5G Network Assignment On Cellular Systems
Question
Task: 5G is the newest mobile network technology that is replacing the current 4G technology by providing high data rate, reduced latency, energy saving, cost reduction, higher system capacity, and massive device connectivity. Mobile service providers are planning to immigrate to this technology to support the growing number of devices that demand internet access, many of them requiring so much bandwidth in order to function normally that 4G simply doesn't cut it anymore.
For further reading, refer to the article “5G Cellular User Equipment: From Theory to Practical Hardware Design” [1]. The article is available on the IEEE Explore platform, which could be accessed via the Melbourne Institute of Technology Library.
The assessment requires the students to identify the challenges in 5G technology compare with the current wireless communication technologies and consider the proposed solutions to address the 5G limitations. Evaluate the wireless communication standards for wireless cyber physical systems and internet of things. The students are required to submit a report, which includes:
1. Comparison of the existing cellular networks generations (5G, 4G, 3G, and 2G) in terms of:
a. Communication spectrum
b. modulation techniques
c. medium access control mechanism
d. Network speed and bandwidth utilization
e. Security techniques and risk
2. Explore the architecture of a 5G network
3. Identify and analyse the 5G attacks on the access and core networks.
4. Identify and analyse the issue related to 5G network coverage? What is a solution to address this limitation?
Answer
Introduction
This study of 5g network assignment is based on the cellular network generations and their related aspects. The practice of connecting two or more programming or computing devices for transferring or sharing data is known as networking. A mix of computer software and hardware makes up the networks [1]. There are various types of systems like LAN (Local Area Network), WAN (Wide Area Network) etc. Before moving forward to the generations oF Network present in the surrounding one needs to understand the basic concept of mobile networking or cellular networking and how it works. Cellular Network is a type of communication network [2]. It is distributed over the land areas within a fixed spacing known as Cells, which is looked by a transceiver (base station) at each fixed- points. Mobile networking provides a wide range of features like BTS (Base Transceiver Station), PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), MSC (Mobile Switching Centre) and many more. Networking has its advantages and disadvantages.
1. Comparison of existing cellular networks generations (5G,4G,3G, and 2G)
A) Communication Spectrum
Range of radio waves (3 kHz to 300 GHz) that are used for communication is known as communication spectrum or word spectrum. Examples of the communication spectrum are FM (Frequency modulation) and AM (Analog modulation).
|
1G |
2G |
3G |
4G |
5G |
|
1G offered AMPS, analog technology, which meant the service provided by it was only telephony and not data. |
2G came up with a slighter higher version that offered to transfer of digital signal (data or text) at 250Kbps speed [3]. |
Spectrum for 3rd generation wireless communication was 200Kbps at least and 3Mbps at most. |
4G offers a communication spectrum of 100Mbps for accessing mobiles and 1Gbps for all wireless access. 4G LTE also came into play later offering two standards. |
5G came up with a wide range of radio spectrum bands like EHF (Extremely high frequency), ELF (Shallow frequency), MF (Medium Frequency), LF (Low Frequency), ULF (Ultra-low frequency), UHF (Ultra High Frequency). All these bands get covered up within frequency range 3 kilohertz up to 300 gigahertz [4]. EHF is having the frequency range of 30GHz to 300GHz. |
B) Modulation Techniques
The concept of modulation in this 5g network assignment is defined as a process of adding information in an optical carrier signal or electronic signal by the conversion of data into radio waves. Modulation is basically of four types analog, digit phase modulation [5].
