Accounting Assignment Analyzing Several Business Scenarios
Question
Task:
Prepare an accounting assignment addressing the following questions:
Question 1:
Asia Pacific Ltd started operating on 1 July 2017 with 12 employees. Three years later all of those employees were still with the company. On 1 July 2019 the company hired 15 more people but by 30 June 2020 only 10 of those employed at the beginning of that year were still employed by Asia Pacific Ltd.
All employees are entitled to 13 weeks’ long-service leave after a conditional period of 10 years of employment with Asia Pacific Ltd.
At 30 June 2020 Asia Pacific Ltd estimates the following:
- The aggregate annual salaries of all employees hired on 1 July 2017 is now $1,200,000.
- The aggregate annual salaries of all current employees hired on 1 July 2019 is now $800,000.
- The probability that employees hired on 1 July 2017 will continue to be employed for the duration of the conditional period is 40 per cent.
- The probability that employees hired on 1 July 2019 will continue to be employed for the duration of the conditional period is 20 per cent.
- Salaries are expected to increase indefinitely at 1 per cent per annum.
The interest rates on high-quality corporate bonds are as follows:

Required:
- Calculate the total accumulated long-service leave benefit as at 30 June 2020.
- What amount should be reported for the long-service leave provision as at 30 June 2020 in accordance with AASB 119?
- Prepare the journal entry for the provision for long-service leave for 30 June 2020 in accordance with AASB 119.
- Which employee benefits are required to be discounted in accordance with AASB 119?
Question 2:
Big Construction Company signs a contract on 1 July 2019, agreeing to build a warehouse for Buyer Corporation Ltd at a fixed contract price of $10 million. Buyer Ltd will be in control of the asset throughout the construction process. Big Construction Company estimates that construction costs will be as follows:
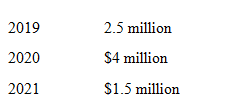
The contract provides that Buyer Corporation Ltd will make payments on 31 December each year as follows: 2019 $2 million 2020 $5 million 2021 $3 million The contract is completed and accepted on 31 December 2021. Assume that actual costs and cash collections coincide with expectations and that cost (an input measure) is used as the basis for assessing progress on the construction contract. Big Construction Company has a financial year ending 31 December.
Required:
- Using the above data, compute the gross profit to be recognised for each of the three years, assuming that the outcome of the contract can be reliably estimated.
- Prepare the journal entries for 2019, 2020 and 2021 financial year to recognise revenue on the assumption that the measure of progress on the contract can be reliably estimated.
- Prepare the journal entries for 2019, 2020 and 2021 financial year, assuming that the measure of progress on the contract cannot be reliably assessed.
Question 3:
Gem Limited commences operations on 1 January 2019. During 2019 Gem Limited explores three areas and incurs the following costs:
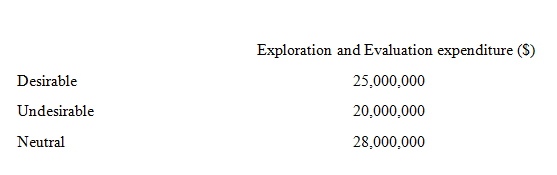
In 2020 oil is discovered at Desirable Site. Undesirable Site is abandoned. Neutral Site has not yet reach a stage that permits a reasonable assessment at the existence or otherwise of economically recoverable reserves, and active and significant operations in the area of interest are continuing. In relation to the exploration and evaluation expenditures incurred at Desirable Site and Neutral Site, 70 percent of the expenditures related to property, plant and equipment, and the balance relates to intangible assets.
In 2020, development costs of $48,000,000 are incurred at Desirable Site (to be written off on a production basis). $32,000,000 of this expenditure relates to property, plant and equipment, and the balance relates to intangible assets. The development of Desirable Site is completed but the production is not started yet. (i.e. there is no production, inventory and sales)
Required:
Provide the necessary journal entries using the area-of-interest method.
Question 4:
Alps Ltd has a net income after tax of $1 500 000 for the year ended 30 June 2019. At the beginning of the period Alps Ltd has 900 000 fully paid-up ordinary shares on issue. On 1 December 2018 Alps Ltd had issued a further 300 000 fully paid-up ordinary shares at an issue price of $2.00. On 1 March 2019 Alps Ltd made a one-for-six bonus issue of ordinary shares out of retained earnings. The last sale price of an ordinary share before the bonus issue was $2.50. At the beginning of the current period Alps Ltd also had 500 000, $1.00, 8% cumulative preference shares on issue. The dividends on the preference shares are not treated as expenses in the statement of comprehensive income. The basic earnings per share for the period ended 30 June 2018 was $1.50 per share.
Required:
- Calculate the basic EPS amount for 2019 and provide the adjusted comparative EPS for 2018.
