Business Environment Assignment Analyzing Organizational Background Of Lovisa Jewellery
Question
Task:
You are required to prepare a report on business environment assignment illustrating about the organizational environment of any business organization.
Answer
Executive summary
Lovisa Jewellery, selected in the present context of business environment assignment, is an Australian jewellery chain launched by Brett Blundy in the business year 2010 and has over 400 stores across Australia, parts of Southeast Asia, the USA, New Zealand, and parts of the Middle East. The company’s interlinked and collaborative functional areas including management, human resources, operations, finance, and accounts as well as a marketing play a significant role in accomplishing its business objectives. In addition, the macroeconomic outlook indicates potential opportunities which can be well leveraged by the company to negate the threats. Other than that, Lovisa’s main stakeholders are customers, employees, and management who play a vital role in the growth, success, and competitiveness in the market of Australia.
Introduction
Lovisa Jewellery is a fashion jewellery and retailer chain for women which is headquartered in Sydney, Australia. It offers its fashion jewellery and accessories in Australia, parts of Southeast Asia, the USA, New Zealand, and parts of the Middle East. The company was incorporated in the business year 2010 and operates in the consumer discretionary products industry, (Lovisa.com.au, 2021). Based on such context, this report highlights the business environment of Lovisa with a particular focus on its operations, functional areas, stakeholder analysis, and macroeconomic outlook in the market of Australia.
Functional areas of Lovisa Jewellery
As put forward by Fisch & Block (2018), the five main functional areas assist companies to separate key business operations in terms of expertise which in turn increases efficiency and effectiveness in the entire business. Based on such context, the following are the key functional areas of Lovisa that are highly interlinked with each other for accomplishing business objectives and maximising performance and productivity.
Management: At Lovisa, the management comprises managers, leaders, investors, and shareholders who take active participation in planning, organising, controlling, and leading personnel to accomplish business objectives and elevate performance.
Human resource: This personnel is responsible for hiring, managing, and staffing. It is their duty to communicate with other departments and comprehend the shortages in staffing based on which best fits are hired in terms of the job roles. In addition, they are also responsible for motivating, inspiring, and fostering a healthy work culture to positively influence the staff and contribute towards organisational success, (Vom Brocke & Mendlin, 2018).
Operations: The operation manager is responsible for monitoring and supervising the day-to-day business operations of Lovisa including ordering raw materials to scheduling workers to produce quality and tangible items.
Finance and accounts: This personnel focus on planning, obtaining, and managing the funds of Lovisa along with effective decisions about the allocation of resources. In addition, the information is well passed to other departments which increases efficiency and collaboration, (Tseane-Gumbi, 2018).
Marketing: The personnel in this functional area focuses on identifying customers’ needs based on which the modification or introduction of new products and services are carried out to meet those needs. In addition, through the use of technology and digitisation, Lovisa has capitalised on marketing functions to attract potential customers and increase visibility.
Evaluating the macroeconomic scenario and outlook
In order to assess the macroeconomic scenario and outlook within the context of Lovisa, Australia, the use of PESTEL analysis has been carried out in the following way.
Political: The Australian market is highly stable at present despite the present covid-19 crisis but the need to comply with taxation policies and other regulatory measures is essential for businesses, (Pather et al. 2020). (Opportunity)
However, the covid-19 pandemic has further resulted in changing policies as well as new taxation policies which can affect profitability for businesses. (Threat)
Economic: Along with the political stability, the economic performance of Australia is stable at present due to government expenditure, increasing investment into new industries as well as stable demand in terms of disposable income, (Palepu et al. 2020). (Opportunity)
Social: In Australia, both social and traditional media are significantly growing which can be leveraged by companies to better market and position their products or services.
