Auditing Assignment: IT Audit Report Analysis For NSW
Question
Task:
In this auditing assignment you are required to analyze an IT audit report conducted by the office of the New South Wales Auditor General and asked to do the followings:
- Identify the audit focus and scope
- Describe high risk IT issues in the NSW city councils
- Describe audit findings related to IT governance in the NSW city councils
- Describe audit findings related to IT general controls in the NSW city councils
- Describe audit findings related to cyber security management in the NSW city councils
- Highlight the professional, legal, and ethical responsibilities of an IT auditor.
Answer
1. Background Overview
The Local Government report of 2019 on New South Wales (NSW) general auditor undertaken in the present context of auditing assignment has raised some questions regarding the implementation of IT governance and security in the high priority areas of the IT audit system. The auditor general of NWS is pleased with the new report that highlighted improvement areas at the financial governance and reporting system. On the other hand, the report has generated some flawed areas, such as the appropriate practice of risk management in controlling fraudulence activities, engagement of more audit, improvement, and risk councils at the system, etcetera. The new IT audit and governance process will strengthen the areas related to cyber-security management and information technology at the NSW system.
2. Identification of Audit Focus and Scope
The NSW audit council has generated $15.3 billion in revenue in 2019. The debt service cover ratio and cash expense cover ratio are the higher-performing areas.
The main focus areas of the annual audit program are,
2.1 Fraud Controls
NSW council has strengthened their responsiveness towards fraud control management and its legislative compliances with appropriate policies and practices. The "NSW Audit Office Fraud Control Improvement Kit" heavily emphasize the appropriate leadership qualities that help in promoting good culture governance procedure with the successful implementation of a fraud control framework (O’Connell, 2016). The ethical and legal frameworks related to fraud controls help in restricting the financial and reputational damage of NSW councils.
2.2 Credit Card Management
Local councils from NSW make purchases via using credit cards. In 2019 alone, the credit card expenditure was recorded at $3 million. The implementation of an effective credit card management system will help in reducing associated risks with unauthorized and inappropriate usage of corporate cards. In the 2018-19 report, the audit has reported 135 issues regarding credit card usage, where most of the risks are aligned with a lack of review in payroll reports and employee details at the master file.
2.3 Cyber Security
Cyber Security management is the most important asset at the NSW digital governance process. It covers every measurement and system related to the communication process, stored documents, and system protection software. The capability development within a system structure is important in addressing the challenges associated with cyber-security to minimize risks (Fowler et al., 2017). It sustains the availability, integration, and confidentiality of the information over the State Government's effective cyber-security policies.
2.4 Benefits and Gifts
This is one of the common grouped areas among the NSW councils. The appropriate management system related to the benefits and gifts helps in minimizing risks related to the reputation and integrity at the NSW council.
2.5 Landfill Rehabilitation
NSW councils manage landfill sites to provide a safe and secure facility for the waste disposal system. The councils act as landfill operators in managing legal obligations, provide monitoring process, and aftercare in closing a landfill site. The management process is strict compliance with the "Protection for the Environment Operations Act" 1997.
The scopes aligned with the audit focus areas are related to,
2.6 IT in Financial Audit
The implementation of advanced technologies, such as Blockchain technology in sustaining the auditing system helps in reducing the efforts and workload of the auditors, minimize the fraudulence activities and optimize the existing work process (Abreu, Aparicio and Costa, 2018). Financial auditing with the help of IT can maximize optimization and efforts.
2.7 IT System Management
It is related to the general control system at the IT management related to the user accessibility, software acquisition, maintenance and change process at the IT system, and planning for recovery and monitoring plans. It is essential for ensuring the service delivery system from the councils.
3. Description of High Risks Associated with IT Issues at NSW City Councils
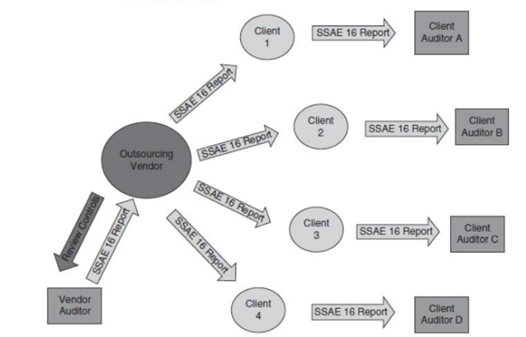
Most of the time, government organizations, such as NSW primarily assess their IT services through outsourcing. A total of 41% of the raised issues are related to the IT governance system related to the accessibility problems and insufficient cyber-security policies. The risks associated with IT at NSW can be,
3.1 Failure to Perform
Sometimes, the acquired IT services from an external vendor can be stopped or restricted in its performing areas, which can lead to an uncertain situation at different councils under the NSW.
