adopted by the researcher. Research philosophy is concerned with the nature, source and development of knowledge. The two chief cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch philosophies are interpretivism and positivism. These philosophies denote two fundamentally distinct ways humans make sense of the world surrounding them.
For this research positivism research philosophy and positivism were undertaken. Positivism holds that reality exists independently of the subject being studied hence the meaning of the phenomenon is parallel and consistent between subjects. As a research philosophy, positivism sticks to the view that only real or factual knowledge is garnered through observation encompassing measurement is trustworthy (Nickerson, 2022). Positivism is largely dependent on quantifiable observations which lead to statistical analyses. Positivism as a philosophy is following the empiricist view that knowledge comes from human experience and has an ontological, atomistic view of the world as containing discrete, observable events and elements which interact in a determined, regular and observable manner. The five primary principles of positivism are:
• There is no distinction between the logic of inquiry in sciences
• The research must aim to predict and explain
• Research must be empirically observable through the human senses
• Common sense must not be allowed to pose bias in research findings
• Science must be free of value and judged only based on logic.
The main aim of this cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch was to evaluate the impact of cross-cultural factors on leadership decisions while reflecting on the leadership practices of the MNC Unilever. Through undertaking the positivism philosophical approach, the study was observed, measured and recorded to derive essential knowledge and information on the chosen topic. The main aim of positivist research is that it facilitates researchers to study the relationships and patterns behind social factors which facilitate them to make adequate and accurate predictions about social and societal change.
3.2 cross cultural leadership assignmentResearch Approach
Research approaches can be described as the collection of plans and procedures to decide the overall methods of research. The methods for data collection, data interpretation and data analysis are determined by the research approach. The research approach's concept is followed across the entire research process. There are various factors of research approaches such as the experience of research, research objective and the selection of the research study audience. Research approaches can typically be one of two types: quantitative and qualitative. Qualitative methods are used when researchers want to determine the degree of the presence of elements. The quantitative approach utilises advanced statistical techniques on the other hand qualitative approaches employs open-ended queries which use direct quotations.
For this cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch inductive approach was undertaken which is also known as inductive reasoning. The inductive approach begins with theories and observations which are presented towards the end of a cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch process as a consequence of observation. This approach encompasses the search for patterns from observations along with the development of theories and explanations for those patterns through a series of hypotheses. No hypothesis or theories would apply in inductive research at the initiation of the research and the researcher can alter the direction of the study after the commencement of the research process. It is imperative to stress the inductive approach does not mean disregarding theories while formulating research objectives and questions. The inductive approach aims to generate meanings from the information set collected to identify relationships and patterns to build a theory. The inductive approach, however, does not deter the researcher from utilising an existing theory to create thecross cultural leadership assignment research question which will be explored.
Inductive reasoning starts from the detailed observation of the world, which then proceeds toward more abstract ideas and generalisations. While following an inductive approach, the researcher develops an empirical generalisation and recognises preliminary relationships while progressing through the research. Due to this factor, the inductive approach is often denoted as the bottom-up approach to research since the researcher utilised observations to garner some idea about an issue or topic being researched (Woiceshyn and Daellenbach, 2018). The inductive approach is a highly adaptable research subject which is the main reason for the selection of this approach in this research study. The data-centric approach of inductive research facilitated identifying the trends in cross-cultural factors along with leadership approaches and allowed make for suitable research by assisting in examining the underlying theories and data about the causes of the information.
3.3 cross cultural leadership assignmentResearch Design
The cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch design refers to the overall strategy which has been selected to inculcate the several components of the study coherently and logically while also ensuring that the research questions and queries are addressed effectively. Research design is the arrangement of the terms for collecting data and analysing in a manner that is aimed toward inculcating the purpose or the relevance of the research to the economy and the procedure. Research designs are of various types such as explanatory, exploratory, descriptive and experimental designs (Pawar, 2020).
The research design's main function is to ensure that the material obtained enables the researcher to effectively address the research queries and problem as unambiguously and as logically as possible. A research design that is effective and good is characterised by adjectives such as flexibility, appropriateness, efficiency and economics (Akhtar, 2016).
For this cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch, the explanatory research design was undertaken which works towards explaining and exploring a given topic. Explanatory research can be described as a strategy utilised for accumulating data for explaining a phenomenon. As the phenomenon initiates with a single piece of data, the researcher can determine if he/she wants to collect more fragments of data. Explanatory data in other words is utilised to examine a phenomenon that had not been studied or evaluated before in an efficient way. For this research, the phenomenon of cross-cultural factors was analysed concerning its impacts on leadership decisions. The main purpose of the explanatory resign design is to find out the potential answer to a specific problem. The explanatory method enables one to find the information which works and undertake measures to develop better alternatives that can improve the process or issue being studied. The primary goal of explanatory research is to answer the query of how a phenomenon works the way it does and why some phenomenon does not work.
As stated by Boru (2018) explanatory research is conducted when there is not enough known about a phenomenon and an issue has not been defined clearly. This design does not aim to facilitate the conclusive and final answer to the cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch questions but it explores the research topic with different levels of depth. The undertaken research has sought to discover more data about how cross-cultural factors tend to impact leadership decisions with a specific focus on the MNC of Unilever and its cross-cultural leadership practices.
3.4 Data Collection
Effective and efficient methods of data collection are crucial to undertaking a well-researched decision. Data collection is an imperative element of research and the process encompasses collecting information and data from available sources to derive a solution for a research issue or problem. The data collection process evaluates the outcome and forecasts the possibilities and trends for the future. The are two primary methods of collecting data: Primary data collection method and Secondary data collection method. The primary source of data refers to the data which is garnered by the researcher directly from the source on the other hand secondary source of data refers to the collection of data from prior cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch (Parveen and Showkat, 2017).
