Critical Analysis On The Appreciative Inquiry Case Study
Question
Task: Conduct an in-depth analysis and prepare a report critically analysing the Appreciative inquiry case study in regards with the healthcare sector.
Answer
Introduction
The present report is based on the Appreciative inquiry case study that highlights the concept of appreciative enquiry within the healthcare sector or hospitals along with the methods’ description, application of the methods and its evaluation. Within the contemporary healthcare scenario, the Appreciative Inquiry refers to the approach towards the change in the organisational process that focuses upon the strengths rather than the weaknesses. This approach is widely different from any other approaches as the other focuses upon the problems and deficits.
Hence, as per the views of Moorer et al., (2017), appreciative inquiry is an essential part of the healthcare system as it helps in determining the appreciation and value of what the team or individuals refer to for the development of the organisation. This helps in designing the plan and compelling of the vision that builds the strength for the future. Thus, the healthcare sector or can be said the hospital then moves to the fulfilment of the designing system or processes, for aligning with the strengths and the best practices to deliver high standard performances. The Appreciative inquiry case study used to prepare the proposed study mentions that the appreciative inquiry helps in energising the individuals, encourages the innovation and creativity, which helps in inspiring the positivity within the healthcare sector as well as in realizing their dreams, while referring to the guidance of the caregivers and the requirement of cultural change within the hospital. The Patient Experience team uses the Appreciative Inquiry as a tool for engaging the staff and leaders for identifying, celebrating along with the spreading of the best practices for the improvement of the outpatient experience and develop the healthcare system with providing high-level performances.
As per the views of Trajkovski et al., (2013), there are certain challenges faced by an organisation like the fact that general public has become least tolerant regarding the poor standards of the healthcare system which tends to raise the demands of the consumer for the adoption of the advanced policies of health development. The traditional procedures for the management of the contemporary system of healthcare cause the limitation for meeting the patient needs and the requirement of the healthcare staff and the entire organization. It is also observed in the Appreciative inquiry case study that the Health Behaviour Changes are based upon the philosophies, which suggest with not performing the specific behaviour is considered to be a deficit or a problem that has to be solved. However, with the increase in the fiscal constraint that also leads to the roles of the traditional nurses and their responsibilities that face challenges.
Thus as per the observation of Moore and Charvat (2007), the Appreciative Inquiry considers the organisation not to be the problem rather it is a mystery that should be embraced. The AI replaces the deficit thinking of the problem solving into the possibility of thinking. This thinking possibility is realized through the systematic inquiry with utilising the question set for appreciating and valuing the best for the future. The role of appreciative inquiry examined in the Appreciative inquiry case study helps in facilitating the workforce engagement along with the promotion of organisational learning with positive changes within the healthcare sector and work as per the needs and requirements of patients and other consumers.

Figure 1: Appreciative Inquiry
Source: (Jones, 2018)
Method description
The approach of the Appreciative Inquiry discussed in the scenario of Appreciative inquiry case study is considered to be the approach in the change management which focuses upon the identification of the criteria working well, analysation of the reason behind the criteria for which it is working well and lastly, developing and enhancing the criteria for the future development of the organisation. The basic principle of Appreciative Inquiry accounts that the organisations will get developed in the direction in which the individuals within the organisation focuses upon their attention. As per the views of Clarke et al., (2018), if the overall attention of the organisation is focused upon its strengths, it will be the best thing for the organisation to build their strength for future development. The procedure of the AI needs a specific way of asking guided questions, which encourage positive thinking and the staff-to-staff interaction within an organisation such as even in the Healthcare sector.
As per the findings obtained from the Appreciative inquiry case study it is clear that there are five core principles of Appreciative Inquiry, which have been listed below,
The Simultaneity Principle: The change begins with the moment of the question asked. The First question that is asked prepares the setting of the stage regarding what is discovered or found. All of these data get transformed into the stories from which the future of the organization is conceived, constructed and further discussed.
The Anticipatory Principle: The present behaviour of the individual within an organisation influences the future development. As per the views of Doody, (2018), the more the behaviours are positive in the present helps in the creation of the hopeful image in the future.
The Constructionist Principle: The human handles the organisation and its management and hence, the belief of the individuals will affect the way they act according to the organisational change.
The Poetic Principle: The Future, Present and the past of an organisation counts for the endless source regarding the learning, interpretation and inspiration (Fry, 2017). Thus, the individuals of the organisation must inquire all such sources and learn of this.