|
1G |
2G |
3G |
4G |
5G |
|
The modulation technique used for first generations cellulaR Network was the analog cellulaR Network which accesses only calls and not image or video. The significant technological development that made the difference between the previous generations and 1G or first generations cell phones was the use of multiple numbers of cell sites and being able to pass on that call from one cell site to another as the user travelled [6]. |
With the development of 2G, it was first started the use of digital transmission of data other than analog. Also, there was development in the production of advance fast mobile phones to network signalling. This era also came up with the feature of prepaid mobile phones and even texted messaging became possible. |
The modulation technique used by the third-generation mobile network users was High-Speed IP data networks. At this time, the demand for data services, i.e. the need for the internet by the internet using people increased. Packet switching transmission of data was removed by circuit switching, and this came out as one of the essential differences [7]. |
Growth of mobile broadband was the modulation technique used by the users of the fourth-generation cellular network using people. 4G is nothing but the extension of more bandwidth in the 3G technology. |
The modulation technique that has been considered for 5G to overcome the PAPR issue is Amplitude Phase Shift Keying or APSK. |
C) Medium Access Control Mechanism
It is stated in this 5g network assignment that to ingress a common channel or medium access control mechanism protocols are used. It is a sub-layer of DLL, i.e. Data Link Layer which is mentioned in the OSI or Open systems interconnection model.
|
1G |
2G |
3G |
4G |
5G |
|
These are cellular networks in which the access control mechanism is through the base station, which is divided into orthogonal networks. These orthogonal structures are used to provide voice communication. The use of orthogonal channels restricted the number of users. The scheme of MAC used in 1G is frequency division multiple access [8]. |
The 2G also used the orthogonal structure, but the difference is in the use of MAC scheme as it used time division multiple access and code division multiple access. |
In 3G, division of the orthogonal structure was brought in with the application of orthogonal frequency division multiple access/multiplexing. There were two different uplinks and downlinks networks which improved the resources allocation method.
|
This generation saw the addition of MIMO technology over the 3G networks which brought in the advantage of three-dimensional scheduling involving space, frequency & time: this significantly improved capacity and energy efficiency [9].
|
Mm, Wave bands are the key technology used in 5G, wherein the data rates are ultrahigh. |
D) Network Speed And Bandwidth Utilization
The bit rate of the network device is known as network speed, and the amount available for use from speed is known as bandwidth. Bandwidth utilisation is a network statistic which is not very nicely understood. Various factors need to be looked after when we are dealing with bandwidth.
|
1G |
2G |
3G |
4G |
5G |
|
Network Speed of 2.4 Kbps, analog signal used, the frequency band of 824-894 MHz & channel capacity of 30 kHz |
Network speed up-to 64 kbps for data, digital messages used, the frequency bandwidth of 30-200 kHz |
The network speed of 2 Mbps for data, the frequency bandwidth of 15-20 MHz, communication speed, got faster |
Network speed capability of 10 Mbps to 1 Gbps for data, extremely secure connections |
ExpecteD Network speeds up to 20 Gbps for data |
e) Security Techniques and Risk
Security techniques and risk can be said as an approach to security and risk management that requires to check upon an unsafe zone, identification and verification and then mitigating and patching up of those.
|
1G |
2G |
3G |
4G |
5G |
|
There was effectively no security in the 1st generation of mobile networks, and the spectral efficiency was very poor, which resulted in poor voice quality. Also, the lack of security could lead to eavesdropping by third parties [10]. |
The main drawback for 2G was the limited data rate and its inability to support the increasing demand for e-mails and internet |
The major problem with the 3rd generation was the failure of WAP which led to issues in the access of internet and performance failed to match the standard during such instances |
The hardware requirement is expensive, and the setup is complicated. The battery usage is increased manifold. |
It faces the risk of latency, and the success of this Network is dependent on the innovations to make this successful.
|
2. 5g network assignment exploring the Architecture of 5G Network
5G is, or we can say 5th generation cellular network technology. It provides ingress to broadband. It follows all 4G, 3G and 2G associated technologies such as LTE, GSM, LTE Advanced Pro, UMTS etc.
Architecture of 5G
For a better understanding of 5G architecture, one needs to understand its system model, which is IP based and is designed for mobile networks or wireless systems. The below diagram in this 5g network assignment depicts the computer system having the main terminal is connected through a significant autonomous and independent radio access technologies [11]. For the internet world outside these technologies are considered to be the IP link. Designing of the IP technology ensures satisfactory control data for intelligent routing of IP packets associated with a specific device connection, i.e. sessional meet (session protocol of an OSI) between the client-server on the internet [12].
