Conduct a nursing assignmentbased on role of aerobic exercise in reducing the risk of diabetes in adults
Question
Task: Can you write a nursing assignment based on role of aerobic exercise in reducing the risk of diabetes in adults? Include evidence to addresses the question and the implications for clinical practice.
Answer
Introduction
Diabetes is considered as a chronic life limiting health complication that impacts the body that turns food into energy. According to AIHW (2022), 1 in every 20 Australians, which is equivalent to 4.9%, or 1.2 million has been reported to suffering from diabetes in the year 2017–18. Diabetes does not have any cure as per the nursing assignment, hence it needs to be managed regularly, else it might lead to other health condition such as cardiovascular disease and other complication (Trikkalinou, Papazafiropoulou and Melidonis, 2019). Therefore to manage the condition, different strategies are there and one of such is Aerobic exercise. For individuals having type 2 diabetes can be benefitted through aerobic exercising. Regular training of aerobic exercise lowers A1C, blood pressure, triglycerides, insulin resistance which are most important concerns for treating diabetes 2. There are several interventions for treating diabetes like medication, different types of exercises etc. Hence, the nursing assignmentwill share its concern about the role and efficacy of aerobic exercise in treating diabetes type 2 in adults. In the evaluation of the role and deficiency of aerobic exercise, the nursing assignmentwill focus on the implication of aerobic exercise on the diabetic patient and the outcome for the same by revealing scholarly articles the content of the paper however will take care of the facts like having the finding a concept of the literature as for the research question to confirm the alignment to justify or address the research questions successfully. The nursing assignment will further describe the implication of the evidence for midwifery practice in nursing to confirm the relevance of the interventions.
Research question for the nursing assignment:
What is the role and efficacy of aerobic exercise in managing and reducing the risk ofdiabetes type 2 in adult patients?
Literature analysis:
Aerobic exercises are accounted for exercise or activities which tend to make the volume move for a prolonged duration in order to maintain body play demo demolition. These exercises induce walking, jogging, biking, hiking, and many more. Aerobic exercises have a potential role in enhancing the body's ability to process glucose as well as increase insulin sensitivity. Because they have been accounted as one of the most significantly used and effectively functioning exercises for patients with diabetes, it is considered for this nursing assignment. Most nursing assignmentregarding the impact of any physical activity or exercise on the glycemic aspects in the case of type 2 diabetes focus on aerobic exercise intervention. It is a rhythmic large muscle group's continuous movement, like jogging, cycling, and walking. Contemporary guidelines of ADA have stated that individual sessions for aerobic activity need to be at least 30 minutes every day along with the continuation needs to be 3 to 7 days every week (Hwang et al. 2019 pp. 8). It is usually observed in the nursing assignment that 70%-90% of the maximum aerobic exercise training initiates VO2max cardiac output, those get accommodated with considerably lowered cardiovascular along with death risk for patients having type 2 diabetes (Cobbold, 2018 pp. 4). Hence American Diabetes Association recommends aerobic exercise to treat type 2 diabetes. ADA also suggests that a combination of aerobic exercise with resistance training is the most influential exercise modality to control lipids as well as glucose for type 2 diabetes.

Figure: Notes of American Diabetes Association
Source: (Kirwan et al. 2017)
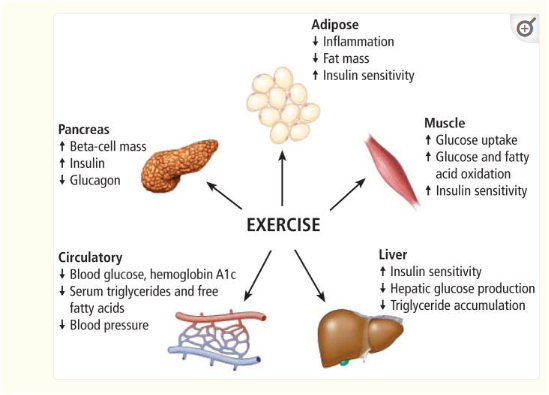
Figure: Impact of exercise
Source: Kirwan et al. (2017)
Kirwan et al. (2017 pp. 4), in their nursing assignmentalso highlights the fact that a combined training program does not only initiate insulin sensitivity compared to aerobic exercise in individual suffering from type 2 diabetes, but also in women with the postmenopausal issue who have type 2 diabetes. As per the nursing assignment, a significant recovery is usually observed after 16 weeks of intervention among individuals performing aerobic exercise only with greater insulin sensitivity.