3.2 Reduced Security
The outsources IT services are aligned with a restricted security system and other vulnerabilities. The increasing cyber-security risks are most of the time associated with cloud networks on a public server and usage of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the operational processes (Mohammad and Lakshmisri, 2018). Assessing automation in the IT system can reduce potential issues.
3.3 Losing Strategic Advantages
It is possible that sometimes the initial planning does not align with the acquired services afterward. Unnecessary complications and complex service processes led the councils in losing their strategic planning and advantage areas largely.
3.4 Costs Exceeding the Benefits
The cognitive differences between the supplier's interpretation with the IT service buyer's expectation lead organizations to spend more money than the actual service acquisition (Ashok, Day and Narula, 2018). NSW faces financial loss due to various confusion regarding proper cyber-security management and user access among the councils makes the IT service process more complicated.
4. Description of Audit Findings Associated with IT Governance at NSW City Councils
IT governance or information technology provides benefits to the city council. It is corporate governance, which focuses on the management of IT resources. The main aspects of IT governance are to decrease the risk of the council and ensure better investment in the IT resources, which will be advantageous to the council. In the council, all the corporate stakeholders should act as active participants in the IT decision. Information technology governance controls the organizational structures of the IT function. It helps to do a computer's operations and also gives a solution if any problem happens in the council.
The audit has focused on the risks and challenges the government is facing. In 2018-19 financial audits are discussed about the credit card management and the employee’s performance report also been discussed in the findings. It will also help to mitigate the risks if the council faces any. Flexible IT architecture will help to sustain the performance of the IT governance of the council (Mikalef, Pateli and van de Wetering, 2020). Decentralizing the system will help to mitigate the risk and capable to do perform better.
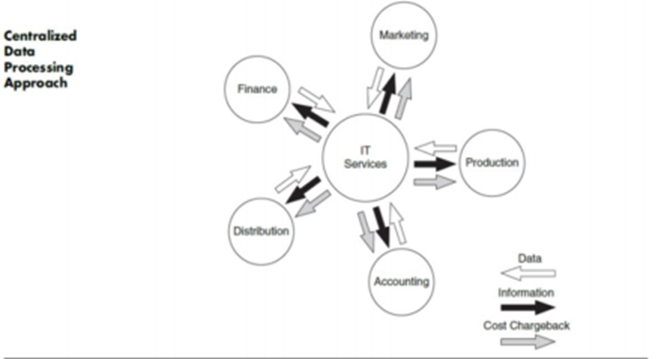
The corporate IT function has centralized data processing to perform better. By centralizing the data processing, it gives services to the database administrator. It also controls the data in the system and maintains the data library. The IT function also helps to develop the system and also checks on the system activities.Information technology also maintains the physical locations of the computers in the council. Maintains access to who is using the computers and database on the system. IT governance also set strategies that can be achieved by the council. It will become an improvement for the council.
IT governance can do better performance by implementing the COBIT 5 framework. It will be valuable for the council. IT governance maintains the effectiveness, efficiency of the council. The COBIT 5 framework is the most commonly used audit information system which will help to do better performance in the council (Andry, 2016). COBIT 5 framework basically focuses on the domain of DDS (delivery, service, and support). IT will help to improve the IT governance in the system by aligning, plan, and organized the process in the council. Implementing the COBIT 5 framework in the IT governance, the performance will get better and the council can give better services to the citizens.
5. Description of Audit Findings Associated with IT General Controls at NSW City Councils
The IT generals monitor the basic controls that are applied in the IT system. IT applications, operating systems, databases, and also supports the IT infrastructure. The main object of IT general controls is to maintain the integrity of the data and also helps to process at the same time. In the NSW city councils, the IT general controls the user access management, program change management, and also give solutions to the problem of the council (Lee and Sawyer, 2019). As an IT auditor, IT control is a big responsibility.