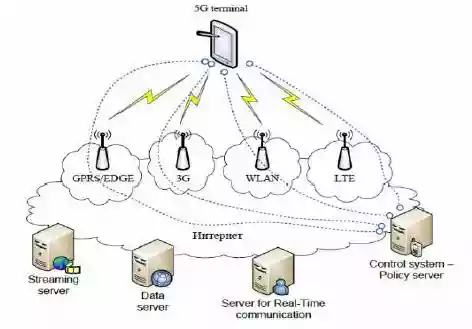
Figure 1: Architecture for 5G
(Source: [13]
The master core technology
In fig. 2 shown below the 5G Master Core is the intersecting point for all the other technologies having their impression on the prevailing wirelesS Network. Interestingly, the design architecture of the 5G Network itself makes it possible for the Master Core to operate in parallel multimode, also including 5G and IP network mode [14]. Network technologies like Different Access Networks (DAT) RAN, and Different Access Networks (DAT) are controlled in this mode. This type of technology is much more efficient than others since the circuitry is less complicated or complex and takes optimum care of all the new extensions (based on 5G) [15].
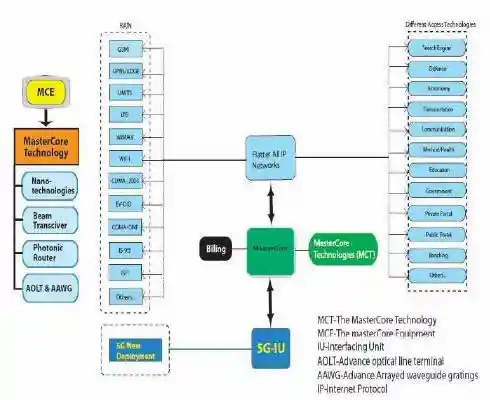
Figure 2: Master Core Technology
(Source: [16])
3. Identification and analysing the 5G attacks on the access and core networks within this 5g network assignment
In recent research, it has been found by the researchers about the various types of privacy attacks on a 5G cellular network. There are privacy breaking flaws, which include intercepting calls, location tracking, fake notifications, fake amber alerts and many more in the 5G mobile protocols. The researchers have found basic three types of attacks based on the use of “Paging Mechanism”. Paging mechanism is a protocol that strives to achieve the equilibrium between the consumption of energy by the device punctual delivery of all the services like cell phone calls [9]. The three attacks are: -
- Torpedo (Tracking via Paging message distribution)
- IMSI- Cracking attack (International Mobile Subscriber Identity)
- PIERCER (Persistent Information Exposure by the core network)
Among this, Torpedo is the primary attack, and the principal offence enables the other two attacks. The Torpedo can be used by the attackers to get the exact location of a particular device and then it can also be injected by (DoS), i.e. denial-of-service attacks or fake paging texts. The other two attacks come into play if the victim's cell phone number is known to the attackers. If they get to see the phone number, then they can quickly understand that person's unique IMSI number, i.e. International Mobile Subscriber Identity, which leads them to easy tracking of their location [11].
4. Identification and Analysis of issues related to 5g Network and solution to address this limitation within this 5g network assignment
4.1 Identification of Issues related to 5G Network
There are many issues related to 5G network like high relatability and security, ultra-low latency etc. But among these, there are a few significant problems that we are going to address now. They are: -
- Huge Data volume – With the advancement of technology, the data volume for networks also increases. The people today are more influences towards video streaming, augmented reality (AR), multimedia gaming applications which needs high-quality speed network for a pleasant experience [14]. This can be solved by increasing the transmitting antennas at the base station.
- Mimo Technology – The main work of this technology is to transmit high-speed data to one individual at a time. The idea to solve this problem is to increase the number of the mobile device and the antennas to maximise the transfer of data at base stations by receiving and sending of the data.
- Security and privacy – There is a significant problem with the security related to 5G. It has been witnessed that there have been significant attacks like Torpedo, IMSI – Cracking attack and PIERCER, which needs to look after before the implementation of This Network all over the globe [12]. A little advancement in architecture if 5G can help us solve this problem.