Similarly, Schwingshackl and colleagues, (2014 pp. 14) have also highlighted with the help of a systematic review, where 14 randomized controlled trials have been reviewed. As per the nursing assignment, adults suffering from diabetes have conveyed that combined training (aerobic along with resistance training) significantly confirmed the better decrease in HbA1c compared to such aerobic or resistance training separately. The research through its finding in the nursing assignmenthas confirmed that combined training is much more beneficial for treating diabetic adults. The finding hence indirectly has addressed the research question as to prove the referred claim it has accepted that aerobic exercise is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus for adults and can offer better results through combined training. For clinical practice hence the referred strategy can be adopted very easing to implement as the nursing intervention. The controller group has established that age is not a bar for the concerned practice hence it can be effective for midwifery treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus for adults.
The Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) was conducted with the primary objective of testing time back of intensive lifestyle intervention program with the name to achieve as well as maintain the significant loss of weight. The objective of nursing assignmentwas to decrease caloric intake as well as enhance the physical activity involved in an individual focusing on improving cardiovascular complications as well as significant quick management in type 2 diabetes patients. It trial is so far the largest randomized trial that evaluates lifestyle intervention for older adults having type 2 diabetes. Under this trial, the group is been contradicted by the diabetes support and education control group. The first group has targeted weight loss of a minimum of 7% by modest dietary energy deficit and minimum175 min/week through unsupervised exercise. Cardiovascular events remain the same for both groups, possibly minimal to better use of the cardioprotective medications for the selected second group. Although, as reviewed by Pi-Sunyer (Colberg et al. 2016 pp. 10), in the nursing assignmentthe first group has confirmed significant greater sustained initiation of blood glucose control, weight loss, cardiorespiratory fitness lipids with a very less number of medications; blood pressure, severe diabetic kidney complication along with retinopathy, lower sleep apnea, urinary incontinence, depression, and knee pain. Besides, maintenance of enhanced physical mobility, as well as the quality of life and sexual dysfunction with lower overall health care costs, is also observed. This nursing assignmentassisted in providing robust evidence regarding the intense health advantage with the help of intensive lifestyle intervention. Furthermore, aerobic exercise if done at regular intervals clearly initiates glycemic control in the type 2 diabetic population. As per the nursing assignment, aerobic exercise should be done for 150 min per week (Pi-Sunyer, 2014 pp. 8).
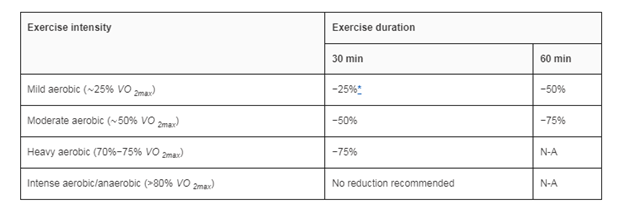
Figure: Exercise and impact
Source: (Colberg, 2016)
Regular exercise as mentioned in the nursing assignmentcan confirm health benefits apart from betterment in cardiovascular fitness. The improvements include blood lipids, and insulin sensitivity along with lowered low-grade inflammation, enhanced glycemic control, initiated vascular function, with weight loss (Kumar et al. 2019 pp. 16). Aerobic can initiate better skeletal muscle, liver, pancreatic function, and adipose tissue. Better whole-body insulin sensitivity can be seen at the very moment after doing exercise which remains for approximately 96 hours. This exercise offers substantial metabolic benefits in the context of diabetic cohorts, glucose control maintenance with insulin sensitivity which gets initiated by physiologic adaptations as occurs only with a long duration of exercise training.