The process of data collection encompasses identifying the types of data, their sources along with the methods that are being used. Data collection also encompasses qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data is non-numerical research that gathers information on thoughts, concepts and experiences. Qualitative results are usually useful for topics that are experienced based (Ghauri, Grønhaug and Strange, 2017). Quantitative data on the other hand is the opposite of qualitative and collects statistical or numerical information.
This cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch has been conducted through the secondary source of data collection in which information that is already available has been utilised. Secondary data collection encompasses collecting information from previous research which originates from researchers that have originally conducted the topics for another project and then made their research findings public for entities that have published the research for awareness like nonprofits or government organisations. Some of the sources of secondary data are books, newspapers, websites, podcasts and scholarly papers or journals. The undertaken study has encompassed information from various sources of secondary data such as websites, scholarly journals and articles, news reports etc(Kabir, 2016). There are varied advantages of secondary data collection methods as the method is a cheap way to obtain data from authentic sources. Apart from that the data derived from a secondary source of data uncovers the point of view of another individual and exposes things that otherwise might have been neglected. Secondary data is also highly accessible and has the feasibility of both international and longitudinal comparative studies which increases due to the method (Pérez-Sindín, 2017).
The cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch explored qualitative research by focusing on ideas and then formulating a hypothesis or theory. The research analysed key factors in cross-cultural information and its impacts on leadership practices. To evaluate the notion in depth and garner meaningful insights while undertaking Unilever as a key MNC, Hofstede's cross-cultural dimension was analysed wherein the nations of the United Kingdom and the United States of America were evaluated on Hofstede's dimensions of power distance, tolerance to uncertainty, masculinity vs femininity, long term vs short term orientation, indulgence vs restraint and individuality indexes.
3.5 cross cultural leadership assignmentResearch Analysis
Research analysis refers to the detailed procedure of analysing, transforming and presenting key information to form conclusions and support the decision-making process. Data or research analysis helps conclude terms of the variables which are prevalent in the research (Bhasin, 2019). The approach to data analysis is largely dependent on the research which is being carried out. The cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch has been undertaken with the use of content analysis which denotes the specification of specific concepts, patterns, phrases, themes, sentences or characters within the recorded content of the communication. To conduct content analysis, data are gathered from various sources. The main purpose of content analysis is to simplify the content, gain an in-depth and clearer meaning of the language, identify the uses of language and understand the concept (Parveen and Showkat, 2017a). Content analysis can be described as a scientific exploration of content for the attainment of systematic inferences and references to the meanings, objectives and contexts contained within the text (Mihailescu, 2019).
This cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch paper has worked towards determining how different decision-making and hierarchy processes impact global leadership and how cultural differences in leadership styles can often lead to unexpected misunderstandings. The research has also analysed the MNC of Unilever and reflected on its global leadership practices. The answers that are facilitated by an explanatory analysis are not definite in terms of their nature however they facilitate knowledge and insight into what is potentially coming. It has been evaluated by the research that the corporation of Unilever as a global brand has understood the vitality of having an effective corporate social responsibility, responsibility, respect and integrity pioneering from the basics of their leadership practices. Culture significantly impacts cross-cultural leadership by shaping the vision of the leader, influencing their decision-making process and shaping their communication patterns, hence for any entity it is crucial to managing its cultural power dynamics (Davidaviien and Majzoub, 2022).
Chapter 4: Findings and discussion
4.1 Findings
Hofstede's cultural dimension model has been followed to reflect on the cultural differences in the UK and US. All the six dimensions are focused to reflect on cultural differences between UK and US. In the UK, the power distance is low and the score is 35, which means the society in the UK believes that inequalities among individuals need to be reduced. People in the UK maintain high individualism as the individualism score is 89, which means more ME culture is followed. Masculinity score is 66 in the UK, which means the UK is a masculine society and driven by achievement, competition and success (Hofstede Insights, 2022). The score of uncertainty avoidance is 35, which means people in the UK do not feel threatened by unknown situations and are ready to take on challenges. People in the UK are more comfortable within ambiguous situations, which also indicates that they are ready to adapt to any situation. The long-term orientation score is 51, which indicates dominant preference in the culture has not been determined. The high score in indulgence (69), indicates that people in the UK, are willing to realise their desires and impulses and keep positive attitudes towards life. The figure below indicates the scores of the six dimensions of Hofstede’s based on the UK.
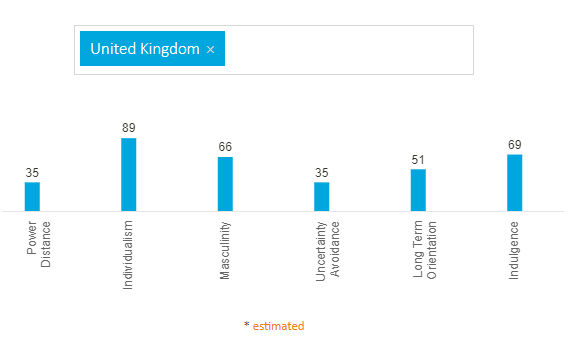
Figure 2: Hofstede’s cultural dimensions based on the UK
Source: (Hofstede Insights, 2022)
The power distance score for the US is 40, which is more than the UK. The power distance score is still low, which means likewise in the UK, the people in the US also support justice and liberty for all. The US have a more individualistic society with a score of 91, which means they are more into individual performance and in terms of business scenario, the employees take initiative and are self-reliant. The promotion and hiring of the individuals are based on individual performance, not group performance. The masculinity score is 62, which is almost similar to the UK, and it indicates thee people are more progressive towards success (Hofstede Insights, 2021). Uncertainty avoidance is 46, which is more than the score of the UK but is low, which means the people do not feel threatened by unexpected things or do not try to avoid unexpected events. The long-term orientation score is low (26) and the score is much lower than the score of the UK. It means the businesses in the US measure the performance of individuals based on short-term and financial statements issued on a quarterly basis. The indulgence score is 68 for the US. The figure below indicates the scores on six dimensions of Hofstede's based on the US culture.
