Business Strategy Assignment: Business Expansion Of Tesco Plc In Italy
Question
Task: Prepare a detailed report on business strategy assignment critically exploring the global strategy, development and implementation of Tesco Plc in Italy.
Answer
Introduction
The present business strategy assignment is focused on the business case of Tesco Plc, a prevalent British multinational retail chain headquartered in Hertfordshire. It is a popular groceries and general merchandise retailer, which was established in the year 1919. Tesco Plc is the third largest retailer in this world in terms of measurement of gross revenue. On the other hand, Tesco Plc is the ninth largest retailer in this world in terms of revenue. Tesco Plc is a public limited company and operates in the retailing industry. The company has a strong presence in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary. In the year 2020, the total revenue of Tesco Plc was 82.776 Billion US Dollars (Macro Trends, 2021). Tesco Plc is functioning with almost 7000 stores across the globe. Tesco Plc is operating around the globe with different supermarkets, hypermarkets, superstores, and convenience shops. Tesco Plc is one of the largest employers in the global retail industry. The employee strength of Tesco Plc is 4, 23,092.
The company has adopted and implemented several competitive strategies in the business operation process to gain competitive advantages and enhance profitability growth. Effective implication of cost-leadership strategy and product differentiation strategy has helped Tesco Plc to become one of the profitable and competitive organisations within the global retailing industry. Apart from these, Tesco Plc also has adopted international business expansion strategy to enhance positive business growth. Tactical planning about expansion of business in international market and significant application of global expansion strategy has allowed Tesco Plc to attain positive market share growth. Already the company has become effective in establishing a strong customer base across the globe due to high-quality and differentiated products at economic price level. Now, the company is planning to expand its business in Italy and it is important to develop effective strategies to do business in Italy.
Porter’s Diamond Model
Porter’s Diamond Model is also acknowledged as The Theory of National Competitive Advantage of Industries. This model is a diamond-shaped framework, which is applied to analyse the external competitive environment of the organisations. Application of this model usually helps the organisations to determine relative strengths and describes why some industries have become competitive. The regional advantages for Tesco Plc can be assessed below with the help of four important factors, such as Firm Strategy and Rivalry, Demand Conditions, Related and Supporting Industries, and Factor (Input) Conditions.
In terms of Firm Strategy and Rivalry, intensive market competition in UK retail industry has allowed Tesco Plc to adopt innovative strategies and improve quality control. Asda, Sainsbury’s, Morrisons, Aldi, Ocado, and Marks & Spencers are considered as potential players within the UK retail industry. In order to overcome this threat of high market competition, the management of Tesco Plc has adopted innovative and effective business level strategies.
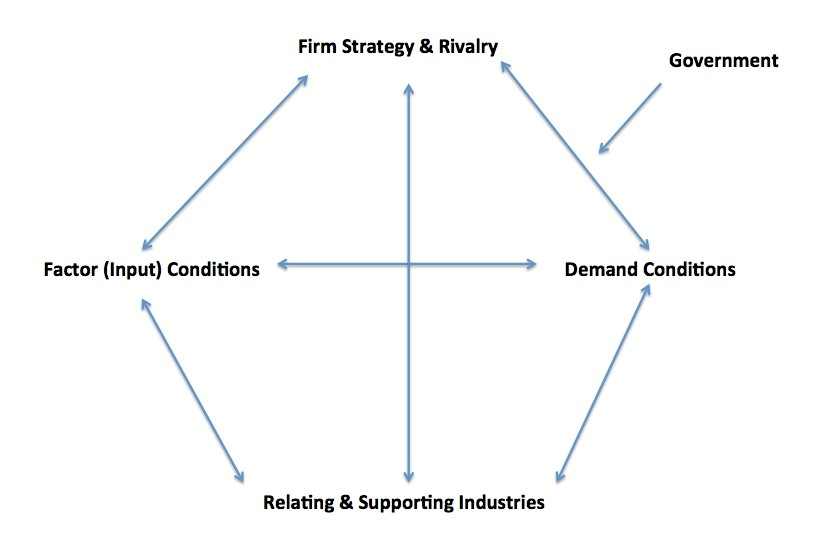
Figure 1: Porter's Diamond Model
(Source: Tran, 2016)
In terms of Demand Conditions, people of the United Kingdom have strong demands for advanced, high-quality, cost-effective, innovative, and differentiated products. These factors have created market competitiveness for the organisations. Tesco Plc has successfully adopt cost-leadership and differentiation business level strategy in order to satisfy the needs of target customers for advanced, high-quality, cost-effective, innovative, and differentiated products in the United Kingdom (Suzuki and Okamuro, 2017).
