Competitive Strategy Assignment Exploring Key Strategy Management Tools
Question
Task:
Purpose:
This competitive strategy assignment aims at ensuring that students have familiarised themselves with the foundational strategy development models and are able to relate them to current practical business examples.
Details:
Write an essay explaining what the main strategy development tools are and how they are used in business. Your essay must contain a comprehensive discussion of 3 of the following: PESTEL, Five Forces, Resource-Based View, PROFIT, Input/Output, SWOT Analysis (you may include Cross Impact Analysis), Generic Strategies, Ansoff, Ghemawat, with reference to academic journals and practical examples from industry.
In this essay, sub-headings are permitted.
Be sure to use paragraphing.
Be sure to reference your sources in-text and provide a list of references at the end, all in Harvard style.
Answer
Introduction
In this competitive strategy assignment on key strategy development tools a comprehensive discussion is given on three different strategy models with practical examples of three Australian organizations of different industries. The various business analysis models are used by organizations to analyze and evaluate the market before producing any new product to customers. For this evaluation, PESTLE, Ansoff matrix, five forces models are considered. The models help in analyzing the organization's functions or activities from other companies or industries. In this essay, the selected industries are the Pharmaceutical industry, consumer goodsretail industry, and tourism industry. The different companies selected in this essay are Woolworths group whihc is an Australian chain of grocery stores and supermarkets controlled by Woolworths Group. The company is specialized in grocery items such as meat, fruit, vegetables, packaged foods, beauty and health products, baby and pet supplies, household items, and stationery. The second company is AstraZeneca Pty Ltd that produces and distributes pharmaceutical goods. The company provides medicines for neuroscience, infection, gastrointestinal, oncology, respiratory, anesthesia, and pain management. The last company is Intrepid travels whihc is the largest small group travel adventure organization in the world.
PESTEL Analysis of Woolworths Group
In this method of pestle analysis external environment factors are described that face the organization. A PESTEL stands for economic, Political, social, environmental, technological and legal. In promotion strategy, before implementing any plan it is a basis to carry out a situational analysis. The political factors describe the stability and policies of taxation, trade, and fiscal determined by the government. Economic factors consist of employment, interest rate, and foreign exchange rates. The company also affects by demographics, society trends, attitudes, and lifestyle of the public in society. The technological success and modernization could impact the industry. The environmental factors involve water disposal, carbon footprint, sustainability, etc. and at last company must follow the consumer law, safety and health, trade restrictions, and regulations (Rastogi and Trivedi, 2016).
Woolworths is a popular name in supermarkets of Australia, the political factors change the environment of business by giving the company with appropriate success opportunities. The ban on plastic decreases the sales of Woolworths in the beginning month of a particular year. The company is growing due to stability in politics as the business partners and foreign investors have an interest in keeping trade and business functions. Woolworths faced high loss in the financial crisis at the time of closing its business with the UK, 30,000 people became unemployed who was working in supermarkets retail shops (Rastogi and Trivedi, 2016). The exchange rate of Australia makes a positive impact on the international trade of Woolworths. Customers are moving towards purchasing healthier products; the quality of Woolworth’s goods has increased in the market to attract more customers. Woolworths has service-oriented architecture and RFID technology for effective inventory management at storesand easily available to customers. The company follows all requirements of food licensing, and quality of eatables available at supermarkets as per regulations of the country. Woolworths is involved in recycling functions to reduce wastage amount and natural resources (Jabeen, et. al., 2016).
Ansoff Matrix of AstraZeneca
It also refers as a market or product extension grid, and this method is used by organizations to evaluate and plan the strategies of success. The four strategies of the matrix are market penetration, its emphasis on enhancing sales of available goods to the present market. Product development emphasis launching new goods to the active market, the third one is market growth that focuses on using available goods in the new market. Diversification means launching new goods into a new market.
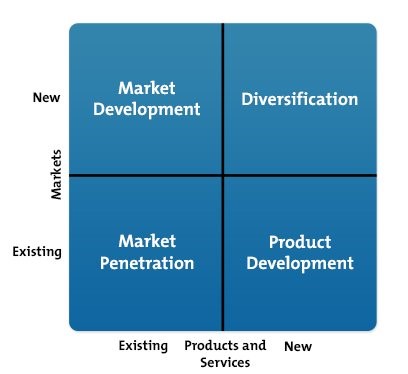
Source: (Mind Tools, 2020)
AstraZeneca used the Ansoff matrix model to achieve corporate success and growth. It helps the organization in focusing on the present and potential products and markets. Market penetration is an essential strategy for development, by selling more medicines in the current market. It all related to enhancing the sales of medicines in the present segment of the market. To grow and penetrate the consumer base in the current market, the organization has to cut prices, increase its network distribution, and spend more on advertising. AstraZeneca can launch various other medicines in the existing market for the customers; it may improve the value of the company among customers and product portfolio. The company can enhance the aesthetics of drugs and medicines by modifying its visual personality. The market development strategy motivates the AstraZeneca to connect to new customers and other segments of the market. Market development is measured to be riskier than a market penetration strategy because it is typical to understand the issues in a new market. It means establishing branches of the company into different areas, as AstraZeneca located in various cities. The approaches of the market development are new distribution channels, new geographical location, new goods packaging, and several policies of prices (Fuller, et. al., 2016).The last strategy of the model is diversification; it is based on the research and development capabilities of the organization. It is identified that the strength and position of the company is strong so it can diversify the market with products, but it is still risky than other strategies. The diversification is divided into two types such as related diversification and unrelated diversification. Related diversification is incoming into a new different market with new goods which is related to existing goods of the company. On the other side, unrelated diversification means entering into a new market with new goods which is unrelated to existing goods of the company (Fuller, et. al., 2016).