It has been discussed in the nursing assignmentthat aerobic exercise is effective for diabetic patients, however, it is important to do such exercise as recommended by the healthcare professional or under proper supervision. Patient suffering from diabetes is more prone to cardiovascular risk and injury and hence in such case, improper exercise might increase the volume and intensity which might increase the risk of cardiovascular risk or injury. Though in common, the risk of such exercise-induced harmful events is very low for adults with type 2 diabetes, supervision is still necessary (Shawahna et al. 2021). In short, exercise can be stated as the first lifestyle suggestion for patients who are recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Along with behavior modification, exercise and a healthy diet are important for a beneficial lifestyle that can prevent and manage type 2 diabetes. Every exercise in nursing assignment, like aerobic resistance training, has its own significance to improve glucose regulation. For cardiovascular benefits, promoting healthier skeletal muscle can be easy through long-term exercise, with the added advantage of the better liver, adipose tissue, and pancreas function. Exercise plans among individuals suffering from type 2 diabetes need to be of adequate strength with satisfactory volume to initiate the metabolic benefit to avoid injury as well as cardiovascular risk. Therefore, it can be stated in this nursing assignmentthat the clinical intervention of aerobic or combined exercise hence is much more effective in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults. Not only in treatment rather in prevention aerobic exercise is significant for type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in adults. Most important the research confirms that so far the intervention does not have any negative impact hence can be implemented as a nursing intervention or midwifery treatment of type 2 diabetes Mellitus for adults. However, it needs to be remembered that the intervention would be accompanied by proper intensity volume and guidance. Although combined training is proven superior still effective and thus the role of aerobic exercise for type 2 diabetes mellitus for adults is recommended for treating diabetic adults. Nursing assignmentcan be used in terms of nursing intervention as well as midwifery treatment for patients suffering from type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. The clinical training or practice can further evaluate the outcome of the intervention.
Evidence addressing research question:
Aerobic exercise in the nursing assignmentcan be referred to as a well-established way of lowering weight and enhancing lipoprotein metabolism and lipid regulation which further helps in managing the glucose level. It has also been recorded in the article that 6 months of regular aerobic exercise in adults carrying type 2 diabetes confirms assists in a decrease in HbA1c, insulin resistance, fasting insulin, and systolic blood pressure as compared to the others who do not indulge themselves in any such activity (Kirwan et al. 2017). Hence ample evidence is there to prove that one of the most effective tried-and-true exercises is an aerobic exercise to manage and prevent type 2 diabetes, which further helps in assessing the concern of the research question that aerobic exercising is effective and important in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus for adults. To prove the same, Kirwan et al. (2017) in nursing assignmenthave depicted resistance training with aerobic training with the help of a proper "head-to-head meta-analysis” along with controlled trials required to examine the metabolic impacts of aerobic, combination, and resistance training among patients carrying diabetes. Each exercise mode individually has provided recommendable impacts on HbA1c, insulin sensitivity, postprandial glucose levels, fasting, and fasting insulin levels, however, the differences between exercise modalities can be referred to as trivial. The finding of the nursing assignmenthence clearly connects with the research question by proving the fact that aerobic exercise is significant for treating diabetic type 2 patients.
Implication for nursing intervention or midwifery practice in the nursing assignment
Considering its significance, aerobic exercise is even used by nurses to treat patients for a better outcome which confirms it is a better nursing intervention. On the other hand, midwifery treatment is also facilitated through aerobic exercise under professional supervision to get better results for the diabetic group. Aerobic exercise has a significant and positive implication on nursing practice as it guides nurses and other professionals to provide evidence-based and quality care to the patient. With the significant exercise and activities that must be provided to the patients, nursing assignmentcan help patients to manage their health, especially in the case of diabetes (Fleming et al., 2020). Therefore, to motivate the patient that is required them to indulge themselves in such beneficial activities, nurses and midwives play an important role. They need to make the patient either suffering from diabetes or at the risk of having diabetes understand the benefits of aerobic exercise and should also help them to implement such activity in their day-to-day cycle. In order to implement the intervention in the patient's daily life, the nurses can collaborate with community care provides to make the patients more acknowledged with the factmentioned in the nursing assignment(Lambrinou, Hansen and Beulens, 2019). Midwifes, on the other hand, can practice under supervision of trainers to get the best result for their diabetes patient through aerobic exercise.