In terms of Related and Supporting Industries, the management of Tesco Plc significantly depends on the efficacy of the suppliers and distributers. UK is a potential market for producing quality raw materials and resources for garment industry. The management of Tesco Plc also sources high-quality, differentiated, and cost-effective garments from Italy as such garments are easily produced in Italy in cost-effective ways. Therefore, it can be stated that fashion industry and garment industry of Italy can be considered as the supporting industry for Tesco Plc in the United Kingdom (Ren et al., 2021).
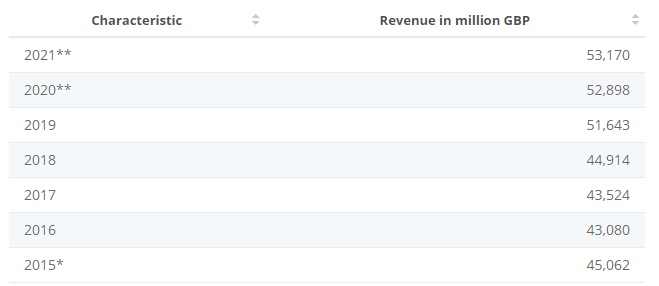
Figure 2: Increased Revenue for Tesco Plc in UK and Irish Market
(Source: Blazquez, 2021)
In terms of Factor (Input) Conditions, the management of Tesco Plc. depends on skilled employees, infrastructure, education of staffs, capital investment, and implied technological applications to become profitable. For example, the company has employed 4, 23,092 skilled employees across the globe, which has allowed the company to become one of the largest employers. These favourable Factor (Input) Conditions have helped Tesco Plc to increase annual revenue of the company in the United Kingdom and Ireland from 2015 to 2021. Hence, the decision of further internationalisation of the company is highly justified. These will ensure potential competitive advantages for Tesco Plc in future internationalisation.
Strategy to Internationalise the Business
Multinational organisations generally consider different kinds of strategies to internationalise the business. The internationalisation strategies for the multinational companies include multi-domestic strategy, global strategy, international strategy, and transnational strategy. Tesco Plc also has applied a specific internationalisation strategy to do business in global market. Before evaluating that particular strategy, it is important here to briefly discuss all the strategies to internationalise business.
International Strategy
In terms of international strategy, organisations used to keep most of their business operations in the home country, when those businesses concentrate on imports and exports. Manufacturers of luxurious products, wines, and different unique food products follow this kind of strategy.
Multi-Domestic Strategy
In terms of multi-domestic strategy, the organisations usually focus on implication of different marketing strategies, sales strategies, pricing strategies, and product strategies in different international markets. In such strategic approaches, the companies use many small country-specific brands in different international markets rather than focusing on marketing of products depending on only one global brand (Hendriks, 2020). Large food and confectionary company Nestle has adopted this multi-domestic strategy.
Global Strategy
In terms of global strategy, organisations do business and marketing of products depending on one global brand. Example of iPhone of Apple Inc can be considered here, which has adopted global strategy in business (Smart Ling, 2021).
Transnational Strategy
Multinational companies with transnational strategy follow a specific international business structure where the global business activities of those multinational companies are coordinated via interdependence and cooperation between its head office, internationally located subsidiaries, retail outlets, and operational divisions. Generally retail chains or fast food chains follow this particular strategy.