The Positive Principle: The question within the AI needs to be positive to guide the organisational change, which helps in the long-lasting durability and the effectiveness of the changes.
Difference between the Problem-solving approach and the Appreciative inquiry based on the Appreciative inquiry case study is mentioned below:
|
Approaches |
Problem-Solving |
Appreciative inquiry |
|
Definitions and attributes |
This comprises of certain ideal ways regarding the things to be done. |
The things are constructed socially by the system of the organization and could be changed. |
|
If the situation is raised within the organisation is not as per the preference of the individuals would require it to be, then a problem or conflict usually arises, which needs to be solved (Lewis et al., 2016) |
As per the information provided in the Appreciative inquiry case study it is noted that within any situation of the organisation, the individuals would find out the ways regarding the excellence for developing it. |
|
|
The process of solving the problems within an organisation through this approach is to break the problems into various parts and then gradually analysing it. |
The organisation possessing this approach would build upon the excellence of seeking out certain examples and share certain stories regarding the exceptional performance within the system (Locke, 2018). |
|
|
This approach helps in fixing the whole situation by fixing up the broken parts. |
This approach helps in creating the excellence of the organisation’s image, which helps the overall system to move toward the image and achieve it with higher potential. |
Table 1: Difference between Problem solving approach and Appreciative Inquiry
(Source: Developed by the learner)
Hence, the Appreciative inquiry case study explored in the present report illustrate that the distinguished details describe the importance of Appreciative inquiry within the organisation like healthcare or any other to achieve a positive image and move forward for the future development.
The history of the Appreciative Inquiry
The Appreciative Inquiry has been pioneered in the year of 1980s by Suresh Srivastava and David Cooperrider, who were the two professors at the Case Western University. As per the opinion of Bushe, (2012), the origin of the AI could be traced by the close relationship among the doctoral project of organisational behaviour at the Case Western University and the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, which are few blocks apart from each other. The Doctoral Project on OB was new in America with stressing upon the rigorous theory in grounding and the research method and also stressing upon the Application of the theory along with the methods of the issues in the organisational leadership and changes. David Cooperrider was employed in the Cleveland Clinic as an intern and gradually started interviewing physician leaders within the organisation, which made the individual more excited about the organisational processes and the governance form.
With the collection of issues and problems identified from the Appreciative inquiry case study, Suresh Srivastava slowly was impressed with David and started encouraging the pupil of keeping aside the problem and focus upon what vitality and life were given to the organization (Cooperrider and Srivastva, 2017). During the end of the 1980s, David was asked to present the appearing them and also put a footnote that this theme does not focus on the deficit rather what gave validity to the extraordinary system which resulted into the tremendous interest in the report. The information obtained from the critical analysis on the Appreciative inquiry case study mentions that the birth of Appreciative Inquiry took place when at the Academy of management in 1984, David Cooperrider presents the diagram, which contrasted the problem solving as well as the appreciative analysis, which proposes that instead of taking up the organisational drawbacks, the mystery of the organisation, and its positivity must be appreciated for the further development.
The 4D model of Appreciative Inquiry
As per the observation of Gaskin and Williams (2017), the Appreciative Inquiry comprises of the inquiry which moves through the four phases such as,
· Discovery phase
This stage determines the direction of change. The readings utilized from the Appreciative inquiry case study mentions that this phase helps the organisation like the healthcare sector to gain the opportunity of growth and development and hence, it gets translated into the affirmative which helps in inviting the formulation. At this stage, the organisation emphasis upon the best facilities, which is present and then pitches it against the previous facilities, which were considered as best. Thus, this is accomplished by conducting face to face interviews with the employees, which focuses upon the detection of method which helps in developing positive feeling among the staff. A deeper understanding along with positive core, deep insight focus with building up collective wisdom and the discussion with outstanding behaviour may result in this phase.
· Dream phase
In this phase, the individuals are assumed to be assessing their achievement within the field of work, life, ambition and relationship versus their dreams. During this stage, the individual nurtures their ambitions and dreams beyond their present limit, to gain a brighter future for the healthcare organisation and themselves. As per the views of Glanz and Heimann (2018), the individuals get more motivated with the energising of the positive core. Thus, the individual started to look forward towards the result-driven project and get more interested in checking their performance. Thus, this results in the Healthcare Organisation to get more innovative in their thoughts, the employees get the positive potential with strategic opportunity and the sense of commitment along with purpose get cultivated within the staff.
