Critical Analysis On IT Audit Report
Question
Task: This assessment is designed to assess students’ ability to apply theoretical learning to practical, real world situations. In this assessment students are given an IT audit report conducted by the office of the Western Australia Auditor General and asked to do the followings:
- Identify the audit focus and scope
- Analyse audit findings in the Recruitment Advertisement Management System of the Western Australia Government
- Analyse audit findings in the Horizon Power
- Analyse audit findings pertinent to the Pensioner Rebate Scheme and Exchange departments
- Analyse audit findings in the New Land Registry office
- Point out the professional, legal, and ethical responsibilities of an IT auditor.
In completing this assessment successfully, you will be able to learn how to analyse an IT audit report, learn relevant legislation, generally accepted auditing standards and ISACA’s CORBIT framework, which will help in achieving ULO1, ULO-2, ULO-3, ULO-4, ULO-5, ULO-6, and ULO-7.
Answer
Introduction
Information technology has created a significant impact on IT audit report. The business firms are undergoing various types of audits for serving varied purposes. The most common types of audit include financial audit, internal audit, as well as fraud audits. In this regard, the report shall focus on analyzing the IT audit report that has been conducted by the Auditor General of Western Australia.
The IT audit report shall be analyzing the focus and scope of the audit conducted and thereby, major findings in the areas of Recruitment advertisement management shall be analyzed. The audit findings shall also be analyzed for the horizon power and PRS and PED. Moving forward in the paper, the audit findings for the New Land Registry Office and various responsibilities of the legal auditor shall be analyzed.
Identification of the focus of audit and scope
The IT audit report comprises major findings and recommendations for addressing the common system weakness that can create an effect on the operating government. The IT audit report focuses on summarizing the results of 2018 annual cycle of the information system audits as well as the review that was completed by the Office. The public sector companies need to consider the areas of the recommendation to the operations (Bunn, 2017). The newly funded Office of digital government has a key role in supporting the entities for addressing the
weakness.
The business application of government entities has been reviewed. Each of the applications is necessary for the operations of the individuals and might create an impact on the stakeholder. The four applications that have been illustrated in the IT audit report are:
- Recruitment advertisement management system
- Horizon Power
- PRS and PED
- New Land Register
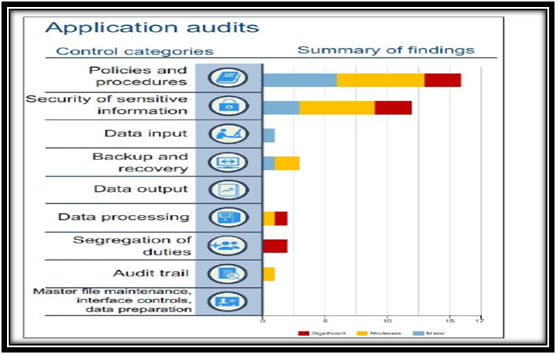
Application Audits
(Source: Gomaa, 2016)
The application view discussed in the IT audit report shall focus on systematic processing as well as operational data handling in the following key elements;
- Policies as well as required procedure
- Effective security management for the sensitive information
- Input data
- Backup as well as quick recovery
- Output data
- Processing of data (Beridze, 2017)
- Duties segregation
- Trail of audits
- Maintenance, penetration of data and controlling interface.
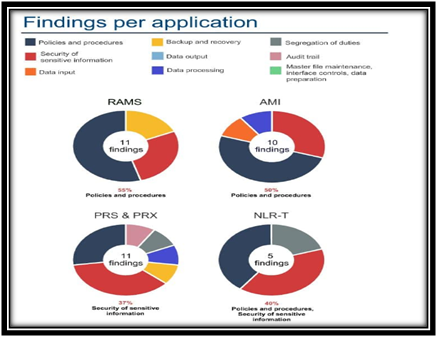
Findings per application
(Source: Han et al., 2016)
Analysis of the findings ofaudit of the RecruitmentManagement Advertisement System in the WA Government It is stated in the IT audit report that the commission has not adopted adequate assurance that the vendor has successfully managed IS controls that are operating in an efficient way. Due to this, the commission specifically does not have any assurance regarding the data in RAMS is safe to ensure its data confidentiality and availability. After costing an audit, the following are the key deficiencies noted in the IT audit report that have been found in the RAMS
- Unsupported software: There was certain software components that typically underpinned the application is not supported by the vendors. There is also 1 component herein; no software updates have been conducted for fixing the security vulnerabilities.