Tesco Plc can Adopt Transnational Strategy
Tesco Plc has adopted transnational strategy in operation management activities to internationalise the business. The company always focuses on maximisation of local responsiveness. The company also focuses on attaining global integration approach to reduce overall business operation cost. The management of Tesco Plc considers local responsiveness in the business operation activities in order to improve flexibility of the business. Basically, Tesco Plc focuses on meeting the needs of local business standards in different international markets by following regulations and cultural orientation of host countries (Pattanik et al., 2021). These activities in business operation processes indicate that Tesco Plc has adopted transnational strategy to internationalise the business.
Country Analysis: Tesco Plc in Italy
It is already identified that Tesco Plc looks for support from the Italian fashion and garment industry as the company becomes successful in sourcing quality raw materials from Italy. In order to enhance cost reduction, business operation flexibility, and business profitability, the management of Tesco Plc has decided to expand the business in Italian market considering the market potentiality of Italy.
Country Attractiveness: PESL Framework on Italy
It is an imperative strategic management analytical framework. Use of this framework will benefit in identifying the attractiveness of external macro environmental factors of Italy for Tesco Plc.
Political Attractiveness
Italy follows a parliamentary framework. The country is a democratic republic and a multi-party system has ensured political sustainability of the country. Italy is the founding member of the European Union. Most importantly, the organisation has a positive relationship with several foreign countries due to effective diplomacy of the Italian government. The Italian government has imposed low tariff rate on different foreign businesses to attract FDI (Abd Aziz et al., 2020). These facts easily indicate the degree of political attractiveness of Italy is high for Tesco Plc to make market entry and do business.
Economic Attractiveness
The economy of Italy is capitalist in nature and the country has a high GDP per capita. The country is fourth largest around the globe in terms of gold reserves. Most importantly, the per capita GDP, purchasing power of people, and disposable income of people in GDP are quite healthy. The country is also improving its employment growth rate in the European Union rapidly. Different multinational organisations are looking for market entry and investment in Italy considering the economic sustainability. These facts easily indicate that the degree of economic attractiveness of Italy is high for Tesco Plc to make market entry and do business.
Social Attractiveness
Italy was nominated as sixth most internationally valued country in the year 2009 considering its diversity in socio-cultural dimensions. People of different religions and cultural backgrounds used to live in the societies of Italy. Diversity and cultural differentiations are important themes of socio-cultural perspectives of Italy. Most importantly, demands for differentiated apparel goods, groceries, food products, vegetables, stationary goods, and retail products are seen in Italy (Nambisan et al., 2019). On the other hand, Tesco Plc offers differentiated apparel goods, groceries, food products, vegetables, stationary goods, and retail products to satisfy the demands of target customers of different socio-cultural backgrounds. These facts easily indicate that the degree of socio-economic attractiveness of Italy is high for Tesco Plc to make market entry and do business.
Legal Attractiveness
The Government of Italy has developed strict regulations for equal employment opportunities, safety of the products, consumers’ rights, and workplace safety and good health of employees. There is strict law on standard working hours and sustainable work-life balance for the employees in Italy. Violation of these regulations can lead to different kinds of legal challenges for the business enterprises. Hence, Tesco Plc needs to be aware of all the business laws, employment policies, and regulations regarding doing business in Italy.
From the analysis, it is clear that the social attractiveness, economic attractiveness, and political attractiveness of Italy for retail chain business will influence Tesco Plc to enter into the potential Italian retail chain industry.
Country Environment Analysis: Five Forces
Michael Porter has proposed Five Forces analytical framework to determine the impacts of micro-environmental factors of a country on business operation activities and business performance of an organisation. In this case, application of Five Forces Framework will help in analysing the influences of external micro-environmental factors of Italy on business enactment of Tesco Plc (Siamagka and Brouthers, 2020).