· Design phase
This phase is designed for the implementation of thoughts within the practices and involves the overall steps for making the dreams real. The organisational priorities are also determined along with the essential elements within the team proposition, which is necessary for invoking the strong thoughts. As per the views of Gray et al., (2019), this proposal is the positive note and the organisational quality that is wished to be delivered. Thus, this results in yielding of ideas, which are implemented over time.
· Destiny phase
In this stage, the working teams are formed within the healthcare organization and their works are assigned to them in this stage. Several goals and plans are defined along with work which is delegated to the different teams that depend upon the expertise. Thus, the overall employees are invited by the management to take part in these working groups. The participants are requested to fulfil their task as per the commitment. According to the statement of Hastie et al., (2019), this results in changes taking place in the healthcare organisation in great numbers. Hence, the most essential change mentioned in the Appreciative inquiry case study is the collaborative effort, which helps the organization to function.
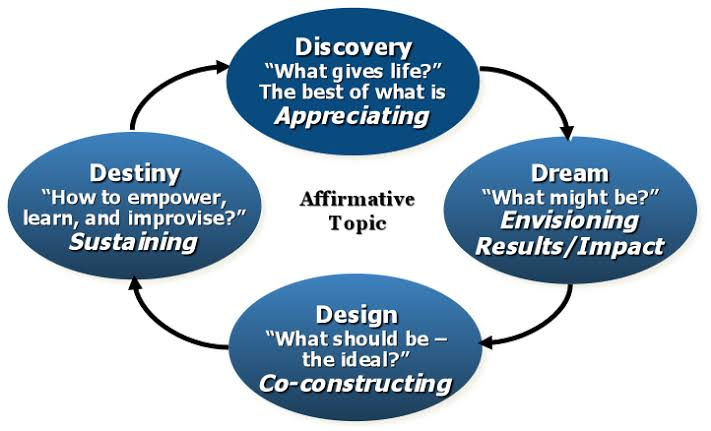
Figure: 4D Model of Appreciative Inquiry
Source: (Jarvis et al., 2016)
Characteristics of Appreciative Inquiry
There are certain advantages of the Appreciative Inquiry discussed in the Appreciative inquiry case study such as:
- It leads to the production of the positive effects between the employees and the leaders. It builds up the trust and shares positive spirits. This may also lead to an increase in the creativity, integration and resilience in the thinking.
- The leaders enter within the change process as the positive focus makes it easier. This generates the needed commitment and energy for the production of significant improvement.
- This helps in the production of the high energy and the change within the efforts. It is the integrated system which comprises of the ways of working, underlying assumptions and values regarding the nature of individuals within an organisation.
- There is certain discipline along with the thoughtful collection of methods which could be learned and can be utilised. As per the views of Hoque (2017), this approach works along with the strengths of the organisation and develops it for future growth.
Thus, this shows that it is very harmful to the organisations like Healthcare to focus only on the weaknesses and the dissatisfaction rather living in the perceptual dissatisfaction focus on strength can help in future development.
There are certain disadvantages of the Appreciative Inquiry for instance
- The dreams and visions consisted of the AI produces momentum for a few months and there can be the need for the action of planning and the monitoring of the system for making the project successful
- The leaders of the organisation easily dismiss the focus on positivity, as they believe that the change must be occurring when there is the involvement of the fear of loss.
- It is a closed system, as the practitioners tend to the discount of the research, practice and theory which does not fit into the Appreciative Inquiry. Hence, as per the views of Hung et al., (2018), the approach has become so popular that many of the Healthcare Sector think that the can easily implement the AI methods but they lack both the understanding of the procedures and also the skills needed.
- There is a need for sensitivity in many of the occasion within the healthcare sector where there is a need to address the weaknesses within a regular interval and to provide space for the appreciative processes.
- This can even lead to the addiction and can also give rise to the situation in which the individual and the management of the Healthcare Sector never find satisfaction in any of the changes they made and tries to bring more and more changes without judging it to be necessary or not. This raises the gap between the present criteria and the things to be developed for strengths in the future.
Method application
Appreciative inquiry case study 1:
According to Watkins et al., (2016), appreciative inquiry is an effective intervention that renders an ability to change and improve nursing practice. To explain the above-mentioned fact in a wider manner, the Appreciative inquiry case study that has been discussed in the article written by Watkins et al., (2016), has been explained. In the given Appreciative inquiry case study it has been evaluated that a healthcare sector failed to render effective healthcare service to a high profile patient. After the failure of the healthcare service provider, the centre identified that there is a huge requirement of transformational development so that the centre can avoid any other failed cases in rendering effective services to its patients in the future.