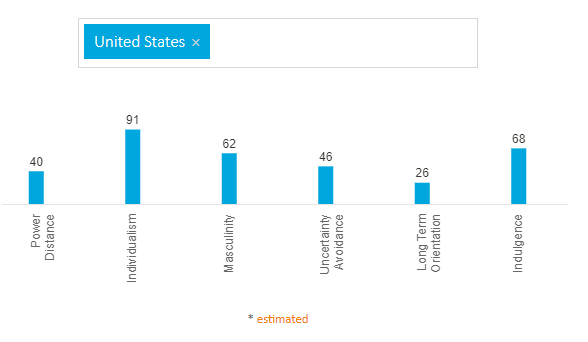
Figure 3: Hofstede’s cultural dimensions based on the US
Source: (Hofstede Insights, 2021)
Based on the comparison of two different cultures (UK and US), it can be said that there is less dissimilarity between the two cultures. The common things that have been found in the two cultures are- both have low power distance, a highly individualistic society, are more masculine, care less about uncertainties, and have high indulgence. The cultural differences and their actual impact on the leadership decision and practices of Unilever are reflected by analysing to which extent the leadership practices of the company is influenced by the two different cultures.
Power distance at Unilever- The leadership of Unilever has been influenced by both the UK and US cultures as the company provides equal opportunity to its workforce. The company leads to progress in an equitable workplace, where every employee is given equal opportunity irrespective of their gender, race, caste and religious beliefs. Unstereotype is one of the drives that has undertaken by the company, which is also a part of its leadership that indicates unconscious bias, stereotypes and social norms are major barriers in an inclusive culture (Unilever, 2021). Apart from that, the fairness in the workplace and gender equality indicates the leadership of the company is more based on an inclusive culture like the US and UK culture.
Individualism at Unilever- AS Unilever works at the global level; it needs to focus on both teamwork as well as individual performance of employees. There are different work models followed by the company such as U-work, U-renew, and hybrid model. U-work is the model at Unilever that provides flexibility and freedom to the workers and people who works under U-work does not have fixed role and work on assigned work, which indicates more individual performance is valued at Unilever through such model. It means the individualistic culture of the UK and US are followed in the leadership of the work model at the company. The hybrid working model is also followed at the company, which means employees are allowed to work from home as well as work from the workplace (Unilever, 2021b). In a work-from-home work facility, individual performance is more followed as employees who work from home are virtually connected with the team. The leadership for the working model of Unilever follows a more individualistic culture and a certain amount of collectivist culture.
Masculinity at Unilever- As identified previously, both UK and US cultures are masculine and it positively influences the leadership of the company. The potential nature of Unilever allows the company to work in a difficult situations and thrive for success. Unilever follows a future-fit business model and focuses on competitive growth. The positive impact on the growth of the company has increased by 1.2% due to acquisitions (Unilever, 2021c). Based on this fact, it is clear that the existence of a masculinity dimension in both UK and US culture has positively influenced the leadership decision and practices of the company to achieve success.
Uncertainty avoidance at Unilever- There are several challenges that are continuously faced by the company and to address those challenges the company has undertaken different strategies rather than avoiding those challenges. The leadership at Unilever is strong and impactful and even in the challenging situation of covid, the company is able to operate significantly. Due to covid, there are many changes in the workplace rules are undertaken and a Covid action plan has been undertaken. Along with UK and US, in other countries where the company operates, a covid action plan has been undertaken and implemented (Jope, 2020). Even if the covid impact affected many businesses in the UK, US as well as in other countries, Unilever managed to tackle the impact in an effective way. The operating profit of the company has increased by 2.9% during the covid and earnings per share increased by 5.5%, which indicates the company is well adapted to the UK and US culture to work in every challenging situation. Long-term orientation at Unilever- Long-term orientation score is average in the UK and low in the US, which has influenced the leadership practices of the company as the company works both on short and long-term goals. The company publishes quarterly results, half-year results and annual results, which indicates it divides its goals into separate short-term goals (Unilever, 2022). It helps Unilever to achieve its long-term goals in a systematic way. The quarterly results provide more detailed information about the company's progress to its investors and stakeholders, which reflects effective leadership. More exposure of the company to short-term orientation has a positive impact on its leadership.
Indulgence at Unilever- Both scores of indulgence for UK and US cultures are high and it has a positive impact on the leadership of Unilever. Employee engagement at Unilever has increased by 6% from 2019, which indicates the company cares about the employees' well-being and their satisfaction at work. The company supports their employees as well as their families and there are various programs conducted by the company that supports employees such as EAP (employee assistance programme), which indicates the leadership at the company is highly influenced by the indulgence culture of the UK and US (Unilever, 2021d).
The concept of leadership comes with different meanings because of the changing environmental condition of the leaders (Kapur, 2020). Leadership denotes the ability of a person or group to impact and guide the members of the organisation effectively. Leadership also comes with the difficult process of making a decision, developing and circulating a vision, and making it attainable at the same time through consistent focus and determination. An effective leader enchants characteristics such as effective communication, management skills, self-confidence, innovation, risk-taking etc. Within a business context, a person possessing all these characteristics can rise to the managerial executive (Pratt, 2017). The leadership style that these leaders follow is different as per the need of the organisation and the business environment as it highly depends on the external drivers. Leadership plays a crucial role in making the organisation successful and the absence of effective leadership can lead to the fall of the organisation. There are multiple reasons behind the success of MNCs across the globe and a visionary leadership style is one of them (Mohamed, 2019). Multiple examples can be found behind the success of MNCs where leaders are vital aspects in contributing to those successes.