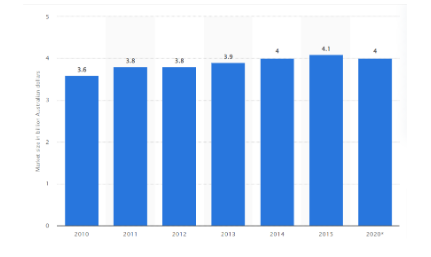
Fig: 1 (Market size of the jewellery sector Australia)
Source: (Statista.com, 2021)
In addition, the fashion and jewellery market of Australia has indicated potential growth in online shopping as well as substantial growth in revenue in the past five years. It also reflects a market size of 4 billion Australian dollars in the business year 2020 (Refer to the above figure). (Opportunity)
Technological: The technology in the retail and fashion sector has reached maturity and has been highly complimenting supply chain partners to develop new products, increase the scope for research and development as well as offer active engagement with customers, (Escobedo et al. 2021). (Opportunity)
Environmental: In Australia, renewable technology is getting significant acceptance and customers are becoming highly aware of sustainable and environment-friendly business operations. This means that businesses must comply with environmental regulations in Australia for enhancing their reputation, brand image as well as to attract potential customers from the market, (Campbell et al. 2020). However, these regulations put potential pressure on companies to enhance their CSR practices and initiatives. (Opportunity and threat)
Legal: The companies operating in Australia need to comply with business laws as well as data protection laws for embracing ethical aspects in business operations, (Burns et al. 2020). This means that compliance with such laws can assist firms to increase their credibility and market concentration. (Opportunity)
Internal and external stakeholders and their role
|
Internal stakeholders |
Role |
|
Employees |
They play a defining role in operations, strategy, and tactics the company Lovisa carries out in terms of both time and financial investments. |
|
Management |
They have a direct responsibility to other stakeholders of the company including investors and shareholders to run a transparent and profitable business, (Lovisa & Waqas, 2020). |
|
External stakeholders |
|
|
Customers |
They are an integral part of a company as they assist the company with every purchase which further provides a direction for developing the products and services as per their demands and needs. |
|
Government and regulatory authorities |
They are considered a significant stakeholder in Lovisa as they collect taxes from the people, company, and the spending Lovisa incurs. However, their interest and power are limited towards Lovisa. |
|
Suppliers |
They are the indirect stakeholder of Lovisa but a collaborative approach is put forward at the company as it builds their reputation on the quality of materials and goods they offer. |
|
Local communities |
Engaging local communities has assisted the business as it resulted in enhanced decision-making capabilities, legitimacy, and competitiveness. |
|
Competitors |
They assist Lovisa to get the best possible quantity, prices, and quality of products and services, (Bertola, 2018). |
The nature and degree of main stakeholders’ interest and implications of conflicting interests
As per the analysis above, it has been identified that the main stakeholders of the company Lovisa are customers, management, and employees who will be highly influenced in terms of any strategic, operational, or structural changes as well as initiation of new policy or products. Based on such context, the below section highlights the nature and degree of main stakeholders’ interest and implications of conflicting interests.
Customers: The level of interest of the customers is high as their engagement with the company’s products and services assist to devise operational and strategic action for Lovisa. In addition, their main interest lies in terms of quality, affordable pricing, convenience, and fulfilment of needs. According to Vanessa (2017), customers seek improvement in quality and product offerings so that they can get better value in terms of their spending. For instance, a new product portfolio or line is initiated at Lovisa which will be widely accepted by customers due to innovation and management in terms of profits but it can create conflicts of interest for employees as they will be facing the complexities in offering the new product.
Employees: Employees play a vital role in the growth and performance of a company in the market. However, conflicts arise when a decision is taken by the management such as a new business model or operational changes, the employees suffer the most as it directly influences their roles and responsibilities, as per (Chauvet & Vesterlund, 2018). As a result, it can lead to poor performance and lower the productivity of the firm at a significant level. Hence, it is essential for Lovisa to comply with the interest of employees as their contribution highly influences customer share as well as the growth of the company.
Management: The need to balance the interests of the main stakeholders of the company as neglecting employees’ interests can affect decisions of management, the accomplishment of business objectives as well as customer satisfaction. For instance, in case Lovisa introduces a new product with moderate quality at a competitive price will benefit the investors and shareholders of the company as they will enjoy greater profits but will act against the customers in terms of quality and price. On the other hand, in case the employees are not satisfied in the process, it can lead to increased turnover leading to poor management structure and lack of customer base, (Efron & Efron, 2020).
The level of main stakeholder’s influence
Stakeholder matrix
It has been identified in the above section that there are different types of stakeholders of Lovisa’s business but the most significant stakeholders include customers, management, and employees. The influence of customers, management, and employees is significant to consider by the company in order to accomplish its business objectives and grow successfully in the market of Australia.
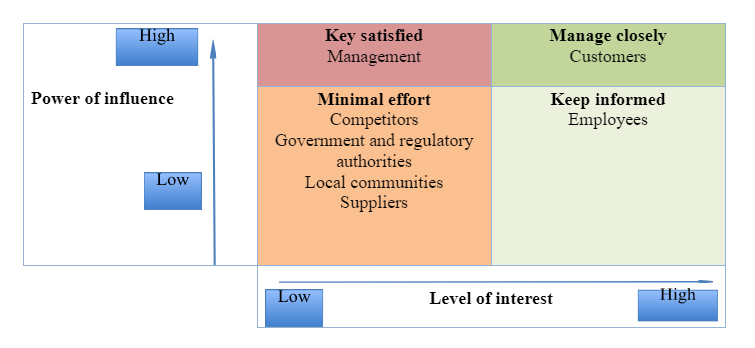
Fig: 2 (Stakeholder matrix for Lovisa)
Source: (The researcher)
Customers: The customers are of high power and interest as they are the main stakeholders and it is the responsibility of Lovisa to analyse the market trend and offer products and services as required. As per Barbieri et al. (2020), the fashion jewellery industry is expected to decline in the forthcoming years by 8.4% due to the covid-19 pandemic that led to economic and social resistance among the customers. This means that Lovisa must balance this influence by offering quality and creative products at an affordable price to attract and retain existing and potential customers. As a result, a positive influence can be experienced in terms of satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Management: At Lovisa, the management possesses high power but low interest because they are the decision-makers of the company. Their focus on directing employees for executing and accomplishing business objectives by laying down the objectives requires minimal efforts. Specifically, the investors and shareholders of the company are essential parts of the management. Therefore, keeping them satisfied as well as informed is essential for Lovisa, specifically in this present covid-19 crisis, (Halafoff et al. 2021).