- Disaster recovery is not tested: It has bene found that the vendor has not supported a full recovery of the disaster test since the year 2015 (Wright et al., 2019). Thus, the commission cannot be sure enough that applications can be covered as per requirement
- Outdated technical specification documentation: The technical documentation illustrates that the application does not specifies the existing application areas. Thus, the commission cannot be certain that the necessary controls are in the appropriate place for protecting the application.
There is an absence of risk assessment in the IT audit report that has resulted in lack of IS requirements in the contract. The commission did not analyses the IS risks of RAMS application as well as the information during the time of contract. Thus, without a formal risk assessment, there is less chance for the commission to know whether the controls documented within the contract, address the risks as well as vulnerabilities. Thus, it is considered as critical as controls are well defined in the service contract. Apart from this, there are certain key weaknesses that have been identified. This includes no right for conducting the security audits, no controls assurance, no specification of encryption, unspecified data retention (Mazza & Azzali, 2018). It is necessary that the contract must be as per the State Record Office and must be disposed of within seven years.
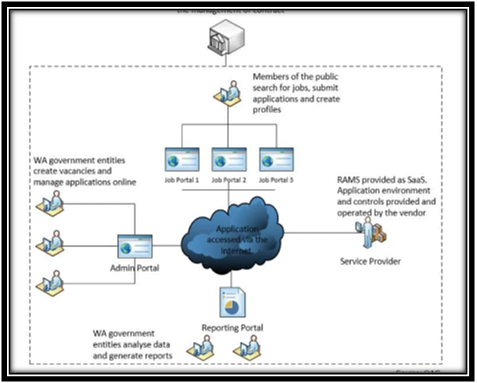
Overview of RAMS
(Source: Ghosal & Conti, 2019)
Apart from this, there is also a lack of access control which has resulted in an increased risk of unauthorized misuse. It has been identified that there are certain weaknesses, such as ineffective user account management. The commission does not illustrate policy for managing the entity user accounts adequately and includes highly privileged accounts. Moreover, there is a lack of processes for reviewing the activity of users as well as access levels. Lack of effective user accounts has resulted in causing a high number of enabled accounts (Banerjee & Gupta, 2019). The presence of weak password configuration does not meet with the good practice requirements in the context of passwords. It also does not limit the re-usage of password and is particularly granted after illustrating appropriate information. It has been found that fifty-five entities imply the generic accounts for accessing the internet caring the reporting portal. The generic accounts, as well as passwords, are easily shared through the eyes, and cosine does not know the particular individual who has shared the information.
There is a weakness in the communion's business continuity, which has further resulting increase in RAMS that might not be restored in a timely fashion. The outdated business plans risk and ensures that RAMS might not operate efficiently during incidents. There is also weakness in managing the SLA by the commission (Bower et al., 2018). It has resulted in an increased risk that the commission would no longer receive any contract agreements with the service delivery to the vendor.
Analyze audit findings in the Horizon Power
The IT audit report focused on an application that lies within the advanced Metering infrastructure that is commonly used by the Regional power Corporation, trading as Horizon owner. This aims at recording the bill for electricity consumption. As per the finding of IT audit report, there are processes through which it becomes easy to detect as well as remedy the error in composition before issuing the bills (Ghosal & Conti, 2019). Horizons are considered an appropriate process for detecting the errors in consumption readings.