Unilever is among those MNCs which has successfully gained success because of the vision and determination of its leader. The CEO of Unilever, Alan Jope believes in a new leadership model because of the changes that occurred after the pandemic. The view on the leadership of Unilever is based on two components i.e., inner and outer game sequentially (Pham, 2021). As per the CEO of Unilever to strengthen the inner game the leaders must have incredible skills adequate for uncertainty. He has also highlighted that unless the inner game is not strong enough the organisation cannot operate effectively and enhance its performance effectively inspiring people and attracting skilled talents. It has been found that Unilever is always ahead of motivating and encouraging its existing employees. In the UK the company has launched a series of competencies for its managers to strengthen their skills and ultimately enhance its business operations. In addition to that Unilever has transformed drastically in the previous years because of the reluctant CEO and his leadership style. He is considered one of the strong leaders who have changed the image of the industry (White, 2021). The leaders of Unilever are focusing on and exploring leadership and its need to have a successful transition till 2050. The leaders are found to be innovative setting multiple agendas for the company’s sustainability.
Moreover, the success of Unilever can be said partly based on its existing leaders who support organisational culture, performance and quality at the same time (Gregory, 2015). For example, the leader mainly uses market-based along with outcome-based methods to handle its business which ultimately drives the performance of the organisation higher. With such an approach by Unilever's leader, multiple areas of the business environment get achieved considerably. For instance, the market-based approach of Unilever’s leader helps to use the information so that changes can be made in its management strategies. On the other hand, the outcome-based approach allows focusing on the attainment of the desired result of the organisation. Unilever operating within consumer goods business gets charged up with such approach of their leaders which eventually enhances their performance and productivity at the same time (Gregory, 2015). It can be said that the leadership along with the managerial approach of Unilever is a crucial factor that successfully manages its organisational culture as a whole. Unilever successfully reinforces its corporate culture of performance and standards with continuous monitoring by its leaders and its evaluation. The leaders not only monitor the work but also contribute a lot by providing intense commitment and support to their team members.
A leader within an organisation is a very crucial part of the transformed culture indeed it is the centre of transformation (Capgemini, 2022). Similarly, Unilever is seen as enabling its leaders with different new skills and with a deeper understanding of digital technologies. The leadership in Unilever is not taken for granted however they are always encouraged to take part in different programs so that they can enhance their skills and ability to assist the people and organisation as a whole. The leadership approach of Unilever, UK develops a sense of enthusiasm for change within the organisation. On the other hand, the leadership approach of Unilever in the US is also based on similar principles. It has been found that Unilever in the US make sure the enhancement of its leadership and its supporting activities are intrinsically connected to the company’s business strategy (Hakikat, 2014).
Although the effective leadership approach of Unilever is a crucial success factor however the leader struggles in maintaining competition in marketing talent. Being a leader the hiring of skilled talent is very important. It has been found that the leaders of Unilever are found to be following the traditional style of promotion etc. Therefore it creates a challenge for the leaders of Unilever to keep attracting talented people into its organisation (Fleming, 2018). The leaders should walk as per the need of the current business environment so as the leaders of Unilever so that such challenges can be mitigated. Almost every successful organisation possesses and shares strong leadership as a common factor and in recent times developing a sustainable business is another shared aspect. While considering the case of Unilever within its set of leadership development the leaders are motivated to recognise their personal aim so that to support their prospect profession at the organisation. The challenging factor for the leaders of Unilever according to Polman and Bhattacharya, (2016), is to maintain the sustainability of the business. Although the leaders are supposed to link their personal values with the organisational objectives so that sustainable business can be developed.
Furthermore, the aim to align the leader’s aim with that of the organisational objectives is to eliminate the remoteness of individual values and to make them perceive best based on the business interest. In addition to that, the senior leaders of Unilever are found to have direct interaction with its shareholders through quarterly result broadcasts including conferences and meetings. They tend to discuss various topics and issues the organisation has been facing so that adequate strategies can be made (Annual Report, 2020). The feedback from their shareholders is thoroughly considered by the leaders of Unilever who have made changes accordingly. The organisational management of Unilever also supports significantly its leaders and makes them go through multiple training programs to ma them able to lead the entire people within the firm.
The findings have highlighted that although there are multiple challenges to the leaders of Unilever both in the UK and the US they have somehow managed to retain their positivity and successfully lead the organisation. It has been a huge drive in terms of leadership in Unilever since its existing leaders like Alan Jope understand the need for change and make the organisation walk towards a sustainable path. The finding highlighted that along with being a leading retail MNCs operating across the globe the leadership approach of Unilever is also commendable which has equally contributed to its success and development. It has also been found that both in the UK and the US Unilever has functioned its leadership development based on their fundamental principle with different approaches. Therefore, it can be said that the findings overall denote that as a whole the leadership approach of Unilever is very effective and capable enough to make changes and differences in the organisation however few improvements are required which recommendation has been provided below.
4.2 Discussion
The chapter of discussion has been developed analysing the above literature where different authors have been reviewed accordingly to analyse the impact of cross-cultural factors on leadership decisions of MNCs. Based on the overall findings of the study it can be said that the leadership decision and practices at Unilever are highly influenced by cultural factors. While comparing the cultural differences of the UK and US cultures based on the six dimensions of Hofstede's, it has been identified that there are more similarities between the two cultures rather than dissimilarities. While comparing the cultural dimensions of both UK and US cultures with the leadership practices of the company, it has been identified that the company follows the cultural factors and has a positive impact of those factors on the leadership decision and practices of Unilever. While reflecting on the findings of the study, it is important to align the findings with the reviewed literature. The study of Ao (2016), Agodzo (2015), Milosevic (2018) and Zamanabadi(2015) reflected on the cultural dimensions of Hofstede and provided a detailed overview of each dimension. The reviewed literature indicates the way the cultural dimension model of Hofstede is crucial to identifying the cultural differences among countries. The cultural dimensions model has been implemented to reflect on the cultural differences between the UK and the US and how they are related to the leadership of Unilever. The UK and US are selected for reflecting on differences as the two nations are major operating areas of Unilever.