- Explain what diluted EPS is. Give one example of a security that can dilute the basic EPS.
Question 5:
Fujitsu Ltd purchases inventory from DFO Ltd, a listed British company. Relevant events and the spot rates at each date are shown as follows:
|
Date |
Event |
Spot rate |
|
15 March 2019
|
Order £300,000 of inventory
|
A$1.00 = £0.37 |
|
11 May 2019
|
Purchase takes place as inventory shipped to Fujitsu Ltd (FOB)
|
A$1.00 = £0.41
|
|
30 June 2019
|
End of financial year
|
A$1.00 = £0.43
|
|
02 July 2019
|
Inventory arrives at warehouse
|
A$1.00 = £0.42
|
|
14 August 2019
|
Payment of £300,000 to supplier
|
A$1.00 = £0.39
|
Required:
- Prepare appropriate journal entries for each relevant event (Round amounts to the nearest dollar). Show your working.
- What is a qualifying asset? Provide two (2) examples.
Answer
Answer 1:
a. As per the first case scenario given in this accounting assignment, all employees are entitled to 13 weeks’ long-service leave after a conditional period of 10 years of employment with Asia Pacific Ltd.
Some of the employees joined in 2017 and some of them joined in 2019 and hence none of them completed 10 years of service at Asia Pacific Limited
The accumulated benefit is calculated on the basis of present salary.
Also, since the employees are working currently, the probability of staying in service is 1
No. of conditional year=10
|
(All terms are in $) |
Present Salary |
Number of years remaining |
Entitlement = PV of Salary * (13 weeks /52 weeks)* (no. of years in the job/ no. of conditional years) |
Probability of Staying |
Expected Entitlement |
|
Employees who Joined in July 1, 2017 |
1200000 |
7 |
90000 |
0.4 |
36000 |
|
Employees who Joined in July 1, 2019 |
800000 |
9 |
20000 |
0.2 |
40000 |
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
40000 |
Hence accumulated long service leave benefit is $40000 as on June 30,2020.
b.As per AASB 119, Long service provision is calculated at present value of the future salary since the company is not expectedto pay the amounts within next 12 months. This present value is calculated based on expected future salaries or payments for employment or service. The future payment is calculated by increasing the present salary according to yearly increment rate. Then that future expected payment is discounted back to the present value. This discount rate should be equal to market yield rate having tenure equal to remaining years of possible future payment.
So, Present Value = Entitlement Amount/ (1+ rate of corporate bond) years remaining to maturity
|
For Employees Joining On July 1, 2017 |
|||||
|
Year |
Increment Rate |
Projected Salary |
No. of Year From Now |
Discount Rate |
PV of Projected Salary |
|
2020 |
1200000 |
0 |
|
||
|
2021 |
1% |
1212000 |
1 |
6% |
1143396.226 |
|
2022 |
1% |
1224120 |
2 |
6% |
1089462.442 |
|
2023 |
1% |
1236361.2 |
3 |
6% |
1038072.704 |
|
2024 |
1% |
1248724.812 |
4 |
6% |
989107.0107 |
|
2025 |
1% |
1261212.06 |
5 |
6% |
942451.0196 |
|
2026 |
1% |
1273824.181 |
6 |
6% |
897995.7829 |
|
2027 |
1% |
1286562.423 |
7 |
6% |
855637.4912 |
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
6956122.677 |
|
For Employees Joining On July 1, 2019 |
|||||
|
Year |
Increment Rate |
Projected Salary |
No. of Year From Now |
Discount Rate |
PV of Projected Salary |
|
2020 |
800000 |
0 |
|
||
|
2021 |
1% |
808000 |
1 |
8% |
748148.1481 |
|
2022 |
1% |
816080 |
2 |
8% |
699657.0645 |
|
2023 |
1% |
824240.8 |
3 |
8% |
654308.9214 |
|
2024 |
1% |
832483.208 |
4 |
8% |
611900.0098 |
|
2025 |
1% |
840808.0401 |
5 |
8% |
572239.824 |
|
2026 |
1% |
849216.1205 |
6 |
8% |
535150.2058 |
|
2027 |
1% |
857708.2817 |
7 |
8% |
500464.5443 |
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
4321868.718 |
All employees are entitled to 13 weeks’ long-service leave after a conditional period of 10 years of employment with Asia Pacific Ltd.