From the Appreciative inquiry case study, it has been evaluated that the healthcare centre has preferred to conduct an appreciative inquiry as an approach for bringing and exploring necessary change in the social system. According to Morgan et al., (2017), it has been evaluated that appreciative inquiry is an exclusive approach that is integrated by most of the healthcare sectors along with the other business sectors to adapt and implement necessary changes flexibility so that they can incorporate with accurate strategies and practices to overcome its challenges and obstacles. In the Appreciative inquiry case study, the appreciative inquiry has been determined as merit to resolve the complexities in rendering human healthcare experiences.
The respective healthcare centre has incorporated with electronic database like a cumulative index of nursing, PsychINFO, Scopus and Web of Science, PsychARTICLES along with Cochrane Library in associated with appreciative inquiry to improve its social and cultural system of the centre. This would enable the centre to enhance the nursing practices, due to which the issues of inappropriate healthcare services countered the reputation of the respective organization. All the above methods and techniques are associated with Artificial Intelligence solution in aspects to appreciative inquiries. Thus, it can be determined that an organization facing in delivering proper and accurate healthcare services to its patients would be solved technically and in a systematic manner. The tools mentioned above enabled the healthcare centres to standardize its performance of the nurses by examining them through data extraction instruments, systematically (Tomlinson et al., 2019).
With an effective appreciative inquiry, practice healthcare identifies the performance of its every nurse along with analyzing the areas where the improvement and development are necessary. According to Kelly et al., (2016), appreciative inquiries enable an organization to eliminate the negative factors while accentuating the positive and strength of the overall organization. This enables the company to understand how they can utilize those identified strengths of an organization for rendering transformational changes. From the Appreciative inquiry case study, it has been evaluated that after integrating with the appreciative inquiry the centre successfully sustained high-quality nursing practice renders standard healthcare service experience to its future patients. Thus, from the given Appreciative inquiry case study it has been evaluated that appreciative inquiry has helped the healthcare centre to shift its focus towards organizational strength rather than evaluating its weak areas.
Appreciative inquiry case study 2:
In the article of Kelly et al., (2016), it has been evaluated that persuading the safety of the patients are determined as a key component for the healthcare centres to endeavour and improve its services in healthcare. This can be done by minimizing the adverse outcomes of the errors and accidents countered by the healthcare centres. Human errors in rendering healthcare service are identified as a major issue in the Appreciative inquiry case study, which is mandatory for the respective sectors to overcome with accurate and suitable practices. It has been observed by Trajkovski et al., (2016), the scope of appreciative inquiry is very limited.
From the Appreciative inquiry case study, it has been evaluated that this approach of AI can be highly effective for the patients falling under second victim criteria. Victims in this criterion include anxiety, depression along with detachment, which if not accurately solved can hamper cognitive functioning of the clinic (Sturm et al., 2019). Patients suffering from long-standing issues, sleep disturbance, post-traumatic disorder or any such related mental disorder is situational avoided may lead to counter heavy loss, both to the victims along with the clinic. Thus, these identified issues can be exacerbated if the healthcare professions indulge with punitive approaches associated with appreciative inquiry. According to Chauke et al., (2015), the appreciative inquiry approach leads to rendering healthcare professionals perceptions in aspects to workplace discrimination along with disciplinary actions, which ultimately leads to avoid human errors while rendering standard healthcare service experience to its patients. Thus, it can be stated that this approach and practice would help the healthcare service providers to reduce the rate of its future engagement in errors and incidence.
According to Watkins et al, (2019), it has been evaluated that as per the psychological research it is proven that individuals can learn from their positive reinforcement along with negative reinforcement. Thus, this fact is discussed in the given Appreciative inquiry case study as an approach to an appreciative inquiry by enhancing the positive influence on the workforce of the clinic. Also, positive deviance is related to an effective AI approach that oversights variations in the performance of the healthcare service providers, resulting in a positive and healthy outcome rather than rendering any kind of harm. Learning from experience is another approach in the appreciative inquiry which aims in rendering continuous learning from self and peer actions (Schutt, 2018). In the given study, the concept of excellent study with effective integration of appreciative inquiry has been discussed with include in-depth consideration about SIRI (Serious Incident report investigation) along with IRIS (Improving, Resilience, Inspiring success) are found to be an effective approach to improve the professional healthcare practices.