Buyers’ Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of the customers is high for the companies of Italian retail chain industry. The degree of saturation of the industry is high and people are seeking for high quality as well as differentiated products from their preferred retail chains at economic price level. In case of dissatisfactions, the customers switch over other brands (Krasulina et al., 2019). Hence, the companies have to be on the edge to adopt innovation and competitive approaches frequently. These facts indicate that the threat of bargaining power of the customers is high for Tesco Plc in Italy.
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power
Threat of bargaining power of the suppliers is low for Tesco Plc in Italy as sufficient availability of cost-effective and efficient supply chain options in Italy will make sure high-quality and effective supply chain and distribution activities for Tesco Plc. The company will easily find out an efficient and cost-effective supply chain option.
Threat of New Entrants
Threat of new entrants is low for Tesco Plc in Italy as the industry is already occupied by the potential players. The companies have to deal with strict industry entry regulations and high market entry cost. These can hamper the business sustainability of the new players initially. Looking into these risk associates, very few of the new entrepreneurs will intend to do business (Xu and Hitt, 2020). Hence, threat of new market entrant is limited for Tesco Plc in Italy.
Threat of Substitutes
E-Commerce companies can be considered as the potential substitutes of the brick-and-mortar retail chains. Esselunga, ePrice, Decathlon, Zalando, Unieuro, eBay, and Amazon etc. are considered as popular e-commerce websites for Italians through which they buy goods. These are popular substitutes of brick-and-mortar retail chains across Italy. Demands of these substitutes are significantly increasing among the Italians. Hence, it is clearly indicative that the threat of substitutes will be high for Tesco in Italy.
Industry Rivalry
Threat of industry rivalry in Italy is high for Tesco as the Italian retail chain industry is highly saturated and competitive in terms of characteristics. A&O, Aldi, Carrefour, Conad, Coop, Crai, Despar, Sigma, and Margherita etc. are considered as some leading, growing, and popular retail chains across Italy (Villar et al., 2018). These retail chains have high demands and market share growth in Italy, which will pose real competitive threat for Tesco Plc.
It is clear from the analysis that effective supply chain support will influence Tesco to enter Italy and do business. In addition, differentiated product offerings and cost-leadership strategy of Tesco Plc will allow the company to overcome the industry rivalry and high buyers’ bargaining power related threats in Italy.
A multinational company needs to select an appropriate market entry mode to make an entry in international market and do business. There are different kinds of market entry modes, such as licensing, franchise, merger & acquisition, and joint venture. Before selecting and justifying an appropriate mode of market entry, it will be important to get a brief overview on every market entry mode.
Licensing, Franchising, Merger & Acquisition, and Joint Venture
Licensing can be referred to an arrangement between licensee and licensor, where licensee can acquire the right to use the products and licensors keep the ownership right. Franchising also can be considered as an important market entry mode, which is an arrangement between franchisee and franchiser where the franchisee enjoy the ownership of the business on behalf of a franchiser. Merger & acquisition is also an important international market entry mode. Both of these terms refer to the joining of two different companies, but there is a common difference between these two. A merger occurs in an international business when two separate business entities combine the business operation resources to create a new and joint organisation (Zahoor et al., 2021). On the other hand, acquisition is referred to the takeover of one business entity by another. Merger & acquisition process can be completed to expand the reach of a business company or improve the market share growth of a company in an attempt to develop a potential shareholder value. Joint-venture is also known as an important international market entry mode in which two or more than two organisations seek for development of a single enterprise in order to reduce business risk and improve profitability.
Tesco Plc will Adopt Joint Venture Market Entry Mode
Tesco Plc will adopt joint-venture market entry mode to do business in Italy. This entry mode will enhance new expertise and new business capacity for Tesco Plc in Italy. In addition, it will help in utilising better resources. The associated risks will be shared through this joint-venture model. On the other hand, Tesco Plc can successfully adopt cross-cultural diversity in business in Italian market through this joint-venture market entry mode.
Three Managerial and Organisational Problems
It is quite possible that Tesco Plc can face different kinds of managerial and organisational problems if the companies decide to do business in Italy.