Based on the analysis, it has been identified that UK and US have fewer cultural dimensions and it is clear that out of 6 dimensions, 5 dimensions have almost similar scores. It indicates UK and US have similarities in their culture. In terms of the six dimensions, the leadership decision and strategies of the company are analysed and it has been identified that the cultural factors positively influence the leadership decision as well as related practices at the company. While analysing the impact of six dimensions in the context of company leadership and practices of Unilever, there are several aspects that have been revealed such as the company follows a more inclusive and equal workplace culture and there are leadership practices to implement the inclusive culture such as Unstereotype. Apart from that the findings of the study also indicate that the company have a challenging aspect that helps to lead even in a critical and unexpected situation such as covid, which indicates that low uncertainty avoidance is followed in the leadership of the company.
The masculinity cultural factors also influence the leadership decision of Unilever as the company is progressing towards newer opportunities. The findings of the study help to obtain the first objective of the cross cultural leadership assignmentresearch study as Hofstede's model is well implemented in the research to reflect on the cultural differences and their impact on the leadership decision of Unilever. Based on the findings it is clear that the cross-cultural factors significantly influence the leadership decisions of MNCs like Unilever and to implement better leadership practices MNCs need to focus more on cross-cultural differences to develop better and unified practices. For MNCs, it is important to ensure cultural differences while operating in different countries as cultural differences can be the major reason for conflict.
Culture plays a significant factor in impacting the decision-making process of the leaders within an organisation as it directly influences the way through which leaders act and behave. A cross-cultural factor that counts language, background, cultural identity, communication etc, influences the pattern of leadership (Vailati, 2014). It is said that leadership pattern needs to be designed and implemented based on specific cultural characteristics and it may get difficult for them to make a decision where individual from different culture works under one roof. In the case of Unilever, multiple factors influence the process of decision-making in Unilever such as stakeholders, employees, etc. Cross-culture has an impact to another extent acting as a huge barrier for the leaders in making a decision for the business operations. In addition to that cross, culture has always been a supporting factor for Unilever although in some cases it appears to be a hugely influential factor for the organisation.
Moreover, the cross-culture approach of Unilever has helped in developing a multicultural workforce where the leaders are supposed to develop a benchmark of the functions and norms which is advantageous for the entire team and their efficiencies (Smith and Peterson, 2017). Leaders within an organisation are supposed to develop an ability to engage and manage people from different backgrounds and their culture should be adopted and respected at the same time. As it is identified above that in the cross-cultural organisation i.e., Unilever people from different cultural backgrounds have diverse views and perspectives that directly impact one’s goals and social interactions. Therefore, it ultimately impacts their behaviour and attitudes making it difficult for the leaders of Unilever in making an adequate decisions. As it is evident that leaders need to take along all the associates within the organisation together in every operation and project hence, different views and cultures potentially develop a sense of conflict. Therefore, the leader responsible for managing those employees comes under a challenging situation when it comes to making a decision that can align and consider every associated individual. In addition to that, the process of decision-making of the leaders relies on various internal and external factors and each factor comes with a different level of severity. Among all the factors cross-cultural factor is the one that needs adequate consideration by the leaders of the organisation. As it is evident that because of the cross-cultural factor multiple behaviours of an individual get influenced for instance the way they behave, beliefs, prefer things etc. Therefore, making a decision that does not hamper the values and beliefs of those individuals comes under the shoulder of the leader. Therefore, Unilever creates uncertainty temporarily and sometimes it acts as a huge issue to be solved. One of the above authors has reviewed that cross-cultural issues have mostly hampered the decision-making of Unilever's leaders(Jayasundera and George, 2017). For example, leaders are responsible for managing and controlling diverse projects so that efficient performance can be achieved. The success of those projects depends upon the hand of the existing leaders and the way they deal with circumstances. This is where the practice of decision-making comes and plays a vital role in collaborating all the individuals belonging to different backgrounds and making them work together.
In such cases, because of the communication barriers, the effectiveness of communication seems to be very low and the involved members sometimes perceive the project differently leading to disagreements. Such disagreements of ideas and concept while working together develops a sense of conflict and makes it difficult for the leaders to conclude and come up with one decision. It has been observed that most of the time the process of decision-making becomes difficult for leaders of Unilever because of ineffective communication and conflict of interest among the existing team members. The different decision-making approach of Unilever's leaders has helped a lot to manage its operations however most of the time one decision appears to be ineffective when it comes to another culture. Therefore, the discussion has highlighted that it was not easy for Unilever’s leaders to make a decision on one particular aspect in deed the leaders are supposed to consider the values and beliefs of every individual involved. In addition, the level of motivation of every individual appears to be different which has also influenced the process of decision-making process challenging.
As discussed in the above literature it can be said that people belonging to different countries have their own beliefs and values which may not match with people belonging to another nation. Most MNCs encourages multicultural organisation so that diverse concept can be made on one particular idea so that to differentiate it from other organisation. Unilever is among those MNCs that have encouraged cross-cultural organisation and has created a diverse platform open to people belonging to different countries. However, the concept of the multicultural organisation was not successful every time for Unilever as discussed above that has created a huge issue within its organisation most specifically in leadership development. The leaders in Unilever are responsible for managing all the conflicts and misunderstandings among the employees of different backgrounds and to make them work collaboratively is another challenge. However, Unilever has somehow managed its cross-cultural approach and room for enhancement still exists for which recommendation has been provided below.
Chapter5: Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1 Conclusion
After the overall analysis, it can be said that the globalization has increasingly encouraged international trade, while providing new opportunities to the firm to expand their business, resources, and explore new markets across the globe. The growth of the MNC has been rapid in the current era, as an outcome of globalization and innovative technologies. MNC, while operating in other nations come across the diverse culture which significantly impact the business operations, performance, and leadership practices and style of the organization. The significance of culture within the organization cannot be neglected as it plays a vital role in terms of shaping the environment and workforce of the organization. The existing literature review has identified that the corporate culture is generally comprises of various patterns, behaviors, and values that influence and impact the various operations, and decision making process f the organization. There is no denial with the fact that having diverse workforce, form the different cultural background provides various advantages to the firm by generation innovative ideas, and solutions to uplift the firm. However, the challenge of having cross cultural workforce within the organization is another significant factor, wherein most of the MNC’s are facing in the global context. It is because the cross cultural factors is likely to impact the leadership style, and communication process of the organization, while having an adverse impact on the working style of the individual or organization as a whole. Such influence and impact of cross cultural factor can be noticed in the case of Unilever, as the leadership and organizational culture of the firm is interrelated.