Five Forces model of Intrepid travels
The model of five forces is an evaluation tool to determine the competitive intensity in the industry and the level of profitability. The five forces are the bargaining control of suppliers, risk of new entrants, risk of alternative goods and services, bargaining power of purchasers, and existing competitors. New entrants in the market bring more capacity and want to achieve market share. Examples of entry barriers are the demand for economies of scale, the large requirement of capital, high consumer loyalty for available brands, government policies,etc (Bertozzi, et. al., 2017). The risk of new entry for Intrepid travels is low to medium, because to start a travel company takes large investment. New entrants also requires insurance, licenses, qualification and distribution channel.
The bargaining capacity of the supplier evaluates how much capacity and control have a supplier to increase the prices and decrease the quality of goods and services. The bargaining control of travel industry suppliers is very high. The travel company majorly dependent on aircraft and fuel and these are highly affected by the external environment. The bargaining capacity of purchasers evaluates that at what level consumers have the power to put the organization into pressure (Bertozzi, et. al., 2017). Consumers can check rates of various tour operators fast by online websites and can compare with other competitors of the market. Threat of substitutesforces buyers to search for substitute goods and services with striking rates or good quality, then purchasers can switch from one service to different. Travelling is the basic need of customers and there are certain alternatives available in the market such as G Adventures, World Expeditions, etc. The last factor of the model is rivalry among competitors, it determines how strong the existing competition in the marketplace. Competition is high when a large number of competitors are present in the market and equal in power and size. It includes web design, estate agents, and stationery (Wicker, et. al., 2015). The tourism industry is highly competitive due to various reasons that include strict regulation, high definite cost, and barriers to exit. It is considered that competition among existing companies in tourism is high.
Conclusion
It is concluded from the essay that, three different models played a different role in various industries. The PESTEL model is used by Woolworths to monitor and analyse the external factors of environment that creates an impact on business organisation. After analysisng all exterbal factors it is easy for the company to take effective business decision for the Woolworths Group. Changes in the business environment can develop opportunities for the organisation and creates significant issues. The Ansoff matrix model is used by AstraZeneca, which describes four main strategies, it is concluded from the model that company tool strategic planning decision after understanding and evaluating market penetration, market development, product development and diversification. So the market development and market penetration are the best strategy to adopt for the company. The last model is Porter’s Five forces analysi, whihc analyses and identifies the market competition and to identify the company’s potential profitability. It is very supportive, when company understand the five forces of industry or environment that may affect the profitability fo business.
References
Bertozzi, F., Ali, C.M. and Gul, F.A., 2017. Porter’s Five Generic Strategies; A Case Study from the Hospitality Industry. International Journal For Research In Mechanical & Civil Engineering, 3(2), pp.09-23..
Fuller, N., Spadola, L., Cowen, S., Patel, J., Schönherr, H., Cao, Q., McKenzie, A., Edfeldt, F., Rabow, A. and Goodnow, R., 2016. An improved model for fragment-based lead generation at AstraZeneca. Drug Discovery Today, 21(8), pp.1272-1283.
Grimmer, L., 2018. The diminished stakeholder: Examining the relationship between suppliers and supermarkets in the Australian grocery industry. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 17(1), pp.e13-e20.
Intrepidtravel.com., 2020. Small Group Tours & Travel, Big Adventures | Intrepid Travel. [online] Available at: https://www.intrepidtravel.com/en [Accessed 24 Apr. 2020].
Jabeen, R., Aliyu, M.S. and Mahmood, R., 2016. The moderating effect of external environment on the relationship between market orientation and business performance: A quantitative approach. Competitive strategy assignmentInternational Postgraduate Business Journal, 8(1), pp.16-25.
Mind Tools, 2020. The Ansoff Matrix. Understanding the Risks of Different Options. [Online] mindtools.com. Available at: https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_90.htm
Rastogi, N.I.T.A.N.K. and Trivedi, M.K., 2016. PESTLE technique–a tool to identify external risks in construction projects. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 3(1), pp.384-388.
Wicker, P., Soebbing, B.P., Feiler, S. and Breuer, C., 2015. The effect of Porter’s generic strategies on organisational problems of non-profit sports clubs. European Journal for Sport and Society, 12(3), pp.281-307.