Organisational Co-Ordination
Organisational co-ordination problem can be considered as a real possible challenge for Tesco Plc to do business in Italy. The degree of co-ordination and collaboration between employee and management is different in UK market. The level of co-operation and co-ordination has been established in the UK stores depending on organisational behaviour and specific work culture of UK. The same level of co-operation and co-ordination cannot be similarly effective in the Italian market. Hence, it might create a serious challenge for Tesco Plc in Italy.
Cultural Problems: Hofstede Analysis
Cross-cultural problems also can be developed for Tesco Plc in Italy as there are cultural differences between Italy and UK. Cross-Cultural Dimension Theory of Greet Hofstede can be applied in this assignment to determine the cultural differences between Italy and UK, which will predict some possible cross-cultural challenges for Tesco Plc in Italy.
According to the Cross-Cultural Dimension Theory of Greet Hofstede, every country has six different cultural dimensions, which decides a particular cultural orientation of that country. These six cultural dimensions are Power Distance Index, Individualism Vs. Collectivism, Masculinity Vs. Femininity, Uncertainty Avoidance Index, Long-Term Orientation Vs. Short-Term Orientation, and Restraint Vs. Indulgence.
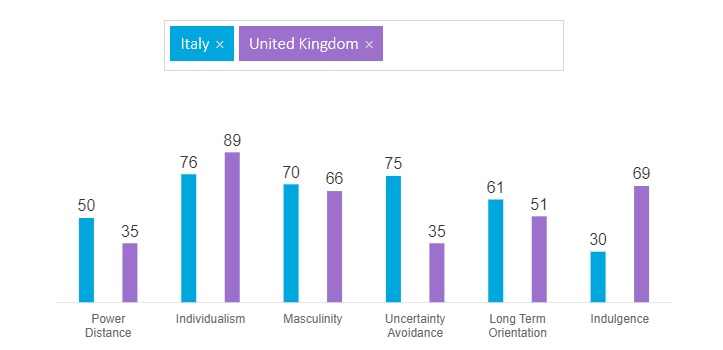
Figure 3: Comparison of Cultural Dimensions between UK and Italy
(Source: Hofstede Insights, 2021)
The score on power distance index refers that societies of UK are habituated with equal power distribution among people compared to the societies of Italy. In terms of individualism vs. collectivism, societies of UK prefer more individualistic approaches compared to the societies of Italy. In terms of masculinity Vs femininity, both UK and Italy follow similar kinds of social approaches in which the people believe in success orientation and achievement. In terms of uncertainty avoidance index, the scores indicate that the Italians are not comfortable with ambiguous situations, but people of UK acknowledge and get prepared for these situations. In terms of long-term orientation Vs short-term orientation, the score indicates that Italian culture is pragmatic compared to the UK culture (Hofstede Insights, 2021). In terms of indulgence Vs restraint, the scores indicate that Italian culture is more restraint and pessimistic. Hence, it is quite possible that cross-cultural challenges can be created for Tesco Plc if the company follows similar kinds of workplace culture and organisational behaviour in Italy.
Organisational Structure: Centralisation Vs Decentralisation
The management of Tesco Plc follows decentralised structure and culture in the business operation processes of United Kingdom. Now, the company is planning to expand in Italy. It is quite possible that the company might face employee management issue in Italy as decentralisation will not help Tesco Plc in Italy. The above cultural-dimension analysis has indicated that the degree of masculinity and degree of restraint is high for Italy compared to UK. Therefore, decentralisation may affect the business performance of Tesco in Italy.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Tesco Plc has a strong global market presence. The entity has expertly adopted cost-leadership and differentiation strategy in the business operation activities to offer quality and differentiated products at economic price level. The business environment of Italy is highly attractive and supportive for Tesco Plc. The company will adopt joint-venture approach to do business in Italy. However, the company has to make different adjustments with cross-cultural differences of Italy to ensure profitability and success. Following recommendations can help Tesco Plc in improving business growth in Italy.