As opined by Whitney et al., (2019), it has been evaluated that with an effective adoption of appreciative inquiry, healthcare centres can explore innovative and creative ideas and solutions, which help an organization in improving its medical practices.
Evaluation
From the above discussion on the articles based on the Appreciative inquiry case study, it can be evaluated that appreciative inquiry fosters the growth of the healthcare sector by tapping into core values, strengths along with motivational factors that lead to energize and inspire the overall workforce to flexibly adapt necessary changes (Tschannen-Moran and Hofer, 2018). Thus, it is recommended for all the healthcare centers to integrate with the AI techniques as this approach would enable the organization to sustain benefits without any drawbacks. This approach illustrated in the several sections of Appreciative inquiry case study eliminates the weak areas hampers the operations and functioning of healthcare sectors in renders standard healthcare services to the patients. But to focus on the strengthen areas which can be accentuated more to improve the weak areas by motivating and encouraging positively. Thus, it can be determined that AI is an approach that enables the healthcare sectors to maintain an ethical working environment while ensuring continuous improvement in nursing and any other healthcare practices. As opined by Ioana , (2013), health centers that are effectively collaborating with the changing demand pattern can skip the integration of AI approach. As it has been evaluated that is not always necessary for the health centers to change their organizational structure if the organization are running accurately implementing core values and ethics.
The critical analysis on the Appreciative inquiry case study signifies that the process of AI is identified to indulge in group work that is efficient enough to improve organizational competency (Pill, 2016). In the above discussion how the healthcare centres improve their clinical quality management with the effective outcome with the help of different tools and techniques associated with appreciative inquiry has been exhibited (Wall et al., 2017). The AI practices focus on standardizing the overall structure and healthcare services, provided by any healthcare centres. Thus, it can be observed that an effective appreciative inquiry practice can render intervention implication by connecting the strengths and motivational factors of an individual to the changing and transformational objective of the healthcare centres.
References
Bushe, G.R., 2012. Foundations of Appreciative Inquiry: History, criticism and potential. Appreciative inquiry case study AI Practitioner, 14 (1), 8-20. Accessed online, 11(18), p.13. (Main)
Chauke, M.E., Van Der Wal, D. and Botha, A., 2015. Using appreciative inquiry to transform student nurses' image of nursing. curationis, 38(1), pp.1-8.
Clarke, C.L., Titterton, M., Wilcockson, J., Reed, J., Moyle, W., Klein, B., Marais, S. and Cook, G., 2018. Risk time framing for wellbeing in older people: a multi-national appreciative inquiry. The Journal of Mental Health Training, Education and Practice, 13(1), pp.44-53.
Cooperrider, D. and Srivastva, S., 2017. Appreciative Inquiry in Organizational Life?. In Research in organizational change and development (pp. 81-142). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Doody, M.C., 2018. Maintaining an Organizational Culture of Humanism and Respect: An Appreciative Inquiry Action-oriented Study Appreciative inquiry case study (Doctoral dissertation, Fielding Graduate University).
Fry, R., 2017. Agents of World Benefit: Business: An Appreciative Inquiry into Business as an Agent of World Benefit. AI Practitioner, 19(2).
Gaskin, S. and Williams, M., 2017. Developing orientation leader training using appreciative inquiry. Journal of College Orientation, Transition, and Retention, 24(1).
Glanz, J. and Heimann, R., 2018. Encouraging reflective practice in educational supervision through action research and appreciative inquiry. The Wiley Handbook of Educational Supervision, p.353.
Gray, S., Treacy, J. and Hall, E.T., 2019. Re-engaging disengaged pupils in physical education: an appreciative inquiry perspective. Sport, Education and Society, 24(3), pp.241-255.
Hastie, P.A., Rudisill, M.E., Boyd, K. and Johnson, J.L., 2019. Appreciative inquiry case study Examining the Pathway to Motor Skill Competence in a Mastery Motivational Climate: An Appreciative Inquiry. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, pp.1-11.
Hoque, Z., 2017. Appreciative inquiry for accounting research. Appreciative inquiry case study In The Routledge Companion to Qualitative Accounting Research Methods (pp. 153-168). Routledge.
Hung, L., Phinney, A., Chaudhury, H., Rodney, P., Tabamo, J. and Bohl, D., 2018. Appreciative inquiry: Bridging research and practice in a hospital setting. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 17(1), p.1609406918769444.