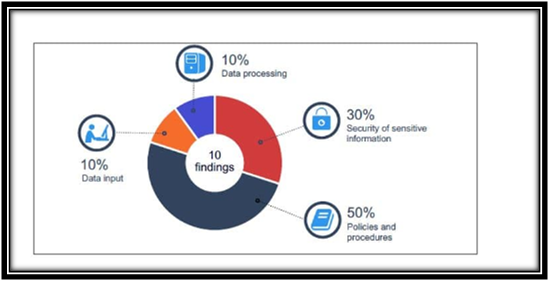
Advanced Metering Infrastructure
(Source:El-Hallaq & Eid, 2020)
In the year 2017-2018, the Horizon corrected the errors that were valued at $1.43 billion. The error mostly comprised $1.42 billion for the commercial range of individuals and $8.5 million for the other range of customers. Such a high error of $.42 billion rose for the manual readings of the customer meters where there is no support of the network (Dragomir, 2017). The remaining errors that have been identified were majorly due to factors such as incorrectness in the rates that are applied to the customer. Inefficient methods for contractor managementaccess ad human resource security: The policies of Horizon do not specifically need for background checks about criminal historyfor the staff. There were certain new staffs who were employed without any criminal history checks and are provided with the aces of power infrastructure as well as system. There was a lack of background checking for the staff though the overall recruitment process inclined medical tests as well as check for qualification, criminal history checks were not included (NGUYEN et al., 2020). It has also been found in the IT audit report that the aces management of the third-party staff has not been effective due to the inappropriate HR records. Six enabled contractors have been reviewed to develop this IT audit report, and it has been found that Horizon mostly outsourced the ICT functions. There has been increasing risk in these accounts and can be used for attacking the IT network of Horizon.
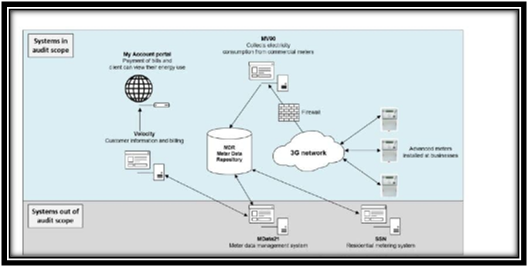
Overview of the AMI system
(Source: Kamal & Tariq, 2019)
Risk of errors and disclosure for system information: Even though Horizon informed regarding the data validation procedure from the forms in the application, there is a lack of clarity as there is no such document. Thus, the data errors will go unnoticed, and there would be a risk regarding the data validation process (Ikpehai et al., 2016). The use of private email accounts for transmitting the sensitive accounts information further increases the risk of intentional disclosure.
No scope for security enhancement in the context of records and network (Tarek et al., 2017). The confidentiality of information along with its constant accessibility are not protected by the network and the data base security control systems in place within Horizon. The inappropriate configuration of network firewall will separate the AMI network from the Horizon.
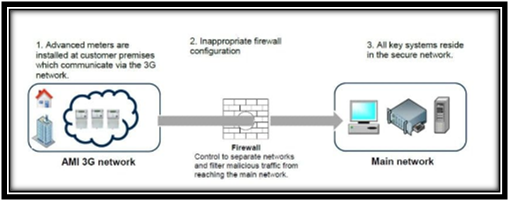
Inappropriate configuration of the firewall
(Source: Siqueira et al., 2018)
It has been found in the IT audit report that the manner is not being configured properly. This results in an increased risk of cyber-attacks and threats to the key systems of Horizon. Firewall software is outdated and does not address security vulnerabilities. Apart from this, there is a weakness in data security that makes it vulnerable to unauthorized access (Han et al., 2016). The network access accounts are also not managed, and there is a weak configuration of the webserver.
Analyze audit findings pertinent to the departments of the Schemes of Pension Exchange and Rebates
The revenue of the state has not been effectively performed for the landowners as well as the occupancy checks. This has resulted in increasing the payment risks that are made for the ineligible candidates. The state revenue took the responsibilities from LGs and stopped its checking. Appropriate process of validation shall help in reducing the risk of inappropriate concessions that are paid to the pensioners as well as senior staff (Sheldon, 2019). The checking was halted due to a large number of claims for payment that was made was entirely false. These were rejected due to the inaccurate occupancy of land as well as ownership in LG further claims the records.