4.2 Solutions to overcome 5G network limitations
- To ensure a reliable 5G signal, need to implement lots of 5G antennas and cell towers in the locality,
- Automated network design tool set can be used to improve the network design quality since one needs to look after the efficiency of network as 5G will automatically increase the network density.
- Security and privacy in a 5G network can be looked after by structuring the network with strong segmentation. This will keep all the discrete parts separate to keep the attacker away from the vital systems.
Conclusion
After analysing the context of 5g network assignment, it can be stated that 5g Network is designed in such a way that it can work with several apps, but it only needs to look after the complexities it has. There are many things that This Network needs to overcome like security and privacy, transmission protocols and many more services that it offers. Many big companies are investing in this celLular Network with a big expectation of having a higher transfer rate of data. To conclude, one can say that for a 5G network to be successful all over the globe and not just limited to few countries; it needs a successful breakthrough or implementation of the challenges it is currently facing.
5g network assignments are being prepared by our computer network assignment help experts from top universities which let us to provide you a reliable assignment help online service.
Reference List
[1] S. Li, L. Da Xu, and S. Zhao, “5G Internet of Things: A survey,” Journal of Industrial Information Integration. 2018.
[2] N. Panwar, S. Sharma, and A. K. Singh, “A survey on 5G: The next generation of mobile communication,” Phys. Commun., 2016.
[3] P. K. Agyapong, M. Iwamura, D. Staehle, W. Kiess, and A. Benjebbour, “Design considerations for a 5G network architecture,” IEEE Commun. Mag., 2014.
[4] N. Yang, L. Wang, G. Geraci, M. Elkashlan, J. Yuan, and M. Di Renzo, “Safeguarding 5G wireless communication networks using physical layer security,” IEEE Commun. Mag., 2015.
[5] A. Abubakar and B. Pranggono, “Machine learning based intrusion detection system for software defined networks,” in Proceedings - 2017 7th International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies, EST 2017, 2017.
[6] M. A. Ferrag, L. Maglaras, A. Argyriou, D. Kosmanos, and H. Janicke, “Security for 4G and 5G cellular networks: A survey of existing authentication and privacy-preserving schemes,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications. 2018.
[7] D. Fang, Y. Qian, and R. Q. Hu, “Security for 5G Mobile Wireless Networks,” IEEE Access, 2017.
[8] T. E. Bogale and L. B. Le, 5g network assignment “Massive MIMO and mmWave for 5G Wireless HetNet: Potential Benefits and Challenges,” IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag., 2016.
[9] M. Tehrani, M. Uysal, and H. Yanikomeroglu, “Device-to-device communication in 5G cellular networks: Challenges, solutions, and future directions,” IEEE Commun. Mag., 2014.
[10] I. Ahmad, T. Kumar, M. Liyanage, J. Okwuibe, M. Ylianttila, and A. Gurtov, “5G security: Analysis of threats and solutions,” in 2017 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking, CSCN 2017, 2017.
[11] S. Wu, H. Wang, and C. H. Youn, “Visible light communications for 5G wireless networking systems: From fixed to mobile communications,” IEEE Netw., 2014.
[12] D. Baxter, “Wireless Systems,” in A Practical Guide to Television Sound Engineering, 2007.
[13] I. Ahmad, T. Kumar, M. Liyanage, J. Okwuibe, M. Ylianttila, and A. Gurtov, “Overview of 5G Security Challenges and Solutions,” IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag., 2018.
[14] Q.-T. Vien, “Network analysis, architecture, and design,” in Network Design, Modelling and Performance Evaluation, 2018.
[15] Z. Yan, P. Zhang, and A. V. Vasilakos, “A security and trust framework for virtualized networks and software-defined networking,” Secur. Commun. Networks, 2016.
[16] P. Gandotra and R. K. Jha, “A survey on green communication and security challenges in 5G wireless communication networks,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications. 2017.
Get Top Quality Assignment Help and Score high grades. Download the Total Assignment help App from Google play store or Subscribe to totalassignmenthelp and receive the latest updates from the Academic fraternity in real time.