Ioana, A., 2013. Metallurgy’s impact on public health. Revista de Cercetare ?i Interven?ie Social?, (43), pp.169-179.
Jarvis, J.M., Bell, M. and Sharp, K., 2016. Leadership for differentiation: An appreciative inquiry of how educational leadership shapes pedagogical change. Appreciative inquiry case study Leading and Managing, 22(1), p.75.
Jones, A., 2018. School Leadership and Appreciative Inquiry in Culture of Care.
Kelly, N., Blake, S. and Plunkett, A., 2016. Learning from excellence in healthcare: a new approach to incident reporting. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 101(9), pp.788-791.
Lewis, S., Cantore, S. and Passmore, J., 2016. Appreciative inquiry for change management: Using AI to facilitate organizational development. Kogan Page Publishers.
Locke, J.W., 2018. Using Appreciative Inquiry as a Tool for Congregational Change. Appreciative inquiry case study Discernment: Theology and the Practice of Ministry, 4(1), p.2.
MacCoy, D.J., 2014. Appreciative inquiry and evaluation–Getting to what works. Canadian Journal of Program Evaluation, 29(2).
Moore, S.M. and Charvat, J., 2007. Promoting health behavior change using appreciative inquiry: moving from deficit models to affirmation models of care. Family & Community Health, 30, pp.S64-S74. (main)
Moorer, M.B.A., Kunupakaphun, S., Delgado, E., Moody, M., Wolf, M.S.N., Moore, R.N. and Eamranond, M.D., 2017. Appreciative inquiry case study Using appreciative inquiry as a framework to enhance the patient experience. Patient Experience Journal, 4(3), pp.128-135. (main)
Morgan, S.J., Pullon, S.R., Macdonald, L.M., McKinlay, E.M. and Gray, B.V., 2017. Case study observational research: A framework for conducting case study research where observation data are the focus. Appreciative inquiry case study Qualitative health research, 27(7), pp.1060-1068.
Pill, S., 2016. An appreciative inquiry exploring game sense teaching in physical education. Sport, Education and Society, 21(2), pp.279-297.
Schutt Jr, D.A., 2018. A Strengths-Based Approach to Career Development Using Appreciative Inquiry. National Career Development Association. 305 North Beech Circle, Broken Arrow, OK 74012.
Sturm, E.C., Mellinger, J.D., Koehler, J.L. and Wall, J.C., 2019. An appreciative inquiry approach to the core competencies: taking it from theory to practice. Journal of Surgical Education.
Tomlinson, K.C., Hrabe, D.P., Zurmehly, J. and Warren, B., 2019. Using Appreciative Inquiry to Decrease Incivility and Promote a Healthy Work Environment: A Literature Review.
Trajkovski, S., Schmied, V., Vickers, M. and Jackson, D., 2013. Using appreciative inquiry to transform health care. Appreciative inquiry case study Contemporary nurse, 45(1), pp.95-100. (main)
Trajkovski, S., Schmied, V., Vickers, M.H. and Jackson, D., 2016. Experiences of neonatal nurses and parents working collaboratively to enhance family centred care: the destiny phase of an appreciative inquiry project. Collegian, 23(3), pp.265-273.
Tschannen-Moran, M. and Hofer, M., 2018. Appreciative Inquiry: Building on Strengths for Integrating Information Technology in Schools. Second Handbook of Information Technology in Primary and Secondary Education, pp.1-8.
Wall, T., Russell, J. and Moore, N., 2017. Positive emotion in workplace impact: the case of a work-based learning project utilising appreciative inquiry. Appreciative inquiry case study Journal of Work-Applied Management, 9(2), pp.129-146.
Watkins, K.E., Marsick, V.J. and Wasserman, I., 2019. Appreciative inquiry case study Action Research, Action Learning, and Appreciative Inquiry: Interventions That Build Individual and Group Capacity for EBOCD. In Evidence-Based Initiatives for Organizational Change and Development (pp. 76-92). IGI Global.
Watkins, S., Dewar, B. and Kennedy, C., 2016. Appreciative Inquiry as an intervention to change nursing practice in in-patient settings: An integrative review. International journal of nursing studies, 60, pp.179-190.
Whitney, D., Trosten-Bloom, A. and Vianello, M.G., 2019. Appreciative Inquiry: Positive Action Research. In Action Learning and Action Research: Genres and Approaches (pp. 163-177). Appreciative inquiry case study Emerald Publishing Limited.