The state revenue is not provided with appropriate cases despite recording confidential information.
The inappropriate user access control does not allow a regular review of PRS and PRx user accounts (Bunn, 2017). There were a large number of accounts that came with administrator privileges. These mentioned in the IT audit report are considered as high-level access and are targeted by the attackers. The 60 users that have been identified with appropriate files and deleted pensioner eligibility illustrates risks of unauthorized access as well as significant changes to the information. The payment files were mainly plain texts, and payment verification was not adequate. There is no restriction to the shared folder wherein the esports and files have been kept (Fan et al., 2018).
Thus, it becomes easy to guess the database passwords and the presence of ineffectiive password check and controls further increase the risks associated with faulty authorization accessibility towards the system. The lack of segregation of duties increases the risk of fraudulent activities. The system activities are not significantly supported and monitored as the revenue of the state does not have the policy for proactively measuring the user activity (Han et al., 2016). State revenue has not developed any acceptable usage policy. It has been found that 925 PRX users are usually from LGs. However, state revenue has not developed any acceptable usage of the policy. There is a lack of sufficient vulnerabilities in the society management as there is a lack of installation of anti-malware software on the line server. The state revenue also does not have any process for identifying the vulnerabilities in PRS (Beridze, 2017). It is necessary to update the information on the security policies as well as procedures that help in better user management of access. Apart from this, the establishment of a process for updating the system user should be supported with documentation.
Analysis of findings of audit in the New Land Registry office
As per the IT audit report findings, it can be stated that the changes to land information have not been subjected to review. The land gate in the NLR never reviews the transactions for accuracy. A review of 8 land transactions has been conducted, and out of that, only two are identified to land title changes. It results in an increased risk of NLR titles and is also considered a breach of the act.
Lack of access controls result in misuse of data: It has been found that user access control is weak and can pose the misuse of information (El-Hallaq & Eid, 2020). NLR uses cloud infrastructure and is used by various entities. There is a lack of segregation of duties, executives’ rights for user access and irregular review of user access. Apart from this, the absence of network penetration testing raises the vulnerabilities that go undetected. The credit card data also poses a major risk that can further expose the system to vulnerabilities (Raškovi? et al., 2019). It has also been found in the IT audit report that contracted services are not reviewed, and hence, it is necessary for a land gate to review the policies and assess the risk that arises for the transactions. There is a need for enhancing the vulnerability management and establishing adequate controls for protecting sensitive information.
Roles and Responsibilities of an IT auditor in terms of professional, ethical and legal grounds
Professional responsibilities: The auditor's profile is to help the firm through safeguarding the internal controls as well as data within the system. They focus on protecting the sensitive information through identification of weakness within the system network. It also aims at creating strategies through which the weakness within the system network can be identified. Apart from this, the security breaches within technology can also be prevented (Gomaa, 2016). The IT auditor has also actively involved in the planning as well as execution of the internal audit procedures well as the creation of internal IT audit report. It is necessary for the IT auditor to work in a collaborative manner and create a solid IT infrastructure with respect to the security issues.
Legal responsibilities: The IT auditor is entirely responsible for obtaining assurance regarding the financial statements that are considered as a whole and are free from any kind of misstatement (Barrainkua & Espinosa-Pike, 2018). If the compliance is successfully identified, the auditor needs to respond in an adequate manner.
Ethical responsibilities: The auditor needs to express the opinion on the area when it is entirely based on knowledge as well as honest conviction (García-Marzá, 2017). The facts must speak for themselves opinions that are given must be based on solid
Conclusion
The IT audit report has thoroughly discussed the analysis of the major audit findings for the found key application. It is necessary to ensure good security practices and up to date software updating as well as regular testing for the computer system. Entities need to ensure that IT risks are thoroughly defined and treated within the appropriate timeframes. These practices must be included within the core element of the business activities. Apart from this, ongoing reviews must be entered for the user to access the system and theory implement mechanisms to continuously raise information as well as cybersecurity awareness. ?
References
Banerjee, P., & Gupta, R. (2019). Talent Attraction through Online Recruitment Websites: Application of Web 2.0 Technologies. IT audit reportAustralasian Journal of Information Systems, 23.