Entitlement = PV of Projected Salary * (13 weeks /52 weeks)* (1/ no. of years remaining)
|
Employees |
PV of Projected Salary |
no. of years remaining |
Entitlement |
Probability of Staying |
Expected Entitlement |
|
Who Joined on July 1, 2017 |
6956122.677 |
7 |
248432.95 |
0.4 |
99373.18 |
|
Who Joined on July 1, 2019 |
4321868.718 |
9 |
120051.91 |
0.2 |
24010.38 |
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
123383.56 |
Hence, the amount that should be reported for the long-service leave provision as at 30 June 2020 in accordance with AASB 119 is $123383.56
c.
|
Journal Entry for the provision for long-service leave |
|||
|
Date |
Particular |
Debit |
Credit |
|
June 30, 2020 |
Employee Benefit Cost |
$123383.56 |
|
|
|
Provision for long-service leave |
|
$123383.56 |
|
|
(To account for expected long-service benefit) |
|
|
d. Long term benefits are those where employees are not assumed or expected to settle the leaves within 12 months.
In accordance with AASB 119, annual leave benefits are required to be discounted. These are classified as other long- term employee benefits. This discounting will be done according to expected salary levels in the future period when the leave is expected to be taken.
Answer 2:
a. Total contract price = $10 Mn
Estimated total cost = $8 Mn
Estimated Profit = $2 Mn
|
(All amounts are in $ Mn) |
Years |
||
|
|
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
|
Cost Incurred Till date |
2.5 |
6.5 |
8 |
|
Cost remaining to be incurred |
5.5 |
1.5 |
0 |
|
% Completion |
31.25% |
81.25% |
100.00% |
|
Estimated cumulative gross profit |
0.625 |
1.625 |
2 |
|
Estimated gross profit for the year |
0.625 |
1 |
0.375 |
b.
|
Journal Income for 2019,2020,2021 for Big Construction Company (All figures are in $ Mn) |
|||||||
|
Assumption that the measure of progress on the contract can be reliably estimated |
|||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
|||
|
S.No. |
Account |
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
|
1 |
Construction In Progress |
2.5 |
|
4 |
|
1.5 |
|
|
Cash |
|
2.5 |
|
4 |
|
1.5 |
|
|
(To include already incurred costs) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
2 |
Account Receivable |
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
Construction In Progress |
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
(To consider the due amount) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
3 |
Cash |
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
Account Receivable |
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
(To record cash receipt) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
4 |
Construction In Progress |
0.625 |
|
1 |
|
0.375 |
|
|
Construction Expense |
2.5 |
|
4 |
|
1.5 |
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
3.125 |
|
5 |
|
1.875 |
|
|
|
(To recognise yearly income) |
|
|||||
|
|
|||||||
c.
|
Journal Income for 2019,2020,2021 for Big Construction Company (All figures are in $ Mn) |
|||||||
|
Assuming that the measure of progress on the contract cannot be reliably assessed |
|||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
|||
|
S.No. |
Account |
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
|
1 |
Construction In Progress |
2.5 |
|
4 |
|
1.5 |
|
|
Cash |
|
2.5 |
|
4 |
|
1.5 |
|
|
(To include already incurred costs) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
2 |
Account Receivable |
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
Construction In Progress |
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
(To consider the due amount) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
3 |
Cash |
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
Account Receivable |
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
|
(To record cash receipt) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
4 |
Construction Expense |
2.5 |
|
4 |
|
1.5 |
|
|
Revenue |
|
2.5 |
|
4 |
|
1.5 |
|
|
(To recognise yearly income) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
5 |
Construction In Progress |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
Contract Liability |
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
(adjusting entry as Construction In Progress account have credit balance) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
6 |
Construction In Progress |
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
Contract Liability |
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
(Reversal of adjusting entry ) |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
7 |
Construction In Progress |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
Revenue from contract |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
(Ro recognise total profit ) |
|
||||||
Answer 3:
a. For Desirable Site:
|
Journal Entries for Desirable Site (Amt. are in $) |
||||
|
Date |
Particular |
Debit |
Credit |
|
|
2019 |
Exploration and Evaluation Expenditure |
2,50,00,000 |
|
|
|
Cash |
|
2,50,00,000 |
|
|
|
(To recognise the exploration and evaluation expenditure) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
2020 |
PPE |
3,20,00,000 |
|
|
|
Intangible Asset |
1,60,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
Cash |
|
4,80,00,000 |
|
|
|
(To recognise development cost in this year) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
PPE |
1,75,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
Intangible Asset |
75,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
Exploration and Evaluation Expenditure |
|
2,50,00,000 |
|
|
|
(To recognise the carry forward of exploration and evaluation cost of earlier year as oil is discovered in this year) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
For Undesirable Site:
|
Journal Entries for Undesirable Site (Amt. are in $) |
|||
|
Date |
Particular |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2019 |
Exploration and Evaluation Expenditure |
2,00,00,000 |
|
|
Cash |
|
2,00,00,000 |
|
|
(To recognise the exploration and evaluation expenditure) |
|
|
|
|
2020 |
Impairment Loss |
2,00,00,000 |
|
|
Exploration and Evaluation Expenditure |
|
2,00,00,000 |
|
|
(To write off the exploration and evaluation expenditure as no the field is abandoned) |
|
|
|
For Neutral Site:
|
Journal Entries for Neutral Site (Amt. are in $) |
|||
|
Date |
Particular |
Debit |
Credit |
|
2019 |
Exploration and Evaluation Expenditure |
2,80,00,000 |
|
|
Cash |
|
2,80,00,000 |
|
|
(To recognise the exploration and evaluation expenditure) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
2020 |
PPE |
1,96,00,000 |
|
|
Intangible Asset |
84,00,000 |
|
|
|
Exploration and Evaluation Expenditure |
|
2,80,00,000 |
|
|
(To recognise the carry forward of exploration and evaluation cost of earlier year as oil is discovered in this year) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Answer 4:
a.