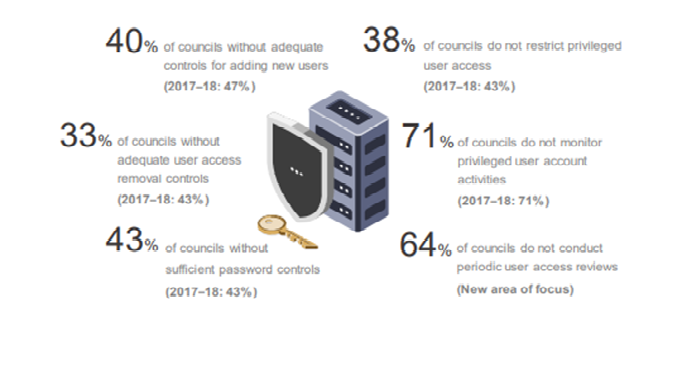
The city council's financial audit involves the review of IT general controls, which give a look into the economic system of the council and how the financial statement should be prepared. As the IT generals control the data security in the system (Lee, Jeon and Lee, 2019). It will be helpful to maintain the quality of the performance of the council and also maintain the system quality. The IT general improves the user access area of the system. IT generally improves service quality and also maintain unauthorized access in the system. The main aspects which effects user management area are:
- To develop the system IT generals should approve the new access and also change the access of the IT system from time to time.
- To maintain the security of user access management, a strong password should be implemented.
- IT generals should review the access of the periodic user and inappropriate user.
- IT generals should control the privileged activities of the appropriate staff.
The council has already improved its management but it has shown that further improvements are need for controlling the privileged account holder.
Program change management changes in the council are needed to be improved. In the council, IT infrastructure should be checked and authorized before implementing it into the system. The main risks that can be faced in the council because of the poor IT system are:
- Illegal changes in the systems or program. It will also affect the data integrity of the system.
- The weak database can make errors in financial reporting.
The audit findings, it has shown that the council has not improved the system yet, but they should improve it. Otherwise, the council cannot give proper service to the citizen.
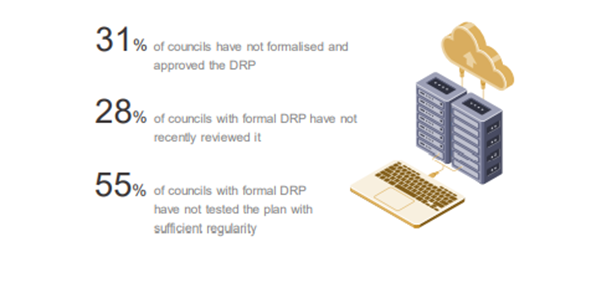
Disaster management help to minimize the problem in the council and it also analyzes the system in the council. The management may not predict big risks but they can identify the maximum outages and also with proper planning they can resolve the issues rapidly.
6. Description of Audit Findings Associated with Cyber Security Management at NSW City Councils
Remote Data breaches have been a major problem since the advent of Information Technology (IT) into the conventional business process. The IT sector has helped connect all the essential and non-essential aspects of various businesses. The integration has helped businesses grow exponentially and profitably and has boosted the globalization process. But since with great powers comes greater risks, the potential risk of data breaches and compromising of security of these businesses has increased multifold. Service NSW has been the target of one such attack in recent times. On the 7th of September 2020 the largest database agency, Service NSW suffered a major security breach due to a cyber-attack. The data breach caused the personal data of almost 186,000 employees and clients to be released from security by the method of email phishing. Among the lacked data, the email account information of 47 staff members was compromised. The phishing attack was initiated earlier in the year 2020 and has severely damaged the moral status of the Service NSW company.
A thorough study and investigation of the event were necessary and have been requested. A massive task of scanning 3.8 million potentially compromised documents is suggested by the investigation body that was recruited in April of 2020 for looking into the security breach. The Audit body will be analyzing the severity of the breach and find out the leaked data. According to Damon Rees, the chief executive of Service NSW, the essential first leg of investigation revealed that almost 500,000 documents containing or referring to personal data of the staff and clients have been leaked. These data were in the form of scanned copies of personal documents, handwritten forms and notes, and various records of applications of transactions.
The Cyber Security Management of the NSW city council has been breached off of 738 Gigabytes of data. The data breach was not all personal data but some arbitrary data were also leaked. However, the investigation did not find any evidence of compromised databases of Service NSW or account information of individual MyServiceNSW accounts. The customers under the risk have been notified of the breach via their mail ids. Additional information for future preventive and preclusive measures from the customer side has been included in the mail. The customers are warned against randomly getting calls and asking for e-mail id regarding this or any other data breaches. The company has promised to provide any kind of relative assistance to the victims.