In the study of Hofstede’s cultural dimension model, it has been identified that there are six different dimensions which impact the leadership decision and operations of the firm. The dimension such as power distance, individualism, uncertainty avoidance, and masculinity-femininity, states how the individual form diverse cultural background differs in terms of interests, interests, perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors. Thus, while managing the individuals for diverse culture poses significant challenges to the leaders of the organization, while influencing leadership decision. Unilever, being one of the largest multinational companies, has a massive number of stakeholders, managers, employees, and customers from across the globe, which influence the decision making process of organization’s leadership. In the case of Unilever, it has been found that the cross cultural factor has had both the positive and negative impact on the leadership decision of the firm. Despite of having diverse workforce, in some aspects, the firm has established efficient communication and management style among the leaders and the employees, while particularly carrying a similar motive, vision, and objective for the organization. Along with cross cultural factors, leadership is also one of the significant factors that play a vital role in terms of leading and shaping the organizational culture and workforce. Therefore both of these factors are interrelated, and hence the cross cultural factor is likely to have a major impact on the leadership decision.
Though the leadership factor have been one of the significant reason for the success of the firm, however operating in the diverse cultural environment poses various challenges for the leaders of the firm. Since the leader of the firm followed a traditional style of promotion, it was quite challenging for the leaders to attract the talents of diverse cultural background, in order to contribute towards achieving the organizational goal. On the other hand, due to diverse workforce, market segment, and consumer demand, the leaders of the firm also face the challenge of maintaining the sustainability of the business. Thus the cross cultural factors primarily in terms of language, communication style, and cultural identity impact the decision making process of the leaders, which can create both the opportunity as well as the challenges for the leaders of the organization. Hence, for the completion of this research, appropriate research methodology has been applied, aiding towards the convenient and reliable data collection, analysis, and research design, which provided the clear understanding of the knowledge of the chosen topic. Hence, to foster the business efficiently both in the local and global market, it is crucial for the organization to focus on the organizational culture as well s the leadership style and practices of the organization.
5.2 Recommendations
Based on the challenges faced by Unilever, the following recommendations are provided from this cross cultural leadership assignment research to enable cross-cultural leadership patterns which will garner effective outcomes for the organization.
Development of Flexibility in the leadership pattern
Unilever follows a traditional leadership pattern which has contributed to the challenges faced by leaders to achieve optimal organizational success. There have been instances of limited promotion for employees at Unilever due to its traditional leadership style. Therefore it is significant for the leaders of Unilever to acknowledge the significance of cross-cultural management within the workforce and adapt to the innovative leadership styles. With the advent of globalisation, the workforce is getting diversified and the inclusion of people from varied cultural backgrounds is inevitable. Thus, it is vital for organizations to develop and implement cross-cultural practices that will determine the effectiveness of the decision-making of leaders. Unilever must adopt flexibility in its recruitment process and hire people irrespective of their cultural background. This will incorporate an organizational culture driven by diversity and inclusion. Flexibility in the workplace will enable effective decision-making, enhance adaptability, provide the required attention to employees and handle conflicts that arise within the organization (Vaari, 2015).
Encourage inclusivity and diversity in the workforce
Recruiting people from different cultural backgrounds will ensure inclusivity and diversity at Unilever. This will contribute to gaining effective outcomes and ensure the accomplishment of organizational goals. A diverse workplace will ensure that employees are valued and that their creativity and ideas are taken into account. This provides them with a feeling of inclusion which motivates them to perform better (O’Donovan, 2018). The commitment levels, as well as the productivity of employees, are enhanced. This contributes to the personal as well as professional development of the employees. A culturally diverse organization will definitely gain a competitive edge before other organizations and yield enhanced profitability.
Ensure Cultural Competence
A culturally competent company ensures building a team that consists of individuals belonging to varied cultural backgrounds or belief systems. Since Multinational companies like Unilever are expanding their business to thrive in the international competitive market, it is significant that cultural competence is incorporated into the business operations. Globalisation has contributed to the significance of being competent while communicating with the workforce that consists of individuals belonging to various backgrounds. The lack of knowledge and understanding of new cultures contributes to misunderstandings and creates communication barriers within an organization. Therefore, Unilever must acknowledge the significance of cultural competency and implement necessary changes to align with the values of cultural competency.
Build a sustainable work environment
Unilever lacks sustainability in the workplace because of the absence of effective cross-cultural management. Hence, it is recommended that the organization realizes the impact of this and develops practices that will ensure sustainability. The business environment has become global which has led to an increase in competition among various organizations (Tompos and Mihalyka, 2018). Therefore, it is vital for Unilever to acknowledge the fact that cultural differences can hinder the growth of the organization and work efficiently on the sustainability of diversity in the workforce. A culturally sustainable and diverse organization will garner better outcomes which will contribute to the organizational values and yield success.
Embrace Cultural Diversity
Multinational companies have been facing the challenge of managing people who have their roots in varying countries. Culture has become of prime significance that dictates the success of an organization and affects the decision-making of leaders within an organization (Kinkhabwala, 2019). Therefore, Unilever must pay attention to this situation and implement cultural diversity by appointing and effectively maintaining people from varied ethnic backgrounds. It is imperative for the leaders at Unilever to fathom the cultural differences among the employees and team members. This will contribute to boosting the productivity of the workforce and facilitate improved decision-making processes. Diverse employees will bring more talent and creativity to the workforce which will contribute to developing inventive solutions to varying challenges. There will be an increased innovation amongst the employees and they will tend to perform better. The communication barriers in the workforce can be reduced by leaders who are culturally sensitive and are focused on achieving organizational goals. A culturally diverse organization is bound to be successful and garner productive results.