Conclusion
The nursing assignmenthas shared its concern regarding the role and efficacy of aerobic exercise in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults. As per the finding of several scholarly articles mentioned in the nursing assignment, it is quite clear that aerobic exercise is much more influential to offer better result for treating diabetes type 2; however proper intensity volume and guidance is needed to get the best result. The nursing assignmenthas even confirmed that not only in treatment rather in the prevention or to avoid any negative effect of other interventions for treating type 2 diabetes, but aerobic exercise is also really significant.
References:
AIHW 2022. Diabetes. Accessed on 4th July, 2022 from:https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-health/diabetes#:~:text=Prevalence,2017%E2%80%9318%20National%20Health%20Survey.
Cobbold, C., 2018. Type 2 diabetes mellitus risk and exercise: is resistin involved in nursing assignment. The Journal of sports medicine and physical fitness, 59(2), pp.290-297. https://europepmc.org/article/med/29498254
Colberg, S.R., Sigal, R.J., Yardley, J.E., Riddell, M.C., Dunstan, D.W., Dempsey, P.C., Horton, E.S., Castorino, K. and Tate, D.F., 2016. Physical activity/exercise and diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes care, 39(11), pp.2065-2079. https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/39/11/2065/37249/Physical-Activity-Exercise-and-Diabetes-A-Position
Fleming, G.A., Petrie, J.R., Bergenstal, R.M., Holl, R.W., Peters, A.L. and Heinemann, L., 2020. Diabetes digital app technology: benefits, challenges, and recommendations. A consensus report by the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Diabetes Technology Working Group. Diabetes care, 43(1), pp.250-260. https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article-pdf/43/1/250/530012/dci190062.pdf Hwang, C.L., Lim, J., Yoo, J.K., Kim, H.K., Hwang, M.H., Handberg, E.M., Petersen, J.W., Holmer, B.J., Casella, J.A.L., Cusi, K. and Christou, D.D., 2019. Effect of all-extremity high-intensity interval training vs. moderate-intensity continuous training on aerobic fitness in middle-aged and older adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Experimental gerontology, 116, pp.46-53. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0531556518305102 Kirwan JP, Sacks J, Nieuwoudt S. The essential role of exercise in the management of type 2 diabetes. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017 Jul;84(7 Suppl 1):S15-S21. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.84.s1.03. PMID: 28708479; PMCID: PMC5846677
Kumar, A.S., Maiya, A.G., Shastry, B.A., Vaishali, K., Ravishankar, N., Hazari, A., Gundmi, S. and Jadhav, R., 2019. Exercise and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of physical and rehabilitation medicine, 62(2), pp.98-103. sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877065718314830
Lambrinou, E., Hansen, T.B. and Beulens, J.W., 2019. Lifestyle factors, self-management and patient empowerment in nursing assignment. European journal of preventive cardiology, 26(2_suppl), pp.55-63. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2047487319885455
Pi-Sunyer, X., 2014. The look AHEAD trial: a review and discussion of its outcomes. Current nutrition reports, 3(4), pp.387-391. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13668-014-0099-x
Schwingshackl, L., Missbach, B., Dias, S., König, J. and Hoffmann, G., 2014. Impact of nursing assignmenton different training modalities on glycaemic control and blood lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetologia, 57(9), pp.1789-1797. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00125-014-3303-
Shawahna, R., Batta, A., Asa’ad, M., Jomaah, M. and Abdelhaq, I., 2021. Exercise as a complementary medicine intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with narrative and qualitative synthesis of evidence. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 15(1), pp.273-286. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1871402121000102
Trikkalinou, A., Papazafiropoulou, A.K. and Melidonis, A., 2017. Type 2 diabetes and quality of life in nursing assignment. World journal of diabetes, 8(4), p.120. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5394731/