7. Highlight of the Important Areas of an IT Auditor
7.1 Professional Responsibilities
Internal control: The internal audit is an important part of the investigation where the company sanctions an internal team made of trusted company employees to go through the breach process. According to (Endaya and Hanefah, 2016), an internal auditor’s personality and knowledge characteristics increase the effectiveness of the internal audits. The author suggests that the auditors recruited for the auditing team should have a thorough knowledge of the area of audit and should have an unbiased attitude towards the subjects of the audit. The auditors are selected based on their general and educational qualifications, their field of work, and reporting skills. The internal auditing system compares various policies and practices to check the proper function of the internal control system of the organization.
7.2 Legal Responsibilities
IT governance control: Auditing the administration block of the company can provide the solid ground on to base all the sitemap of a breach on. The administration or the governance body is responsible for the managerial and control aspects of the organization. According to (Andry, 2016), a robust and non-corrupt governance department that has been enabled with IT capabilities provide higher effectiveness, functionality, and efficiency. Auditing the IT governance unit of the organization can help the organization notice loopholes in the administrative policies of the organization.
7.3 Ethical Responsibilities
Operating systems and networks: Operating Systems (OS) and the networking facilities of a company’s IT department enable the whole system to function. The operating system used enables the IT department to create the functional framework of the organization. While the networking capability enables the admit o control the whole organization by sharing information via networking. According to (Li and Suo, 2020), various breaches occur purely due to the size of network branches and also due to the open system data sharing within the organization.
Database Systems: The database of the organization comprises all the Client details that are connected to the organization. According to (Rasin et al., 2018), centralized storage of databases in a physical storage device can cause easy security breaches. The author suggests a method to audit information in centralized storage devices without the help of log files or other file metadata.
8. References
Abreu, P. W., Aparicio, M. and Costa, C. J., 2018. ‘Blockchain technology in the auditing environment’, in 2018 13th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI). IEEE, pp. 1–6.
Andry, J. F., 2016. ‘Audit of IT Governance Based on COBIT 5 assessments: A case study’, Jurnal Nasional Teknologi dan Sistem Informasi, 2(2), pp. 27–34.
Ashok, M., Day, M. and Narula, R., 2018. ‘Buyer (dis) satisfaction and process innovation: The case of information technology services provision’, Industrial Marketing Management, 68, pp. 132–144.
Endaya, K. A. and Hanefah, M. M., 2016. ‘Internal auditor characteristics, internal audit effectiveness, and moderating effect of senior management’, Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences.
Fowler, S., Sweetman, C., Ravindran, S., Joiner, K.F. and Sitnikova, E., 2017. Developing cyber-security policies that penetrate Australian defence acquisitions. Australian Defence Force Journal, (202), p.17.
Lee, L. and Sawyer, R., 2019. ‘IT General Controls Testing: Assessing the Effectiveness of User Access Management’, AIS Educator Journal, 14(1), pp. 15–34.
Lee, S., Jeon, S. and Lee, B., 2019. ‘Security controls for employees’ satisfaction: perspective of controls framework’, SAGE Open, 9(2), p. 2158244019853908.
Li, Z. and Suo, H., 2020. ‘Research and Evaluation of Security Audit Technology in the Era of Network Security Level Protection 2.0’, in Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, p. 12002.
Mikalef, P., Pateli, A. and van de Wetering, R., 2020. ‘IT architecture flexibility and IT governance decentralisation as drivers of IT-enabled dynamic capabilities and competitive performance: The moderating effect of the external environment’, European Journal of Information Systems, pp. 1–29.
Mohammad, S. M. and Lakshmisri, S., 2018. ‘Security automation in Information technology’, INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CREATIVE RESEARCH THOUGHTS (IJCRT)–Volume, 6.
O’Connell, D., 2016. ‘Leadership styles and improved governance outcomes’, Governance Directions, 68(4), p. 202.
Rasin, A., Wagner, J., Heart, K. and Grier, J., 2018, October. Establishing Independent Audit Mechanisms for Database Management Systems. In 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
9. Appendices
9.1 Audit System in Outsourcing IT Services
9.2 Centralizing Data Processing
9.3 User Access Management
9.4 Council’s Implementing Changes System

9.5 Uses of DRP