Recommendations
Looking into the Hofstede dimensions of Italy, it will be important for Tesco Plc to adopt centralised approach in business as Italian societies have higher degree of pessimism and cultural restraint. Hence, centralisation will ensure effective control on decision making and employee management activities to optimise the skills of employees.
Secondly, it will be important for Tesco Plc to focus on equal distribution of power among the store managers as people of Italy are comfortable with equal distribution of power in societies as well as workplace culture. Equality and empowerment will be important for the management of Tesco Plc in Italy.
Last but not the least; two-way communication approach needs to be promoted in Italy as it will help Tesco Plc to work on feedbacks of employees regarding possible workplace dissatisfaction as it will help in motivating the employees.
References
Abd Aziz, N.A., Hanafiah, M.H., Abd Hamid, H. and Isa, R.M., 2020. The Barriers Of International Expansion: A Study On Education And Learning Centre Franchisors. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(5), pp.888-895.
Blazquez, A., 2021. Annual revenue of Tesco Group in the United Kingdom (UK) and the Republic of Ireland from financial year 2015 to 2021. [Online]. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/490931/tesco-group-finance-revenue-united-kingdom-uk/. [Accessed on 1 December, 2021].
Hendriks, G., 2020. How the spatial dispersion and size of country networks shape the geographic distance that firms add during international expansion. International Business Review, 29(6), p.101738.
Hofstede Insights., 2021. Country Comparison. [[Online. Available at: < https://www.hofstede-insights.com/country-comparison/italy,the-uk/>. [Accessed on 30 November, 2021].
Krasulina, O.Y., Rossokhin, V.V., Krepkaia, T.N. and Rubtsova, A.V., 2019, July. Assessment of the probability of the Arctic Council expansion. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 302, No. 1, p. 012090). IOP Publishing.
Macro Trends., 2021. Tesco Revenue 2006-2021. [Online]. Available at: < https://www.macrotrends.net/stocks/charts/TSCDY/tesco/revenue>. [Accessed on 30 November, 2021].
Nambisan, S., Zahra, S.A. and Luo, Y., 2019. Global platforms and ecosystems: Implications for international business theories. Journal of International Business Studies, 50(9), pp.1464-1486.
Pattnaik, C., Singh, D. and Gaur, A.S., 2021. Home country learning and international expansion of emerging market multinationals. Journal of International Management, 27(3), p.100781.
Ren, S., Fan, D., Huang, X. and Li, Z., 2021. The micro-foundation of ambidextrous opportunity identification in international expansion. Business strategy assignment International Business Review, 30(1), p.101764.
Siamagka, N.T. and Brouthers, K.D., 2020. International Market Entry and Expansion. The Routledge Companion to Strategic Marketing, pp.377-390.
Smart Ling., 2021. What Is a Transnational Strategy [Online]. Available at: https://www.smartling.com/resources/101/what-is-a-transnational-strategy-5-examples/. [Accessed on 30 November, 2021].
Suzuki, S. and Okamuro, H., 2017. Determinants of academic startups’ orientation toward international business expansion. Administrative Sciences, 7(1), p.1.
Tran, P., 2016. Strategy 1: Porter’s Diamond explained with an example. [Online]. Available at: < https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/strategy-1-porters-diamond-explained-example-peter-tran>. [Accessed on 30 November, 2021].
Villar, C., Dasí, À. and Botella-Andreu, A., 2018. Subsidiary-specific advantages for inter-regional expansion: The role of intermediate units. International Business Review, 27(2), pp.328-338.
Xu, K. and Hitt, M.A., 2020. The international expansion of family firms: The moderating role of internal financial slack and external capital availability. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 37(1), pp.127-153.
Zahoor, N., Donbesuur, F., Nwoba, A.C. and Khan, H., 2021. Regional expansion of emerging market SMEs: the roles of domestic market environmental uncertainty and international alliance partner diversity. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, pp.1-31.