Provide Cross-cultural training
Unilever must effectively introduce a cross-culture training program for its employees and leaders. Cross-cultural training refers to the intervention implemented by varied organizations to improve the knowledge, capabilities and skills of employees which will help them sustain in a new environment (Reiche, Lee and Qintanilla, 2014). Cross-cultural training is dependent on several factors as identified on this cross cultural leadership assignmentsuch as understanding an individual’s cultural background, language skills and family background and enables an environment of cultural diversity in the workplace. It will help them gain mutual respect for one another and develop cultural competencies within the organization.
References
Abdussamad, Z. (2017). The role of leadership functions and organizational culture improving employee performance. [online] ResearchGate. cross cultural leadership assignmentAvailable at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323974790_The_role_of_leadership_functions_and_organizationa
l_culture_improving_employee_performance [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Agodzo, D. (2015). (PDF) Six Approaches to Understanding National Cultures: Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284732557_Six_Approaches_to_Understanding_National_Cultures_Hofstede [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Alapo, R. (2017). Culture and Leadership in the 21st Century. Journal of Cultural and Religious Studies, cross cultural leadership assignment[online] 5(4). doi:10.17265/2328-2177/2017.04.001. Anjorin, R., Jansari, A. and Nazir, I. (2018).Managing Cultural Diversity at Workplace Title: Managing Cultural Diversity at Workplace. [online] Available at: http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1217258/FULLTEXT01.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Annual Report (2020). Purpose-led, future-fit, Annual Report Unilever. [online] Available at: https://assets.unilever.com/files/92ui5egz/production/e665693f2bd2efbbde5658baf84043df7937cfd7.pdf/annual-report-and-accounts-2020.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Ao, Y. (2016). The Impact of Cross-Cultural Communication on Foreign Managers Leadership Style in China-Based International Organization. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308494130_The_Impact_of_Cross-Cultural_Communication_on_Foreign_Managers_Leadership_Style_in_China-Based_International_Organization [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Arshed, N. and Danson, M. (2015).(PDF) The Literature Review.cross cultural leadership assignment [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291345630_The_Literature_Review [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Beugelsdijk, S. and Welzel, C. (2018). Dimensions and Dynamics of National Culture: Synthesizing HofstedeWithInglehart. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, [online] 49(10), pp.1469–1505.doi:10.1177/0022022118798505. Capgemini (2022). Digital Leadership: An interview with Rahul Welde, Unilever. [online] Capgemini. Available at: https://www.capgemini.com/insights/research-library/digital-leadership-an-interview-with-rahul-welde-unilever/ [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Das, R. (2015). (PDF) Leadership in Cross-Cultural Environment – A Comparison of Asian and Non-Asian Managers.ResearchGate. [online] Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321489731_Leadership_in_Cross-Cultural_Environment_-_A_Comparison_of_Asian_and_Non-Asian_Managers [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Fleming, M. (2018). The five challenges facing Unilever’s new CEO. [online] Marketing Week. Available at: https://www.marketingweek.com/the-five-challenges-facing-unilevers-new-ceo/ [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Gantasala, S. and Omar, A. (2016).(PDF) Examining Cross-cultural Leadership: Evidence from a UAE based Bank. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312237384_Examining_Cross-cultural_Leadership_Evidence_from_a_UAE_based_Bank [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Gregory, L. (2015). Unilever’s Organizational Culture of Performance. [online] Panmore Institute. Available at: https://panmore.com/unilever-organizational-culture-of-performance [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Hakikat, E. (2014). Unilever’s keys to leadership success. [online] Inside HR.cross cultural leadership assignment Available at: https://www.insidehr.com.au/unilevers-keys-to-leadership-success/ [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Hofstede Insights (2021). United States - Hofstede Insights. [online] Hofstede Insights. Available at: https://www.hofstede-insights.com/country/the-usa/. Hofstede Insights (2022). United Kingdom - Hofstede Insights. [online] Hofstede Insights. Available at: https://www.hofstede-insights.com/country/the-uk/. Jayasundera, A. and George, B. (2017).CROSS-CULTURAL ISSUES IN EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE AND TALENT MANAGEMENT IN THE MIDDLE EAST. [online] Available at: https://www.palermo.edu/economicas/cbrs/pdf/pbr16/PBR_16_01.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Jenifer, D. and Raman, G.P. (2017).(PDF) ‘CROSS CULTURAL COMPETENCE AN ESSENTIAL SKILL FOR EMPLOYEES IN TODAY’S MNC’. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333640750_CROSS_CULTURAL_COMPETENCE_AN_ESSENTIAL _SKILL_FOR_EMPLOYEES_IN_TODAY [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Jiang, Y. (2019). A Study Of Effect Of Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions Theoryon Employee Loyalty: The Mediating Effect Analysis Of Theleader-Member Exchange Relationship. [online] Available at: https://e-research.siam.edu/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/IMBA-2019-IS-STUDY-OF-EFFECT-OF-HOFSTEDE%E2%80%99S-CULTURAL-DIMENSIONS-THEORY-byYUNXI-JIANG.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Jope, A. (2020). From our CEO: We will fight this pandemic together. [online] Unilever. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/news/news-search/2020/from-our-ceo-we-will-fight-this-pandemic-together/. Kapur, R. (2018). (PDF) Organization Development. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323825290_Organization_Development [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Kapur, R. (2020). (PDF) Introduction to Leadership. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344327077_Introduction_to_Leadership [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Kinkhabwala, B.A. (2019). Strategies to deal Cross Cultural differences by MNCs. [online] ResearchGate.cross cultural leadership assignment Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333641515_Strategies_to_deal_Cross_Cultural_differences_by_MNCs [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Li, W. (2018).Culture n organization --- Study on Unilever.www.academia.edu. [online] Available at: https://www.academia.edu/16862963/Culture_n_organization_Study_on_Unilever [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Lin, C. (2020). (PDF) Understanding Cultural Diversity and Diverse Identities. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335608907_Understanding_Cultural_Diversity_and_Diverse_Identities [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Maity, T. (2018). CROSS-CULTURAL MANAGEMENT-EMERGING ISSUES AND CHALLENGES BEFORE MANAGERS OF MNCS. [online] 6(1), pp.2320–2882. Available at: http://ijcrt.org/papers/IJCRT1803056.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Milosevic, D. (2018). Dimensionalizing Cultures: The Hofstede Model in Context.Online Readings in Psychology and Culture, [online] 2(1). Available at:
https://www.academia.edu/41920293/Dimensionalizing_cultures_The_Hofstede_model_in_context [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Mohamed, A. (2019). 5th International Lean Transformation and Digitalization Conference & State of Readiness Masterclass and Workshop. [online] Operational Excellence Society. Available at: https://opexsociety.org/body-of-knowledge/five-leadership-styles-behind-the-success-of-giant-mncs/ [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Nicholson, R.R., Carr, C. and Smith, S. (2020). Cross cultural leadership adjustment: A strategic analysis of expatriate leadership at a British multinational enterprise. Thunderbird International Business Review, [online] 62(6), pp.675–687. doi:10.1002/tie.22176.