Barrainkua, I., & Espinosa-Pike, M. (2018). The influence of auditors’ professionalism on ethical judgement: Differences among practitioners and postgraduate students. Revista de Contabilidad, 21(2), 176-187.
Beridze, T. (2017). Information Technology Audit in Georgia. European Scientific Journal, 13(25), 72-93.
Bower, C., Watkins, R. E., Mutch, R. C., Marriott, R., Freeman, J., Kippin, N. R., ... & Tarratt, L. (2018). Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder and youth justice: a prevalence study among young people sentenced to detention in Western Australia. BMJ open, 8(2).
Bunn, M. L. (2017). The Development of Public Sector Audit Independence: The Colonial Experience in Western Australia (Doctoral dissertation, Curtin University).
Dragomir, R. G. (2017). The audit of the quality control system within the information technology field. Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People, 6(2), 45-54.
El-Hallaq, M. A., & Eid, M. I. E. S. (2020). DEVELOPMENT OF A GIS-BASED LAND REGISTRY SYSTEM FOR THE GAZA STRIP. International Journal of Engineering Technologies and Management Research, 7(4), 1-19.
Fan, K., Chan, E. H., & Qian, Q. K. (2018). Transaction costs (TCs) in green building (GB) incentive schemes: Gross floor area (GFA) concession scheme in Hong Kong. Energy policy, 119, 563-573.
García-Marzá, D. (2017). From ethical codes to ethical auditing: An ethical infrastructure for corporate social responsibility communication. El profesional de la información (EPI), 26(2), 268-276.
Ghosal, A., & Conti, M. (2019). Key management systems for smart grid advanced metering infrastructure: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 21(3), 2831-2848.
Gomaa, M. I. (2016). Electronic And Paper Document Retention And Auditors’ Responsibilities.IT audit reportReview of Business Information Systems (RBIS), 20(1), 5-12.
Han, S., Rezaee, Z., Xue, L., & Zhang, J. H. (2016). The association between information technology investments and audit risk. Journal of Information Systems, 30(1), 93-116.
Ikpehai, A., Adebisi, B., & Rabie, K. M. (2016). Broadband PLC for clustered advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) architecture. Energies, 9(7), 569.
Kamal, M., & Tariq, M. (2019). Light-weight security and blockchain based provenance for advanced metering infrastructure. IEEE Access, 7, 87345-87356.
Mazza, T., & Azzali, S. (2018). Information technology controls quality and audit fees: Evidence from Italy. Journal of Accounting, Auditing & Finance, 33(1), 123-146.
NGUYEN, A. H., HA, H. H., & NGUYEN, S. L. (2020). Determinants of Information Technology Audit Quality: Evidence from Vietnam. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business, 7(4), 41-50.
Raškovi?, V., Muchová, Z., & Petrovi?, F. (2019). A new approach to the registration of buildings towards 3D land and property management in Slovakia. Sustainability, 11(17), 4652.
Sheldon, M. D. (2019). A primer for information technology general control considerations on a private and permissioned blockchain audit. Current Issues in Auditing, 13(1), A15-A29.
Siqueira de Carvalho, R., Kumar Sen, P., Nag Velaga, Y., Feksa Ramos, L., & Neves Canha, L. (2018). Communication system design for an advanced metering infrastructure. Sensors, 18(11), 3734.
Tarek, M., Mohamed, E. K., Hussain, M. M., & Basuony, M. A. (2017). The implication of information technology on the audit profession in developing country. International Journal of Accounting & Information Management.
Wright, B. R., Albrecht, D. E., Silcock, J. L., Hunter, J., & Fensham, R. J. (2019). Mechanisms behind persistence of a fire-sensitive alternative stable state system in the Gibson Desert, Western Australia. IT audit reportOecologia, 191(1), 165-175.
Bibliography
https://audit.wa.gov.au/reports-and-publications/reports/information-systems-audit-report-2019/general-computer-controls-and-capability-assessments/