|
Calculation of Net Income |
||
|
Particular |
Calculation |
Amount |
|
Net Income After Tax |
|
$1500000 |
|
Less: Preference Dividend |
($500000*1*8/100) |
($40000) |
|
Net Income for Equity Shareholders |
|
$1460000 |
|
Calculation of Weightage Average Number of Shares |
||||
|
Particular |
Calculation |
Duration (Months) |
Number |
Weighted Number |
|
Shares in the beginning |
12 |
900000 |
900000 |
|
|
Fresh Share issued |
7 |
300000 |
175000 |
|
|
Bonus Share Issued |
(900000+300000)*1/6 |
12 |
200000 |
200000 |
|
Total |
1275000 |
|||
For 2019,
Basic Earnings Per Share (EPS) = (Net Income for Equity Shareholders/Weightage Average Number of Shares outstanding)
=($1460000/1275000) = $1.145
For 2018,
EPS = $1.5
Hence Net income = EPS * Number of shares outstanding
=$1.5 * 900000
=$1350000
Number of shares outstanding in 2018 = 900000 + 900000/6 = 1050000
Adjusted basic EPS = $1350000/1050000 = $1.29
4.b.
Diluted EPS
Diluted EPS is a profitability metric used in to measure any company's quality of earnings per share with the assumption of all convertible securities being exercised.
Diluted EPS includes all convertible securities which can be converted into equity or common stock.In contrast, EPS only includes company's common shares.
Diluted EPS=(Net income?Dividends on preferred stock)/(Average outstanding shares+Diluted shares)
Examples:Convertible Debt instruments or preference shares that are convertible into equity shares
Question 5:
a.
|
Calculation of Foreign Exchange Difference for purchase |
|||
|
|
Euro Amount |
Spot rate in Euro for 1 A $ |
Amount in A $ |
|
Purchase of Inventory on May 11,2019 |
300000 |
0.41 |
731707.3171 |
|
Foreign Exchange on June 30,2019 |
300000 |
0.43 |
697674.4186 |
|
Foreign Exchange Loss |
|
|
34032.89847 |
|
Calculation of Foreign Exchange Loss for payment to creditor |
|||
|
|
Euro Amount |
Spot rate in Euro for 1 A $ |
Amount in A $ |
|
Payment to Creditor on August 14,2019 |
300000 |
0.39 |
769230.7692 |
|
Foreign Exchange on June 30,2019 |
300000 |
0.43 |
697674.4186 |
|
Foreign Exchange Difference |
|
|
71556.35063 |
|
Journal Entries for Fujitsu Limited |
|||
|
Date |
Particular |
Debit |
Credit |
|
May 11, 2019 |
Purchases A/c |
A$731,707.32 |
|
|
DFO Ltd. A/c |
|
A$731,707.32 |
|
|
(To record the purchase of inventory |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
June 30,2019 |
DFO Ltd A/c |
A$34,032.90 |
|
|
Foreign Exchange Gain/Loss A/c |
|
A$34,032.90 |
|
|
(To Record the difference in form of foreign exchange gain or loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
August 14, 2019 |
DFO Ltd. A/c |
A$769,230.77 |
|
|
Cash A/c |
|
A$769,230.77 |
|
|
(To record the payment) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
August 14, 2019 |
Foreign Exchange Gain/Loss A/c |
A$71,556.35 |
|
|
DFO Ltd. A/c |
|
A$71,556.35 |
|
|
(To record effect of foreign exchange) |
|
|
|
b.
Qualifying asset:
A qualifying asset is an asset which takes a considerable period to get ready for intended use or sale, as the case maybe.
Qualifying assets could be, plant,properties, equipment or investment properties, any intangible assets like R&D establishments etc., inventories (which are under process for delivering order)
The borrowing costs those are incurred for manufacturing, construction of these assets during this period are normally capitalised to the qualifying asset.
Example:
- A refinery construction of which would take a considerable time to get ready to produce refined hydrocarbons like Petrol, diesel
- A building which is being made for leasing for rentals as office spaces; this building will take substantial period for full construction
- R&D establishments for pharmaceutical companies