Nickerson, C. (2022). Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions Theory. [online] www.simplypsychology.org. Available at: https://www.simplypsychology.org/hofstedes-cultural-dimensions-theory.html [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
O’Donovan, D. (2018). (PDF) Diversity and Inclusion in the Workplace. [online] ResearchGate.cross cultural leadership assignment Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320674512_Diversity_and_Inclusion_in_the_Workplace [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Ogunremi, Y. and Bako, G. (2019). The Effect of Cross-Cultural Management On the Performance of Multinational Companies in Nigeria. The Federal Polytechnic, [online] 16, pp.133–144. doi:10.22624/AIMS/iSTEAMS-2019/V16N2P17. Pham, M. (2021). Unilever’s CEO on the ‘new mode of leadership’. [online] Marketing Week. Available at: https://www.marketingweek.com/unilever-leadership/ [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Polman, P. and Bhattacharya, C. (2016). Engaging Employees to Create a Sustainable Business (SSIR). [online] Ssir.org. Available at: https://ssir.org/articles/entry/engaging_employees_to_create_a_sustainable_business# [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Pratt, M. (2017). What is leadership? - Definition from WhatIs.com. [online] SearchCIO. Available at: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/leadership [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Rao Nicholson, R., Carr, C. and Smith, S. (2020). Cross cultural leadership adjustment: A strategic analysis of expatriate leadership at a British multinational enterprise. Thunderbird International Business Review, 62(6), pp.675–687. doi:10.1002/tie.22176.
Reiche, B.S., Lee, Y.T. and Qintanilla, J. (2014).Cross-cultural training and support practices of international assignees. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303016078_Cross-cultural_training_and_support_practices_of_international_assignees [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Shyanka, A., Abeysekera, N. and L.S., R.P. (2014).The impact of leadership on organisational performance with specific reference to multinational companies in Sri Lanka. [online] ResearchGate. cross cultural leadership assignmentAvailable at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305408911_The_impact_of_leadership_on_organisational_ performance_with_specific_reference_to_multinational_companies_in_Sri_Lanka [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Simiyu, A. (2015). (Pdf) Role Of Leadership In Organizational Development. [Online] Researchgate. Available At: Https://Www.Researchgate.Net/Publication/273766248_Role_Of_Leadership_In_Organizational_Development [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Smith, P.B. and Peterson, M.F. (2017).Cross Cultural Leadership. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319443969_Cross-Cultural_Leadership [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Song, H. and Yap, K. (2014). Leadership in a Cross-Cultural Context A Qualitative Study of Cross-Cultural Leadership Competence in a Multinational Organization in China. [online] Available at: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:866578/FULLTEXT01.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Tompos, A. And Mihalyka, L.A. (2018).The Sustainability Of Cultural Diversity In The Workplace: Cultural Values And Intercultural Mindset. [Online] Researchgate. Available At: Https://Www.Researchgate.Net/Publication/325775538_The_Sustainability_Of_Cultural_Diversity_In_The _Workplace_Cultural_Values_And_Intercultural_Mindset [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Unilever (2021). Equity, Diversity & Inclusion. [online] careers.unilever.com. Available at: https://careers.unilever.com/diversity-and-inclusion#:~:text=We [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Unilever (2021b). Future workplace. [online] Unilever. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/planet-and-society/future-of-work/future-workplace/. Unilever (2021c). Strong full-year results demonstrate Unilever’s resilience and agility. [online] Unilever. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/news/press-and-media/press-releases/2021/strong-full-year-results-demonstrate-unilevers-resilience-and-agility/. Unilever (2021d). Employee wellbeing. [online] Unilever. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/planet-and-society/responsible-business/employee-wellbeing/.
Unilever (2022). Results, presentations and webcasts. [online] Unilever. Available at: https://www.unilever.com/investors/results-presentations/ [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Vaari, A. (2015). Anttivaari Flexibility In The Core Of Effective Leadership. [Online] Available At: Https://Core.Ac.Uk/Download/Pdf/38127232.Pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022].
Vailati, F. (2014).How does culture affect leadership Case study Thailand. [online] Available at: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:721416/FULLTEXT01.pdf [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. White, A. (2021). Leadership 2050: Andrew White and Alan Jope. [online] Saïd Business School. Available at: https://www.sbs.ox.ac.uk/oxford-answers/leadership-2050-andrew-white-and-alan-jope [Accessed 20 Jul. 2022]. Zamanabadi, K.I. (2015). Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions and HSE Culture Behavior.Nigerian Chapter of Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, cross cultural leadership assignment[online] 3(1), pp.45–49.doi:10.12816/0011647.