Employees: Other than management and customers, the employees also have a direct influence on the business of Lovisa as they are also of high interest but with low power. This means the need to keep them informed and boost motivation to enhance theory performance and productivity is essential for Lovisa. Therefore, the need to provide adequate training for enhancing their digital and technological attributes can assist the company to gain competitiveness and success, (Gem & Congress, 2020).
Stakeholder mappings
In terms of the above analysis, the below figure indicates the stakeholder mappings for Lovisa in terms of their level of interest and influence.
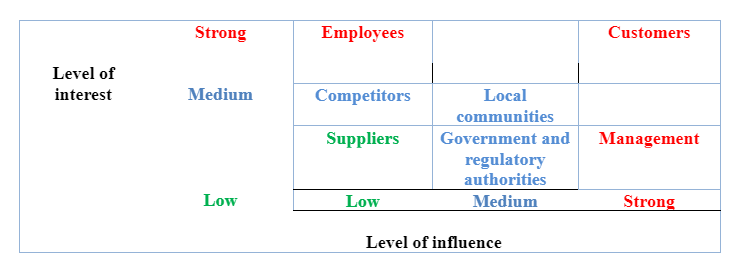
Fig: 3 (Stakeholder mappings for Lovisa)
Source: (The researcher)
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be stated that the functional areas of Lovisa highly contribute towards the success and growth in the market of Australia due to the enhanced level of collaboration and engagement between different functional areas. The macroeconomic scenario indicates the projected growth and feasibility for businesses like Lovisa to exploit the potential opportunities and negate the threats through effective stakeholder engagement. It has been identified that customers, employees, and management are the major stakeholders of Lovisa who have a direct influence on the accomplishment of business objectives and competitiveness in eth marketplace.
References
Barbieri, P., Boffelli, A., Elia, S., Fratocchi, L., Kalchschmidt, M. & Samson, D. (2020). What can we learn about reshoring after Covid-19?. Operations Management Research, 13(3), pp.131-136.
Bertola, P. (2018). Reshaping fashion education for the 21st Century World.
Burns, R. 2020. Adult Learner at Work: The challenges of lifelong education in the new millenium. Routledge.
Campbell, C., Sands, S., Ferraro, C., Tsao, H.Y.J. & Mavrommatis, A. (2020). From data to action: How marketers can leverage AI. Business Horizons, 63(2), 227-243.
Chauvet, C. & Vesterlund, I. (2018). Brand Personas with a Story-How they are created and categorized.
Efron, N. & Efron, S.E. (2020). Optometry in times of pandemic: Spanish flu (1919) versus COVID?19 (2020).
Escobedo, M.B., Zheng, Z. & Bhatt, B. (2021). Socially oriented sharing economy platform in regional Australia: A Polanyian analysis. In Sharing Economy at the Base of the Pyramid (pp. 53-73). Springer, Singapore.
Fisch, C. & Block, J. (2018). Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and management research.
Gem, D. & Congress, C.I.B.J.O. (2020). Learning Opportunities.
Halafoff, A., Marriott, E., Smith, G., Weng, E. & Bouma, G. (2021). Worldviews Complexity in COVID-19 Times: Australian Media Representations of Religion, Spirituality and Non-Religion in 2020. Religions, 12(9), 682.
Lovisa, K. & Waqas, K. (2020). What affect the auditor independence in appearance?: from the perspective of the clients.
Lovisa.com.au. (2021). | Official Site | Fashionable Jewellery & Accessories. Retrieved 20 November 2021, from https://www.lovisa.com.au/
Palepu, K. G., Healy, P. M., Wright, S., Bradbury, M., & Coulton, J. (2020). Business analysis and valuation: Using financial statements. Cengage AU.
Pather, N., Blyth, P., Chapman, J. A., Dayal, M. R., Flack, N. A., Fogg, Q. A., ... & Lazarus, M. D. (2020). Forced disruption of anatomy education in Australia and New Zealand: An acute response to the Covid?19 pandemic. Business environment assignment Anatomical sciences education, 13(3), 284-300.
Statista.com. (2021). Australia - market size jewelry industry 2010-2020 | Statista. Statista. Retrieved 20 November 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/719955/australia-market-size-jewelry-industry/.
Tseane-Gumbi, L.A. (2018). Business Social Responsibility and Functional Areas of a Tourism Business. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 7(3), 1-9.
Vanessa, A. (2017). Corporate Finance Overview. Without Prejudice, 17(5), 50-51.
Vom Brocke, J. & Mendling, J. (2018). Business process management cases. Digital Innovation and Business Transformation in Practice. Berlin et al.: Springer.












